How Nockchain Reconstructs PoW Blockchain with Zero-Knowledge Proofs
- Core Viewpoint: Nockchain proposes a novel consensus mechanism called Zero-Knowledge Proof-of-Work (ZKPoW), aiming to combine the decentralization and security of traditional PoW with the efficient verification of zero-knowledge proofs. It redefines "work" by having miners generate meaningful zero-knowledge proofs to replace meaningless hash computations.
- Key Elements:
- Core Mechanism: Nockchain replaces traditional hash mining with the generation and verification of zero-knowledge proofs. Miners compete to generate valid proofs to earn block rewards, with network security stemming from the verifiable work itself.
- Token Economics: The native token NOCK has a fixed total supply, issued solely through mining with a decreasing release curve. Long-term security depends on whether transaction fees can gradually replace block rewards.
- Ecosystem Structure: Its ecosystem is built around verifiable computation, divided into the proof generation layer, proof verification layer, and on-chain coordination layer, prioritizing verification efficiency over execution throughput.
- Competitive Positioning: Differentiating itself from traditional PoW chains and ZK-native chains, it attempts to achieve a ZK-native security model while retaining the permissionless participation characteristic of PoW.
- Main Risks: Challenges include early-stage protocol maturity risk, potential centralization in proof generation, limited developer adoption, and long-term economic sustainability.
In the early days of blockchain, Proof of Work was seen as an unshakable security foundation. The greater the hashrate, the more secure the network, and the more robust the decentralization. However, over time, one issue has been magnified: the computational power consumed itself has no inherent meaning. It exists solely to win the right to produce a block.
Meanwhile, Zero-Knowledge Proofs took a different path. They proved one thing: complex computations can be efficiently verified. But in pursuit of performance, most ZK systems ultimately chose to rely on a small number of provers or semi-centralized architectures, which inadvertently weakened the original intent of decentralization.
Nockchain did not choose between these two paths but instead attempted to stitch them back together. It retains the open participation and economic security of PoW but replaces the "meaningless computational consumption" with zero-knowledge proof generation. Miners no longer compete in hashing but in who can generate verifiable proofs more efficiently.
On Nockchain, security no longer comes from waste but from the verifiable work itself. This is not just a rewrite of PoW but also a new answer to the question of "where computational power should be applied."

TL;DR Quick Summary
- NOCK is the native asset of the Nockchain, a Layer 1 public chain based on Zero-Knowledge Proof-of-Work (ZK PoW).
- Nockchain replaces the traditional hash-based mining mechanism with zero-knowledge proof generation.
- Network fees and scalability depend primarily on verification efficiency rather than re-execution.
- Token value stems from proof participation and real network usage.
- Compared to narrative hype, the quality of execution and adoption is the long-term key.
Nockchain (NOCK) Overview
Role in the Nockchain Tech Stack
Nockchain is a Layer 1 blockchain secured by Zero-Knowledge Proof-of-Work (ZKPoW). Unlike traditional mining mechanisms that rely on hash computations, Nockchain's network security is guaranteed by the generation and verification of zero-knowledge proofs. In this system, the true security resource is not computational hashrate but the verifiable proof itself.
NOCK is the native asset of the Nockchain ecosystem. Its core function is to support the operation and economic security of this "proof-centric" network. NOCK is issued through mining, used to pay on-chain transaction fees, and serves as an incentive mechanism to coordinate and attract participants to provide proof generation and verification capabilities. This places NOCK squarely at the infrastructure layer of the system, not the application layer.
Unlike smart contract platforms focused on execution performance, Nockchain emphasizes efficient verification over repeated execution. NOCK's use cases are a direct reflection of this design philosophy: it is used to anchor network settlement costs, incentivize miners to generate valid proofs, and maintain the network's permissionless participation and security without solely relying on energy consumption.
Roles NOCK Does NOT Assume
NOCK is not a consumer-facing payment token, nor does it aim to be a universal Gas Token within complex DeFi ecosystems. It does not compete with EVM-compatible public chains in terms of composability or application throughput. Instead, NOCK is better viewed as a long-cycle infrastructure-type asset: its long-term value depends on whether the "proof-centric work mechanism" can truly replace traditional PoW while maintaining decentralization and achieving economically sustainable operation.
NOCK Tokenomics
NOCK adopts a fixed total supply, mining-based issuance token model, designed to support the network's long-term security within a zero-knowledge native (ZK-native) environment. NOCK has a clear maximum supply cap. All tokens are issued solely as block rewards to miners who generate valid zero-knowledge proofs. There is no pre-mine, team allocation, or foundation reserve.
Regarding the issuance mechanism, NOCK employs a decreasing emission curve. Higher block rewards in the early stages are for network bootstrapping and security establishment. Over time, new issuance gradually declines. The network's security budget will progressively shift from block subsidies to transaction fees, a logic consistent with the long-term evolution path of traditional PoW networks.
