TradFi Explained: Understanding Traditional Finance in the Era of Cryptocurrency Exchanges
- Core Insight: Traditional finance and digital finance are converging.
- Key Elements:
- TradFi provides stability and trust but suffers from inefficiencies.
- DeFi and CeFi bring innovation, challenging traditional centralized models.
- TradFi institutions are entering the crypto market through products like ETFs.
- Market Impact: Brings more capital and legitimacy to the crypto market.
- Timeliness Note: Long-term impact.
The financial world is undergoing a significant transformation. New technologies like blockchain have paved the way for decentralized finance (DeFi) and centralized cryptocurrency exchanges (CeFi), challenging the long-established norms of the global economic system. However, to truly understand this revolution, we must first understand the system being revolutionized. This system is known as traditional finance, or TradFi. This article will delve into the world of TradFi, from its core institutions and products to its role in the evolving digital marketplace.

What is TradFi? A Clear Definition
TradFi, short for Traditional Finance, refers to the conventional financial system that has served as the backbone of the global economy for centuries. It encompasses all the established financial institutions, markets, products, and services that people use daily. It's a world of central banks, commercial banks, stock exchanges, and insurance companies.
At its core, TradFi operates through centralized, regulated intermediaries. When you deposit money into a savings account, apply for a mortgage, or buy shares in a company, you are interacting with the TradFi system. These transactions are managed and validated by trusted third parties like banks and brokers, operating under strict government oversight. This structure is designed to ensure stability, security, and consumer protection within the financial ecosystem.
Core Institutions Powering the TradFi System
The TradFi system is a complex web of numerous institutions, each playing a crucial role in maintaining economic function and stability.
Central Banks
Central banks, such as the Federal Reserve in the United States or the European Central Bank, sit at the apex of the financial system. They are responsible for implementing monetary policy, managing currency issuance, controlling interest rates, and ensuring the stability of the overall financial system. Their actions have profound impacts on inflation, employment, and economic growth.
Commercial and Retail Banks
These are the financial institutions most people interact with regularly. Commercial banks like JPMorgan Chase or HSBC provide essential services to individuals and businesses. These services include checking and savings accounts, loans (personal, auto, and business), mortgages, and credit cards. They act as intermediaries, taking deposits from savers and lending them to borrowers, thereby facilitating the flow of capital throughout the economy.
Investment Banks
Investment banks, such as Goldman Sachs and Morgan Stanley, operate in the high-stakes world of corporate finance and capital markets. They assist companies and governments in raising capital by underwriting and issuing securities like stocks and bonds. They also provide advisory services for mergers and acquisitions (M&A) and execute large-scale trades for institutional clients.
Asset Managers and Hedge Funds
Firms like BlackRock and Vanguard manage vast pools of money on behalf of individuals and institutions. They create and manage investment vehicles like mutual funds and exchange-traded funds (ETFs), allowing investors to diversify their portfolios across a wide range of assets. Hedge funds are private investment partnerships that use more aggressive and complex strategies to generate high returns for their accredited investors.
Insurance Companies
Insurance companies play a key role in risk management. They provide products that protect individuals and businesses from financial loss due to unforeseen events. By pooling premiums from many policyholders, they can pay out significant claims related to health, property, liability, and life, providing a critical safety net for the economy.
Financial Products and Markets of TradFi
TradFi offers a vast array of financial products that are traded in well-established markets. These products enable efficient capital allocation and risk management.
- Stocks (Equities): Represent ownership in a publicly traded company. Shareholders have a claim on the company's assets and earnings. Stocks are traded on exchanges like the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) and NASDAQ.
- Bonds (Fixed Income): A form of debt where an investor lends money to an entity (corporate or governmental) that borrows the funds for a defined period at a fixed or variable interest rate. Bonds are generally considered less risky than stocks.
- Commodities: Raw materials or primary agricultural products that can be bought and sold. Examples include gold, oil, wheat, and coffee. These are traded on specialized commodity exchanges.
- Derivatives: Financial contracts whose value is derived from the performance of an underlying asset or group of assets. Common derivatives include futures, options, and swaps. They are used for hedging risk or for speculation.
- Foreign Exchange (Forex): The global marketplace for exchanging national currencies. The forex market is the world's largest and most liquid financial market, crucial for international trade and investment.
Regulation and Compliance: The Blueprint of TradFi
A defining characteristic of TradFi is its stringent regulatory framework. In the wake of historical financial crises, governments and international bodies have built a robust set of rules to protect consumers, prevent illicit activity, and maintain systemic stability.
Key regulatory components include "Know Your Customer" (KYC) and "Anti-Money Laundering" (AML) requirements. Financial institutions must verify their clients' identities and monitor transactions for suspicious activity to combat financial crimes like money laundering and terrorist financing. Regulatory bodies like the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) in the US oversee securities markets to ensure fairness and transparency, protecting investors from fraud. This comprehensive oversight is the blueprint for trust and stability in the traditional finance world.
