Stolen 610 million US dollars, the scene of the hacker attack on Poly Network and O3 Swap
O3, the previous popular star project, must be remembered by everyone, but it collapsed a day ago, and the O3Swap pool was stolen. Because O3’s funds were placed in poly, the poly was hacked and O3 was destroyed; on the evening of August 10, The cross-chain protocol Poly Network was attacked, and nearly US$600 million was stolen from the three chains of Ethereum, BinanceChain, and Polygon. Because the two attacked platforms are backed by the same technical team with NEO endorsement, the reason for the theft is that the project party has reserved super authority for itself in the contract, and hackers use this super authority backdoor to transfer all the coins in the pool to Walk.
LBank Blue Shell Academy is here to popularize science. PolyNetwork was once considered to be the best cross-chain interoperability protocol in the current market, and it truly achieves heterogeneous cross-chain. Currently, the supported heterogeneous cross-chain protocols include: Bitcoin, Ethereum, NEO, Ontology, Elornd, Ziliqa, Binance Smart Chain, Switcheo, Huobi Ecological Chain, etc.
Review events:
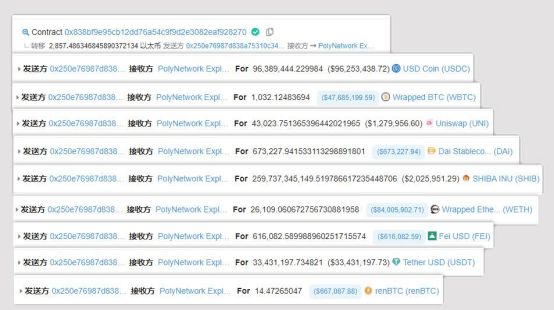
The attack first occurred at 17:55 on August 10. The hacker successively transferred 96.38 million USDC, 1032 WBTC and other assets from the Poly Network smart contract in Ethereum, with a total value of more than 260 million US dollars; 85.08 million USDC was transferred from the smart contract of the project; from 18:08, the hacker transferred 87.6 million USDC, 26629 ETH and other assets from the smart contract of the project in BSC.

This is the largest hacking incident in the history of encryption, surpassing the famous Mt.Gox incident (744,408 BTC, with a total value of about 400 million U.S. dollars at the time), and the 2018 Coincheck case (523 million XEM, at the time total value of approximately US$534 million). Regarding the specific reasons for this incident, the technical team of the industry security organization has been conducting real-time monitoring to track the principle and technical details of the vulnerability.
After analysis, the attacker took advantage of the logic flaws in the EthCrossChainManager contract, called the putCurEpochConPubKeyBytes function in the EthCrossChainData contract through the contract to change the Keeper to its own address, and then used the address to sign the transaction for withdrawing tokens, thereby transferring the A large number of token sets are withdrawn.
Attacker address:
Attacker address:
BSC:
0x0D6e286A7cfD25E0c01fEe9756765D8033B32C71
ETH:
0xC8a65Fadf0e0dDAf421F28FEAb69Bf6E2E589963
Polygon:
Attack transactions:
BSC:
A:
0x7ceA671DABFBa880aF6723bDdd6B9f4caA15C87B(EthCrossChainManager)
B:
0x2f7ac9436ba4B548f9582af91CA1Ef02cd2F1f03(LockProxy)
ETH:
C:
0x838bf9E95CB12Dd76a54C9f9D2E3082EAF928270(EthCrossChainManager)
D:
0x250e76987d838a75310c34bf422ea9f1AC4Cc906(LockProxy)
Polygon:
E:
0xABD7f7B89c5fD5D0AEf06165f8173b1b83d7D5c9(EthCrossChainManager)
F:
Attack transactions:
BSC:
0x3eba3f1fb50c4cbe76e7cc4dcc14ac7544762a0e785cf22034f175f67c8d3be9
0x50105b6d07b4d738cd11b4b8ae16943bed09c7ce724dc8b171c74155dd496c25
0xd65025a2dd953f529815bd3c669ada635c6001b3cc50e042f9477c7db077b4c9
0xea37b320843f75a8a849fdf13cd357cb64761a848d48a516c3cac5bbd6caaad5
ETH:
0xb1f70464bd95b774c6ce60fc706eb5f9e35cb5f06e6cfe7c17dcda46ffd59581
Polygon:
0x1d260d040f67eb2f3e474418bf85cc50b70101ca2473109fa1bf1e54525a3e01
0xfbe66beaadf82cc51a8739f387415da1f638d0654a28a1532c6333feb2857790
On BSC, the attacker first calls the verifyHeaderAndExecuteTx (0xd450e04c) function in the EthCrossChainManager contract by passing carefully constructed data. Since the verifyHeaderAndExecuteTx function calls the internal function _executeCrossChainTx, and the call is used in the internal function, the attacker controls the parameter _method of the call through carefully constructed data (obtaining the data signed by the original Keeper through other vulnerabilities) , successfully called the putCurEpochConPubKeyBytes function in the EthCrossChainData contract as the EthCrossChainManager contract to change the Keeper to its own address (0xa87fb85a93ca072cd4e5f0d4f178bc831df8a00b). This step is to obtain the transaction signed by the valid Keeper in the future, and then withdraw the tokens in the contract.