A core feature of NOCK's token economics is its emphasis on software efficiency over specialized hardware advantages. Zero-knowledge proof generation is computationally intensive, but verification costs are extremely low. This means the key to competitive participation lies not in simply stacking hardware hashrate but in optimizing the proof system and algorithm implementation. This design helps reduce (though not completely eliminate) the centralization risk arising from hardware scale.
Category Parameter Description Maximum Supply ~4.29 Billion NOCK Fixed cap Smallest Unit 2¹⁶ Basic unit of account Distribution Method Mining Rewards No pre-mine, no allocations Emission Curve Decreasing Early bootstrapping, long-term security Block Time ~10 minutes Target average Primary Use Cases Network security, transaction fees Infrastructure layer function
Overall, this token design emphasizes issuance predictability and long-term security over flexible and variable incentive adjustment mechanisms. As new issuance gradually declines, the scale of actual network usage and fee demand will play an increasingly critical role in the security system.
Evaluation Perspective: NOCK's sustainability does not depend on the "fixed total supply" itself, but on whether transaction demand can gradually replace block rewards in the future as the primary incentive source for network security.
Ecosystem dApps / Core Application Structure
Overall, the Nockchain ecosystem is better understood as an infrastructure system built around verifiable computation, rather than an execution-oriented platform with a multitude of applications. Unlike public chains emphasizing consumer-grade dApps, Nockchain's core goal is to complete the generation, verification, and settlement of zero-knowledge proofs in a secure and efficient manner. Consequently, the ecosystem structure is primarily divided into three functional layers: Proof Production Layer, Proof Verification Layer, and On-Chain Coordination Layer.
Proof Production Layer
The bottom layer of the ecosystem consists of proof producers, whose role is equivalent to miners in the network. Participants in this layer are responsible for generating zero-knowledge proofs that attest to the correctness of computations, thereby providing security for the network. Proof generation itself is computationally intensive, typically performed off-chain, relying on highly optimized proof software and matching hardware environments.
In this layer, competitive advantage stems more from software efficiency and system optimization capabilities rather than simply stacking raw hashrate or hardware scale.
Proof Verification Layer
The Proof Verification Layer is where Nockchain differs architecturally. Unlike blockchains that require nodes to re-execute computations, Nockchain confirms the correctness of results by directly verifying submitted zero-knowledge proofs on-chain. This mechanism ensures security while significantly reducing the operational burden on nodes.
This design dictates the type of workload the network prioritizes and reflects its performance orientation: prioritizing verification efficiency over execution throughput.
On-Chain Coordination Layer
The on-chain environment is primarily used for settlement and coordination, not for hosting complex application logic. Relevant transactions revolve around proof submission, verification result confirmation, fee payment, and reward distribution. This orientation makes Nockchain more akin to a specialized underlying network serving verifiable computation, rather than a general-purpose DeFi or consumer application platform.
How to Participate and Acquire NOCK
Acquiring NOCK
NOCK can be acquired through supported trading channels, subject to regional availability and listing conditions. On XT.com, users can directly participate in trading via the NOCK/USDT spot trading pair, providing convenient access to the asset in a centralized exchange environment.
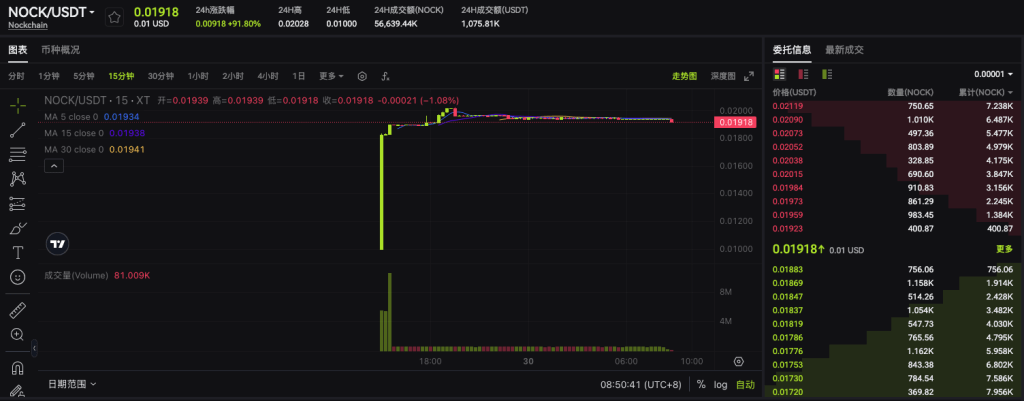
The NOCK/USDT spot trading pair is now live on XT Exchange.
