Structure, Risks, and New Cycle of On-Chain Lending Markets
- Core Viewpoint: On-chain lending is transitioning from a crypto-native leverage tool to a core infrastructure for global capital allocation. Its growth is led by top-tier protocols and driven by RWA assets. While embracing institutionalization and compliance, it faces multiple risks including liquidity, credit, and cross-chain security.
- Key Elements:
- Market Size and Structure: The total TVL of on-chain lending is approximately $64.3 billion, accounting for 53.54% of DeFi's total TVL. Aave, with a TVL of about $32.9 billion, holds roughly 50% market share, forming a "one superpower, multiple strong players" landscape.
- Core Growth Engine: Real World Assets (RWA) have become a significant source of growth. The private credit scale has reached $18.5 billion. Platforms like Aave Horizon are introducing compliant assets (such as government bonds) as collateral.
- Improving External Environment: The macro interest rate environment is becoming more moderate. Regulatory frameworks (like the GENIUS Stablecoin Act) are gradually clarifying, reducing capital flow and compliance costs, thereby creating conditions for institutional capital entry.
- Major Risk Challenges: High dependence on collateral value makes the market vulnerable to chain liquidations during volatility. Uncollateralized lending and RWA introduction bring credit default risks. Over-reliance on token incentives and cross-chain bridging poses security vulnerabilities.
- Future Development Trends: Security tokenization (e.g., US stocks, ETFs) will expand the range of collateralizable assets. US Treasury bonds may become a core collateral asset. The market might bifurcate into a dual-layer structure coexisting with a compliant/stable layer and a high-risk/innovative layer.
Key Takeaways
- On-chain lending functionality is gradually transforming, evolving from an early tool primarily for leverage into a fundamental infrastructure for capital allocation. On-chain lending has become a crucial component of the DeFi ecosystem. Currently, the TVL of on-chain lending protocols is approximately $64.3 billion, accounting for about 53.54% of the total DeFi TVL.
- Aave has become the leading protocol in the on-chain lending sector, with a TVL of around $32.9 billion, representing about 50% of the total lending sector TVL. Meanwhile, protocols like Morpho continue to consolidate their market share, resulting in a competitive landscape characterized by one dominant player and several strong contenders.
- Credit-based assets have become a significant part of on-chain RWA. As more types of debt instruments are introduced on-chain and institutional demand for compliant, traceable collateral continues to rise, RWA lending is poised to become another important growth engine. Simultaneously, dual improvements in the macro monetary environment and regulatory framework are collectively reducing the costs of capital flow and compliance, creating smoother external conditions for market development.
- On-chain lending protocols also face multiple risks. Firstly, they are highly dependent on collateral value and market liquidity, making them susceptible to liquidations during market volatility. Secondly, the introduction of uncollateralized lending and RWA increases credit default and counterparty risks. Additionally, excessive reliance on token incentives artificially inflates scale, and bridge security in cross-chain expansion exposes high risks. Therefore, on-chain lending protocols must balance security, liquidity, and compliance while pursuing growth.
- As securities tokenization and compliant assets like U.S. Treasuries gradually enter the on-chain space, on-chain lending is evolving from a crypto-native financing tool into mainstream financial infrastructure, with a more robust collateral foundation. In this process, inter-institutional on-chain lending is expected to become a significant growth area. Concurrently, the coexistence of fixed and floating interest rates will drive the maturation of the on-chain interest rate system. Regulatory and capital logic may also lead to market differentiation into a dual-layered structure of compliant/stable and high-risk/innovative segments. On-chain lending will accelerate its integration into the global capital market through asset compliance and institutional alignment.
