Establish a Layer 1 evaluation framework from five dimensions
From | Bankless, original author: Lucas Campbell, compiled by Odaily | Moni

The problem of high Ethereum gas fees has always existed, and more and more users have begun to seek other alternatives, such as Avalanche, Solana, Polygon, etc. New users have poured into these alternative networks, and the entire ecosystem has become more prosperous. But the problem is:
Which chain will everyone go?
How to evaluate these Layer 1?
What key indicators and fundamentals should investors focus on?
To this end, we have summarized the five issues that deserve the most attention when evaluating Layer 1:
1. Is Layer 1 safe enough?
2. Is Layer 1 decentralized enough?
3. Are there enough developers in Layer 1?
4. Are there enough use cases for Layer 1?
5. Can Layer 1 be profitable?
secondary title
1. Security
Security is always a top priority when evaluating Layer 1.
The core value of the blockchain lies in the settlement layer. If the settlement layer is not secure, then it has no value. In other words, when users conduct transactions on the network, they must ensure that each transaction is the final result, and those with bad motives are not allowed to tamper with it.
In fact, according to the underlying consensus mechanism, there are many ways to measure security, but there is only one ultimate goal - to realize the impeccable settlement guarantee of the blockchain network.With settlement guarantees, transactions made by traders cannot be tampered with, achieving consistency from beginning to end.
When evaluating settlement assurance, the most critical variable is ledger costliness, which we can split into the following two questions:
1. How much does it cost to take over the network?
The answer to this is to understand the rewards validators receive for submitting valid, honest blocks.
2. What is the total network cost?
The total fee is the amount paid to validators to ensure that all transactions are final.
remember,The higher the fees paid to validators, the more secure the network and the higher the settlement assurance.Because under the incentive of income, miners and verifiers will actively submit, verify and maintain legal blocks.
secondary title
2. Degree of decentralization
The core principle of Web3 is decentralization, and of course security cannot be given up. These are the embodiment of the blockchain spirit.
Therefore, Layer 1 should also be sufficiently decentralized and not controlled by any one participant or entity. Anyone can participate in verification (mining/staking) and maintenance of ledgers (running nodes), while It should not be closed to certain groups of people. If you can't achieve enough decentralization, the next best thing is to see if these Layer 1s use AWS.
Note: To evaluate the degree of decentralization of Layer 1, it can be quantified by the number of network nodes and verifiers.
image description
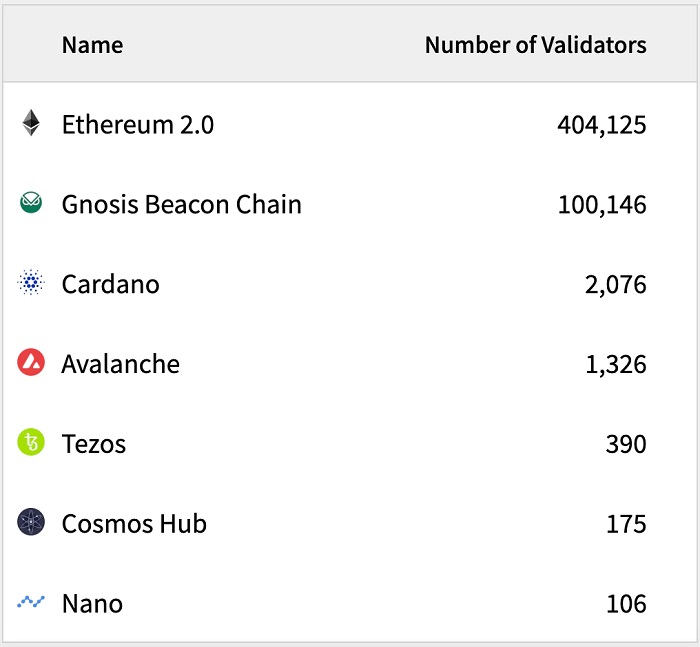
Source: Stakers.Info
secondary title
3. Number of developers
Once Layer 1 realizes its core vision (security and decentralization), it means that developers can reliably build various projects on it. During this time, they don't have to worry about network shutdowns, data rollbacks, or even being hacked.
But then we encountered another problem - in the Layer 1 pyramid, are there any developers on the upper layer who are developing? As we all know,Without developers, there would be no applications; without applications, there would be no users; without users, where would the value come from?
