The real reason why ETH worth $1.9 billion is collectively queuing up to unstake is...
Original article from Galaxy
Compiled by Odaily Planet Daily Golem ( @web3_golem )

Starting on July 16, the number of ETH unstacking requests increased dramatically, with the number of validator exit queues soaring from 1,920 to over 475,000 on July 22, and wait times increasing from less than an hour to over eight days. While the increase in unstacking activity was expected due to ETH’s recent price outperformance and the recent ETH Pectra upgrade’s adjustments to validator staking requirements, the sharp spike was primarily driven by the spike in ETH lending rates that began on July 16. The spike in rates triggered widespread unwinding of ETH revolving lending strategies, which in turn exacerbated the decoupling pressure on ETH-based liquidity staking and re-staking tokens (LST and LRT).
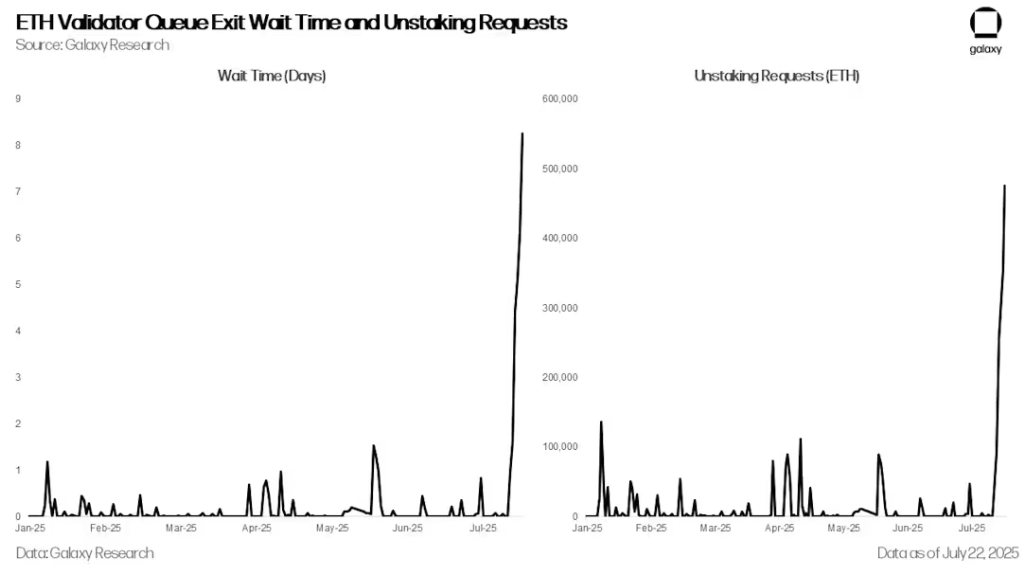
ETH validator queue exit wait time and unstacking requests
Ethereum Staking Queue
Ethereum's stake exit queue is a built-in mechanism designed to manage the orderly withdrawal of staked funds from the network by validators. In order to maintain network stability and prevent large-scale validator exits from jeopardizing consensus, Ethereum limits the number of validators that can exit per epoch. This limit, called the churn limit, varies with the total number of active validators, allowing approximately 8 to 10 validators to exit per epoch (approximately every 6.4 minutes). When a validator initiates a voluntary exit, they enter a queue and must wait their turn to be processed. After exiting, there is a waiting period (approximately 27 hours) before funds can be withdrawn. During periods of high demand for exits, the queue can be severely congested, resulting in wait times of days or even weeks.
This week is not the first time that Ethereum has seen a backlog of unstaked tokens. In January 2024, due to the restructuring of bankrupt cryptocurrency lender Celsius, 550,000 ETH needed to be withdrawn, and the waiting time was as long as six days.
ETH revolving loan strategy fails due to soaring lending rates
Starting on July 14, ETH lending rates on the Aave DeFi protocol began to spike periodically. While lending rates are typically between 2% and 3%, on July 16, 18, and 21, the rate spiked to 18%. The dramatic volatility was caused by a sharp drop in the supply of ETH on the Aave platform, which stemmed from a large withdrawal from the platform by a wallet associated with the HTX exchange. Starting on June 18, the wallet withdrew more than 167,000 ETH. The sudden drop in ETH deposits put pressure on users running ETH revolving lending strategies on Aave and also led to a surge in some redemption requests.
The revolving loan strategy is a strategy widely used by cryptocurrency traders to increase the yield on ETH staking. In its common form, users deposit Liquidity Staking Tokens (LST) or Liquidity Re-staking Tokens (LRT) as collateral on platforms such as Aave, borrow ETH, and then redeem it back to LST and redeposit it again, repeatedly, and continuously accumulate leverage exposure. When the staking yield exceeds the ETH lending rate, the strategy is profitable and users can earn the spread. This strategy can be executed manually or through automated vaults provided by protocols such as EtherFi and Instadapp.
