Amber Group report: Detailed explanation of the architecture design and market trend of automated market maker (AMM)
first level title
summary:
Automated market makers (AMMs) are the backbone of decentralized finance. Automated market makers allow users to trade assets, create new markets, and earn yield 24/7 without the involvement of a centralized entity. Automated market makers have traded over $180 billion since launch.
DeFi has developed rapidly in recent years. In this report, we'll review key AMM architecture designs and market trends, and highlight some projects that we think deserve attention. We will also discuss emergent behaviors induced by AMMs, such as impermanent losses, centralized liquidity management, and instant liquidity.
Automated Market Maker (AMM): Version Upgrade
Automated market makers (AMMs) are the backbone of decentralized finance. It allows users to trade assets, create new markets, and earn yield, all available 24/7 and without the involvement of a centralized entity.Bancor image description
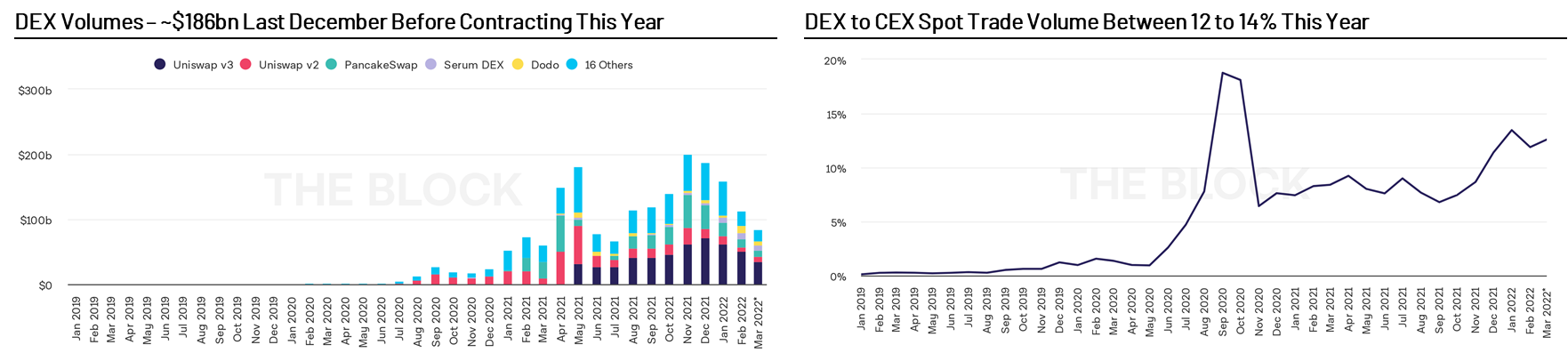
Source: The Block, CoinGecko, as of March 23, 2022
secondary title
Uniswap v2 - Price range from zero to infinity
Let's briefly introduce the constant product formula of Uniswap v2. Uniswap v2 consists of a liquidity pool, a smart contract containing two tokens A and B allows anyone to withdraw and deposit funds according to the formula x*y=k, where x and y are the reserves of the two tokens A and B quantity. k is a constant value, so to withdraw token A from the pool, the user must deposit the appropriate amount of token B to maintain a constant k before fees. For an in-depth look at the protocol, you can find theUniswap documentationThe specific agreement can be found in .
Uniswap v2 has gained market attention since its launch. It applies a decentralized trust mechanism to the creation of liquidity pools, and any liquidity pool can be created without permission, which allows anyone to trade long-tail assets that are usually not tradeable on centralized exchanges. Compared with DEXs that try to replicate the limit order book model on the chain, Uniswap brings users an excellent experience through an intuitive user interface and extremely low gas fees.
Perhaps most importantly, it enables composability with other DeFi protocols. For example, users can pledge their LP tokens, developers can use liquidity pools as price oracles, and protocols can create liquidity mining programs to facilitate the liquidity of their native tokens.
Uniswap v2’s codebase is probably the most forked smart contract in the crypto space, proving its importance. When creating a new Layer 1 or Layer 2 platform, Uniswap v2 is usually substituted.
image description
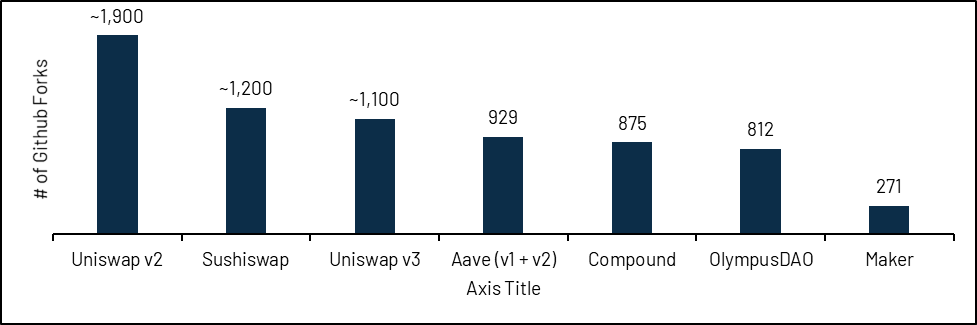
secondary title
Curve - a one-to-one asset solution
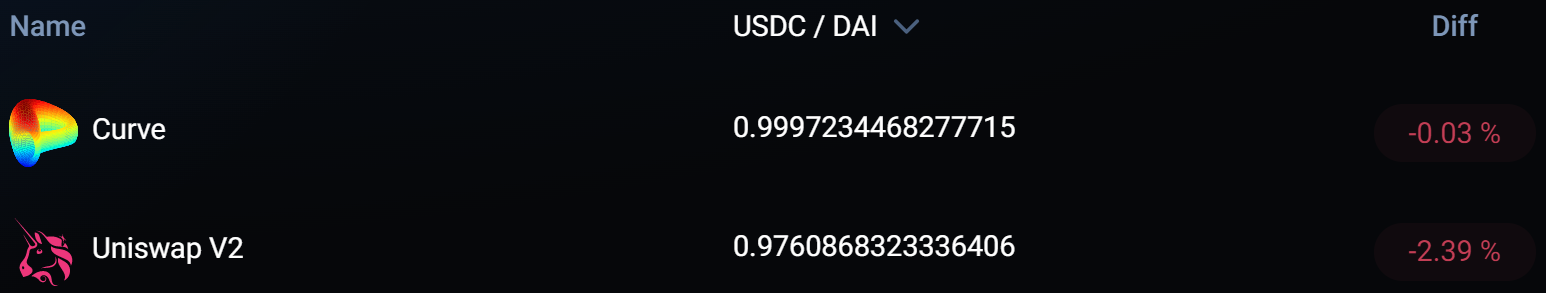
While Uniswap's constant product formula is elegant, it has some drawbacks. The inefficiency of Uniswap v2 is that the model does not apply to swaps between different types of anchor assets, such as stablecoins, which should theoretically be exchanged at a 1:1 exchange rate. For example, most DAI and USDC transactions are done at an exchange rate between 0.99-1.01, so the DAI-USDC pool in Uniswap v2 only uses about 0.5% of the total capital available. Additionally, traders experience high price slippage. At the time of writing,A trader trying to convert 1 million USDC to DAI via Uniswap v2 will result in a 2.4% price slippage, so only about 976,000 DAI can be converted.
A more appropriate pricing formula for stablecoin swaps would be a constant sum formula (x + y = k), where the price correlation of one asset to another is always 1. For example, in a USDC-DAI pool with a constant sum of k=10,000, a user who deposits 500 USDC will receive 500 DAI in return (excluding fees), so k remains constant at 10,000.
However, the problem with the above model is that there is a possibility that the liquidity pool can be completely emptied. An initial pool of 50% USDC and 50% DAI could end up with just one token left. In contrast, one benefit of applying the constant product formula to stablecoin swaps is that the reserves in the liquidity pool cannot be completely depleted.
Curve's stable currency swap (StableSwap mechanism) formula finds a balance between the above two methods.Its StableSwap mechanism formula includes a dynamic variable that adjusts the price as the balance of the liquidity pool changes. When the balance of the liquidity pool is roughly balanced, the price in the pool will fluctuate up and down based on the constant sum formula (x+y=k), providing a stable price close to $1. When the balance of the liquidity pool is unbalanced, the pricing is more like following the constant product formula, making the transaction that exacerbates the imbalance of the pool balance more expensive, so as to encourage liquidity providers to help the pool restore balance. It can be seen more intuitively in the figure below that the constant value of Curve's StableSwap mechanism is between the constant value of Uniswap and the constant value of the constant sum formula.
image description
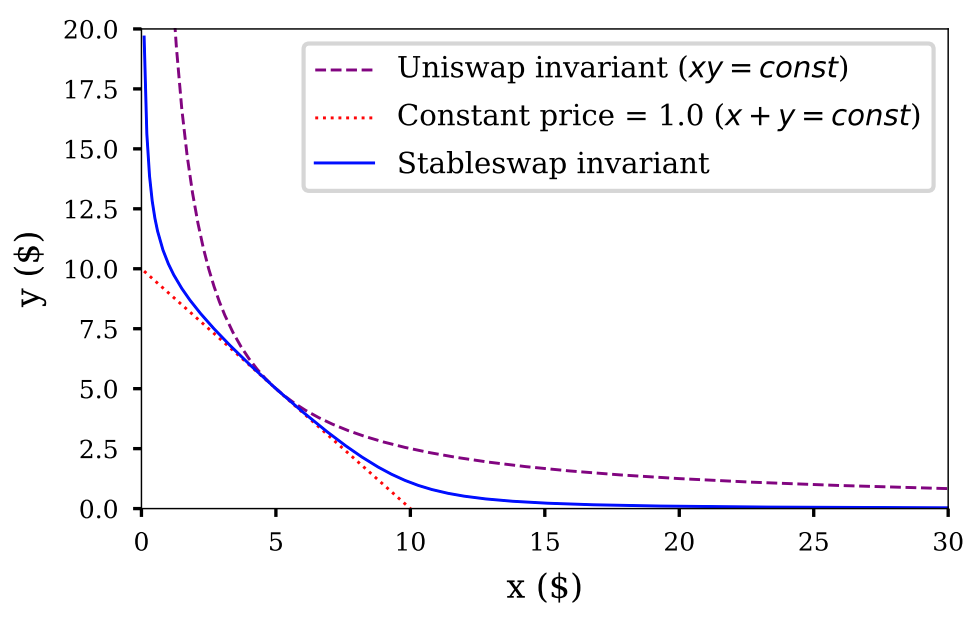
Source: Curve
Therefore, Curve's StableSwap mechanism formula is more practical for swaps between perfectly correlated or highly correlated assets, such as stablecoin swaps, liquidity collateralization of underlying assets (e.g. stETH - ETH), and asset packaging (e.g. wBTC - renBTC ).Similarly, if you exchange 1 million USDC on Curve, you can get 999,700 DAI, and the price slippage is only 0.03%.
image description
secondary title
Uniswap v3 - Universal Automated Market Maker (AMM)
Another flaw in the Uniswap v2 architectural design is capital inefficiency. The liquidity pool provides liquidity from zero to an infinite price range, but in reality most assets do not trade in such a wide price range, so most of the liquidity in the v2 pool is not used.
