NFT Lending Industry Research Report
TL;DR
1. NFT lending is a financial product that occurs during the holding phase, where the core mechanism allows holders to borrow short-term funds by using idle NFTs as collateral without selling them, in exchange for liquidity in the form of cryptocurrencies or fiat currency. This allows holders to enjoy the benefits of holding NFTs while earning profits and improving the efficiency of their funds.
2. In NFT lending protocols, there are mainly two forms: collateralized lending and unsecured lending.
1) Collateralized protocols:
Peer-to-peer (P2P): Suitable for bear markets with low liquidity, as it is not affected by extreme market conditions.
Peer-to-pool: Suitable for bull markets with abundant liquidity.
Hybrid: Based on the standard peer-to-pool model, it offers higher operational convenience.
Collateralized Debt Position (CDP): A good option for those seeking liquidity from blue-chip NFTs without paying high interest rates.
2) Unsecured protocols:
Buy Now Pay Later (BNPL)
Flash loan: Suitable for NFT market users who have the intention to purchase but temporarily lack the full payment capability.
3. Theprofit modelof NFT lending business mainly comes from theloan interestpaid by users for mortgage loans, and if there are additional features such as flash loans, it will also generate correspondingtransaction fees.
4. The main risks of NFT lending are as follows:
Risk of fluctuation in valuation of NFT collateral (risk of bad debts)
High concentration of target users
Limitations on the growth potential of the overall market volume due to limited increase in high-quality asset targets
5. It is expected that within 3 years, theestimated overall market capitalization of NFTsunder a neutral assumption would reach approximately$60 billion, and theNFT lending TVLwould reach approximately$18 billion, meeting a borrowing demand of approximately $9 billion. Theprojected operating revenue of the overall NFT lending industry is estimated to reach $1.3 billion.
1. Industry Landscape
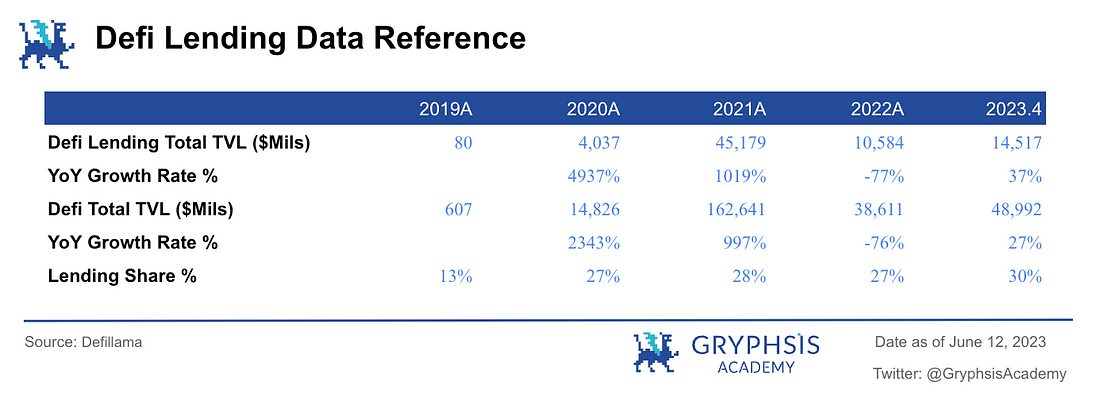
In the past few years, two areas in the crypto industry have experienced rapid growth: decentralized finance (DeFi), which went through the Defi Summer of 2020, and NFT Boom in 2021.
The overall market size of NFTs on Ethereum has gone through a short period of development from around $61 million at the beginning of 2021 to a peak of around $32 billion. Even though the overall market value has fallen sharply, the market size is still around $7.5 billion, representing more than a 120-fold increase in the industry.
Source: NFTGo.io (May 31, 2023)
Nowadays, NFT-Fi, as a combination of NFT and Defi, has quickly evolved from a niche area to an indispensable part of the crypto world.
The financialization of NFTs helps users expand and enhance their consensus and demand for NFTs in a financialized manner. The industry structure can be vertically divided into three layers:
1) Direct trading: This refers to the exchange of value through trading markets, aggregators, AMMs, and other forms of cryptocurrency.
Representative projects: Opensea, Blur
2) Indirect trading: This involves businesses that provide NFT collateralized lending, financing, and custody services.
Representative projects: BendDAO, ParaSpace
3) Financial derivatives: This includes categories of high leverage and trading risks, such as options, futures, and indexes.
Representative project: Openland
Since direct trading has become relatively mature, while financial derivatives are still in the early stages. Indirect trading as an intermediate layer involves the basic attributes of the financial system, such as deposits, loans, and lending, and is still in a rapid development stage. Therefore, this article will mainly focus on the current industry's focus on NFT lending in indirect trading.