Advantages of the TradFi System
Despite the emergence of new financial models, TradFi possesses significant strengths that have allowed it to persist and thrive for centuries.
- Stability and Trust: The system is built on time-tested institutions and comprehensive regulation, which fosters a high degree of public trust and systemic stability.
- Widespread Adoption and Accessibility: Billions of people globally use TradFi services. Its infrastructure is deeply integrated into our daily lives, making it approachable and familiar.
- Strong Consumer Protections: Robust regulations and mechanisms like deposit insurance (e.g., FDIC in the US) protect consumers from institutional failures and fraud.
- High Liquidity and Deep Markets: TradFi markets, especially for major stocks and bonds, possess immense liquidity, allowing for large transactions without significantly impacting price.
Limitations and Criticisms of TradFi
However, the traditional system is not without its flaws, many of which have fueled the development of alternatives like DeFi.
- Centralization and Control: The system is controlled by a handful of powerful intermediaries, creating single points of failure and concentrating power.
- Inefficiency and High Costs: Transactions, especially cross-border payments, can be slow and expensive due to the involvement of multiple intermediaries. Bank fees and trading commissions can also be substantial.
- Limited Access for Some: Despite its widespread reach, an estimated 1.4 billion adults globally remain unbanked, excluded from the formal financial system due to factors like lack of documentation or remote location.
- Opacity: The inner workings of many large financial institutions can be opaque, making it difficult for outsiders to assess risk and for regulators to prevent crises.
TradFi vs DeFi vs Cryptocurrency Exchanges (CeFi)
The current financial landscape presents a dynamic interplay between TradFi, DeFi, and CeFi.
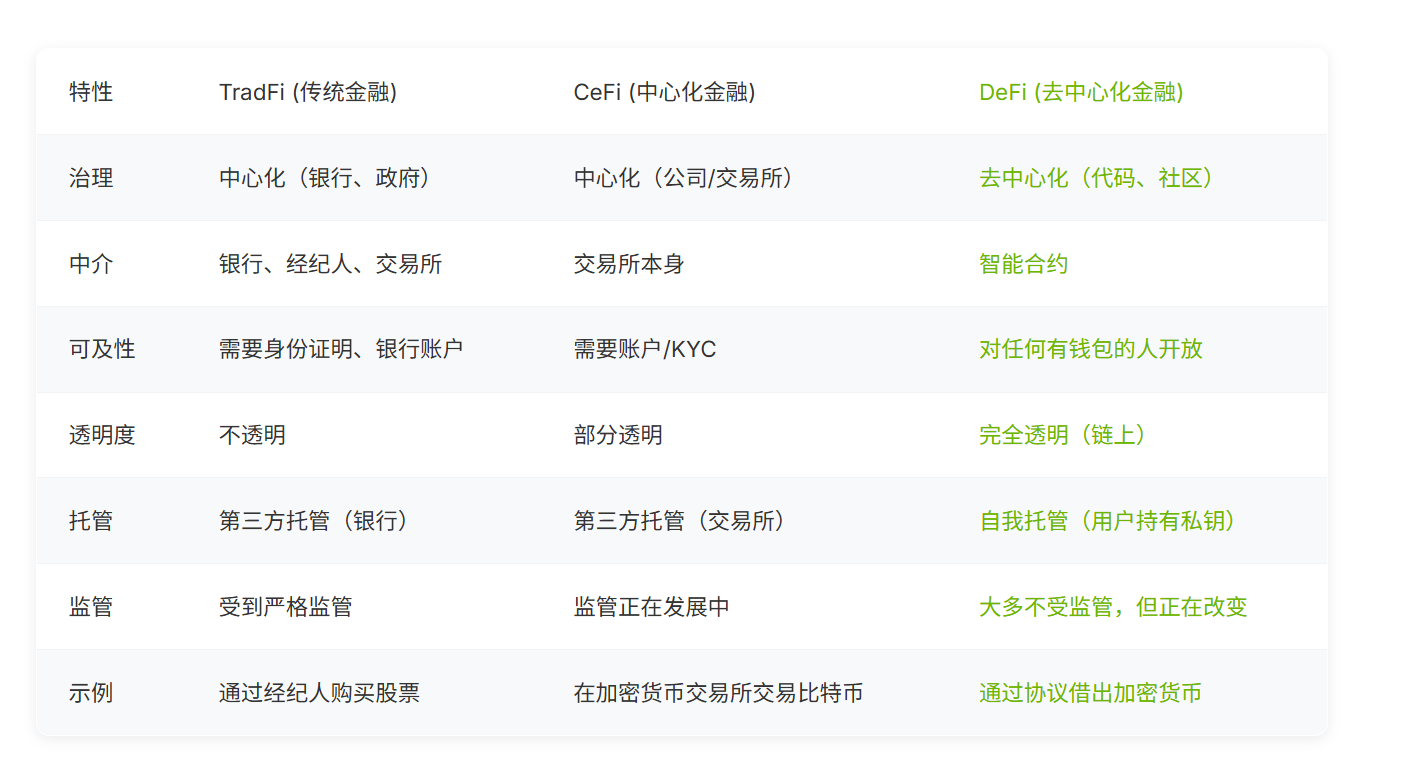
CeFi, represented by centralized cryptocurrency exchanges, acts as a bridge between TradFi and DeFi. It offers a familiar, user-friendly experience akin to online banking, while simultaneously providing a gateway to the innovative world of digital assets.