To solve this efficiency problem, Uniswap will launch v3 in May 2021. Its signature feature is the introduction of centralized liquidity. Instead of providing liquidity across the entire price range, users can specify their desired price range. For example, LP can provide funds in the price range of 0.999-1.001 for the DAI-USDC pool,This results in an approximately 2000-fold increase in capital efficiency.
Uniswap v3 also introduces custom swap fees of 1%, 0.3% and 0.05% per pool, which allows liquidity providers to better adjust their margins by anticipating price fluctuations of trading pairs. For swaps between fully related assets (such as stablecoins), trading pairs match the lowest tier rates. In contrast, long-tail assets usually have a fee rate of 1% due to greater uncertainty.
The recent airdrop of Apecoin by Yuga Lab can reflect the above mechanism. In the first few trading days after the airdrop of Apecoin, because it is in the early stage of price discovery, DEX liquidity is mainly executed at the 1% rate of Uniswap . After the price stabilized between $8 and $15 and price uncertainty decreased, transactions on Uniswap gradually reduced the execution fee rate to 0.3%.
image description
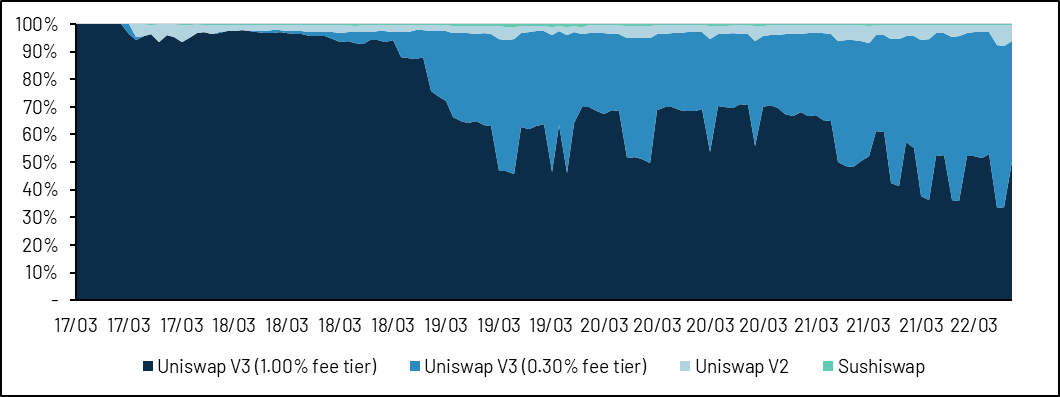
Source: Dune
Uniswap later added a 0.01% rate tier, which is now the standard rate for stablecoins. Under the premise of considering centralized liquidity, the exchange volume of USD stablecoins on Uniswap is now comparable to that of Curve.
image description
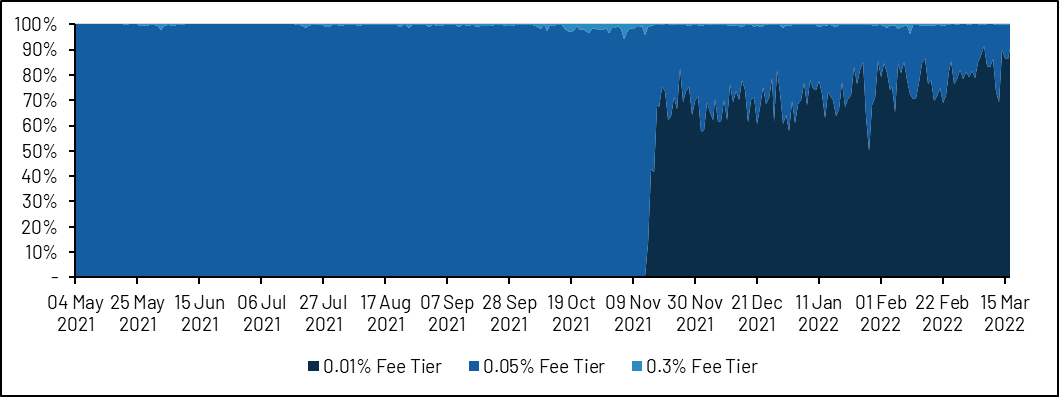
Source: Dune (@pandajackson)
USD Stablecoin Volumes - Uniswap volumes on par with Curve after introduction of v3 and 0.01% fee tier
Finally, v3 also allows users to place limited range orders. Similar to the limit order book model of a traditional exchange, except that orders may be partially executed or recrossed when the price changes direction.
In addition to improving capital efficiency, Uniswap v3 also greatly expands the design space of liquidity provision through customizable price ranges. For example, Dan Robinson of Paradigm showsHow to replicate any static AMM with a series of Uniswap v3 liquidity positions. In addition, you can also take advantage of Uniswap v3'sOption strategy simulation with limited range orders, which is an interesting area worthy of further exploration, but is not discussed in this report.
However, the ever-increasing complexity is causing headaches for LPs. The widespread use of homogeneous liquidity tokens is a common practice, but because Uniswap v3 positions are not mapped to ERC-20 tokens but NFTs, this practice has been broken. Major money markets such as MakerDAO and Aave still do not directly accept Uniswap v3 tokens as collateral. Liquidity providers also don’t enjoy compound returns, instead they have to manually collect fee returns if they want to redeploy liquidity. In addition, in Uniswap v2, LPs were rewarded for sharing the same poor strategy, so LPs could not compete with each other in Uniswap v2, Uniswap v3 is different, Uniswap v3 promotes a competitive environment that is more conducive to market makers, professional trading LPs and field giants who can constantly balance their positions, but at the expense of those retail LPs who hope to "get it done once and for all".
impermanent loss
impermanent loss
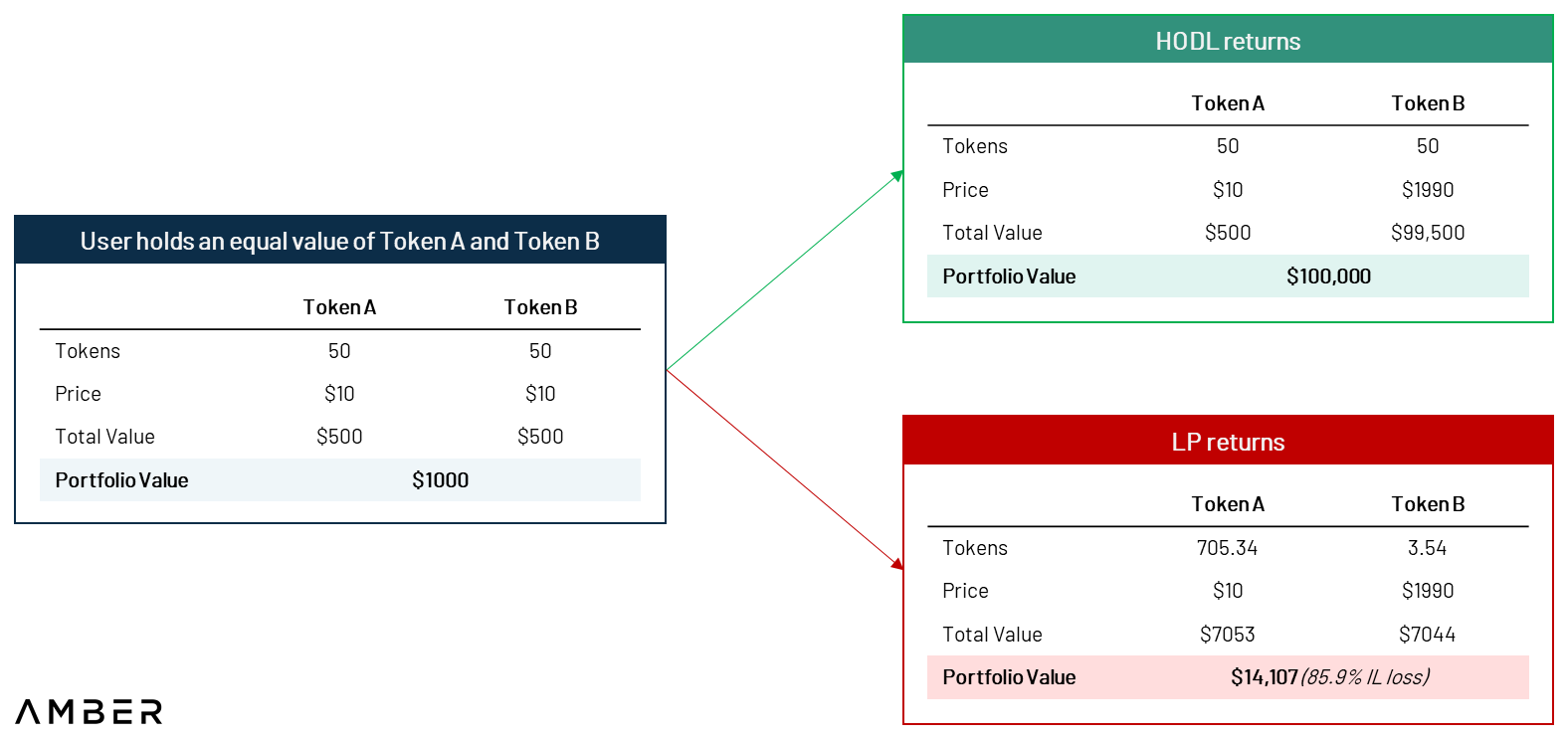
Impermanence loss (“IL”, sometimes called divergence loss) refers to the fact that sometimes even though liquidity providers receive fee income, the value of their pledged assets will shrink. More specifically, generally we can define impermanent loss as the difference in value between depositing tokens in an AMM and simply holding tokens in a wallet.The rationale behind IL is simple: a constant product AMM is always buying underperforming tokens while selling outperforming tokens.Therefore, an investment that would have appreciated 1,000 times outside the AMM only appreciated 14 times inside the AMM.