Table of Contents
1. Overview of the On-Chain Lending Market
1.1. Market Size and Capital Flows
1.2. Macro and Industry Drivers
1.3. Regulatory Dynamics and Compliance
2. Classification of the On-Chain Lending Market
2.1. Collateralized Lending Protocols
2.2. Uncollateralized Lending Protocols
2.3. Modular Lending Protocols
2.4. Integration of RWA and Lending
3. Competitive Landscape
3.1. Leading Protocol Landscape and TVL Changes
3.2. Revenue Structure and Profit Model Comparison
3.3. User Profile and Asset Structure
3.4. Multi-Chain Deployment and Ecosystem Integration
4. Risk Dilemmas and Challenges
4.1. Liquidity Risk
4.2. Credit Default Risk
4.3. Incentives and Illusion of Growth
4.4. Cross-Chain Risk
5. Potential Development Trends
5.1. On-Chainization of Inter-Institutional Lending
5.2. On-Chainization of Securities and Their Collateral Potential
5.3. U.S. Treasuries as a Core Lending Asset
5.4. Coexistence of Fixed and Floating Interest Rates
5.5. Dual-Layer Structural Differentiation in the Lending Market
6. Conclusion
References
On-chain lending protocols have become a vital part of the DeFi ecosystem. Evolving from initial leverage expansion tools, they now encompass diversified capital markets including stablecoins and RWA. These protocols not only reliably host liquidity but are increasingly becoming central hubs for capital pricing and allocation. Currently, the TVL of on-chain lending protocols is approximately $64.3 billion, accounting for about 53.54% of the total DeFi TVL (nearly $120.2 billion). Specifically, Aave dominates about 50% of the lending TVL, around $32.9 billion, while protocols like Morpho hold certain market shares.
Furthermore, the diversity of funding sources and asset categories for on-chain lending is increasing, with RWA becoming a new engine for protocol growth. The structure of the on-chain lending market faces a situation of coexisting growth and challenges. On one hand, protocol TVL has gradually recovered, showing an overall market recovery trend. On the other hand, the market still faces structural challenges: severe liquidity fragmentation, dispersed funds across protocols and chains, and a lack of efficient liquidity integration mechanisms. Traditional stablecoin lending is nearing saturation, while RWA and institutional credit supply remain insufficient, leading to interest rate divergence and differences in risk appetite. The following report will systematically analyze the operational logic, current development status, and trends of the on-chain lending sector from the perspectives of market overview, market classification, and competitive landscape.
1. Overview of the On-Chain Lending Market
1.1. Market Size and Capital Flows
