Original author: duoduo, LD Capital

The derivative DEX field is fiercely competitive, with GMX, dYdX, SNX as the leaders, and Gains Network, MUX, Level, ApolloX as the second-tier players. At the same time, there are also constantly emerging new protocols going online.
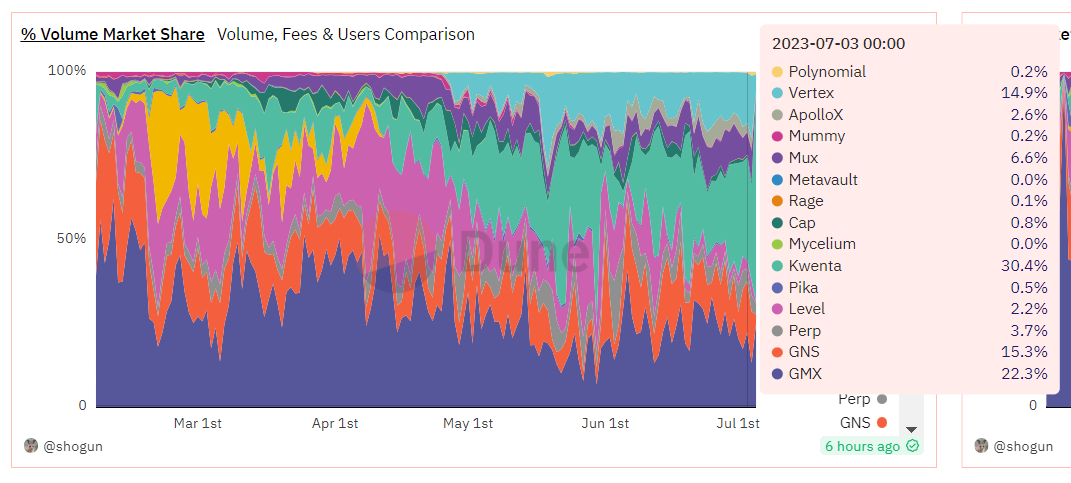
Vertex Protocol is a recently performing well derivative DEX protocol. Since its launch at the end of April 2023, its daily trading volume has accounted for about 10% to 15% of the capital pool-based derivative DEX market, and it received strategic investment from Wintermute in June 2023.
Source: dune
Note: This chart does not include data from DYDX. It compares decentralized exchanges using the liquidity pool model.
I. Business Data
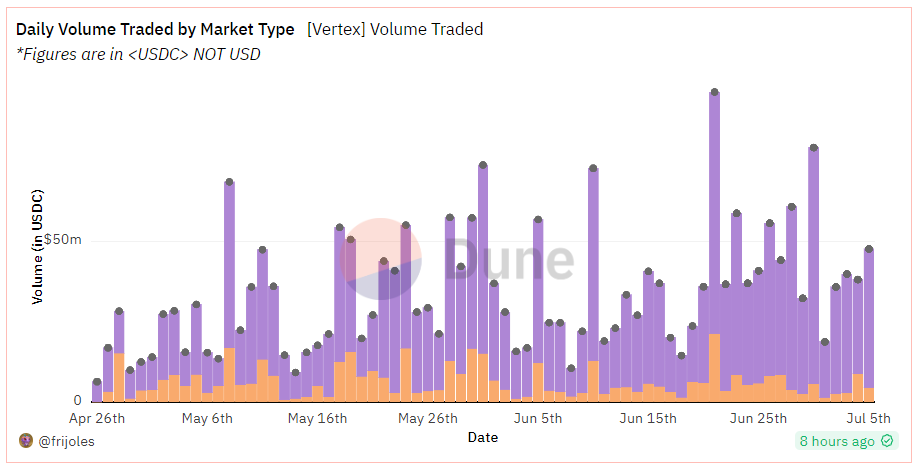
l Trading Volume: A high trading volume has been generated primarily through trading incentives, with an average daily trading volume of approximately $40 million in the past 7 days. The purple section represents derivatives, while the yellow section represents spot trading, with derivatives trading being the main focus.
The daily trading volume of Vertex is lower than that of leading derivative DEXs (DYDX/GMX/SNX), but comparable to second-tier derivative DEXs. Based on the trading volume in the past 7 days, Vertex has already entered the top ten.