Impermanence loss could be permanent
IL can be offset when the token returns to its original value, so we also call it a temporary loss. Transaction fees are designed to compensate liquidity providers for IL risk, but multiple studies have shown thatThe expenses incurred are not sufficient to cover the IL,Liquidity providers usually only profit when the trading pair returns to its original exchange rate。
Concentrating liquidity also concentrates impermanent losses, which is similar to leveraged liquidity, that is, similar to leveraged trading, both gains (from fees) and losses (from impermanent losses) are amplified. More intuitively, when the token appreciates, liquidity providers who set a narrow price range will deplete the token reserve at a faster rate than liquidity providers who set a wide price range, thus generating a larger IL. But if done correctly, these LPs will also get a larger share of transaction fees.
image description
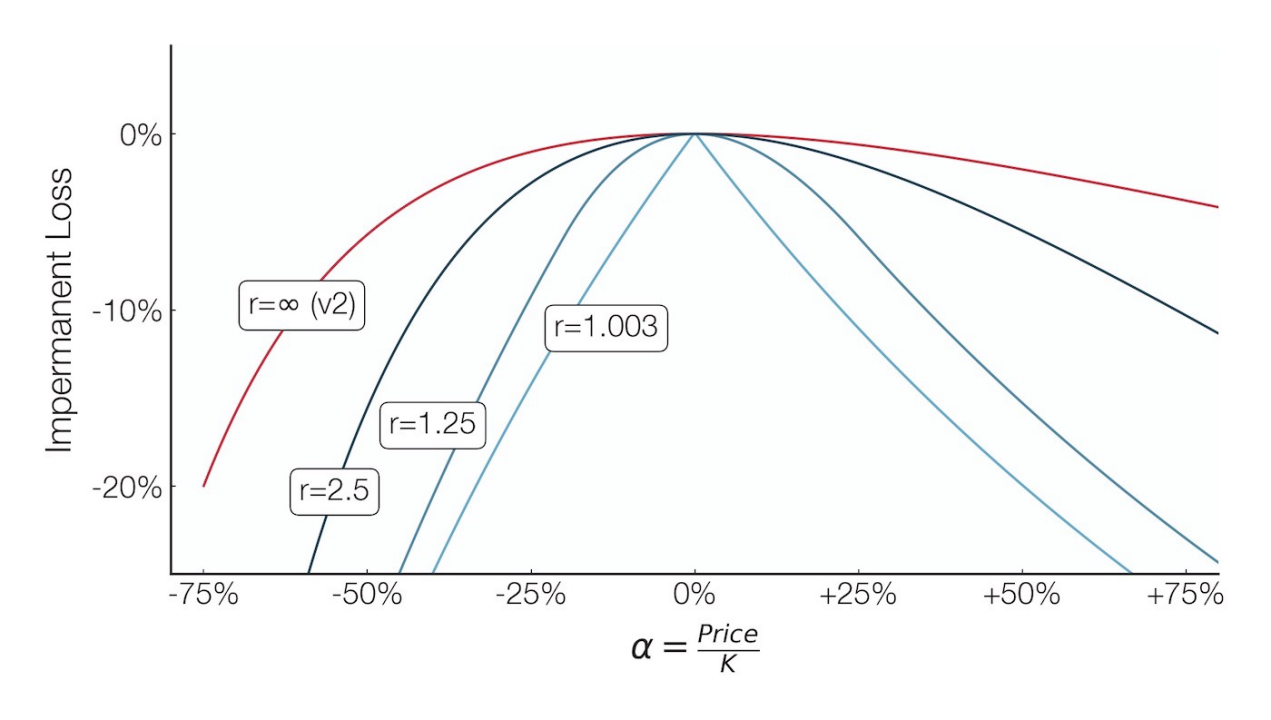
secondary title
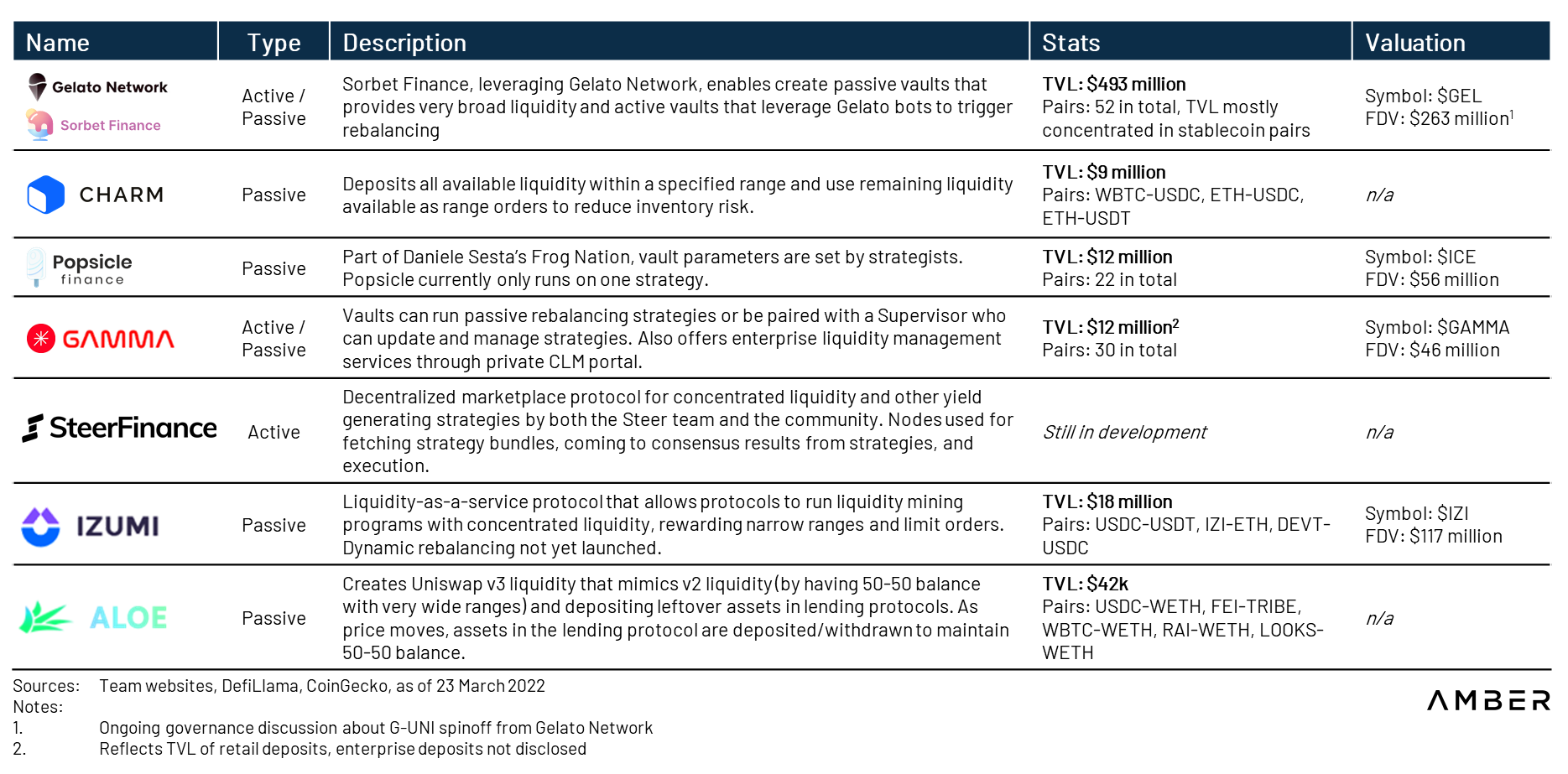
Centralized Liquidity Manager
Considering the complexity of centralized liquidity management, a large number of centralized liquidity managers (CLMs) have been launched on the market. CLM provides several benefits such as:
● Determine the optimal range for providing liquidity by trying to find a balance between fee generation and impermanent losses;
● Adjust range when liquidity is out of range;
● Automatic compounding of fee proceeds back into liquidity positions; and
● Save gas fees through rebalancing.
ERC-20 tokensERC-20 tokens. Additionally, protocols and DAOs can also outsource liquidity strategies and mining procedures to these vaults. Because of the composability of CLM vault tokens,Instadapp、Liquity、OlympusDAOand several other projects apply this in their liquidity management strategies.
Some CLMs such as Charm Finance and Sorbet Finance adopt a passive rebalancing strategy in which rebalancing rules are initially set and published on-chain. Keeper bots are used to monitor the condition of the pool and implement rebalancing strategies when necessary. Other CLMs, such as Gamma Strategies, employ aggressive rebalancing strategies that are enforced off-chain and often proprietary. Some teams are also trying to let the market determine the best strategy. For example, Steer Finance and Sommelier Finance plan to roll out features that allow anyone to create and enforce policies.
Introduction to Centralized Liquidity Manager
The effectiveness of CLM remains questionable if it is evaluated solely on the basis of the benefits it generates. For example, from the perspective of the ETH-USDC vault, Gamma's Hypervisor performed worse than Uniswap v2's equivalent strategy, and Charm's Alpha Vault was only slightly better. Additionally, vaults publishing their rebalancing rules on-chain are vulnerable to front-running, the equivalent of professional market makers broadcasting their strategies to the market before executing trades. Given CLM's relatively modest TVL, this is only a low risk at the moment, but it could be a concern if CLM continues to grow.
image description
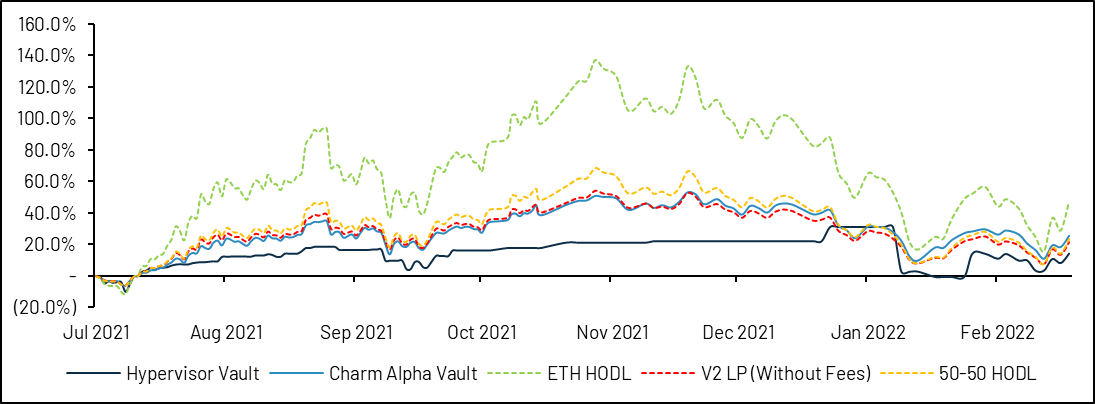
Source: Dune (@vividot)
Research by the Bancor teamIt also finds little evidence that active liquidity management strategies outperform passive LPs. In fact, the only consistently profitable LP strategy that has been found is to provide immediate liquidity, generating fee gains that consistently outweigh impermanent losses, which we discuss in the next section.