2. Market Value of the Industry
First, let's answer a question: Why is there a market demand for NFT lending?
As we all know, NFT, short for Non-Fungible Token, refers to non-fungible tokens that cannot be replicated or substituted. They are a type of unique encrypted asset with characteristics of uniqueness, indivisibility, and non-replaceability. Their pricing is mainly based on subjective judgments or collective consensus.
It is precisely because of these characteristics of NFTs, although they are considered to have artistic and collectible value (as well as potential project empowerment), their lack of a standard benchmark for value anchoring often limits their target audience compared to ordinary fungible cryptocurrencies. Therefore, the liquidity of NFTs is relatively poor in the entire crypto market.
Typically, NFT investors profit from selling when the value of their NFTs appreciates. However, this method is heavily influenced by the current market environment. When the Web 3 environment is in a bear market with low market confidence and low trading activity, liquidity will further shrink, resulting in these NFT assets being mostly idle, and the efficiency of capital utilization is extremely low. Without lending services, users may be forced to sell their unique NFTs to obtain valuable liquidity.
NFT lending is a financial product that occurs during the holding period of NFTs. The core mechanism of NFT lending is to allow holders to borrow short-term funds by using idle NFTs as collateral without selling them, obtaining liquidity in exchange for cryptocurrencies or fiat currencies, while enjoying the benefits of holding NFTs and earning income, thus improving the efficiency of capital utilization.
NFT lending, as a solution to the liquidity problem of NFTs, is experiencing increasing demand in this innovative market. NFT liquidity solutions with smooth user experience and sustainable trading models will soon stand out in the entire NFT-Fi space.
3. Industry Barriers
The industry barrier of NFT lending business lies in how to realize the feasibility of the core business model, mainly including:
1) How to effectively match the system mechanism of NFT lending demand users
Due to the uniqueness of NFTs by definition, users typically need expertise in specific assets and related financial knowledge to link NFT assets with lending and borrowing operations. Designing attractive business models for both lenders and borrowers is the basis for effectively matching user needs.
2) Reasonable pricing mechanism for NFT assets
Pricing is an important component of NFT lending operations. During the estimation of NFT asset value, calculation of Loan To Value (LTV) ratio, and the liquidation process, it is crucial to provide the system with a reasonable quote that is efficient, fast, and relatively accurate. Especially when the number of users in the protocol increases and the demand for operations grows within the same time period, the mechanism and efficiency of quoting and updating data directly impact the overall customer experience of the protocol.
4. Competitive Landscape
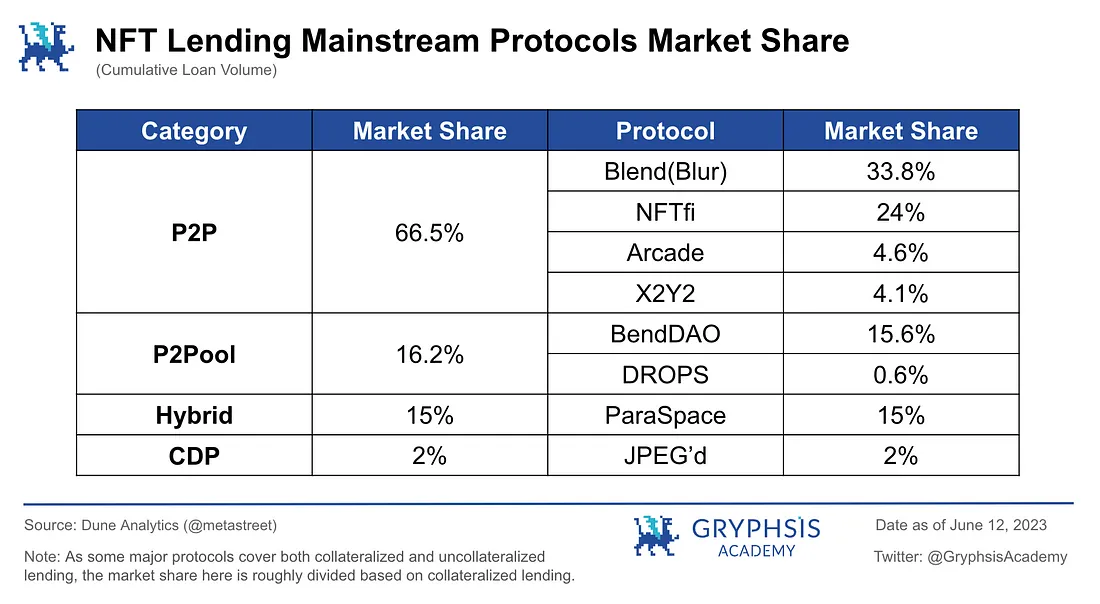
Currently, NFT lending operations are divided into two forms: collateralized lending and unsecured lending.