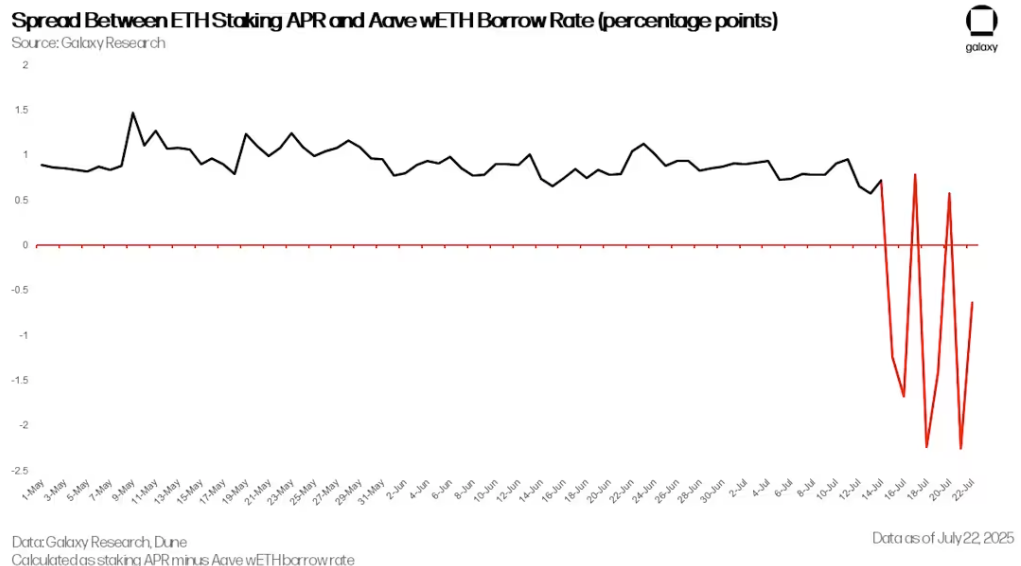
The spread between ETH staking APR and Aave wETH lending rate (percentage points)
However, following the ETH supply crunch that began on July 16, the spread between the staking yield and the cost of borrowing ETH turned negative. By July 21, the spread had fallen to -2.25%, making the strategy unprofitable. This triggered a collective liquidation of positions by traders, with users beginning to withdraw their provided ETH, repay loans, and gradually reduce position leverage. Since many traders used LST or LRT as collateral, they needed to exchange these assets back to ETH or unstake them. This put further pressure on the LST/LRT secondary market and the Ethereum validator exit queue.
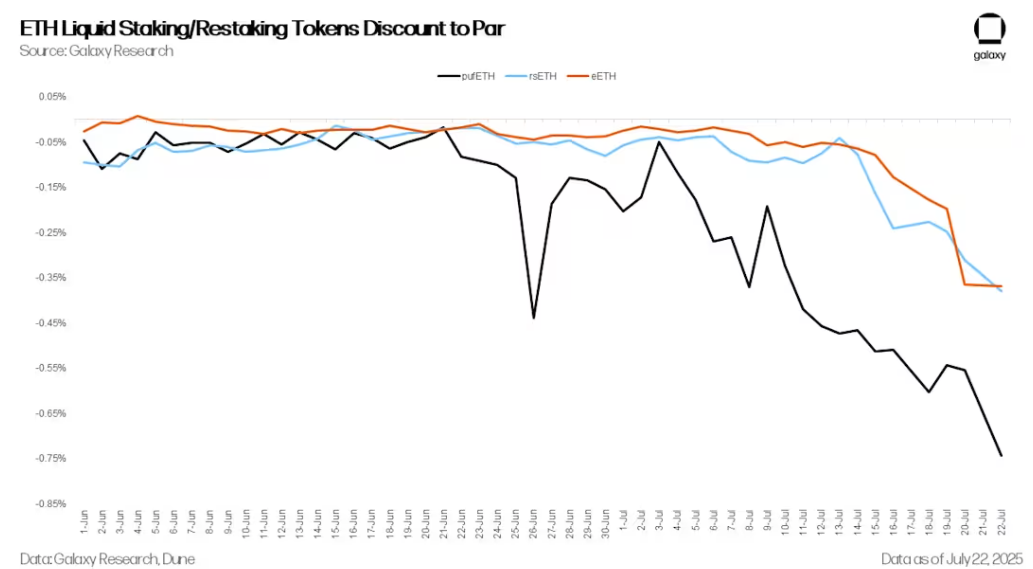
ETH liquidity staking/re-staking tokens below par
As lending rates climb, LST and LRT begin to decouple further from ETH. LST/LRTS typically trade at a slight discount to ETH to compensate for redemption delays caused by the Ethereum exit queue, limited DEX liquidity, and protocol-specific risks (such as penalties or smart contract risks). During forced deleveraging or redemptions, this selling pressure can push LST/LRT prices further below par. In addition, automated revolving loan vaults react differently to disruptions. Some vaults choose to uncollateralize, while others sell directly on the secondary market. For example, as of today, EtherFi's Liquid strategy has approximately 20,000 ETH in the Ethereum exit queue.