We still need to do more research, but the prospects for CLM to perform well are not promising. Sommelier Finance is a blockchain protocol based on the Cosmos SDK, focusing on the Ethereum DeFi strategy, initially focusing on the automation of Uniswap v3 positions. According to the team, even though the teamOn the premise of knowing the future price of the token in advanceBacktesting, automated strategies are still unprofitable because of rebalancing costs (incurred impermanent losses and transaction costs).
secondary title
Flash clips in AMM
Just-in-time (JIT) liquidity is one of the harmful contingencies brought about by Uniswap v3, but its harmfulness is still debated. When a trader (or, more precisely, a trading bot) sees an exchange transaction in the mempool that has not yet been included in the chain, the bot will carefully increase the pooled liquidity in a narrow and alarming range before the exchange is completed. Liquidity is removed after the exchange transaction is completed, which is usually included in a block. Through this type of sandwich arbitrage, bots are able to earn a high percentage of fee gains on “sandwich” exchange transactions with little risk of impermanent losses.
In the latest example below, we take a look at how JIT liquidity works. When a user wishes to exchange about $80,000 worth of Apecoin, the trading botminted a $ETH only(limited range orders) to form a Uniswap v3 position, allowing the user toReplace $APE with $ETH,Thenremove the liquidity. Note that in this example, the bot not only captures an unusually high proportion of fee gains (94%), but also gains from the spread of Uniswap (~$12.80 per APE) and centralized exchanges such as FTX (~$13.19 per APE). profit.
image description
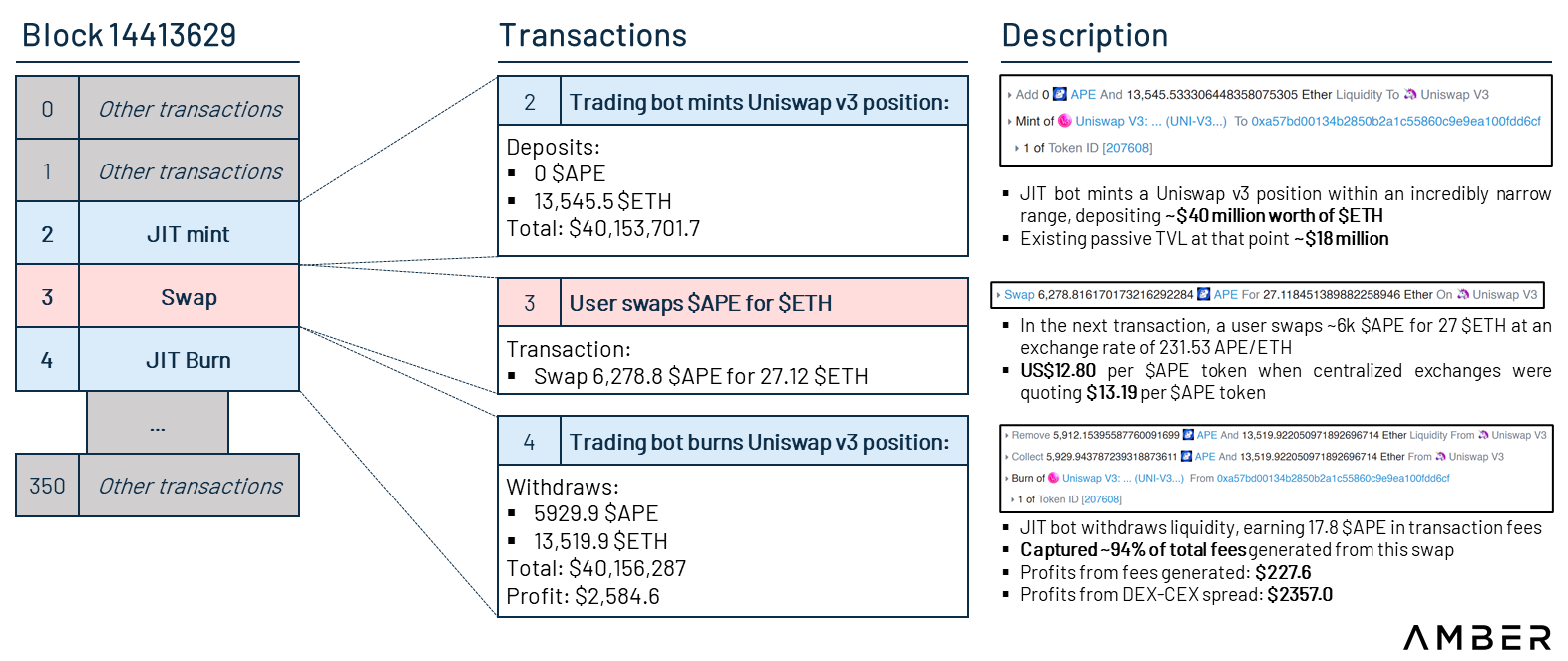
Source: Etherscan, Trading View, Uniswap
There are also some different perspectives on JIT liquidity. For traders, because the sudden surge in liquidity curbs the expected price impact, JIT liquidity improves the trading experience of traders. For example, in the above example, there was only about US$18 million TVL in the pool, and the trading robot injected liquidity of about US$40 million into it, increasing the depth of the pool.
In this case, however, passive liquidity providers are the losers. Because their fee income is diluted by robots, they still need to face impermanent loss exposure and market risk exposure.
Fortunately, the temporary impact of JIT liquidity is relatively minor as only two MEV robots are currently running most of the activity. But the attractive interests have caused the competition between the two robots,The two bots have racked up about $1.3 million since last Junesecondary title
Curve v2 - Provides centralized liquidity for risky assets
As mentioned above, Curve v1 provides centralized liquidity for fully correlated assets such as stablecoins and liquid collateralized tokens at a 1:1 rate. Curve v2 aims to passDynamic Price AnchoringAsset pairs that deal with price fluctuations. Curve v2 calculates an internal price anchor for each pool based on transactions in the liquidity pool,And concentrate liquidity around this anchor value。
image description
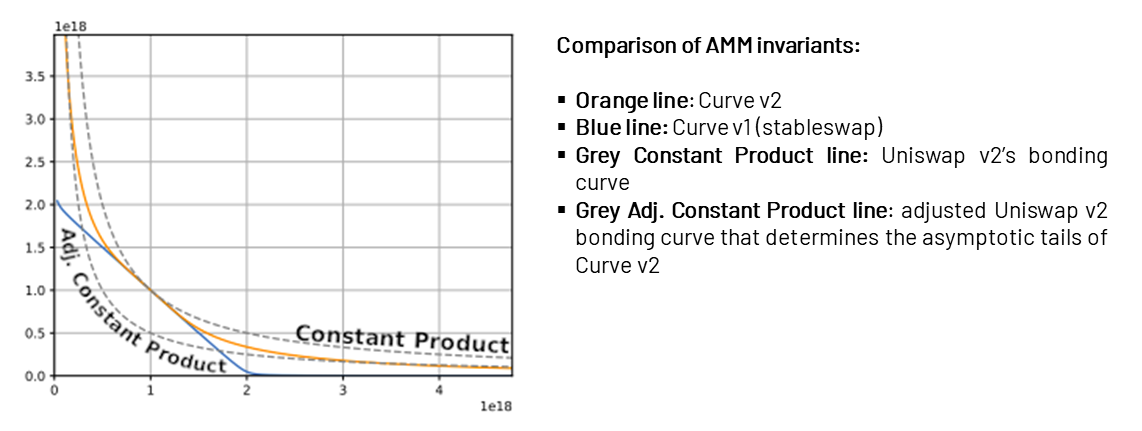
Source: Curve, Nagaking
The internal price is calculated based on a constantly changing exponential average, similar to a moving average, except that a higher weight is given to the latest price, that is, a dynamic weight, which allows for a smoother price transition.
image description
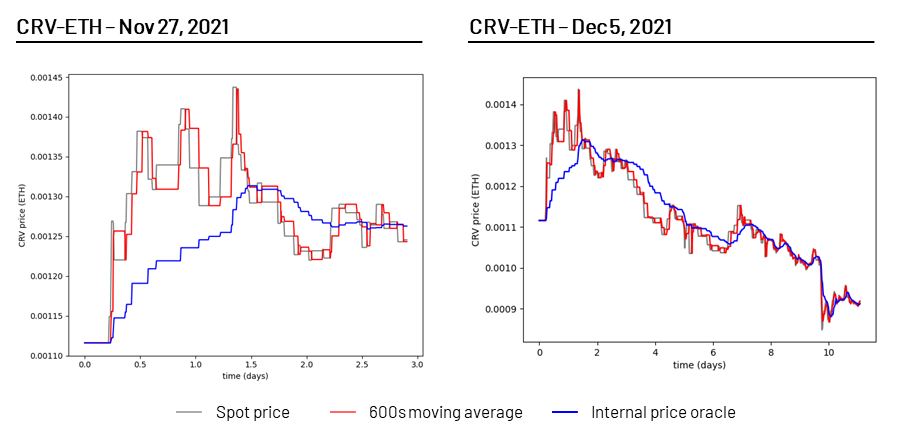
Source: Curve
Sometimes, a sudden asset price movement may require liquidity to be concentrated around another price. However, like adjusting an out-of-range Uniswap v3 position, this creates a permanent impermanent loss. Therefore, Curve's internal price anchoring enables price reanchoring, butProvided it is profitable to do so(i.e. accrued gains from transaction fees since the most recent price re-anchor can compensate for impermanent losses incurred).
Additionally, transaction fees in Curve v2 pools are dynamic. Transaction fees are also low (as low as 0.04%) during times of low price volatility. During the period of price fluctuations, increase transaction fees to hedge against volatility and compensate liquidity providers for impermanent losses in directional movements.
others"Curve War"
Curve v2 enables users to achieve the same capital efficiency as Uniswap v3 without actively managing positions, so it may be very attractive for liquidity providers. Also, since all LPs deposit in the same pool at the same price range, there is no JIT liquidity issue.