Source: dune
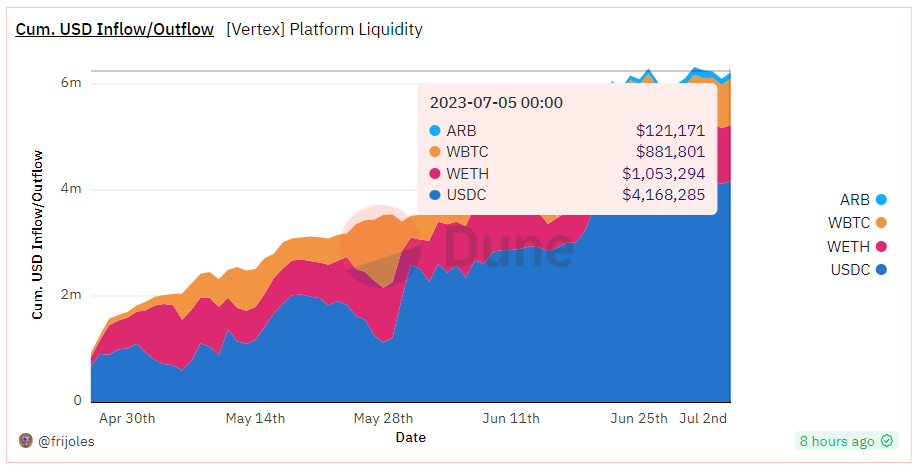
TVL: 6.22 million USD, the scale is still relatively small, including four tokens, as shown in the following figure:
Source: dune
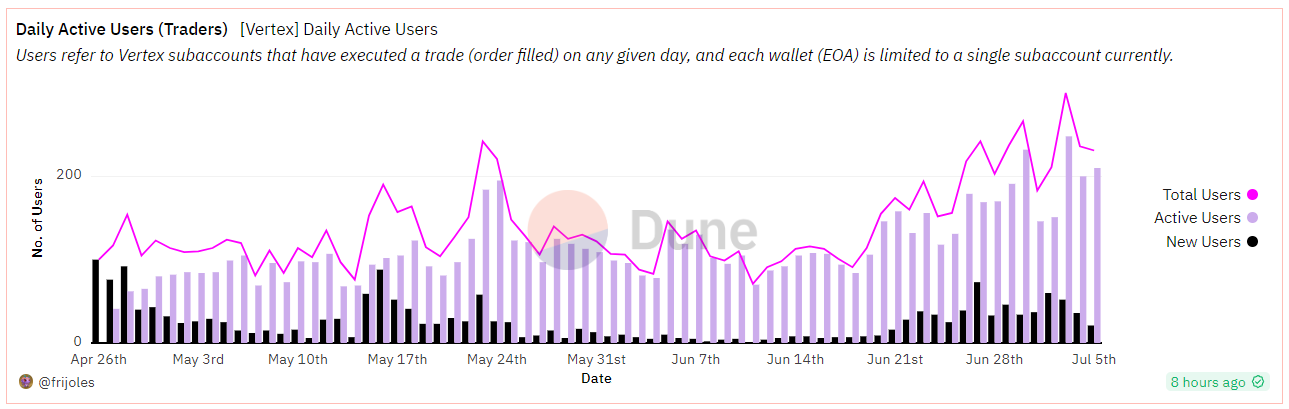
DAU: Cumulative number of users 1842, with approximately 200 daily active users in the past 7 days. In comparison, GMX has more than 1000 daily active users, DYDX is around 700, and SNX is around 500.
Source:dune
Open Interest: There are a total of 7 trading pairs, with BTC and ETH occupying the main share. The current open interest is approximately 5.37 million US dollars. The open interest amount is also relatively low.
DYDX's open interest amount is about 300 million, GMX's open interest amount is about 150 million to 200 million, Gain Network is between 30 million to 50 million, and Mux is between 20 million to 50 million.
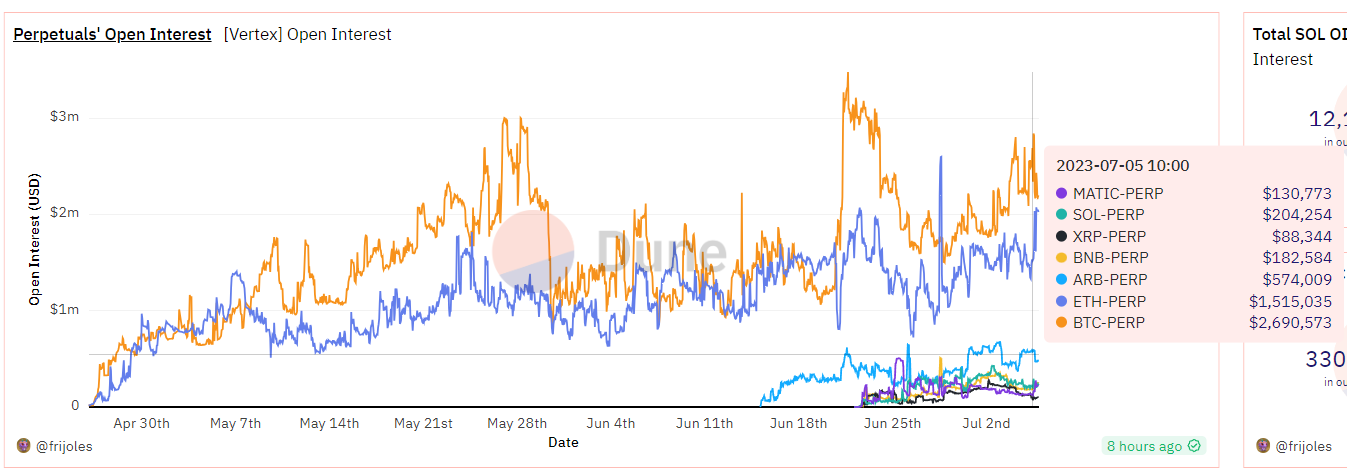
Source: dune
Fee: Accumulated gross income is about $540,000. Deducting commission of $86,000 to the maker, the net income is $460,000.
