NEO Ignites the Robotics Race: A Review of Potential Robotics Projects
- 核心观点:机器人赛道成为区块链新热点。
- 关键要素:
- 1X发布NEO机器人,售价2万美元。
- 多个项目获千万级融资,如OpenMind。
- 代币化机器人农场已实现盈利分配。
- 市场影响:推动AI与区块链融合投资热潮。
- 时效性标注:中期影响
Original title: "NEO Ignites the Robotics Industry, What Robotic Projects Are Worth Watching?"
Two days ago, Norwegian humanoid robot company 1X Technologies officially released the NEO robot and opened pre-orders. It's priced at $20,000 and also supports a monthly subscription model ($499 per month), with deliveries expected to begin in 2026. Tesla has also stated that robots are its next major profit driver. It seems quite possible that robots will become the next major trend.
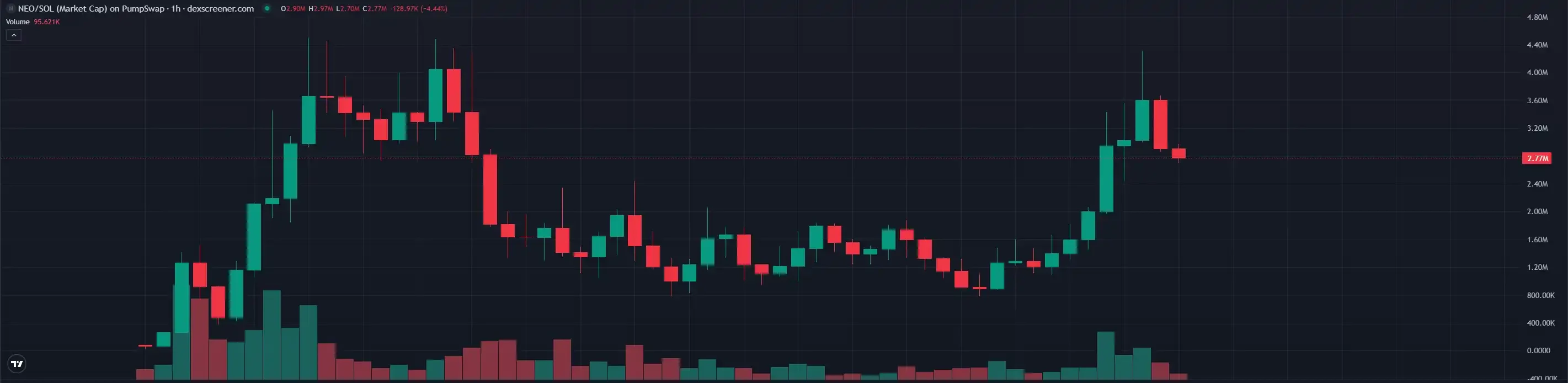
Humanoid robots capable of performing household chores such as taking out the trash, folding clothes, handing items, and setting the table—this is something many of us imagined in our childhood essays, but now it's about to become a reality. Such news has undoubtedly become a focus of attention for many. In the cryptocurrency world, the meme coin $NEO, named after the robot on Solana, once surpassed a market capitalization of $4 million and currently still maintains a market capitalization of $2.7 million.
Additionally, Echo, the on-chain fundraising platform created by Cobie and recently acquired by Coinbase for $375 million, has raised $10 million in Series C funding from 1X Technologies. However, since the funding was conducted in a private group, specific details are not available.
Besides the funding amounts for Meme Coin and Echo, robotics-related projects in the cryptocurrency space have also attracted attention, with many players referring to this sector as "Robotics." This article will provide a summary of projects related to the Robotics sector.
OpenMind
On August 4, according to official news, OpenMind, a Silicon Valley-based intelligent machine infrastructure company, announced the completion of a $20 million funding round led by Pantera Capital, with participation from Ribbit, Sequoia China, Coinbase Ventures, DCG, Lightspeed Faction, Anagram, Pi Network Ventures, Topology, Primitive Ventures, Amber Group, and many other institutions and well-known angel investors.
OpenMind helps robots think, learn, and work by developing open-source software. Its native open-source AI robot operating system, OM1, allows for the configuration and deployment of AI agents in both the digital and physical worlds. Users can create an AI character and run it in the cloud or on a physical robot in the real world.
In layman's terms, OpenMind's development of OM1 is essentially creating an "AI brain" for robots. This "AI brain" can be composed of multiple AI agents working collaboratively, can interact with multiple LLMs, and can acquire data from multiple sources to perform tasks (such as helping users post on social media). Because OM1 is open source, it is also a highly adaptable robot operating system, much like the Android system on mobile phones, which is hardware-independent.
In addition, OpenMind has an on-chain robot identity network called FABRIC, designed to provide a verifiable layer of trust for humans and robots. Humans can earn badges on it by sharing location data on maps, evaluating robot behavior, and developing features. For robots, each robot equipped with the OM1 system joins the FABRIC network, thus possessing a unique and verifiable identity, and enabling the tracking of robot commands, operation logs, ownership, and other related behaviors on the blockchain.
OpenMind has not yet issued its own cryptocurrency.
XMAQUINA