Convergence: TradFi Capital Flows Through Exchanges
The barriers between TradFi and the world of digital assets are becoming increasingly porous. Major TradFi institutions are no longer just watching from the sidelines; they are actively participating. Asset management giants like BlackRock and Fidelity have launched Bitcoin ETFs, offering their vast client bases a regulated avenue into cryptocurrency investment.
This convergence is largely facilitated by centralized cryptocurrency exchanges and other CeFi platforms. These platforms provide the institutional-grade security, liquidity, and compliance infrastructure TradFi firms need to engage with digital assets. As more TradFi capital flows into crypto through these regulated gateways, it brings greater legitimacy, liquidity, and stability to the digital asset markets.
The Future of TradFi in a Hybrid Financial System
TradFi is not going away. Instead, it is evolving and integrating with new technologies. The future of finance is likely a hybrid model that combines the strengths of TradFi and digital finance. We can expect to see:
- Tokenization of Real-World Assets (RWA): TradFi assets like stocks, bonds, and real estate will be represented as digital tokens on blockchains, enabling fractional ownership and faster, cheaper settlement.
- Integration of Blockchain Technology: TradFi institutions will adopt blockchain to streamline back-office operations, improve cross-border payments, and enhance transparency.
- Coexistence of Systems: TradFi, DeFi, and CeFi will coexist, serving different needs. An investor might hold a 401(k) managed by a TradFi firm, trade altcoins on a CeFi exchange, and engage in liquidity mining using a DeFi protocol.
This hybrid system aims to offer the best of both worlds: the innovation and efficiency of digital finance, combined with the stability and consumer protections of traditional finance.
Discover TradFi Products on XT Futures
The convergence of financial worlds is not just a future concept; it is happening now. Platforms are emerging that combine the reliability of traditional markets with the accessibility of digital asset trading. XT Futures is at the forefront of this movement, offering users the ability to trade traditional financial instruments like global indices, forex, and commodities.
This presents a unique opportunity for traders to diversify their portfolios beyond cryptocurrencies. You can speculate on the price of gold, trade major currency pairs like EUR/USD, or take a position on the S&P 500 index, all within a unified platform. Specifically, XT Futures offers perpetual contracts such as METAXUSDT, AAPLXUSDT, AMZNXUSDT, GOOGLXUSDT, COINXUSDT, NVDAXUSDT, CRCLXUSDT, HOODXUSDT, XAUTUSDT and PAXGUSDT. This integration allows you to apply your trading strategies across different asset classes, managing risk and capitalizing on global market dynamics seamlessly. By bridging these two worlds, XT Futures empowers users to build a truly comprehensive and diversified investment strategy.
Conclusion: Why TradFi Still Matters for the Crypto Market
For anyone navigating the crypto space, understanding TradFi is essential. It provides the historical context and foundational principles upon which all financial systems are built. The rules, institutions, and products of TradFi have shaped the global economy for centuries, and their influence continues to define the path forward.
As the lines between traditional and digital finance blur, the principles of regulation, risk management, and market stability pioneered by TradFi become increasingly important for the crypto industry. The influx of institutional capital from TradFi is a major driver of crypto market maturation and adoption. Ultimately, the future of finance is not a story of TradFi versus crypto, but one of their convergence, creating a more efficient, accessible, and robust global financial system for everyone.
About XT.COM
Founded in 2018, XT.COM is a leading global digital asset trading platform with over 12 million registered users, serving more than 200 countries and regions, and boasting an ecosystem traffic exceeding 40 million. The XT.COM cryptocurrency trading platform supports over 1,300 high-quality tokens and more than 1,300 trading pairs, offering diverse trading services including spot trading, margin trading, and futures trading, along with a secure and reliable RWA (Real-World Assets) trading market. Upholding the philosophy of "Explore Crypto, Trust Trade," we are committed to providing global users with a safe, efficient, and professional one-stop digital asset trading experience.