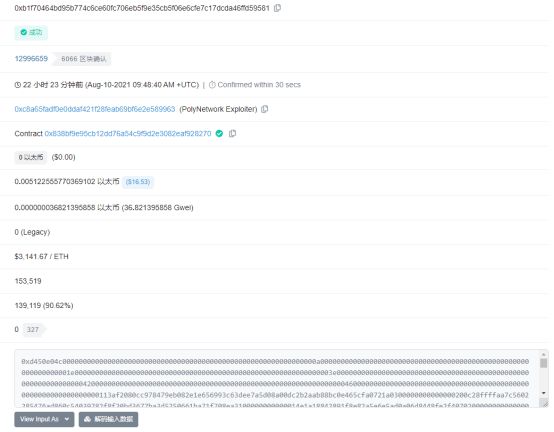
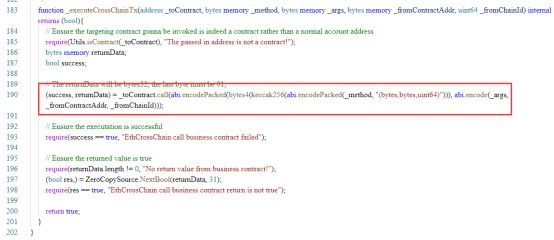
The _method constructed by the above call attacker is not actually putCurEpochConPubKeyBytes, because only the function name in the call call is user-controllable, and the parameters are fixed in number and type. The attacker realized the call to the putCurEpochConPubKeyBytes function in the EthCrossChainData contract by constructing the f1121318093 function with the same function signature as putCurEpochConPubKeyBytes.
After modifying the Keeper, the attacker can sign arbitrary transactions. The attacker withdraws all the ETH, BTCB, BUSD and USDC tokens in the B contract through multiple transactions signed by the valid Keeper (the signature has been modified by the attacker to his own address).
Since ETH and Polygon have the same code and Keeper as BSC, after completing the attack on BSC, the attacker replays the previously constructed data on ETH and Polygon, and modifies the Keeper on ETH and Polygon to its own address (0xa87fb85a93ca072cd4e5f0d4f178bc831df8a00b).
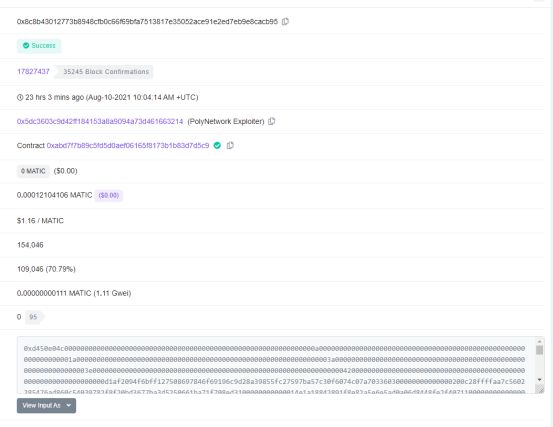
Then, using the same attack method, all the ETH, USDC, WBTC, UNI, DAI, SHIB, WETH, FEI, USDT, and renBTC in the D contract and all the USDC in the F contract were taken out.
The attacker returned 1.01 million USDC to Polygon. Ps: Now a lot of people are sending coins to the hacker’s address to leave a message to ask for coins, because I heard that someone will get 13.5 eth after asking for it
What things do we need to pay attention to?
The main reason for this attack is that there is a problem with the contract authority management logic. Any user can call the verifyHeaderAndExecuteTx function to execute the transaction, and when calling it inside, the function name can be controlled by the user. Malicious users can call by carefully constructing data exceptions partial function. At the same time, the EthCrossChainManager contract has the authority to modify the Keeper. Normally, it is modified through the changeBookKeeper function. However, in this attack, the attacker successfully modified the Keeper address through the call in the verifyHeaderAndExecuteTx function through carefully constructed data, and the Keeper address can The transaction is signed, and the attack event with the largest loss since the birth of Defi is thus generated.
LBank Blue Shell Academy hereby reminds everyone that when using call, developers need to pay special attention to the fact that the parameters are controllable by the user. Some special contracts and functions need to strictly control permissions to avoid irreparable losses caused by abnormal calls .