Among them, collateralized lending can be mainly divided according to the type of agreement:
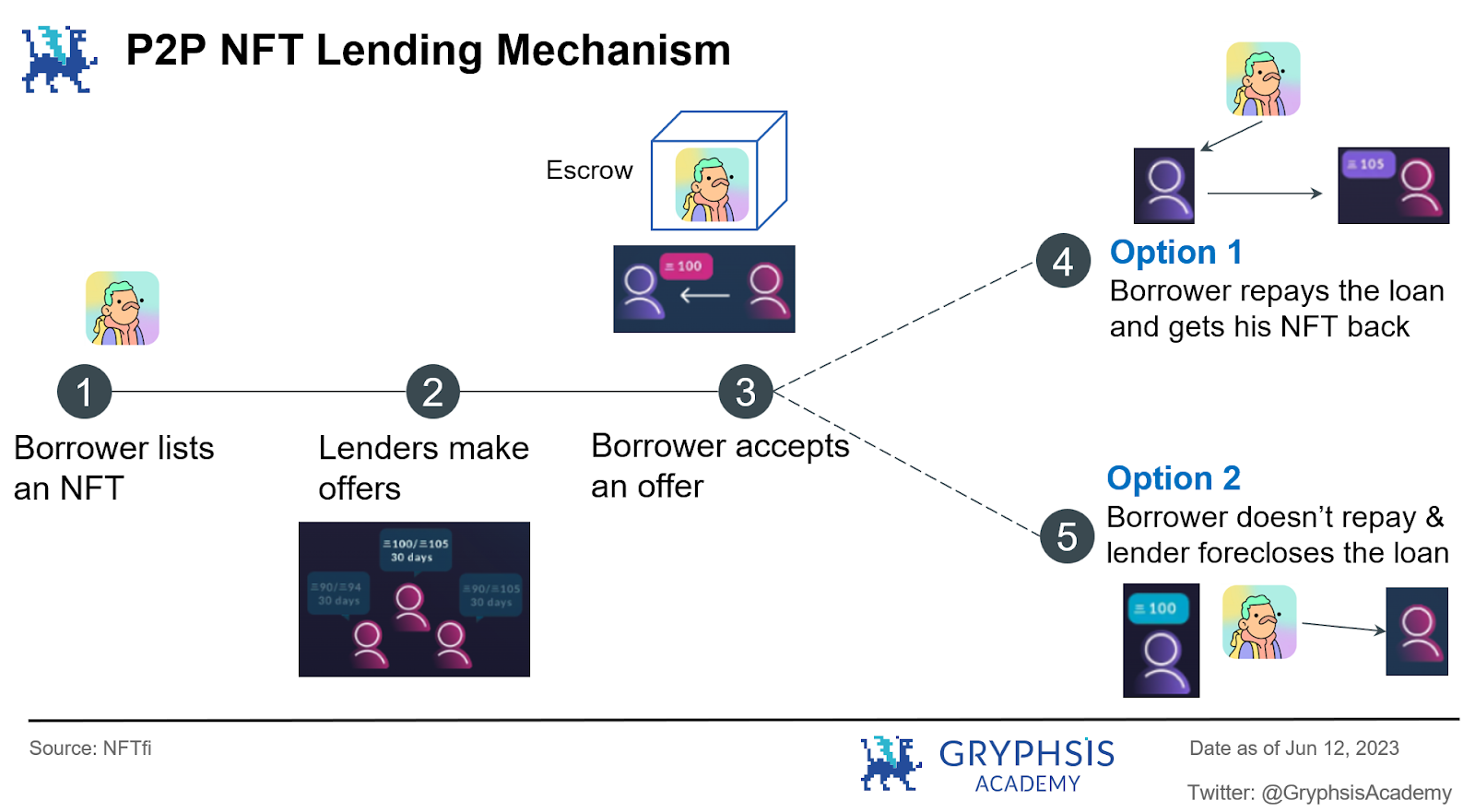
Peer to Peer (P2P)
This refers to the model where loans are matched between users, and lenders and borrowers reach loan transactions after matching in terms of interest rates, terms, types of NFT collateral, etc. Representative projects: NFTfi, Arcade, Blur(Blend)
Peer to Pool
That is the mode in which users and lending pools reach a borrowing agreement. The lender mortgages an NFT to the lending pool to quickly obtain a loan, while the depositor provides funds to the lending pool to earn interest income. Representative projects: BendDAO, DROPS.