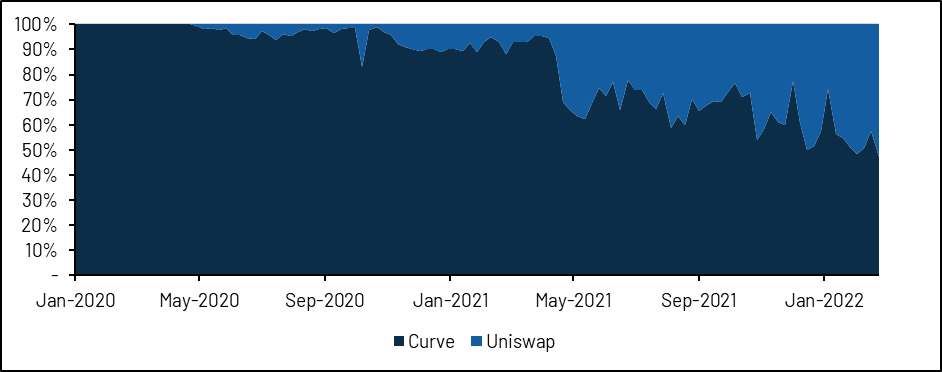
Currently, Curve v2 still only offers a handful of liquidity pools. Its Tricrypto pool (USDT + wBTC + wETH) is the most popular with around $3 billion in monthly transaction volume. Since last year, Tricrypto's trading volume has grown significantly, reaching nearly 40% of Uniswap's trading volume compared to the same trading pair on Uniswap.
image description
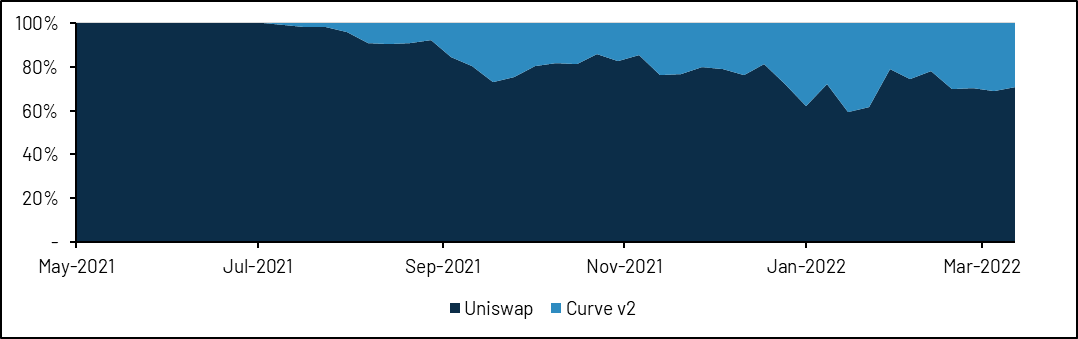
Source: Dune (@momir)
Since its inception, there have only been 20-30 daily active traders and 477 unique users on Tricrypto, and its trading volume is mainly driven by MEV (Miner Extractable Value) bots running arbitrage strategies, DEX aggregators, market makers, and exchanges giant.
image description
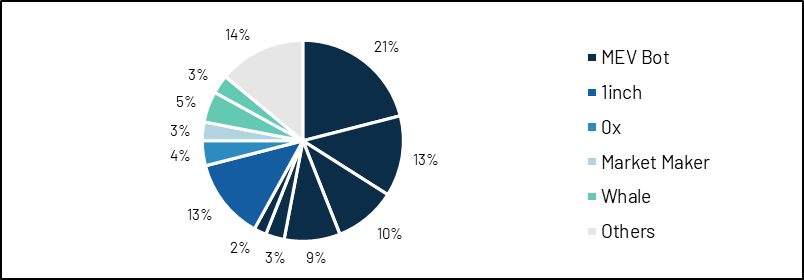
Sources: Dune (@momir), Etherscan, Nansen
Curve also offers v2 pools for a handful of other assets such as CVX-ETH, CRV-ETH, and EURT-USDT. In practice, the exchange rates offered by Curve v2 pools are often on par with Uniswap and other DEXs.
image description
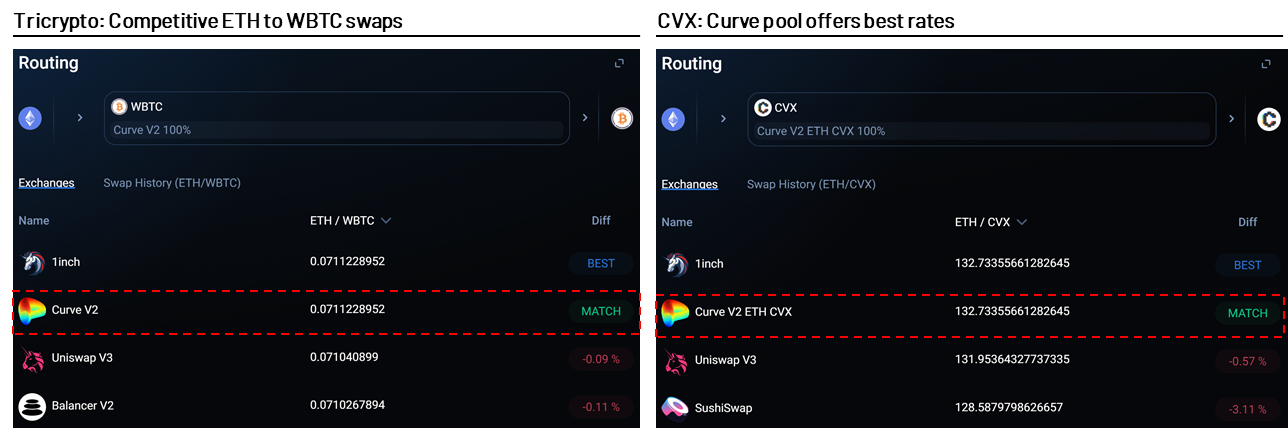
Source: 1inch, as of March 25, 2022
secondary title
Crocswap - Enabling High Frequency Trading (HFT) in DeFi
Since each liquidity pool is aseparate smart contract, and each centralized liquidity position on Uniswap is a unique NFT, so creating new pools and rebalancing centralized liquidity positions on most DEXs requires high gas fees.
Crocswapis an upcoming new decentralized exchange (DEX) that follows first principles to design its blockchain architecture. It integrates all liquidity pools on the exchange into one smart contract, and each single pool is presented in a lightweight data structure. This architecture allows traders to execute multi-step, multi-pool trades in a single smart contract, enabling cross-pool netting. As a result, traders have lower transaction fees and fewer tax issues, which is especially important for traders who frequently trade across multiple trading pairs. The design of a single smart contract also paves the way for a host of other features, such as easier margin trading since all funds are in one place.
Similar to Uniswap, Crocswap allows liquidity providers to provide ambient liquidity (Uniswap v2 style) or centralized liquidity (Uniswap v3 style). The difference is that Crocswap's ambient liquidity and centralized liquidity can exist in the same pool, which has several benefits. First, it supports fungible LP tokens, which have the composability mentioned in the previous chapters. Second, other users and protocols can query the summary of environmental liquidity and the proportion of active concentration liquidity in a single function call. In contrast, while there is a wide range of liquidity in Uniswap v3 equivalent to ambient liquidity, it is impossible to aggregate this liquidity in an on-chain environment.
In addition, the fee income of centralized liquidity providers will be automatically compounded into the environmental liquidity pool, thus saving time and gas fees for liquidity providers. Conceptually, it's like accumulating fees in Uniswap v2 liquidity tokens on Uniswap v3 positions. This can be positive for volatile trading pairs (e.g. ETH-USDC), but less efficient for pegged assets (e.g. DAI-USDC). The team is considering adjusting the architecture for different types of liquidity pools.
image description
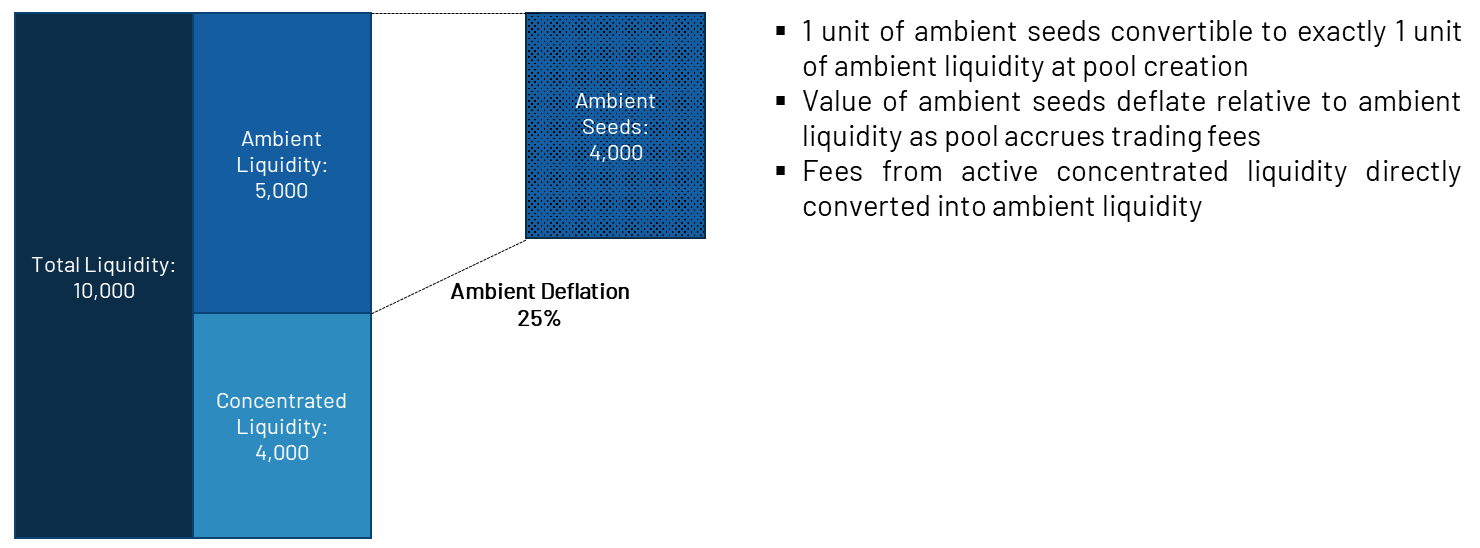
Source: Crocswap
Crocswap also allows pools to set time thresholds from 0 to 255 seconds for depositing and withdrawing liquidity in the pool, which can alleviate JIT liquidity issues. This creates a fairer trading environment for less active liquidity providers, providing traders with more stable quotes while improving price discovery. Nonetheless, since JIT liquidity does improve trade execution quality, the protocol allows whitelisted participants to act as JIT traders.