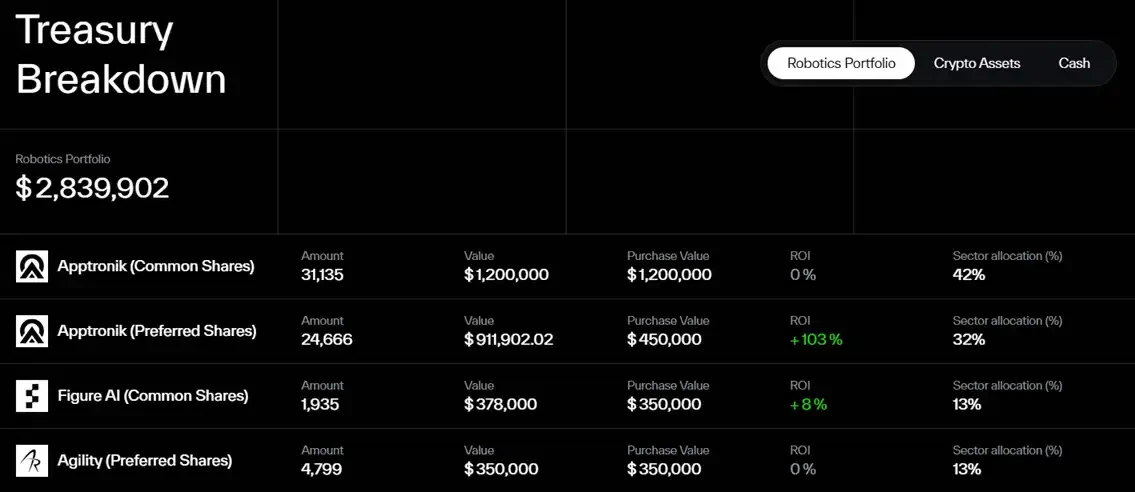
Robots invest in the DAO. Its governance token, $DEUS, has completed three rounds of sales, raising over $5.5 million in crypto assets. The DAO is currently using the proceeds to support Apptronik, Figure AI, and Agility Robotics, all companies in the humanoid robotics field. Screenshots from the official website's vault show that the DAO's investments are already profitable, with some individual investments exceeding 100% returns.
However, $DEUS has not yet undergone TGE. Upon TGE, 33% of the $DEUS sold to the community will be immediately unlocked, with the remaining 67% unlocking linearly over 12 months.
peaq