Hybrid
This is a protocol that combines peer-to-peer and peer-to-pool models. In this mode, the lender sets parameters such as interest rate, term, loan amount, etc., and when requesting a loan on the platform, they are essentially creating a separate lending pool. Multiple borrowers can deposit funds into the lending pool to earn interest income. Representative project: ParaSpace.
Collateralized Debt Position (CDP)
First pioneered by MakerDAO, this is the ultimate model for the NFT mortgage loan market. Representative project: JPEG'd.
Non-collateralized loans can be further divided into:
1) Buy Now Pay Later (BNPL), representative projects: CYAN, Paraspace, Blur(Blend).
2) Flash loan (Down payment buy), representative project: BendDAO.
Source: Dune Analytics@goyem ( 2023.6.12)
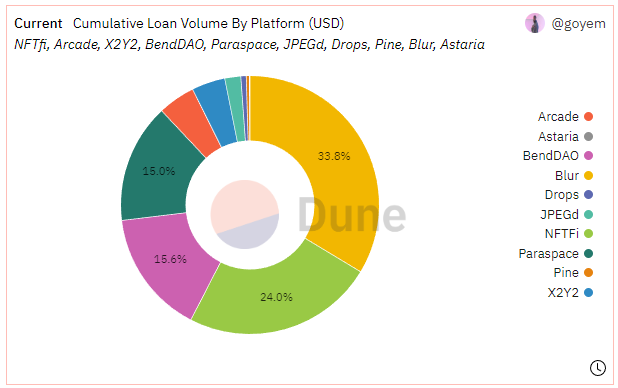
Source: Dune Analytics@goyem (June 12, 2023)
From the two charts above, it can be seen that peer-to-peer and peer-to-pool protocols dominate the entire NFT lending market in terms of scale.
It is worth noting that since the launch of Blend by Blur in May, with the advantage of Blur's position as a leading NFT trading market and its large user base, Blend has quickly taken the top position among mainstream lending protocols, with its trading volume far exceeding that of other protocols for several weeks in a row. Currently, it has become the industry leader in cumulative lending business.
5. Technical Implementation Paths and Their Pros and Cons
Based on the different types of protocols mentioned in the previous chapter of NFT lending business, each has its own characteristics.
5.1 Collateralized Lending
5.1.1 Peer-to-Peer
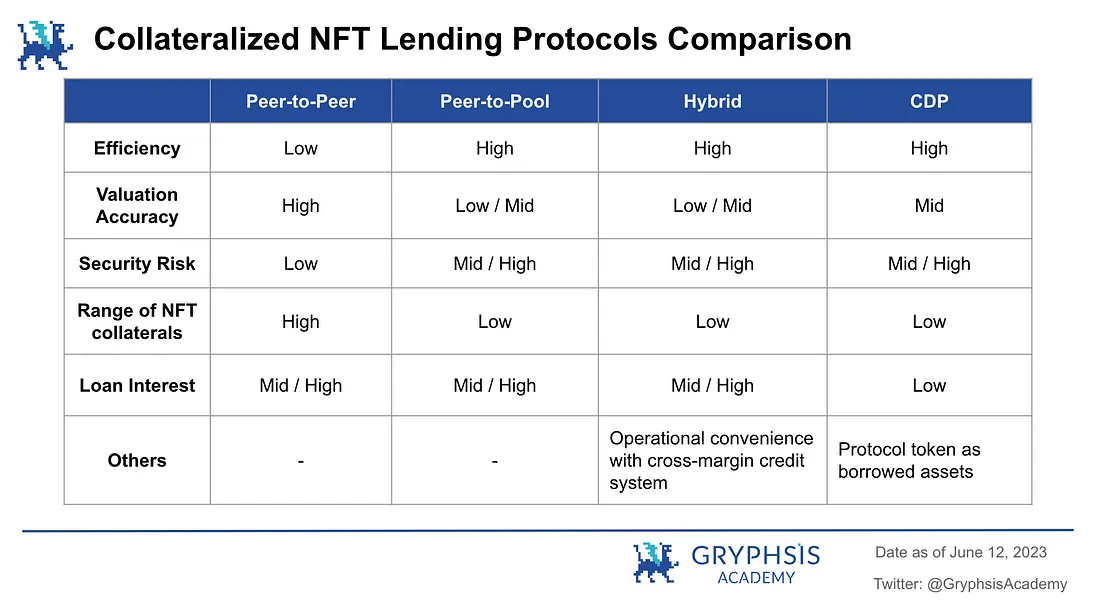
The main method used in peer-to-peer lending is user valuation, where the pricing of NFTs is based on the price estimation provided by users. Users give specific quotes based on the uniqueness of each individual NFT. It has the following characteristics:
Low efficiency: It may take a long time for the pairing of lenders and borrowers.