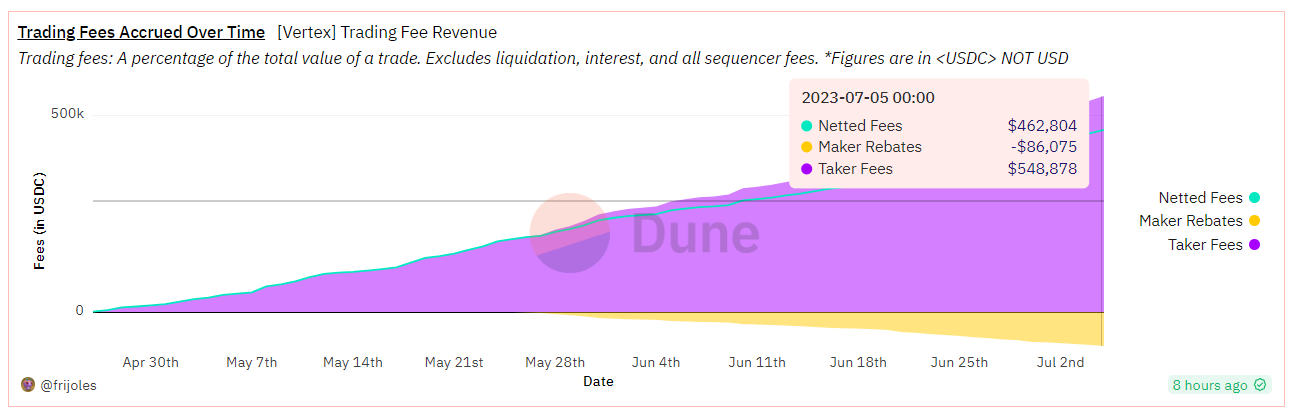
Source: dune
II. Team and Investors
Co-founder Darius is primarily responsible for external marketing activities.
Co-founder Alwin Peng previously worked at Jump trading as a blockchain engineer.
Vertex received strategic investment from Wintermute Ventures in June 2023. Wintermute Ventures is the venture capital division of Wintermute, a cryptocurrency market maker. Wintermute provides market-making services for various well-known projects such as Arb, OP, and Blur.
Wintermute announced its investment in Vertex, stating, "Vertex is led by a strong team of traders and engineers with a proven track record in both TradFi and DeFi markets, at the forefront of smart contract and market innovation."
Previously, in April 2022, Vertex received $8.5 million in seed funding led by Hack VC and Dexterity Capital, with participation from Collab+Currency, GSR, Jane Street., Hudson River Trading, Huobi Capital, JST Capital, Big Brain Holdings, Lunatic Capital and others participated in the follow-up investment. Early investors received 8.5% of the tokens, which means that the seed valuation of Vertex was $100 million. Vertex was originally built on Terra, but after Terra crashed, the protocol migrated to Arbitrum.
Three, Products
Vertex provides a one-stop DeFi service, including spot, contract, and lending markets. The business is mainly focused on contract markets, with most of the trading being perpetual contract trading. Spot and lending markets are more for contract services, so they are classified as derivative DEX. Liquidity supply model: Hybrid order book-AMM model. The liquidity supply model is the main difference between Vertex and other derivative DEX. Vertex believes that off-chain order books processed through FIFO (first in, first out) can reduce MEV attacks and improve transaction execution speed.And the on-chain AMM provides permissionless liquidity support, traders can forcibly conduct transactions, and when there is insufficient liquidity in the order book, it can ensure the effective operation of transactions.Vertex achieves the hybrid order book-AMM mode through the following components:
On-chain trading venue (AMM);
On-chain risk engine for fast liquidation;
Off-chain sorter for order matching.