As of now, the TVL of the lending sector is approximately $64.3 billion. Among them, Aave's TVL is about $32.9 billion, exceeding 50% of the total, making it the leading on-chain lending protocol. In the second tier, protocols like Morpho continue to consolidate their shares, forming a structure of one dominant player and several strong contenders. Overall, capital is concentrating around deep-liquidity, multi-network coverage, and compliant asset-backed top pools. The structural characteristics of capital flows are becoming more distinct, with RWA pools becoming the main line of new growth.
Currently, the leading lending protocol Aave has launched Horizon, a permissioned platform for institutions. It allows KYC-verified institutions to borrow USDC, RLUSD, and GHO using compliant tokenized fund shares as collateral, further bridging traditional capital with on-chain liquidity. Meanwhile, the scale of RWA private credit has reached $18.5 billion, opening a new entry point for on-chain lending protocols to onboard institutional capital.
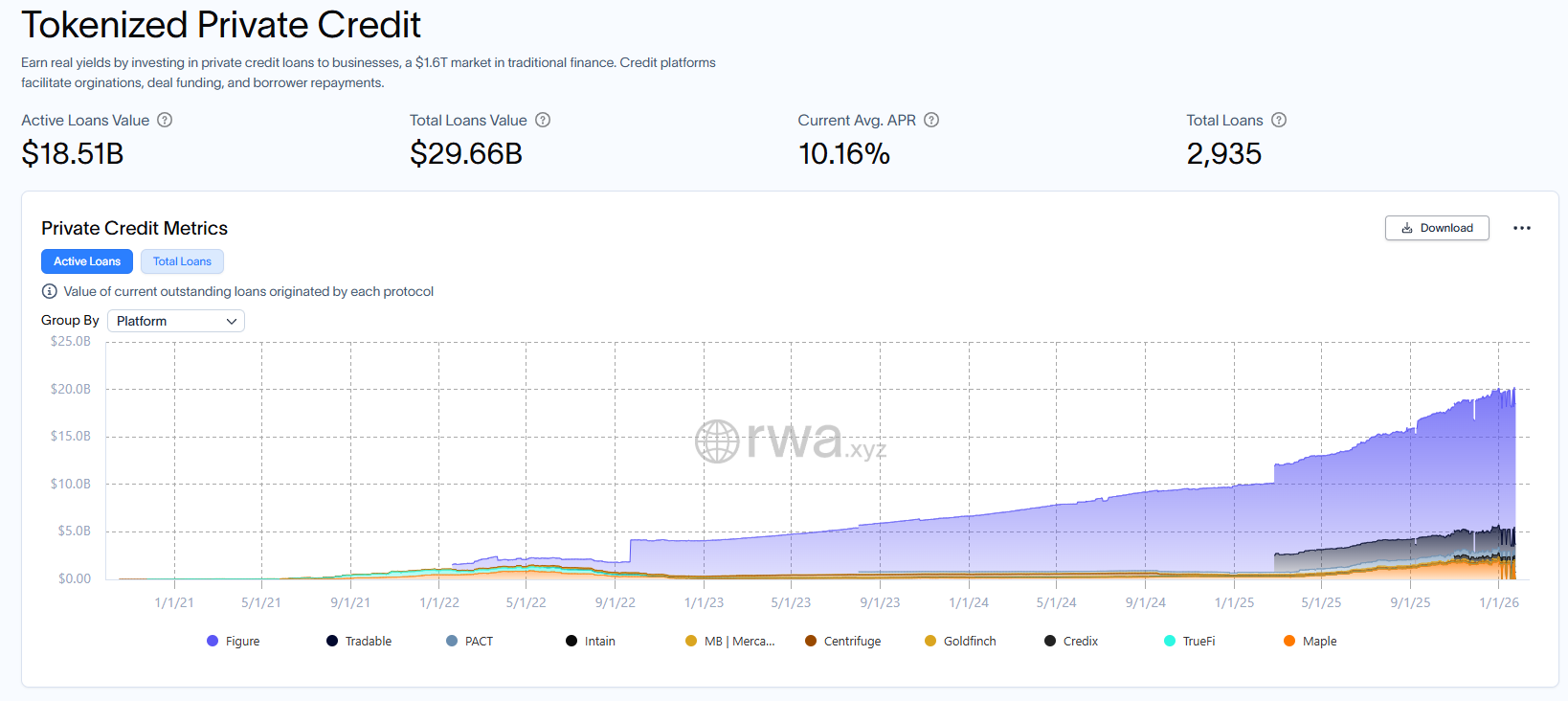
Source:rwa.xyz ,RWA.xyz | Private Credit
1.2. Macro and Industry Drivers
From a macro perspective, the Federal Funds Rate has retreated from its peak in late 2024 to around 3.6%, with the market generally expecting a continued mild easing trend. The European Central Bank has also signaled synchronized rate cuts, promoting liquidity easing in the Eurozone. Against this backdrop, for institutions and high-net-worth capital seeking dollar-alternative yields, the on-chain market not only offers excess spreads but also possesses characteristics unreplicable by traditional money market funds, such as real-time settlement, on-chain transparency, and asset composability. This macro spread effect is driving institutional capital to enter compliance-oriented platforms like Aave more systematically, enhancing the strategic value of on-chain lending in the global capital allocation map.
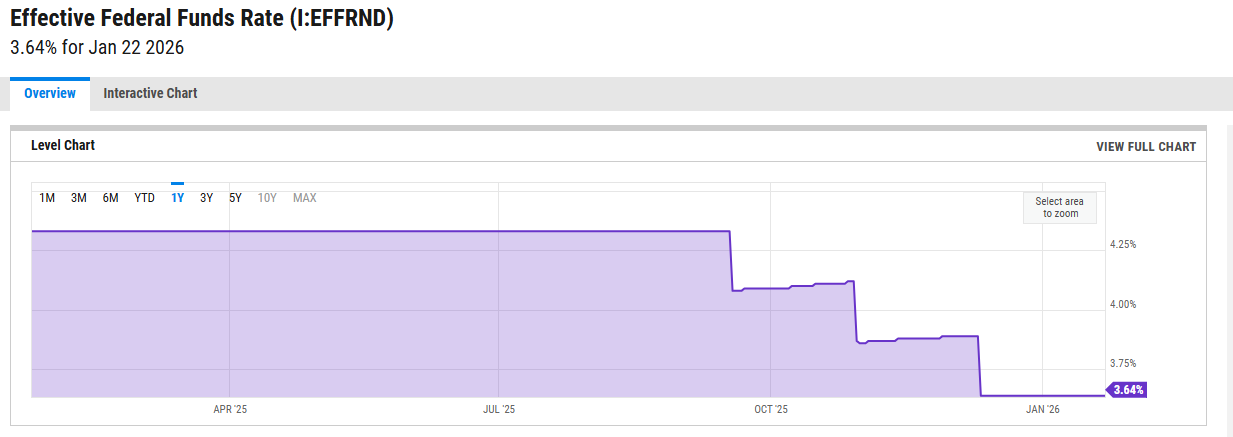
Source:ycharts ,https://ycharts.com/indicators/effective_federal_funds_rate
1.3. Regulatory Dynamics and Compliance
The passage of the GENIUS Stablecoin Act holds significant meaning in establishing a legal status for stablecoins. For on-chain lending protocols, this implies reduced legal risk for collateral, attracting more banks, funds, and qualified institutions to participate in the lending market. Concurrently, the advancement of the Anti-CBDC Act to some extent prevents direct substitution of official digital dollars for market stablecoins, thereby securing the core position of stablecoins in the digital financial system. This policy effectively preserves broader space for the long-term development of the on-chain lending market.