Relatively accurate valuation: The value of different attributes of NFTs in the same series is different. Lending parties can negotiate and determine the valuation based on the attributes of individual NFTs, rather than using a unified floor price for the entire NFT series as the only valuation standard.
High security: When an individual defaults, it only affects the lending parties of that loan and does not spread the risk to other users on the platform.
Support for a variety of NFT collateral: Since it is a peer-to-peer quotation, theoretically any NFT series can be used as collateral for lending.
Summary: The peer-to-peer model is more suitable for a bear market with limited liquidity and is not afraid of extreme market conditions affecting the platform's security.
5.1.2 Peer-to-Pool
The Time-Weighted Average Price (TWAPs) method is widely used in peer-to-pool lending protocols. Oracles like Chainlink can obtain and publish time-weighted average prices of sales and floor prices to create a blended price for evaluating the value of NFTs. This model reduces the impact of exceptional events on prices by averaging multiple prices over a predetermined time period, making it harder for malicious price manipulation to occur.
Its main characteristics are:
High efficiency: Interacts directly with the lending pool, can borrow anytime.
Less accurate valuation: The platform cannot perform detailed collateral valuation for each NFT attribute, and can only determine the valuation based on the floor price of the NFT series. The loan amount that can be obtained for any NFT attribute in the same series is the same.
Security risks exist: Every loan on the platform affects the interests of all depositors on the platform. In extreme cases, a large-scale liquidation of NFTs may trigger systemic risks.
Limited support for NFT collateral: For safety reasons, only blue-chip NFTs with high trading volume, good liquidity, and relatively stable prices are supported as collateral.
Summary: The peer-to-pool model is more suitable for a bull market with abundant liquidity.
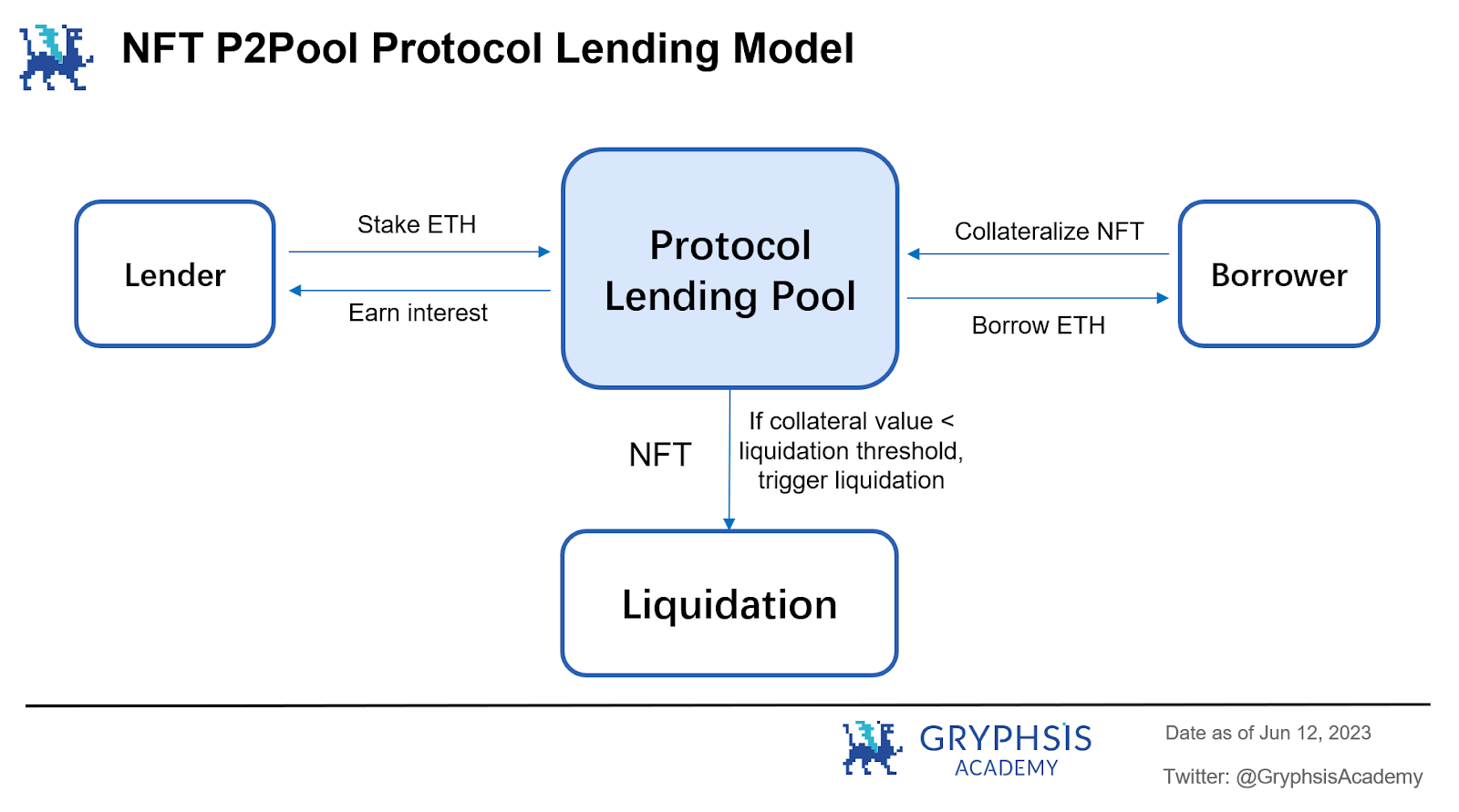
5.1.3 Hybrid
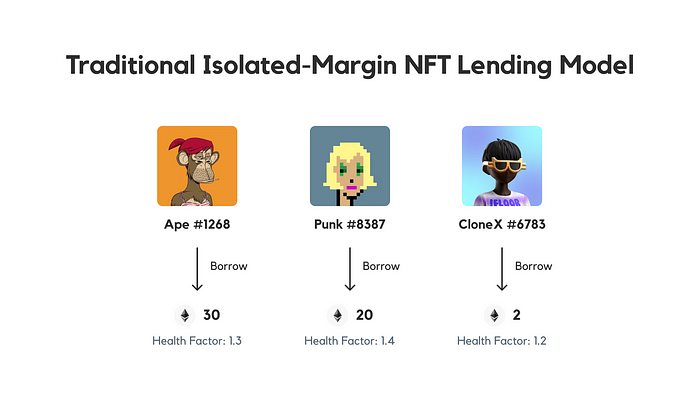
Mixed-type protocols also adopt the Peer-to-Pool model for underlying lending business. Users can borrow in real-time by mortgaging NFTs as borrowers, or provide funds as lenders to earn the interest paid by borrowers. The innovation lies in creating a cross-margin credit system instead of using the isolated margin pool design used by existing platforms. This will allow users to provide loans with a credit limit for all collateral.
Let's explain with an example:
Suppose you own 61 BAYC. You decide to mortgage 5 of them to borrow money and then buy one more. With the existing lending protocols and their isolated margin models, you would need to use these 5 BAYC to borrow ETH and then go to the market to buy new BAYC.
This process has at least two disadvantages:
1. In terms of user experience, users need to perform 5 different on-chain transactions and manage these 5 separate lending positions.
2. If any of your lending positions are about to be liquidated, you must repay the loan immediately to avoid auction liquidation.
The mixed-type protocol, on the other hand, will generate a credit limit for you by mortgaging your NFT assets and generate a health factor for your entire collateral portfolio. As long as the health factor of your entire collateral portfolio remains above 1, none of your NFTs will ever trigger liquidation auctions. To reduce risks, you can always choose to deposit more collateral (NFTs or ERC-20 tokens) to maintain a high health factor.
This credit system is similar to an appraisal system that evaluates the value of all your collateral and automatically approves loans based on that evaluation. As long as your collateral is a supported collateral type in the credit system, you can borrow based on their total value. This is the full-position leverage mode with cross-margin collateral.
It is easy to understand that this model has the characteristics of higher operational convenience in addition to the standard point-to-pool model.
5.1.4 Collateral Debt Position (CDP)
After users deposit NFTs as collateral into the vault, they can mint corresponding protocol currency. The CDP project protocol allows the debt position of the protocol currency to reach a certain ratio of the collateral value, and collects annual interest from it.
When the user's debt/collateral ratio exceeds the liquidation threshold, DAO will execute liquidation. DAO repays the debt and retains or auctions off the NFT to build its vault.
Users can purchase insurance against liquidation when taking out a loan, paying a specified percentage of the loan amount as a one-time payment, which is non-refundable. With insurance, users can choose to repay the debt themselves within a specified time after liquidation (with a fine).
CDP loans are a good option for those seeking liquidity from their blue-chip NFTs without paying high interest rates.
5.2 Non-collateralized Loans
5.2.1 Flash Loans (Buy with Down Payment)
Down Payment Buy is a variant of traditional lending, where users can pay a certain down payment on the agreement to purchase NFTs on the trading market. The remaining funds are provided by a third-party DeFi protocol, such as Aave, through the Lightning Loan service. When the user pays the down payment and the remaining amount obtained through the Lightning Loan, the buyer owns the NFT and can also use it as collateral for borrowing on the NFT lending protocol. The loaned funds are returned to the Lightning Loan by the protocols funding pool, and the interest calculation, repayment mechanism, and liquidation mechanism are all based on the provisions of the lending protocol. When the listing price is higher than the floor price of the NFT in the protocol, the down payment The ratio will also increase accordingly. The fees typically include the down payment fee and the Lightning Loan feature fee.