Figure: Vertex core component architecture
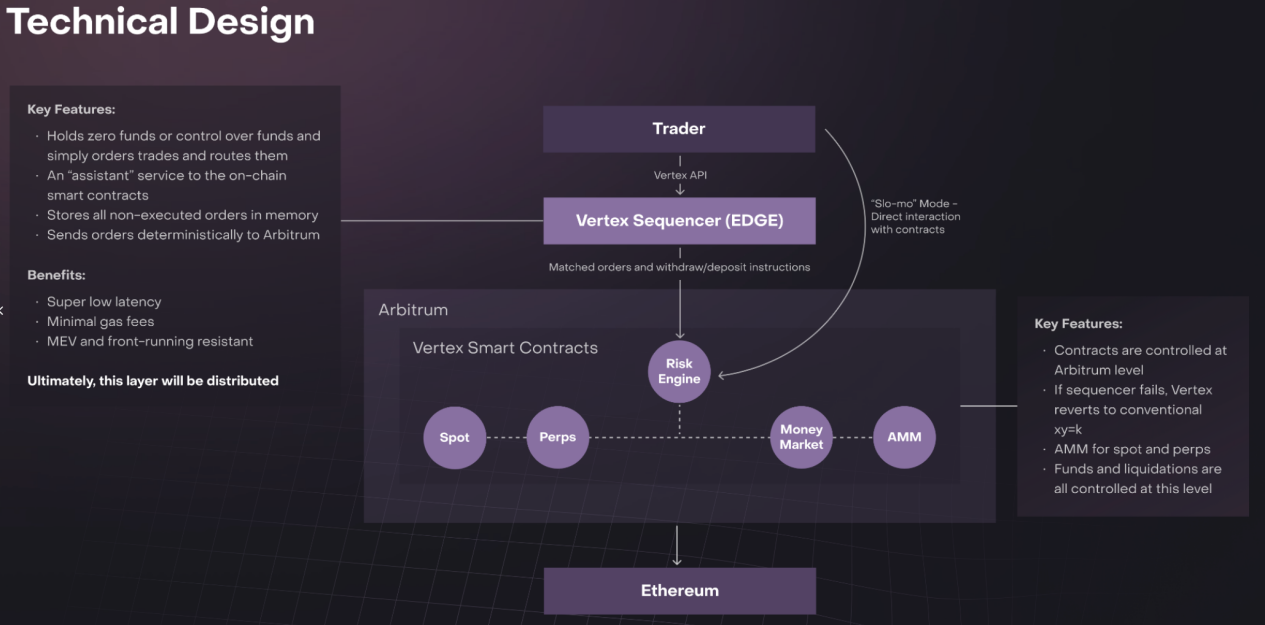
Source: Vertex
This means that in the Vertex trading platform, there are two types of liquidity. One is the order book liquidity provided by market makers through API, and the other is the LP funds provided by smart contracts.
These two types of liquidity are combined by the aggregator, and what is seen on the front-end of the page is a unified liquidity, traded based on the best available price. The diagram below shows how the aggregator utilizes the order book liquidity and LP liquidity to complete trades.
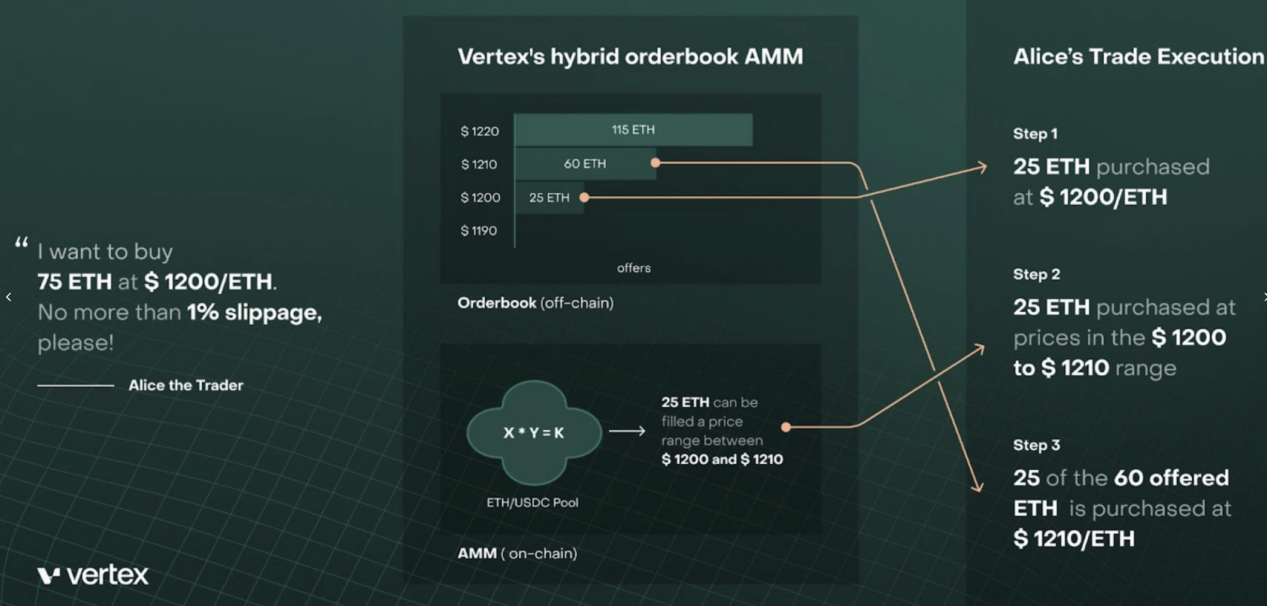
Source: Vertex
Process Analysis:
The trading price of the ETH-USDC currency pair is $1200.