On March 27, Peaq, a DePIN Layer 1 protocol, completed a $15 million funding round led by Generative Ventures and Borderless Capital, with participation from Spartan Group, HV Capital, CMCC Global, Animoca Brands, Moonrock Capital, Fundamental Labs, TRGC, DWF Labs, Crit Ventures, Cogitent Ventures, NGC Ventures, Agnostic Fund, and Altana Wealth.
Although its initial narrative focused on DePIN, the project has shown remarkable market acumen, having followed suit with the recently popular x402. Regarding bots, Peaq released its Robotics SDK in September of this year, enabling bots to acquire autonomous identities, conduct payments and receipts, verify data, and integrate into the on-chain network economy.
In addition, Peaq also has a robot-operated RWA marketplace, tokenizing machines and placing them on-chain as shared revenue-generating assets. Peaq launched its first tokenized, robot-operated farm on the main stage of Korea Blockchain Week 2025, which has been deployed on the Peaq chain and will distribute operating profits to token holders.
Currently, $peaq has a circulating market capitalization of approximately $110 million.
PrismaX

On June 17, PrismaX announced the completion of an $11 million funding round, with investors including a16z CSX, Volt Capital, Blockchain Builders Fund, Stanford Blockchain Accelerator, and Virtuals.
PrismaX is building an open coordination layer that connects remote operators, robot users, and robot companies. Operators can connect with users to remotely control robots, perform practical tasks, and collect valuable data. They can also request practical services such as logistics and advertising.
PrismaX features a protocol for remotely operating bots, allowing businesses to find experienced bot operators capable of handling complex tasks. Operators can choose to stake network tokens to increase their trust level and improve their chances of receiving high-yield tasks. Stakers' rewards are tied not only to the amount they stake but also to the quality of their work, with additional rewards awarded for improved efficiency.
The data accumulated from remote operations will then be used to train the robot to improve its autonomy, which will in turn improve the work efficiency of the remote operator and ultimately achieve a high degree or even complete autonomy for the robot.
PrismaX has not yet issued its own token.
CodecFlow

CodecFlow provides a unified platform that runs seamlessly across the cloud, edge, desktop, and robotic hardware, while supporting popular APIs and legacy systems.
AI-driven operators respond to changes in the UI or the robot environment through perception and real-time reasoning, thus addressing the vulnerability of traditional robot automation processes that rely too heavily on pre-written scripts and are susceptible to even minor changes.
In short, it involves capturing screenshots, camera footage, or sensor data, then using AI to process these external input data to handle observations or instructions, and finally executing decisions through user interface interaction.
Currently, the market capitalization of the token $CODEC is approximately $16 million.
NRN Agents

NRN evolved from AI Arena, a blockchain game where AI agents battle in real-time. On October 28, 2021, developer ArenaX Labs announced the completion of a $5 million seed funding round, led by Paradigm Capital with participation from Framework Venture Partners. On January 9, 2024, ArenaX Labs announced the completion of a new $6 million funding round, led by Framework Ventures, with participation from SevenX Ventures, FunPlus/Xterio, and Moore Strategic Ventures, among others.
While the general process is data collection followed by reinforcement of robot learning, NRN leverages its extensive experience in the gaming industry to offer a browser-based experience. This transforms robot data collection into a game, allowing users to intuitively control the simulated robot through a browser. During gameplay, the behavioral data generated by user actions is used to train the real-world robot system.
At this stage, the project will focus on the robotic arm (RME-1) to validate data collection, real-time learning, and adaptability.
Currently, the market capitalization of the token $NRN is approximately $11.7 million.
Auki

Auki's decentralized machine perception network, Posemesh, connects humans, devices, and AI. At its core is a DePIN (Decentralized Entity Network) architecture that allows devices such as robots and AR glasses to share location and sensor data in real time, collaboratively building a spatial understanding of the physical world. It can provide a shared spatial view for robots, AR, and AI.
The Posemesh protocol incorporates various node roles. Computing nodes provide computing power, motion nodes (robot terminals) upload location information and sensor data, reconstruction nodes generate 3D map models based on this data, and domain nodes manage the 3D space. Each node receives $AUKI token incentives based on its contribution, driving a self-evolving machine vision network.
This network emphasizes privacy protection, avoids a single entity monitoring a user's private space, and can be applied to multiple scenarios, such as retail (product placement optimization), property management (asset tracking), event navigation, and building decoration.
Currently, the market capitalization of the token $AUKI is approximately $52 million.
RobotStack