From this point of view, a strong developer ecosystem is crucial to the successful construction of Layer 1. The picture below is Electric Capital's report on monthly active developers in 2021.
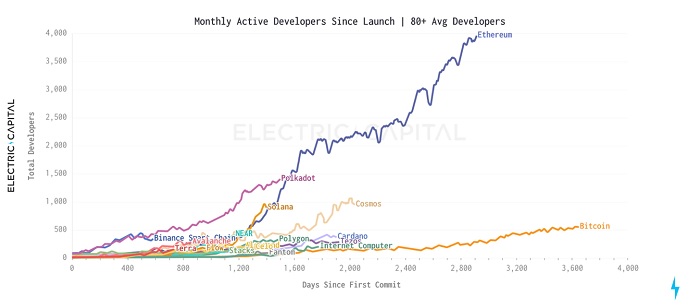
secondary title
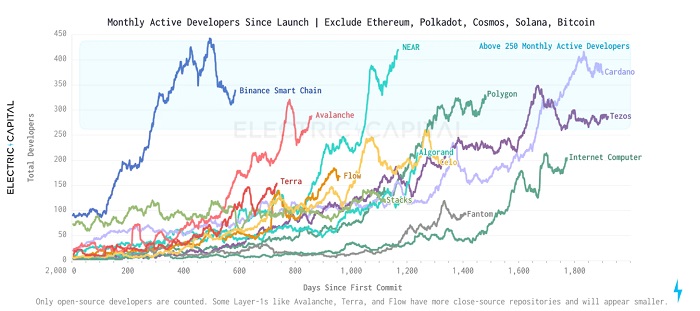
4. Richness of use cases
Now, the Layer 1 evaluation framework has basically been set. If the network is secure, decentralized, and developers are building applications on it, the next thing to watch is whether anyone is actually using those applications.
Of course, there is one more thing that cannot be ignored:Are there users willing to pay for these apps?
The chain's business model is to "sell" blocks and provide services for the continuous decentralized value transfer on the Internet.
Therefore, in order to understand whether Layer 1 is valuable, one of the most basic methods is to know how big the demand for block space is. Through this clear indicator, we can know whether there is a demand for value transfer on the network. There are many ways to measure demand, such as network utilization, fees paid to validators/miners, etc. While each approach has its pros and cons, taken together, it can give you a much clearer picture of whether there is a genuine need on the web.
secondary title
5. Profitability
If it is determined that the network has a demand for block space (blockspace), then there is only one last question to consider - can the blockchain be profitable?
In simple terms, it is actually figuring out whether the blockchain is spending more money than it is earning through transactions for the sake of security. The reality is that no blockchain is profitable today — not even close.
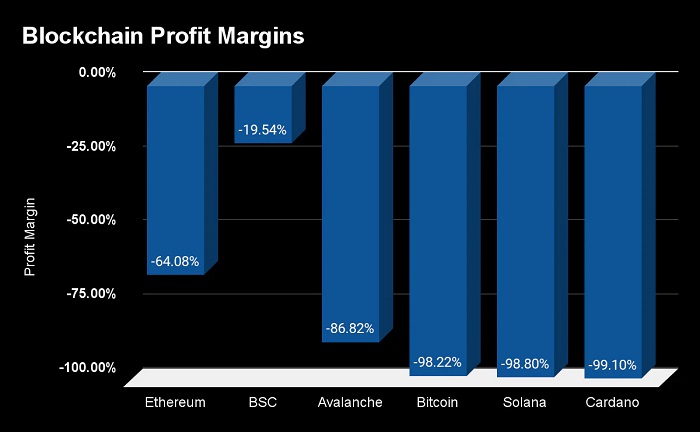
Overall, the current blockchain network spends much more on security costs than its own income.
Summarize
Summarize
Frankly speaking, it is very difficult to evaluate any Layer 1, especially for smart contract platforms. At the beginning of the development of Web2, everyone was not optimistic about Internet startups, but in the end we saw many "unicorns" born. Now, the same thing is happening in the Web3 space.
As the most important Web3 infrastructure, if you want to know the value of Layer 1? Which one has more potential in the future? Perhaps, the above five dimensions can help you build a better evaluation framework.