Alice wants to buy 75 ETH on the market and sets the maximum slippage to 1%.
There is an order worth 25 ETH in the order book at a price of $1200, therefore one-third of the transaction is executed at $1200.Previous order book sell orders (total of 60 ETH) are priced at $1210. However, there are LP positions for 25 ETH in the price range between $1200 and $1210. As a result, the next third of the trades are purchased from LP positions at prices between $1200 and $1210. The final third of the trades are executed at a price of $1210. Efficiency of funds: Expanding margin range through Universal Cross Margin. Vertex aims to improve the efficiency of funds by introducing the concept of "Universal Cross Margin," which expands the range of margins.Currently in derivative trading, there are two common margin modes. One is the Isolated Margin mode, where each trading pair has a separate isolated margin account. In a specific isolated margin account, only the currency of that trading pair can be deposited, held, and borrowed. Each isolated margin account has its own risk rate, calculated independently based on the assets and liabilities of that trading pair. The risk isolation of each isolated margin account means that in the event of a liquidation risk, it does not affect other isolated margin accounts. The other mode is Cross Margin mode, where typically a user has only one cross margin account that can trade all supported currencies. The assets in the account are cross-collateralized and shared; the risk rate is calculated based on all assets and liabilities in the cross margin account. In the event of a liquidation, all assets in the account will be liquidated. It can be seen that the capital efficiency of the Cross Margin mode is higher than that of the Isolated Margin mode. On this basis, Vertex has introduced Universal Cross Margin. In Universal Cross Margin, all funds on the platform (deposits, positions, and investment profits/losses) can be used as margin, including open positions in spot markets, perpetual contracts, and money markets. For example, if a user provides liquidity to a spot pool, they can earn fees and also use their LP funds as margin for contract trading. This improves the efficiency of capital utilization.The content you provided is in Chinese language. I will now translate it into English language:
Universal Cross Margin also allows portfolio margining, where unrealized profits can be used to offset unrealized losses or serve as margin for existing positions or opening new positions.
To facilitate better risk management of user accounts, Vertex also provides account risk level indicators, which allow users to see the health of their accounts directly on the page.
Accounts can be in two states: Initial and Maintenance. Under Initial state, accounts can be classified into three risk levels: low, medium, and high based on the margin-to-liability ratio. Maintenance state means that the initial margin usage has exceeded 100% and no new positions can be opened. It is necessary to supplement the margin as soon as possible to avoid liquidation.
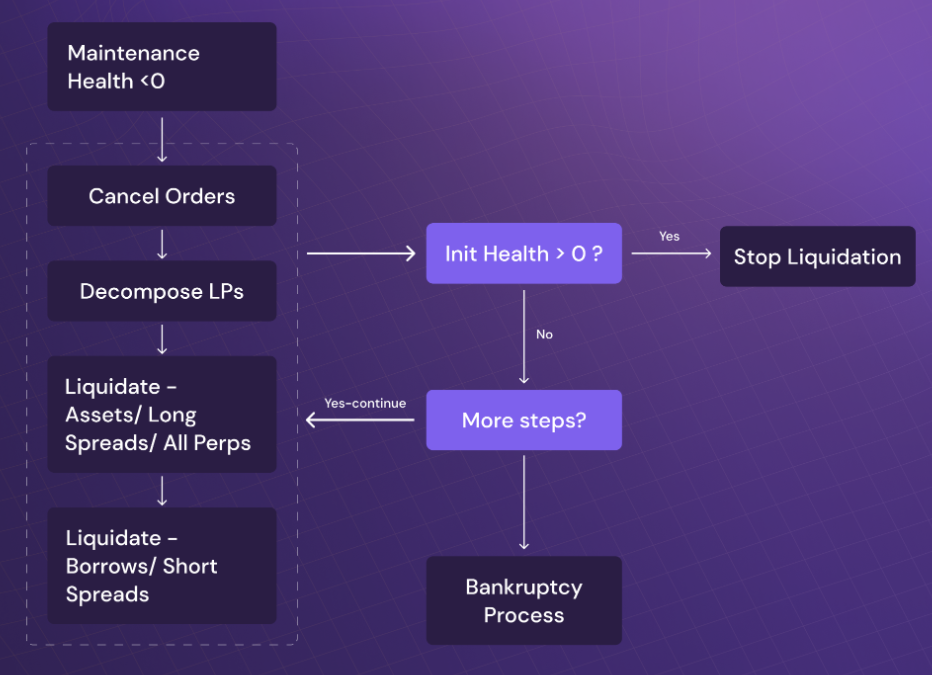
Due to Universal Cross Margin, liquidation also follows full position mode, and will be closed in the following order:
Order canceled, release order funds
LP assets unbound and sold
Assets liquidated (spot balance/contract position)
Liabilities liquidated (loan)
If the account's initial health status recovers to above 0 during the liquidation process, the liquidation will stop.