Finally, similar to centralized exchanges, Crocswap allows liquidity providers to deposit collateral directly on the DEX. Active traders can deposit excess collateral, such as USDC, on an exchange and execute hundreds of trades in a single day, with each trade reflected in the excess collateral balance. This also saves on gas fees since traders only need to make one withdrawal of excess collateral. In addition, Crocswap also provides a collateral pool for other traders to use for flash loans.
secondary title
Platypus - an open liquidity pool for a basket of currencies
Although Curve is highly efficient for the exchange between stablecoins and anchor assets, its architectural design still has some pain points. It is worth noting that separate liquidity pools must be created for each set of tokens (two/three/four, etc.), and similar assets can be replicated across multiple pools. USDC in one pool cannot support the liquidity of USDC in another pool.
image description
Source: Curve Finance
To provide users with sufficient liquidity and prevent arbitrage, new stablecoin projects may need to create and support multiple pools. Plus, the least popular coins are often the growth bottleneck for stablecoin pools.
PlatypusIt is a stable currency exchange protocol launched on Avalanche at the beginning of this year, aiming to solve the above pain points. It allows the creation of open liquidity pools where all similarly anchored assets are mixed. Liquidity providers can deposit and withdraw the same type of tokens.
Above we mentioned that Curve v1 mixes constant sum formula (x + y = k) and constant product formula (x * y = k). Platypus, on the other hand, only modifies the constant sum formula, using the coverage ratio to encourage depositors to maintain the balance of the open liquidity pool. This makes the area at the end of the curve longer and flatter, and speeds up slippage. Therefore, under normal circumstances, Platypus can achieve up to 40% lower transaction slippage compared to other AMMs for large volume stablecoin swaps.
image description
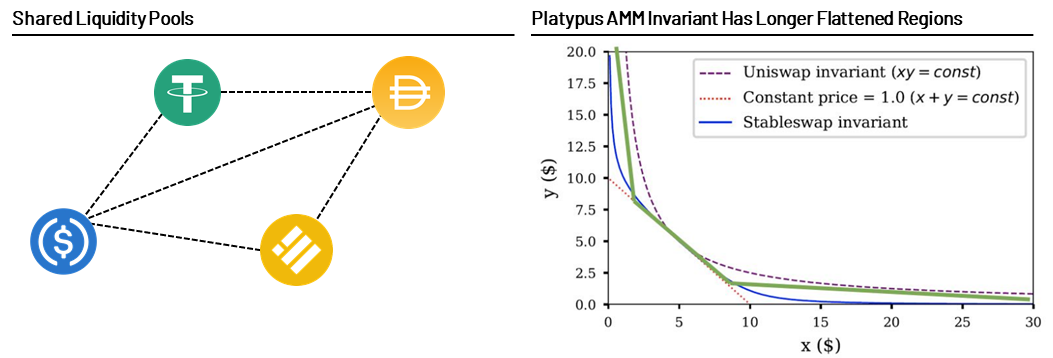
Source: Platypus. The green curve is the constant value of the Platypus AMM.
image description
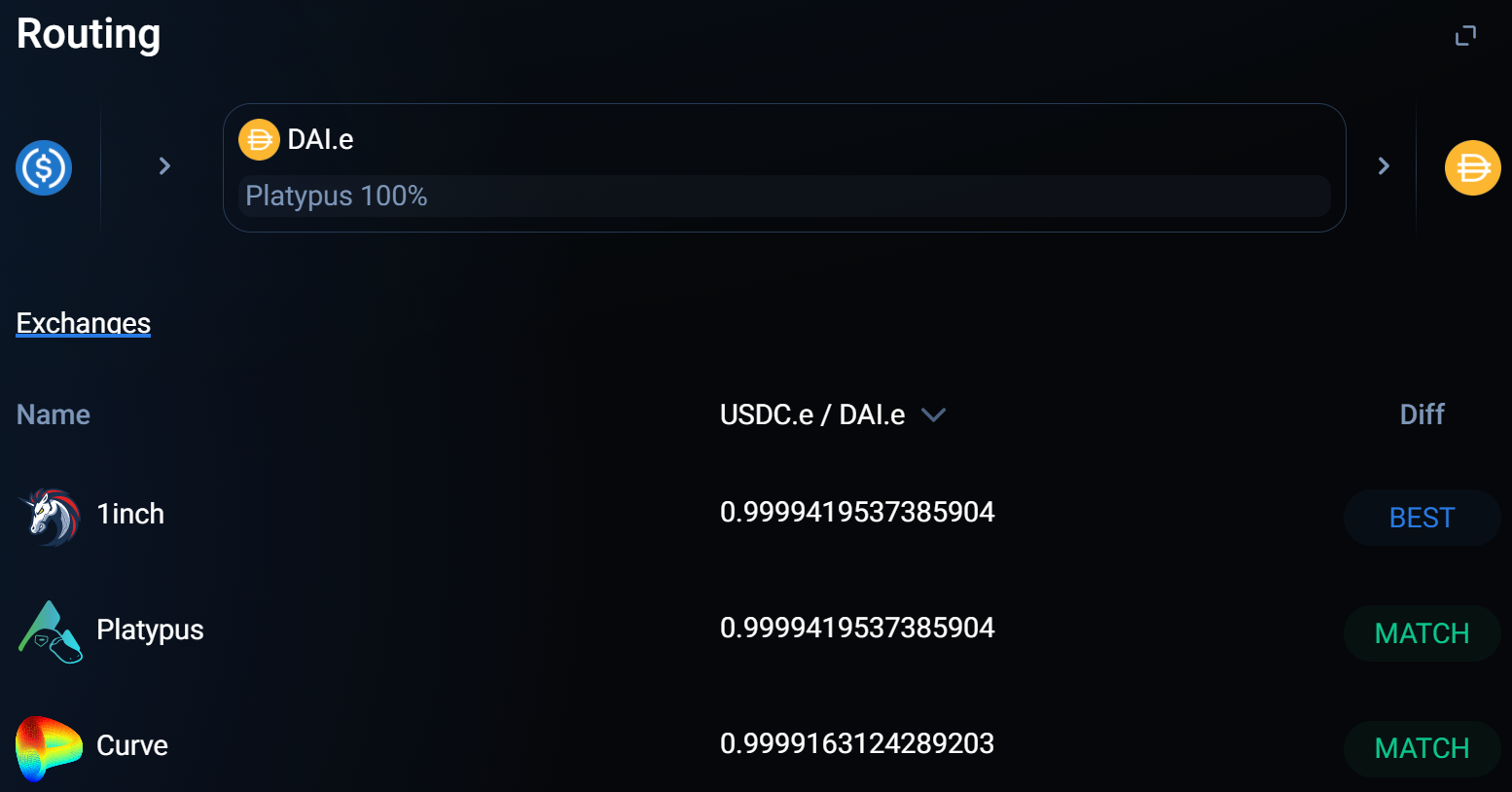
Source: 1inch, as of March 27, 2022
secondary title
text
Bancor v2.1
Bancor has iterated multiple AMM architectures since v1 in 2017. Bancor v2 tried to use oracles to dynamically balance the liquidity pool and avoid arbitrage behavior, but decided to switch due to poor performance (we will discuss the problems faced by oracle-dependent AMMs in the next section).
The current version of Bancor (v2.1), launched in October 2020, has two key features:Unilateral liquidity and impermanence loss insurance.
Bancor was one of the first AMMs to enable side exposure. [Note: The ability to receive LP tokens by depositing only one token is not necessarily one-sided exposure; Consider slippage. 】
Each pool on Bancor contains two tokens: the associated token and Bancor's native token $BNT. For example, if Alice wants to provide wBTC tokens, Bancor's protocol will mint USD equivalent BNT to match the wBTC position. Therefore, the Alice and Bancor protocols each own 50% of the pool. If another trader on the Bancor platform wants to exchange ETH for wBTC, the transaction will go through two pools of ETH-BNT and wBTC-BNT, and Alice will get the fee income from the wBTC-BNT transaction.
Bancor v2.1 also provides impermanence loss insurance for long-term liquidity providers. LPs locked for more than 30 days are guaranteed to receive at least 30% of the principal return. The return rate increases linearly by 1% per day, so on the 100th day of lock-up, LP will be guaranteed 100% principal return. Any IL generated by LPs is first paid for by transaction fees incurred as Bancor matches each LP's position, and IL not yet paid is then covered by minting $BNT.
image description
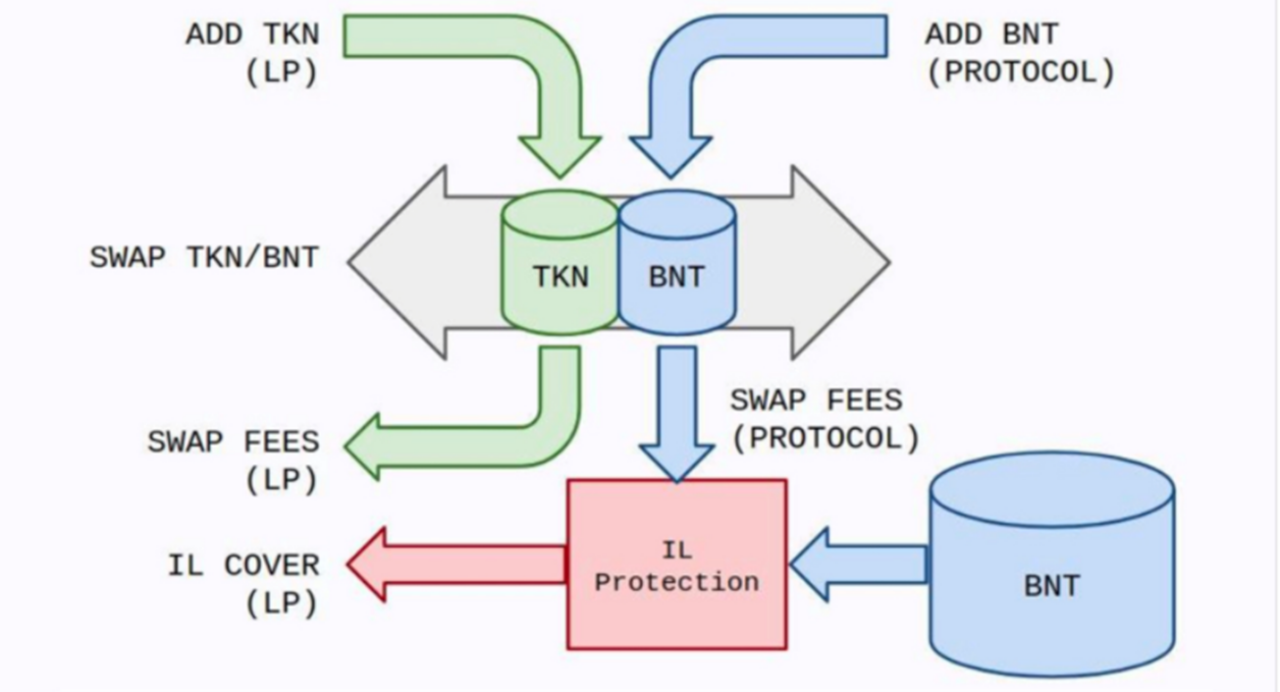
Source: Bancor
However, Bancor's v2.1 architecture design has some problems:
● High gas fees.Due to the architectural design of the protocol and smart contracts, Bancor's gas fee is significantly higher than that of other DEXs. Each transaction involves two transaction pairs (from token A to BNT, and then from BNT to token B), and the calculation of each There is also potential complexity in the IL produced by an LP.