More notably, in June 2025, the new U.S. SEC Chairman Paul Atkins emphasized the self-operating and risk-resilient capabilities of DeFi protocols during the fifth "DeFi and the American Spirit" roundtable, stating continued efforts to promote "innovation exemptions" and lower compliance barriers for on-chain products. As the regulatory framework gradually becomes more detailed and institutionalized, cross-border capital is expected to achieve compliant entry through permissioned lending pools. This not only expands the participant base of on-chain lending but also propels its evolution from a crypto-native market to a foundational financial platform capable of deep integration with the global capital market.
2. Classification of the On-Chain Lending Market
This report will analyze current mainstream lending protocols from four core directions: collateralized lending, uncollateralized lending, modular lending, and the integration of RWA with lending. When evaluating a protocol's development level and efficiency, we will focus on active loan volume, protocol revenue, and token incentive mechanisms to measure platform operational efficiency and risk exposure. Active loans directly reflect real market borrowing demand; protocol revenue reflects capital utilization and sustainability; while token incentives reveal the protocol's attractiveness in competition and its long-term incentive structure. Through multi-dimensional comparative analysis, this report aims to present the true state and operational logic of on-chain lending protocols.
2.1. Collateralized Lending Protocols
Collateralized lending protocols are among the earliest financial applications in DeFi to achieve scale. Their core mechanism involves users obtaining borrowing capacity through over-collateralization of assets, with protocols ensuring system stability through liquidation mechanisms and risk parameters. In this model, credit risk is transformed into collateral risk, and fund flows are fully transparent, making collateralized lending one of the most fundamental markets on-chain. Current representative projects include Aave, Compound, and Sky.
2.1.1 Aave
Since its launch, Aave has never experienced a security vulnerability at the smart contract level, which is a core factor in its rise as the largest lending platform. As of now, the Aave protocol TVL is approximately $32.9 billion, with annual revenue around $100 million, representing a year-over-year growth of about 28%. Aave's market share in lending has also grown to 50%, leading the entire DeFi lending space. Its cross-chain deployment covers multiple public chains including Ethereum, Arbitrum, and Base.
Aave's technological evolution is also a core driver of its growth. In June 2025, during the Ethereum Community Conference, Aave founder Stani Kulechov introduced the Aave V4 upgrade. This V4 upgrade introduces a "hub-and-spoke" liquidity architecture, unifying multi-chain liquidity management in a central pool while supporting modular expansion and on-chain developer custom deployments. It also optimizes cross-chain lending and dynamic risk control. Furthermore, it will achieve deeper integration with Aave's native stablecoin GHO. One of the core innovations of Aave V4 is its deep integration with Horizon. Horizon officially launched in August 2025, aiming to systematically incorporate RWA into the Aave lending system.
Currently, Horizon has introduced some short-term treasury and fund-class assets, allowing them to participate in lending as collateral. Strategically, Aave's official communications in Q2 2025 clearly stated that the combination of V4 and Horizon is just the starting point. Subsequent plans will gradually expand to include RWA staking modules, risk-customized products, and an on-chain capital routing layer, among broader capital market infrastructure. Through this series of iterations, Aave is expected to build a complete asset access and liquidity distribution system at the intersection of DeFi and traditional finance, bringing more stable cash flow and deeper institutional participation to the protocol.