Source: Vertex
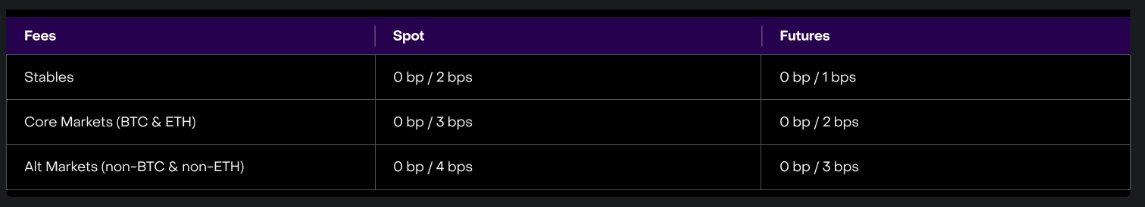
Lower Trading Fees
The transaction fees of Vertex are relatively low. Whether it is spot or contract trading, the fees for makers are currently 0, while the fees for takers range from 0.01% to 0.04%.
Source: Vertex
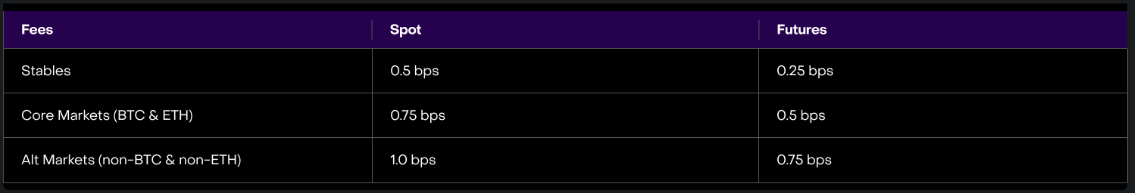
In order to incentivize maker trading, makers who trade more than 0.25% of the total trading volume within a specific period (28 days, an epoch) can also receive rebates. The rebate percentages are as follows:
 Source: Vertex
Source: Vertex
Compared to several major derivative DEX markets, GMX has higher trading fees, with both opening and closing fees at 0.1%; DYDX has trading fees ranging from 0.02% to 0.05%, which decrease with the increase in trading volume; Kwenta has trading fees ranging from 0.02% to 0.06%.
IV. Tokenomics
VRTX is the governance token of Vertex Protocol, with a total supply of 1 billion tokens, of which 90.08% of the tokens will be distributed over 5 years.
The token allocation is shown in the following figure, with 46% allocated for community incentives,including 9% for initial stage token incentives and 37% for ongoing incentives; 41% allocated for the team and financial pool, ecological fund, future contributors; 8.5% allocated to early investors; another 4.5% used for liquidity. this allocation chart was disclosed to the public in early June 2022 and does not include the Wintermute investment portion. In general, it may be allocated to new investors from the treasury.