RoboStack is a cloud-based robot development and deployment platform that provides developers with a simulation environment and sandbox testing. The official description states that the platform can simulate real-world environments in the cloud, featuring a secure sandbox mechanism, high-performance computing capabilities, real-time metrics, and team collaboration features.
To address the challenges of integrating and training robotics technologies that are fragmented across different hardware, middleware, and communication standards, RoboStack proposes the Robot Context Protocol (RCP). This protocol allows secure communication between robots, AI agents, and humans. The simulated environment will include tokenized voting and incentive mechanisms to foster competition among developers and enthusiasts, facilitating the deployment of real-world robotic applications in future multi-chain environments.
Currently, the market capitalization of the token $ROBOT is approximately $3 million.
BitRobot

Developed jointly by FrodoBots Labs and Protocol Labs, the BitRobot Network aims to enable distributed robot work and collaboration. Its key components include: Verifiable Robot Work (VRW, a quantifiable metric for network rewards) for defining and validating robot tasks; Device Node Tokens (ENT, unique identifiers for robots within the system, existing as NFTs) for device ownership and network access; and subnets (resource clusters that create value for the BitRobot Network) serving as the task execution layer.
On February 14, FrodoBots Lab announced the completion of a $6 million seed round of financing, bringing its total funding to $8 million.
Currently, BitRobot has not issued its own cryptocurrency. It's worth noting that FrodoBots Lab is already selling robots; Earth Rovers, resembling a real-life Mario Kart, costs $249. Players remotely control their sidewalk robots in a global treasure hunt game, with data used by researchers to deploy and test their latest AI navigation models. There's a possibility that BitRobot might also issue its own cryptocurrency.
Another gaming robot, ET Fugi, will also be launched in the future, allowing players to remotely control a robotic arm to complete various 3D puzzle games and competitions. ET Fugi is also BitRobot's first subnet.
Original article link and title: "NEO Ignites the Robotics Industry, What Robotic Projects Are Worth Watching?"
Two days ago, Norwegian humanoid robot company 1X Technologies officially released the NEO robot and opened pre-orders. It's priced at $20,000 and also supports a monthly subscription model ($499 per month), with deliveries expected to begin in 2026. Tesla has also stated that robots are its next major profit driver. It seems quite possible that robots will become the next major trend.

Humanoid robots capable of performing household chores such as taking out the trash, folding clothes, handing items, and setting the table—this is something many of us imagined in our childhood essays, but now it's about to become a reality. Such news has undoubtedly become a focus of attention for many. In the cryptocurrency world, the meme coin $NEO, named after the robot on Solana, once surpassed a market capitalization of $4 million and currently still maintains a market capitalization of $2.7 million.

Additionally, Echo, the on-chain fundraising platform created by Cobie and recently acquired by Coinbase for $375 million, has raised $10 million in Series C funding from 1X Technologies. However, since the funding was conducted in a private group, specific details are not available.
Besides the funding amounts for Meme Coin and Echo, robotics-related projects in the cryptocurrency space have also attracted attention, with many players referring to this sector as "Robotics." This article will provide a summary of projects related to the Robotics sector.
OpenMind