The workflow is as follows:
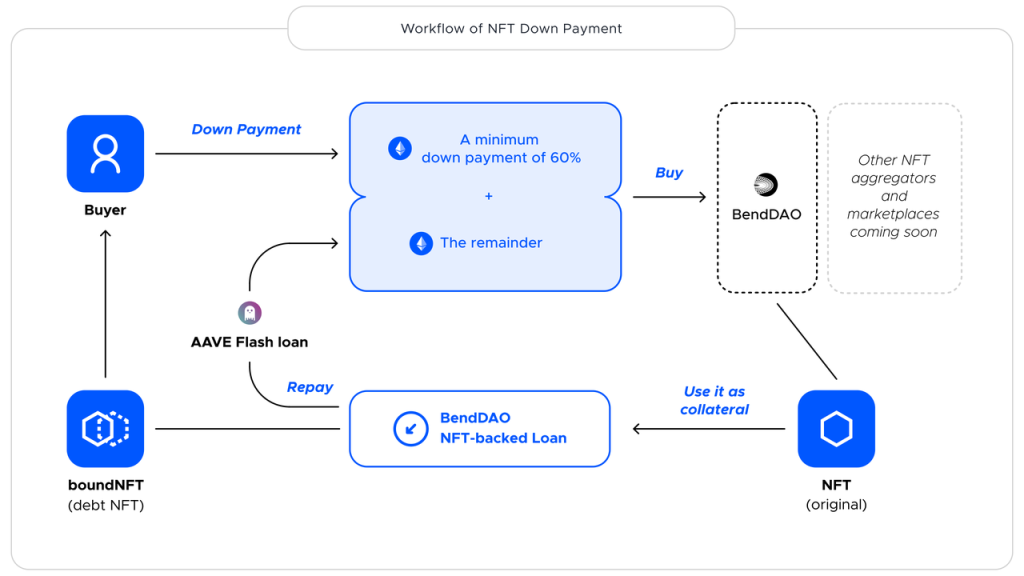
Source: BendDAO
5.2.2 BNPL Buy Now Pay Later
A brief explanation of its operation from the buyer's perspective:
1. Bob wants to buy a Pudgy Penguin. First, he initiates a BNPL plan on the platform to purchase any Penguin currently listed on Opensea, LooksRare, or X 2 Y 2.
2. Then, the platform offers Bob an installment payment plan with a pre-quoted interest rate that he needs to repay within a 3-month period. Regardless of NFT price fluctuations, the installment payments remain unchanged and fixed for the three months.
3. If Bob accepts the plan, he will receive ETH from the platform's funding pool to purchase the NFT and it will be held in custody according to the platform's smart contract.
4. When Bob completes all his installment payments, the NFT will be transferred to his wallet, and he will have full ownership. (Hint: If the price of the NFT appreciates during this period, Bob can pay off the BNPL plan in full in advance and sell the NFT.)
5. Failure to make payments on time will be considered a default, and the NFT will be held in the corresponding platform Vault for liquidation.
The BNPL feature provides a "pawning" service that allows users to temporarily pledge their NFTs as collateral in exchange for a loan. The loan, along with interest, is then repaid, with the interest going directly into the funding pool. To prevent plan defaults, the platform has implemented various risk management measures, such as raising interest rates to regulate loans and prevent holding high-risk NFT products.
You can see that the business model of non-mortgage lending, whether it's flash loans (buy first, pay later) or BNPL (buy now, pay later), actually involves the mortgage taking place after the purchase. It allows users to obtain NFTs with a smaller initial investment by paying a portion of the down payment upfront and then repay the corresponding loan within a defined timeframe. This is suitable for NFT market users who have the intention to purchase but temporarily lack the full payment capability.
Therefore, the characteristics of this type of lending model are:
Reasonable capital utilization, enabling users to make early purchases with a smaller initial investment, thereby reducing financial pressure
Requires a reliable credit evaluation system to assess the risk of each transaction through credit evaluation
The risk control model needs to be tested, especially as the product is in its early stages. It is crucial to effectively control risks and maintain business health when there is a significant increase in user usage in the future.
6. Profit Model
In general, the income sources of NFT lending protocols mainly include: (1) loan interest paid by users for mortgage lending, (2) loan fees generated by services like flash loans, (3) transaction market fees.
The profit model of NFT lending business in the protocol primarily relies on loan interest and loan fee contributions, while transaction market fees are unrelated to lending business.
The distribution of project income may vary based on different protocol settings. It could involve different ratios between the project treasury and token holders/users.