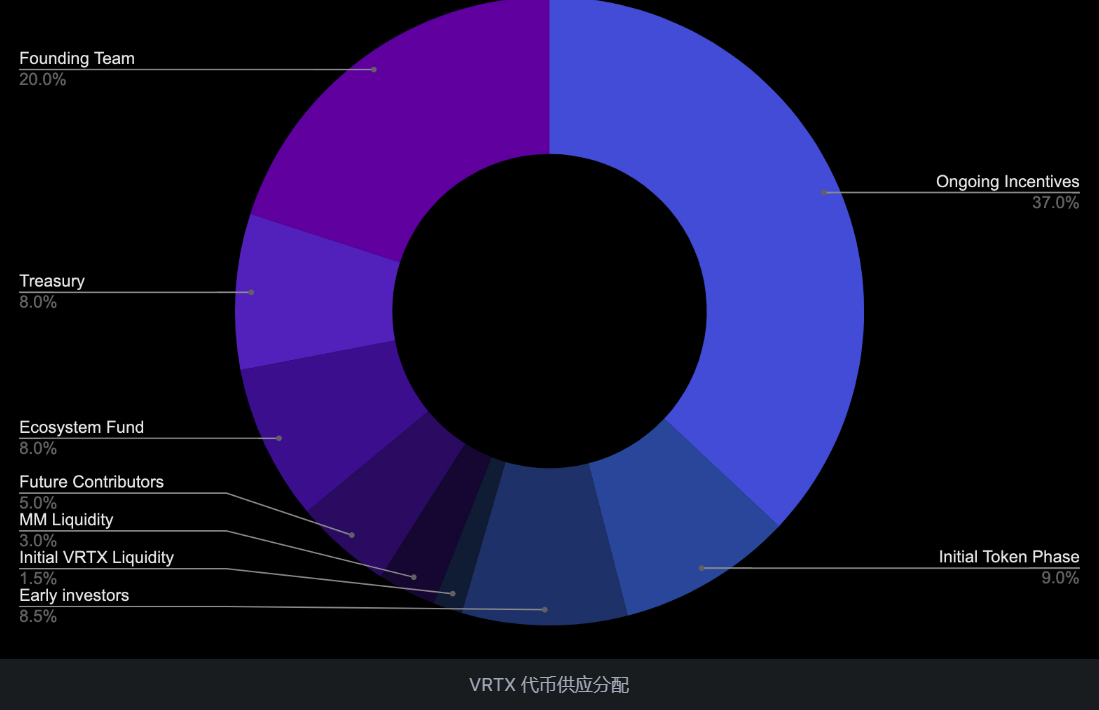
Source: Vertex
Vertex token distribution will take place six months after the mainnet launch, which is expected to happen in October 2023. The token release schedule is as follows:
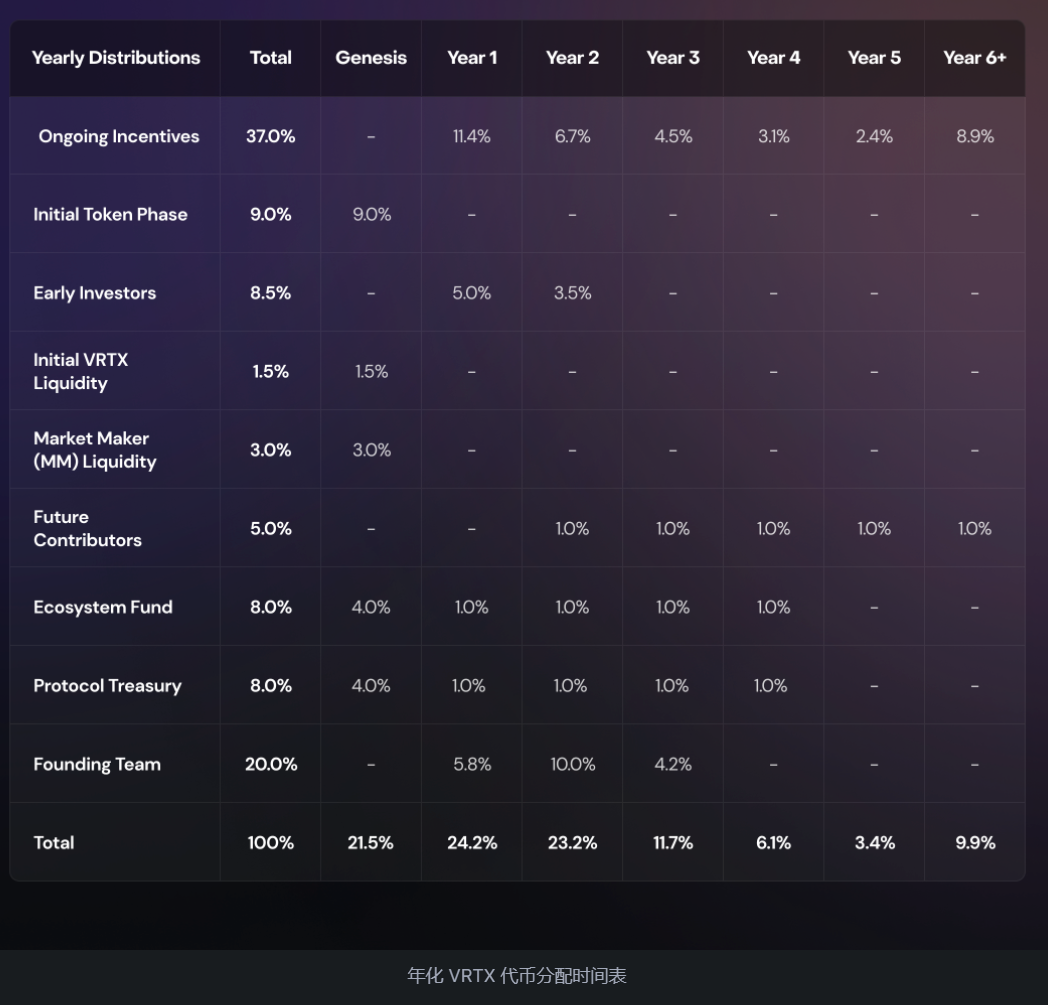
Source: Vertex
The Initial token phase is a part of the token distribution before issuance, and users can track it on the Rewards page of the Vertex application. The official website clarifies that the related incentives can be claimed in October 2023.