In terms of asset structure, ETH and its liquid staking derivatives (weETH, wstETH, rsETH, etc.) constitute the main collateral asset pools. The total ETH supply is about $9.8 billion, with borrowed amounts around $8.2 billion and a borrowing rate maintained at approximately 2.16%. Meanwhile, stablecoins USDT and USDC are the primary borrowing targets, with borrowed volumes of about $4.9 billion and $3.9 billion respectively, corresponding to annualized borrowing rates of about 4.62% and 4.9%.
Additionally, strategic assets like GHO (sGHO) and BTC-class assets like WBTC also hold certain proportions, indicating Aave is gradually expanding into diversified asset types and risk-return combinations. Overall, Aave's asset supply-demand structure remains robust, with lending rate distributions matching asset risk characteristics. ETH dominates the ecosystem, while the continuous introduction of native stablecoins and diverse LSD derivatives meets more flexible DeFi lending needs.
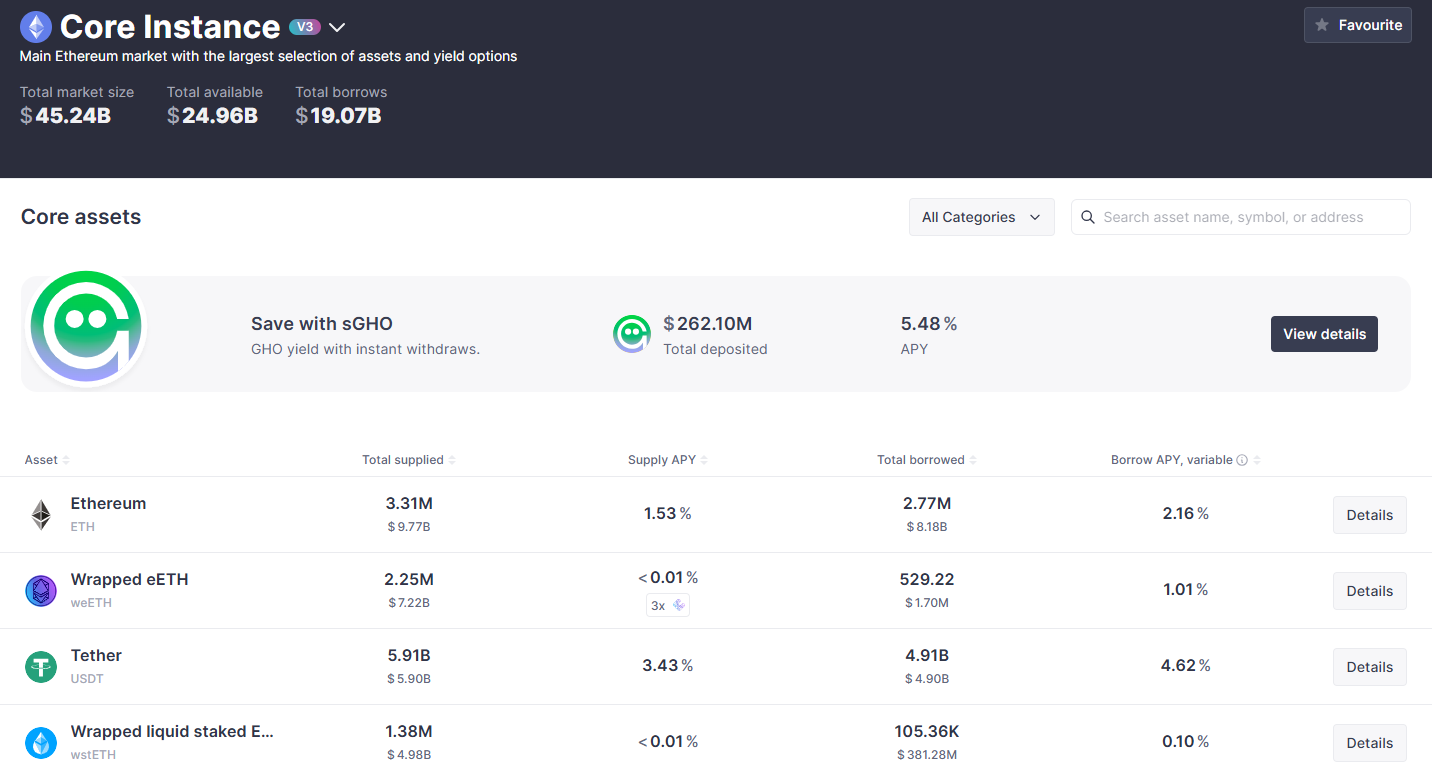
Source:app.aave ,https://app.aave.com/markets/
2.1.1.1 Active Loans
Aave's active loans are primarily concentrated on the Ethereum mainnet and mainstream Layer2s (Arbitrum, Base, etc.), with assets mainly being USDC, USDT, and wETH. Over the past year, Aave's total active borrowing has steadily grown from about $10 billion to the current $23.7 billion, reaching a new annual high with an overall increase exceeding 120%. Particularly since May 2025, borrowing volume has shown steady growth, driven by synchronized recovery in user leverage demand and market liquidity, likely influenced by multi-chain expansion and the growth of the stablecoin GHO's application. However, rapid growth also accompanies potential risks, such as high-leverage asset concentration potentially amplifying liquidation risks during market volatility. Aave needs to optimize risk parameters and incentive mechanisms to stabilize protocol security.