● Limited unilateral liquidity.Due to impermanent loss insurance, Bancor DAO's co-investment will determine that each token pool has a cap. If the pool is full, potential LPs must wait for existing LPs in the pool to withdraw their liquidity before they can join. Popular token pools have long maintained full liquidity, such as ETH, wBTC, and stablecoins.
● Up to 100 days of lockup can be exchanged for impermanence loss insurance.As mentioned above, Bancor's gratuitous loss insurance needs to be locked for 100 days to be fully realized.
● Rewards need to be withdrawn manually.text
Bancor v3
First revealed in November 2021 but not yet available, Bancor v3 attempts to address the above issues by effectively redesigning the protocol while maintaining key features of v2.1.
v3 redesigned the unilateral liquidity architecture. When LPs deposit tokens (TKN), they receive an equivalent amount of Bancor pool tokens (bnTKN). These pool tokens automatically compound the fee yield, so 1 bnTKN is always greater than or equal to 1 TKN. There is no pool token concept in Bancor v2.1, because these pool tokens are mapped to a single underlying asset that does not contain IL, and this pool token concept is likely to become the underlying architecture of other DeFi platforms (for example, as collateral).
Deposited tokens will be put into a smart contract containing all tokens of the platform, so while it may appear from the front end that there are multiple separate liquidity pools, in reality all funds are in one vault with one transaction Logic Layer to coordinate deposits, withdrawals and exchanges.
image description

Source: Bancor
This architecture has many benefits. First, because the intermediary BNT is virtualized, the transaction only needs to happen in one transaction pair instead of two, thus reducing the gas fee. Second, using pool tokens greatly reduces the complexity of calculating IL for each LP, further saving gas fees. BNT stakers also don’t need to choose which specific pool their tokens should be placed in, instead all BNT liquidity providers get the same rewards.
Most notably, this architecture allows for unlimited deposits. Similar to Bancor v2.1, Bancor DAO will determine the liquidity that each token can provide for transactions, but even if the upper limit is reached,Users can still continue to deposit tokens. These excess tokens help 1) offset IL introduced by sudden price changes, and 2) can be used for other fee income strategies outside of the protocol. For example, excess ETH can be pledged to obtain stETH, excess LINK can be pledged, excess USDC can be lent in Aave, etc.
The gratuitous loss protection has also been redesigned in v3. Whereas in v2.1 LPs had to wait 100 days for full impermanent loss protection, in v3 LPs get it immediately. In exchange, Bancor v3 charges a 0.25% withdrawal fee and a 7-day delay to account for any potential attack. also,Other protocols and DAOs may choose to provide IL in their own tokensprotecttext
new dawn (Dawn) dawn
Every AMM must balance users (who want the widest selection, lowest slippage, and lowest fees), liquidity providers (who want the highest yield with limited IL), external protocols (who want low cost for their tokens) holders provide sufficient liquidity) and native token holders (who want to see token appreciation). Bancor v2.1 introduced some innovative solutions to protect LPs and protocols, but users were burdened by high gas fees. Coupled with the deposit cap, it eventually led to a stagnation in the growth of its TVL, transaction volume, and BNT token price.
image description
Source: DefiLlama, CoinGecko
Bancor v3 has the best features ever. With uncapped deposits and instant IL protection, Bancor will likely see a substantial increase in TVL. Bancor DAO can use this assist to increase the liquidity available for trading, increasing pool depth while reducing price slippage for traders. The new architecture can not only reduce the gas fee, but also1inch aggregator for Bancor to increase transaction volume. Through a more substantial IL insurance fund, higher transaction fees can both directly increase IL protection and indirectly promote BNT appreciation. Protocols and DAOs can also promote platform growth by launching customized reward programs. already have30+ DAOs start using Bancor for treasury management, including Nexus Mutual, Yearn Finance, and Woo Network.
But we have yet to see the final results of this transformation. Bancor v3 will be launched in three stages: Dawn (dawn), Sunrise (sunrise) and Daylight (daylight). The first stage includes the key functions of Bancor v3 such as instant IL protection. The first stage may be launched in 2022. Rolled out quarterly, with public bug bounties available. The second phase includes additional features, such as utilizing idle assets to generate superfluid returns.
secondary title
Oracle-Assisted Market Maker
A common problem with simple AMM algorithms such as the constant product formula is that prices are always "out of date". Since the price of the trading pair in the AMM is calculated by a function based on the reserve balance, the price of the trading pair will be updated to the market price later due to the arbitrage transaction. In fact,The majority of trades executed on AMMs are driven by arbitrage。
Impermanent losses can also be thought of as losses suffered by liquidity providers as a result of receiving “Toxic Flow,” a common term used in high-frequency trading to describe informed trading. LPs in an AMM always offer the "wrong" price and rely on other participants trading with them to adjust the price to the correct one. In order to limit the flow of poison, some protocols introduce oracle machines that provide external market quotations, so as to prevent liquidity providers from being squeezed. These AMMs are often referred to astext。
Dodo - Active Market Maker
Dodo is one of the first active market makers launched on the market, using external market prices to focus liquidity around the market price. Dodo can adjust the impact of external prices. On the one hand, Dodo's AMM concentrates liquidity on the external market price and executes buy and sell orders at that price; on the other hand, when the market price has no influence, Dodo's bonding curve actually becomes It became the Uniswap v2 curve.
It seems like Dodo should be able to set up trades to be executed only at external market prices, but again this would increase the risk of arbitrage. For example, suppose a trader knows that the oracle quote for an asset will go up in the next block, then she will try to buy the asset before the price is updated, and sell it on the Dodo as soon as the oracle publishes the updated price on-chain The asset to obtain a risk-free profit. Reducing centralized liquidity mitigates this risk. Therefore, Dodo, which takes this risk of arbitrage into account, sets the parameters not to rely solely on oracles to balance centralized liquidity.
image description
Source: Dodo
Dodo also allows liquidity providers to deposit any combination of the two tokens in the trading pair pool, including single currency staking. For example, LP can separately deposit ETH into the ETH-USDC pool. Therefore, Dodo claims to provide liquidity on their platformno impermanent loss。
But there is no free lunch in the world. Because Dodo obtains token inventory from liquidity providers and acts as a market maker, the elimination of IL risk comes with inventory risk, that is, when the market trend of this pair of currency is unfavorable, the overweighting of the pair of currencies brings risk. This is actually another form of poisonous flow, which Dodo has been working hard to eliminate. Therefore, most of Dodo's TVL is locked in the anchor asset, not the price fluctuation asset.