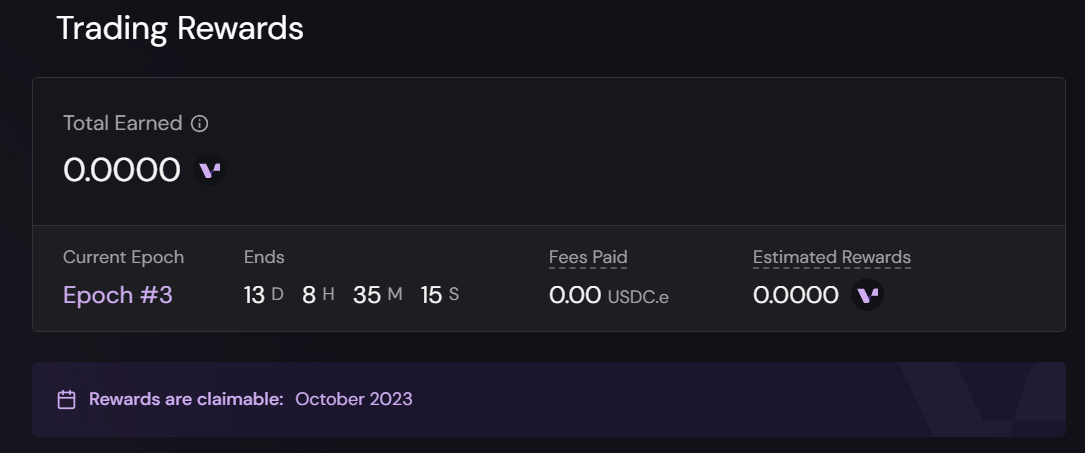
Source: Vertex
Initial token phase has a total of 6 epochs, with each epoch lasting 28 days and rewarding 15 million tokens. Currently, it is the 3rd epoch. The incentive token distribution mainly considers the weight of transaction fees. In addition, different trading pairs have different rewards, as shown in the following figure:
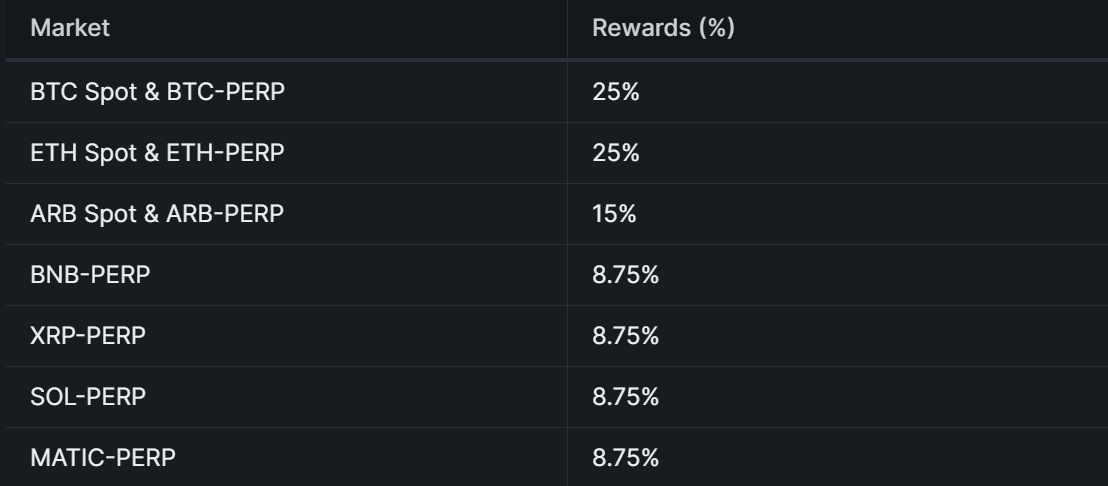
Source: Vertex
The Vertex protocol token has not been issued yet. Due to the existence of trading incentives, it is impossible to avoid wash trading. Currently, the launch of derivative DEX protocols all relies on trading incentives, such as Vela providing trading incentives in its beta version to stimulate trading volume growth. Most protocols still maintain trading incentives after launch, such as DYDX, Kwenta, etc. The fact that Vertex can receive more adoption at this stage indicates that funds have a positive view of the protocol token.
V. Conclusion
The competition in derivative DEXs is already intense. Many projects follow the GMX model, deploying on new blockchains or layer two solutions, offering high APRs to attract funds and earn profits. In comparison, Vertex provides some innovative mechanisms to create better liquidity and higher capital utilization efficiency, which is worth paying attention to.