Before acquiring NOCK, users are advised to carefully verify the official contract information, supported networks, and market liquidity conditions. As an asset highly correlated with underlying infrastructure, asset custody methods and information verification processes are particularly crucial.
Participating in Proof Generation
For participants with technical capabilities, they can choose to directly engage in the network's proof generation process. This role is functionally equivalent to traditional "mining," but the competition is no longer hash computation but zero-knowledge proof generation. Participation typically requires certain technical expertise, appropriate hardware configuration, and an understanding of Nockchain's proof software stack. Network rewards are distributed based on successfully submitted and verified proofs.
Considerations for Network-Level Participation
Direct participation in network operation allows for deeper engagement with the protocol's core incentive mechanisms but also entails higher operational and execution risks. As an infrastructure network still in its development phase, frequent software updates, performance fluctuations, and evolving technical specifications are normal.
NOCK's Competitive Landscape
NOCK operates in a relatively niche segment at the intersection of Proof of Work (PoW) and Zero-Knowledge Infrastructure (ZK). While projects directly combining PoW with zero-knowledge proofs are few, in adjacent fields, various networks exist, making different trade-offs between security, scalability, and computation methods.
Project Comparison Overview
Project Core Focus Key Differences Bitcoin (BTC) Hash-based PoW Mature security model, does not use ZK verification Aleo Zero-Knowledge Execution ZK-native design, but not PoW-secured Mina Recursive ZK Blockchain Lightweight verification, uses alternative consensus Kaspa (KAS) High-Throughput PoW Optimizes block production efficiency, still traditional hash mechanism Bittensor (TAO) Incentivized Computation Targets AI output markets, not ledger settlement
Traditional PoW public chains (like Bitcoin, Kaspa) primarily optimize for block production efficiency or throughput while retaining the hash-based security model. ZK-native public chains represented by Aleo and Mina emphasize execution privacy or lightweight verification, but their consensus mechanisms are not PoW.
Bittensor also views "computation" as economically valuable work, but its core goal is to coordinate AI output markets, not to provide security for a general ledger. This is fundamentally different from Nockchain.
The differentiation of Nockchain lies in its redefinition of the "work" in "Proof of Work": using zero-knowledge proofs as the basis for PoW security while retaining the permissionless participation that is a core characteristic of PoW.
These differences reflect architectural trade-offs more than simple superiority or inferiority. In pursuit of a ZK-native security model, Nockchain introduces higher system complexity while attempting to preserve the decentralization attributes represented by traditional PoW. This design path is precisely its unique position in the competitive landscape.
Risks and Considerations
It should be noted that these risks are not uniformly present. Compared to short-term market volatility, structural risks and uncertainties at the execution level are more likely to have a substantive impact on the network's long-term development.
- Protocol Maturity Risk: Nockchain's overall architecture and supporting tooling are still in early stages. Ongoing adjustments to the zero-knowledge proof system or execution assumptions may affect network performance and participation barriers.
- Proof Centralization Risk: Although Proof of Work is designed for permissionless participation, as proof software and hardware configurations continue to optimize, participation may gradually concentrate among a few highly efficient operators.
- Software Competition Risk: As proof generation technology evolves, competitive advantages may shift rapidly, potentially favoring teams with greater technical and R&D resources.
- Adoption and Ecosystem Risk: The "proof-centric" execution model has a relatively narrow scope for application adaptation. Limited developer adoption may constrain network activity growth and transaction fee revenue.
- Economic Sustainability Risk: The network's long-term security depends on whether transaction fees and proof demand can gradually supplement and replace the decreasing new issuance in the future.
- Security and Operational Risk: As with all underlying infrastructure networks, participants face potential risks from software vulnerabilities, configuration errors, and improper interaction with protocol components.
Nockchain (NOCK) Outlook
Nockchain does not attempt to completely replace Proof of Work but rather aims to systematically reconstruct PoW for the zero-knowledge era. Its success or failure does not depend on aligning with market narratives like AI or ZK, but on a series of practical metrics that can be continuously observed and verified.
 Image Source: Nockchain.org
Image Source: Nockchain.org
Key observation dimensions include: the diversity of proof participants, the stability of verification costs, and the degree of developer adoption of the "proof-centric" design pattern. Price performance alone is insufficient to reflect whether this model is truly functioning.
If proof generation can maintain decentralization in the long term and remain economically sustainable, Nockchain has the potential to evolve into a robust infrastructure layer serving verifiable computation and settlement. Conversely, it may remain an experiment that is technically attractive but economically fragile.
Nockchain (NOCK) Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is Nockchain?
Nockchain is a Layer 1 blockchain secured by Zero-Knowledge Proof-of-Work (ZK PoW).
2. What role does NOCK play in the network?
NOCK is used for miner rewards, on-chain transaction fee payments, and constitutes a key component of the network's economic security mechanism.
3. How is Zero-Knowledge Proof-of