image description
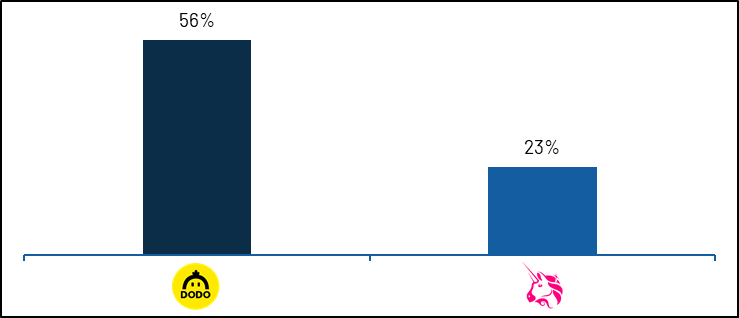
text
Lifinity - Active Market Maker on Solana
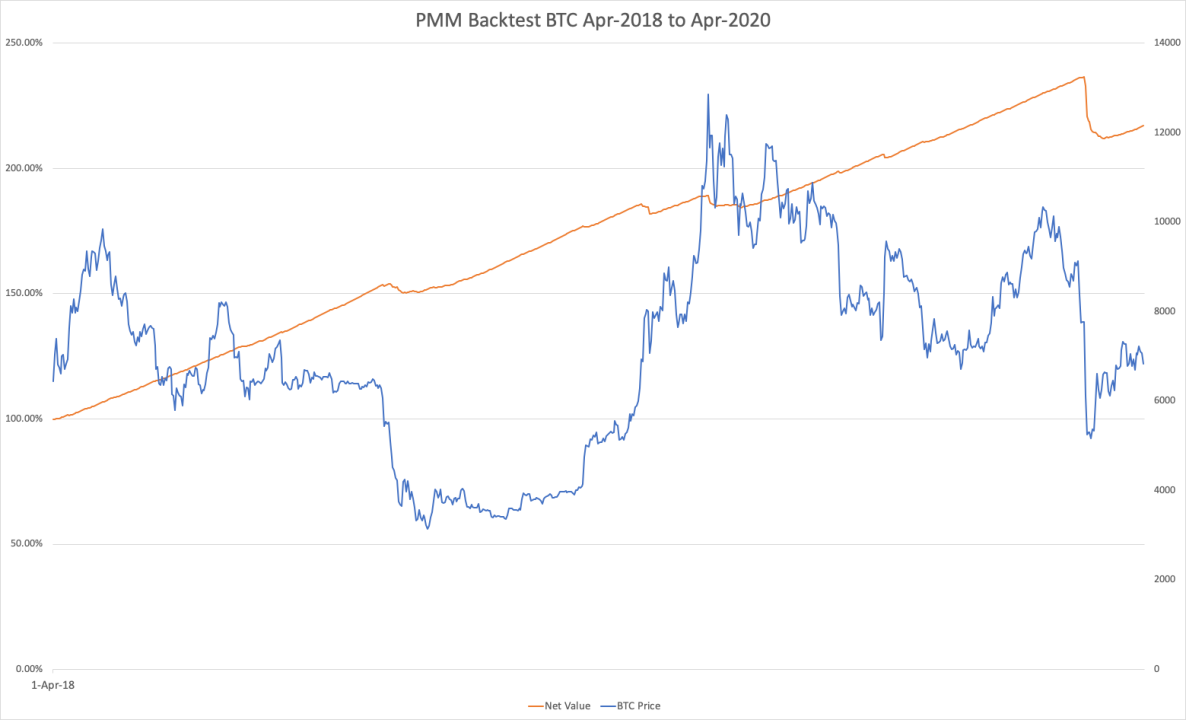
Lifinity is a Dodo-like model, but uses the Pyth Network as an oracle on Solana. Since Pyth lets each data provider put their data directly on-chain, and there is no fee revenue market on Solana, front-running is not an issue for it. Lifinity is currently in beta and can deposit liquidity with closed access, but the test results look good: Lifinity can evenimage description。
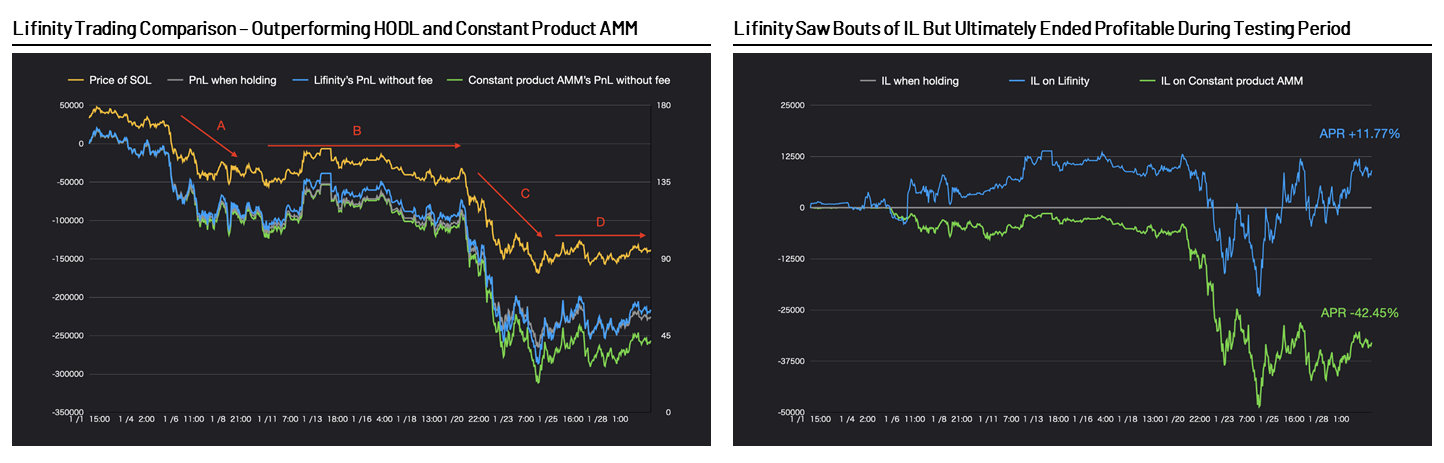
Source: Lifinity
At the beginning of the period, Lifinity achieved the above effect by accumulating more USDC when the price of SOL fell (above period A). As such, it reaps the lucrative benefits of savvy inventory management. Even so, under more volatile market price conditions (Phase C), Lifinity also experienced a period of losses, as Lifinity rebalanced its liquidity pool just before the SOL price plunged.
The real test will come when Lifinity opens up deposits to the broad public. Compared with trading 100 million US dollars, it is easier to achieve excellent results when trading 1 million US dollars. also,Solana's Upcoming Fee Income MarketplaceMay create a vehicle for front-running, also depending on how the fee revenue market is implemented.
Challenges for Proactive Market Makers (PMMs)
price manipulationprice manipulationand front-runningKey Vectors for Attacks. Also, they are limited to large-cap cryptocurrencies. Oracle Market Leader Chainlink Only Covers Ethereum Mainnet104 cryptocurrency pairs; by contrast, Uniswap v2 has more than 1,500 Tokens。
Summarize
Summarize
Key trends in AMM are summarized below:
Greater emphasis is placed on protecting LPs and managing IL risk rather than ensuring capital efficiency.Early last year, there was also increased focus on improving LP capital efficiency. The introduction of Uniswap v3 not only solves this problem, but also demonstrates the lethality of IL to liquidity providers. Therefore, market attention has shifted to extensively establishing mechanisms to protect LPs and manage impermanent losses, from IL protection (Bancor) and price oracles to dynamic adjustment of spreads, etc.
Efficiency improvements are now more focused on protocol architecture design.Mainly through integration to improve price slippage and reduce gas fees. For example, both Bancor v3 and Platypus use the "omnipool" concept to reduce fluid fragmentation and thus improve depth. Likewise, Crocswap consolidates everything into one smart contract, drastically reducing gas fees. The benefits are obvious, but this trend may also increase the risk of smart contracts, and hackers will be able to profit more from successful attacks.
Composability remains a top consideration.While Uniswap v3 won't necessarily disrupt composability, it will be a daunting task for other projects to integrate unique NFT positions rather than fungible tokens. Other AMMs are considering innovative ways to create useful and composable token LEGOs for use by other users and protocols.
We have attempted to cover most of the existing major AMMs and upcoming AMMs in this report, but due to the rapid development of the DeFi ecosystem, we can only focus mainly on EVM-based AMMs. There are plenty of innovative projects beyond the AMMs we mentioned, especially with the emergence of critical enabling infrastructure. High-throughput blockchain platforms have prompted exchanges to return to central limit order books, such as SolanaSerumand on StarkNet/zkSyncZigZag ExchangeOpyn's SqueethOpyn's SqueethDeFi emerging underlying architecture projects allow LPFully hedge against impermanent losses. The introduction of countless cross-chain bridges enables the AMM system to span multiple blockchains, such asOsmosisandCatalog Finance。
image description
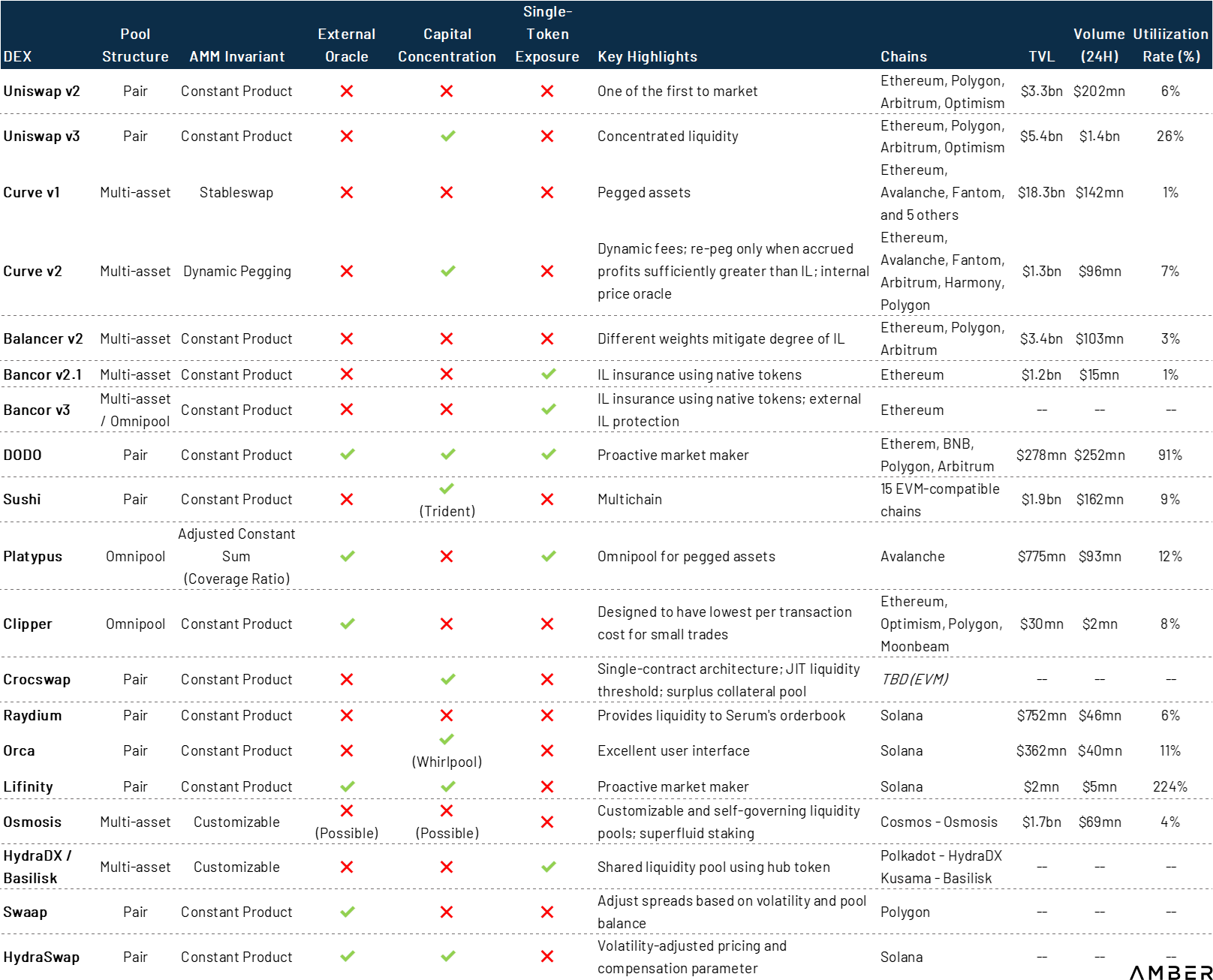
Sources: Project website and whitepaper, DefiLlama, CoinGecko. As of March 27, 2022.
The media often comment that cryptocurrencies are justreplicaupfinancefinance. The high throughput on the L1 and L2 blockchains enables reproducibility of order book mode transactions, which begs the question: what is the use of AMMs?
Original link