On August 4, according to official news, OpenMind, a Silicon Valley-based intelligent machine infrastructure company, announced the completion of a $20 million funding round led by Pantera Capital, with participation from Ribbit, Sequoia China, Coinbase Ventures, DCG, Lightspeed Faction, Anagram, Pi Network Ventures, Topology, Primitive Ventures, Amber Group, and many other institutions and well-known angel investors.
OpenMind helps robots think, learn, and work by developing open-source software. Its native open-source AI robot operating system, OM1, allows for the configuration and deployment of AI agents in both the digital and physical worlds. Users can create an AI character and run it in the cloud or on a physical robot in the real world.
In layman's terms, OpenMind's development of OM1 is essentially creating an "AI brain" for robots. This "AI brain" can be composed of multiple AI agents working collaboratively, can interact with multiple LLMs, and can acquire data from multiple sources to perform tasks (such as helping users post on social media). Because OM1 is open source, it is also a highly adaptable robot operating system, much like the Android system on mobile phones, which is hardware-independent.
In addition, OpenMind has an on-chain robot identity network called FABRIC, designed to provide a verifiable layer of trust for humans and robots. Humans can earn badges on it by sharing location data on maps, evaluating robot behavior, and developing features. For robots, each robot equipped with the OM1 system joins the FABRIC network, thus possessing a unique and verifiable identity, and enabling the tracking of robot commands, operation logs, ownership, and other related behaviors on the blockchain.
OpenMind has not yet issued its own cryptocurrency.
XMAQUINA

Robots invest in the DAO. Its governance token, $DEUS, has completed three rounds of sales, raising over $5.5 million in crypto assets. The DAO is currently using the proceeds to support Apptronik, Figure AI, and Agility Robotics, all companies in the humanoid robotics field. Screenshots from the official website's vault show that the DAO's investments are already profitable, with some individual investments exceeding 100% returns.

However, $DEUS has not yet undergone TGE. Upon TGE, 33% of the $DEUS sold to the community will be immediately unlocked, with the remaining 67% unlocking linearly over 12 months.
peaq

On March 27, Peaq, a DePIN Layer 1 protocol, completed a $15 million funding round led by Generative Ventures and Borderless Capital, with participation from Spartan Group, HV Capital, CMCC Global, Animoca Brands, Moonrock Capital, Fundamental Labs, TRGC, DWF Labs, Crit Ventures, Cogitent Ventures, NGC Ventures, Agnostic Fund, and Altana Wealth.
Although its initial narrative focused on DePIN, the project has shown remarkable market acumen, having followed suit with the recently popular x402. Regarding bots, Peaq released its Robotics SDK in September of this year, enabling bots to acquire autonomous identities, conduct payments and receipts, verify data, and integrate into the on-chain network economy.
In addition, Peaq also has a robot-operated RWA marketplace, tokenizing machines and placing them on-chain as shared revenue-generating assets. Peaq launched its first tokenized, robot-operated farm on the main stage of Korea Blockchain Week 2025, which has been deployed on the Peaq chain and will distribute operating profits to token holders.
Currently, $peaq has a circulating market capitalization of approximately $110 million.
PrismaX

On June 17, PrismaX announced the completion of an $11 million funding round, with investors including a16z CSX, Volt Capital, Blockchain Builders Fund, Stanford Blockchain Accelerator, and Virtuals.
PrismaX is building an open coordination layer that connects remote operators, robot users, and robot companies. Operators can connect with users to remotely control robots, perform practical tasks, and collect valuable data. They can also request practical services such as logistics and advertising.
PrismaX features a protocol for remotely operating bots, allowing businesses to find experienced bot operators capable of handling complex tasks. Operators can choose to stake network tokens to increase their trust level and improve their chances of receiving high-yield tasks. Stakers' rewards are tied not only to the amount they stake but also to the quality of their work, with additional rewards awarded for improved efficiency.
The data accumulated from remote operations will then be used to train the robot to improve its autonomy, which will in turn improve the work efficiency of the remote operator and ultimately achieve a high degree or even complete autonomy for the robot.
PrismaX has not yet issued its own token.
CodecFlow

CodecFlow provides a unified platform that runs seamlessly across the cloud, edge, desktop, and robotic hardware, while supporting popular APIs and legacy systems.
AI-driven operators respond to changes in the UI or the robot environment through perception and real-time reasoning, thus addressing the vulnerability of traditional robot automation processes that rely too heavily on pre-written scripts and are susceptible to even minor changes.
In short, it involves capturing screenshots, camera footage, or sensor data, then using AI to process these external input data to handle observations or instructions, and finally executing decisions through user interface interaction.
Currently, the market capitalization of the token $CODEC is approximately $16 million.
NRN Agents

