DePAI: The next trillion-dollar growth engine for Web3?
- 核心观点:DePAI是解决物理AI深层问题的关键范式。
- 关键要素:
- 区块链去中心化特性可协调异构机器人系统。
- 统一账本与智能合约实现机器间自主交易与支付。
- DAO组织形式变革物理AI的治理与收益分配。
- 市场影响:推动机器经济向去中心化自治网络演进。
- 时效性标注:长期影响
We've seen science fiction scenes like these in movies: R2-D2 in *Star Wars* can converse fluently with humans, use tools autonomously, and is proficient in hacking; the Transformers in *Transformers*, whether in humanoid robot form or transformed into self-driving cars, drones, or robotic dogs, can think independently and act flexibly. These scenes of robots interacting with humans, robots with each other, and robots with the physical world, which once amazed and filled us with longing, are actually closely related to a hot concept this year—"physical AI."
In January of this year, Nvidia CEO Jensen Huang first publicly proposed the concept of applying AI to real-world physical AI, such as robotics, at CES, and regarded it as the last wave of AI development. Tesla, in its "Secret Plan Chapter 4" release, shifted the company's development focus to the fields of AI and robotics, aiming to integrate AI into the physical world on a large scale.
So what exactly is this physical AI that the giants are betting on? And what is DePAI, which combines blockchain with it? How will DePAI solve the deep-seated problems facing physical AI?
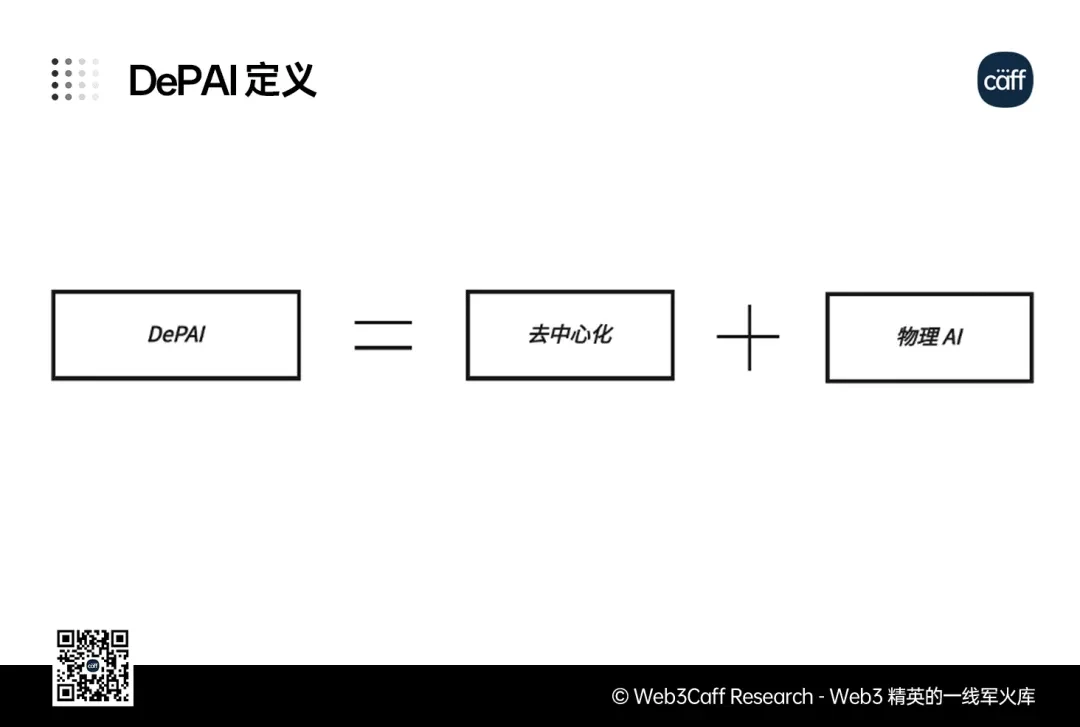
Chart 3: DePAI Definition, Source: Based on "Robotics, Physical AI, DePAI: The Next Trillion-Dollar Opportunity to Rival Bitcoin", this chart was created using Pixso.
DePAI (Decentralized Physical AI) combines decentralized technologies (blockchain/Web3) with physical AI, enabling physical machines with AI capabilities, such as robots, drones, and self-driving cars, to operate on blockchain infrastructure without being owned or controlled by any single company.
Despite the rapid development of physical AI, several deep-seated issues remain: For example, on which platform should robots operating around the world be managed? How should the behavior of robots be coordinated? How should transactions and payments be conducted between various physical AI systems (including autonomous robots, drones, vehicles, androids, etc.)? Is a unified standard necessary? How can physical AI be funded on a large scale and how can we benefit from it? How can we define liability for accidents involving physical AI and conduct transparent audits of robot behavior? These are just some of the questions.
The aforementioned deep-seated problems are very well-suited for being solved using decentralized blockchain technology. The advantages of blockchain technology include:
- Decentralization of nodes: Blockchain network nodes are decentralized, transferring control and decision-making power from a central entity to a distributed network. This eliminates the possibility of a single platform exerting authority or control over each other in a way that diminishes network functionality. The decentralized nature of blockchain eliminates single points of failure, improving system security and reliability.
- Shared unified ledger: The decentralized unified ledger of blockchain can act as a coordination center, enabling robots in heterogeneous systems to find and coordinate with each other without the need for a centralized intermediary.
- Value exchange: As robots become more autonomous, blockchain may facilitate the transfer of value (i.e., payments) between direct, programmable robots and humans, as well as ensure autonomous transactions between machines (e.g., payment transactions between robots, decentralized coordination of multi-robot tasks).
- The organizational structure of DAOs: Traditional funding sources are slow and isolated, hindering industry development. Blockchain-based DAO platforms eliminate these bottlenecks while providing potential incentives for ordinary investors to participate. Similarly, DAOs can leverage smart contracts to allow users to truly "own" their bots and earn rewards from their work.
- Behavioral auditing and oversight: The immutability of blockchain can be used to record robot behavior and decisions, increasing transparency. Integrating formally verifiable behavior into physical AI systems through smart contracts can provide additional safeguards.
The natural synergy between blockchain technology and physical AI makes DePAI an inevitable trend in industry development. DePAI is equivalent to decentralization (blockchain) plus physical AI, representing a fundamental paradigm shift in the management mechanisms, operating models, and revenue distribution of traditional physical AI. Under this new paradigm, machines are no longer seen as corporate assets, but rather as part of a broader shared infrastructure, thus achieving autonomous operation.
This content is excerpted from a research report published by Web3Caff Research: " 29,000-Word Research Report on the DePAI Track: Towards the Ultimate Development Direction of AI, Can It Become the Next Trillion-Dollar Growth Engine for Web3? "
This research report, authored by Felix, a researcher at Web3Caff Research, provides a systematic analysis of how DePAI connects computing power, identity, and collaboration to reshape the machine economy. Key takeaways include:
- AI is moving from "digital intelligence" to "physical intelligence," and DePAI is becoming a key foundational layer for decentralized machine collaboration.
- The track has formed a three-layer architecture of "intelligent agent - computing power - identity", which promotes the evolution of machine networks towards autonomy and collaboration;
- Mainstream projects (Fetch.ai, Bittensor, SingularityNET, etc.) each have their own focus on incentive models and network mechanisms, accelerating the differentiation of their ecosystems;
- DePAI still faces three major challenges: standardization, privacy protection, and resource allocation. A decentralized intelligent network is taking shape.
📊 The report includes a key structure diagram and a matrix of representative projects, presenting the DePAI technology system and ecosystem trends.