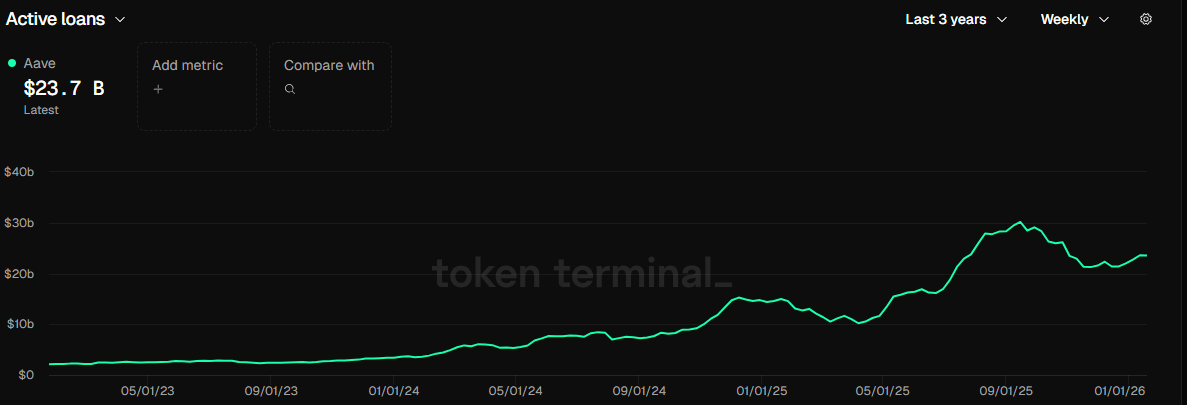
Source:tokenterminal ,https://tokenterminal.com/explorer/projects/aave
2.1.1.2 Protocol Revenue
Currently, Aave's revenue primarily comes from its lending business (V3), with stablecoin GHO-related revenue still constituting a relatively small portion of total protocol revenue. Aave's cumulative revenue has continued to grow since 2022, accelerating noticeably after 2024. In just about the past year, Aave's cumulative protocol revenue increased by approximately $150 million. The revenue curve shows a relatively flat initial phase followed by an upward trend. The period from the second half of 2024 to early 2025 saw the most concentrated revenue growth, with the cumulative revenue slope rising significantly, reflecting simultaneous expansion in lending scale and increased on-chain capital usage activity.
Although cumulative revenue growth temporarily slowed in some phases, the overall trend has not reversed, with cumulative revenue maintaining a steady upward trajectory post-2025. Overall, Aave's revenue growth rhythm is highly correlated with market cycles, but its core lending business has consistently contributed stable cash flow across multiple cycles, demonstrating the long-term resilience and sustainability characteristic of mature DeFi lending protocols.
Aave's revenue remains highly concentrated on the Ethereum mainnet. Despite some quarterly declines, its volume still far exceeds other chains. Meanwhile, Arbitrum and Polygon, as leading scaling networks, maintain secondary importance in the multi-chain layout despite revenue fluctuations. Contributions from chains like Base and Avalanche are relatively limited. Notably, emerging chains like Sonic and Linea began contributing revenue in 2025. Although amounts are still small, this reflects Aave's intent to maintain expansion within the multi-chain ecosystem. The overall pattern shows a hierarchical structure: the mainnet holds absolute dominance, supported by a few scaling networks, with other new chains tentatively growing.