NRN evolved from AI Arena, a blockchain game where AI agents battle in real-time. On October 28, 2021, developer ArenaX Labs announced the completion of a $5 million seed funding round, led by Paradigm Capital with participation from Framework Venture Partners. On January 9, 2024, ArenaX Labs announced the completion of a new $6 million funding round, led by Framework Ventures, with participation from SevenX Ventures, FunPlus/Xterio, and Moore Strategic Ventures, among others.
While the general process is data collection followed by reinforcement of robot learning, NRN leverages its extensive experience in the gaming industry to offer a browser-based experience. This transforms robot data collection into a game, allowing users to intuitively control the simulated robot through a browser. During gameplay, the behavioral data generated by user actions is used to train the real-world robot system.
At this stage, the project will focus on the robotic arm (RME-1) to validate data collection, real-time learning, and adaptability.
Currently, the market capitalization of the token $NRN is approximately $11.7 million.
Auki

Auki's decentralized machine perception network, Posemesh, connects humans, devices, and AI. At its core is a DePIN (Decentralized Entity Network) architecture that allows devices such as robots and AR glasses to share location and sensor data in real time, collaboratively building a spatial understanding of the physical world. It can provide a shared spatial view for robots, AR, and AI.
The Posemesh protocol incorporates various node roles. Computing nodes provide computing power, motion nodes (robot terminals) upload location information and sensor data, reconstruction nodes generate 3D map models based on this data, and domain nodes manage the 3D space. Each node receives $AUKI token incentives based on its contribution, driving a self-evolving machine vision network.
This network emphasizes privacy protection, avoids a single entity monitoring a user's private space, and can be applied to multiple scenarios, such as retail (product placement optimization), property management (asset tracking), event navigation, and building decoration.
Currently, the market capitalization of the token $AUKI is approximately $52 million.
RobotStack

RoboStack is a cloud-based robot development and deployment platform that provides developers with a simulation environment and sandbox testing. The official description states that the platform can simulate real-world environments in the cloud, featuring a secure sandbox mechanism, high-performance computing capabilities, real-time metrics, and team collaboration features.
To address the challenges of integrating and training robotics technologies that are fragmented across different hardware, middleware, and communication standards, RoboStack proposes the Robot Context Protocol (RCP). This protocol allows secure communication between robots, AI agents, and humans. The simulated environment will include tokenized voting and incentive mechanisms to foster competition among developers and enthusiasts, facilitating the deployment of real-world robotic applications in future multi-chain environments.
Currently, the market capitalization of the token $ROBOT is approximately $3 million.
BitRobot

Developed jointly by FrodoBots Labs and Protocol Labs, the BitRobot Network aims to enable distributed robot work and collaboration. Its key components include: Verifiable Robot Work (VRW, a quantifiable metric for network rewards) for defining and validating robot tasks; Device Node Tokens (ENT, unique identifiers for robots within the system, existing as NFTs) for device ownership and network access; and subnets (resource clusters that create value for the BitRobot Network) serving as the task execution layer.
On February 14, FrodoBots Lab announced the completion of a $6 million seed round of financing, bringing its total funding to $8 million.
Currently, BitRobot has not issued its own cryptocurrency. It's worth noting that FrodoBots Lab is already selling robots; Earth Rovers, resembling a real-life Mario Kart, costs $249. Players remotely control their sidewalk robots in a global treasure hunt game, with data used by researchers to deploy and test their latest AI navigation models. There's a possibility that BitRobot might also issue its own cryptocurrency.
Another gaming robot, ET Fugi, will also be launched in the future, allowing players to remotely control a robotic arm to complete various 3D puzzle games and competitions. ET Fugi is also BitRobot's first subnet.