Further exacerbating the queue congestion, some market participants began to use the LST/LRT decoupling for arbitrage. By buying LST/LRT at a discount on the secondary market and exchanging it for the full value of ETH by redeeming the collateral, they could earn the difference between the two. This led to a surge in the number of ETH exit queue requests.
Demand for staking and becoming a validator is increasing
The surge in requests to redeem collateral was offset by a surge in demand for new collateral. Since June, ETH collateral requests and queue lengths to become a validator have risen to their highest levels since April 2024.
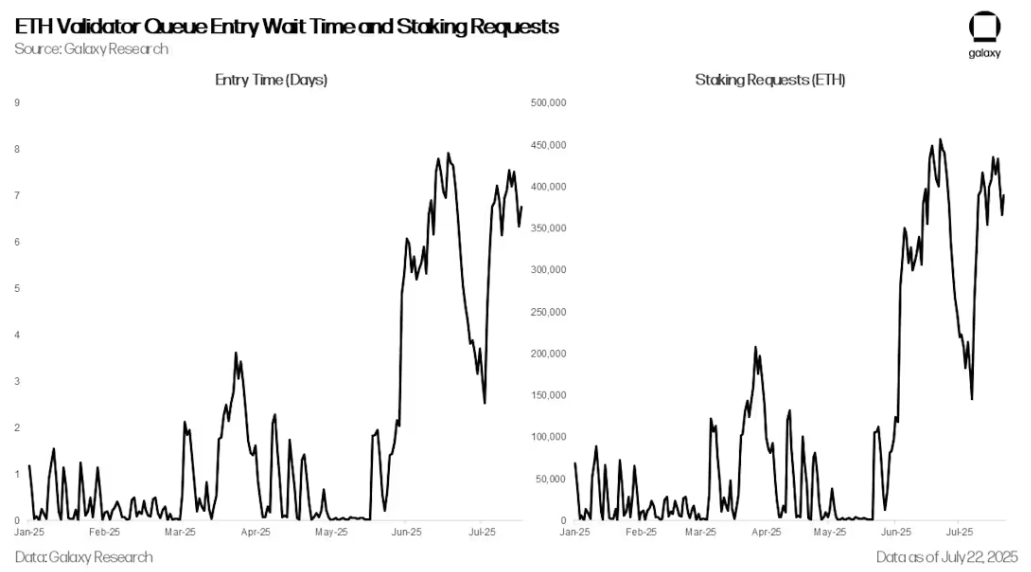
ETH validator queue entry waiting time and staking requests
This is due to ETH’s recent outperformance against Bitcoin and the establishment of several digital asset finance companies (DATCOs), which have purchased more than $2.5 billion in ETH in recent months, sparking enthusiasm for ETH.
Outlook
While the overall data for unstaked ETH may initially suggest a wave of profit-taking, a closer look reveals that most of the activity is driven by volatility in the ETH lending market and a sharp rise in lending rates starting on July 16. At the same time, new staking demand remains strong, almost offsetting the continued withdrawal volume, so investors don't need to panic.
Despite the increase in demand, ETH's staking architecture is still functioning as intended. While some may complain about the significant increase in queue times, this is a feature of the network, not a bug. It is designed to limit the speed at which validators can enter or exit, thereby protecting the stability and security of Ethereum's Proof of Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism.
However, this incident highlights the continued fragility of the ETH liquidity staking and re-staking ecosystem. These assets remain sensitive to leveraged strategies and are prone to stress in extreme market conditions. The widespread impact of LST/LRT decoupling and redemption delays reinforces the importance of considering term risk and liquidity bottlenecks.
Looking ahead, protocols that rely solely on Ethereum’s native exit mechanisms may face increased scrutiny. We expect to see growing interest in solutions that increase redemption flexibility, such as peer-to-peer exit markets, improved LST/LRT automated market makers (AMMs), and protocol-native liquidity vaults designed to ease exit queue congestion and smooth fund flows.
Related Reading
Ethereum's 1.9 billion unstaking wave: profit-taking or a new starting point for the ecosystem?