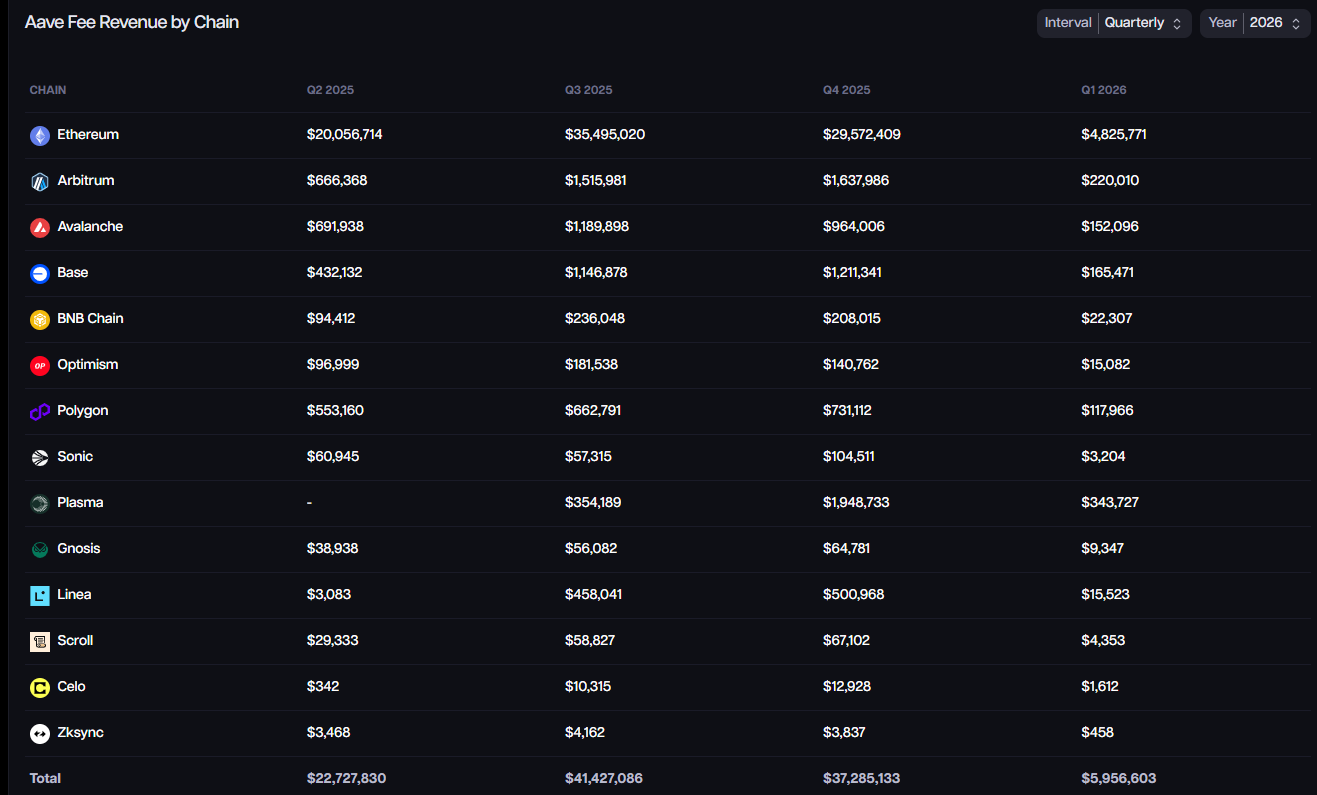
Source:aave.tokenlogic.xyz ,https://aave.tokenlogic.xyz/revenue
Simultaneously, the Aave DAO initiated a six-month AAVE buyback plan starting April 2025, allocating up to $1 million weekly for market repurchases, cumulatively buying back over 50,000 AAVE tokens. This plan is backed by real revenue generated from core business activities like lending spreads, reflecting Aave's robust cash flow and sustainable profitability. Unlike platforms driven by subsidies, Aave's mechanism of returning revenue to token holders enhances token value support, making it more transparent and attractive to institutional investors in the long term.
Aave founder Stani Kulechov stated that Aave's future revenue structure will consist of three core businesses: first, traditional DeFi lending services, relying on stable interest income; second, the GHO stablecoin business, generating stable minting spread revenue through over-collateralization mechanisms; and third, the newly launched Horizon, supporting RWA as collateral, expanding the institutional user market, and bringing new revenue sources like collateral management fees and cross-border