7. Industry Valuation
Adopting a top-down valuation method, it is estimated based on the size of the DeFi lending market. The growth logic mainly lies in the continuous growth of the NFT market size with the development of the entire Web 3 industry. As NFT lending is still in its early stages, there is considerable room for overall growth in this field.
7.1 Valuation Assumptions
The cryptocurrency market is cyclical and is currently in a phase of temporary bearishness. The overall scale of the NFT industry will fluctuate with the market's macrocycles. However, the penetration rate (Total Value Locked) of NFT lending will rise relatively quickly.
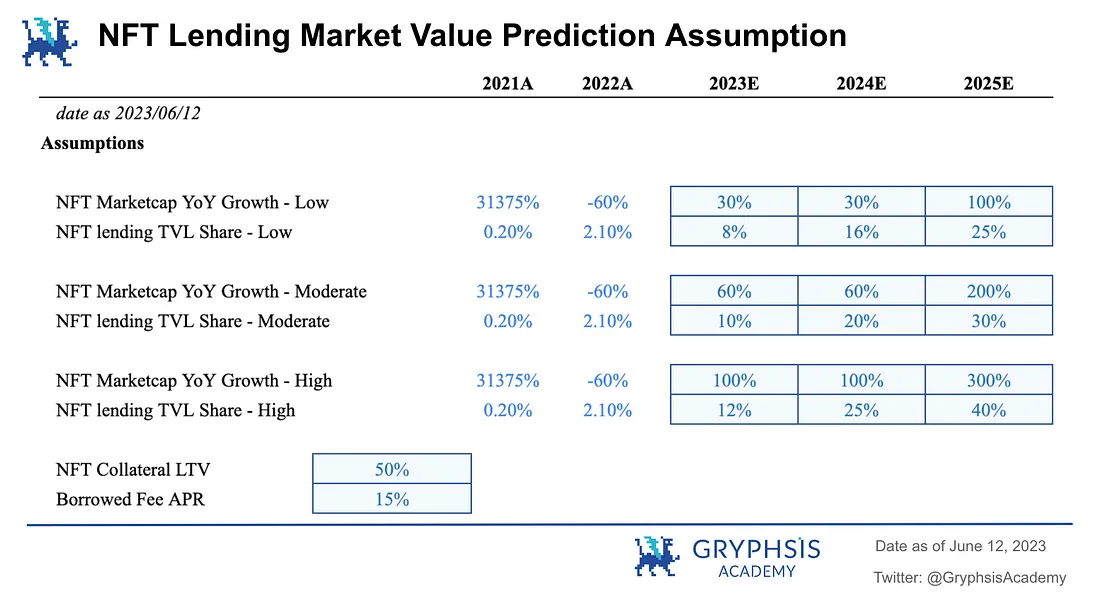
(a) Industry Market Value Growth Rate
Referencing the development of the Defi lending market from 2019 to the present, it can be seen that in the first two years of rapid industry growth, and under the condition of a relatively healthy market environment, due to the small market size, the overall market scale will experience rapid growth of several tens of times. However, in 2022, due to the weak overall market, the total market value experienced a significant retreat. The trend of the NFT market in the past two years is similar to this. Since the beginning of this year, the overall Defi market value has shown some recovery based on the year 2022. If the slow recovery continues, there is hope of recovering the retreat from last year over the course of a whole year.
Therefore, assuming a 60% overall industry market value growth for the entire year. Also, referring to the bull and bear cycle, assuming that year 24 is also a stable period with the same growth rate as year 23, and year 25 is a period of bull market outbreak, with a growth rate three times that of the stable period.
Take the above assumptions as neutral assumptions. The conservative assumption takes 50% of the neutral assumption's annual growth rate, while the aggressive assumption gives a high expectation based on the neutral assumption.
(b) NFT Lending TVL ratio
Referencing the lock-up penetration rate of lending business in the overall Defi market over the past 3 years, it has been in the range of 25% ~ 30%. The NFT lending TVL is expected to reach a similar ratio in the year 25, with 30% taken as the neutral assumption. Take 25% as the conservative assumption and 40% as the aggressive assumption.
(c) NFT Collateral LTV
Based on the LTV data of several mainstream NFT lending protocols currently, take 50% as the collateral's LTV assumption.
(d) Loan Interest Rate APR
Referring to the annual interest rates of Defi lending and current NFT lending, take 15% as the APR interest rate assumption for NFT loans.
7.2 Market Valuation Forecast
In the next 3 years, if we estimate based on the neutral assumption in the valuation model, that is, the overall market value of NFTs steadily grows at 60% annually in 23/24 and may experience a significant increase in the bull market cycle in 25 (yearly growth of 200%). NFT lending TVL accounts for 30% of the overall industry market value. LTV = 50% and loan APR = 15%.
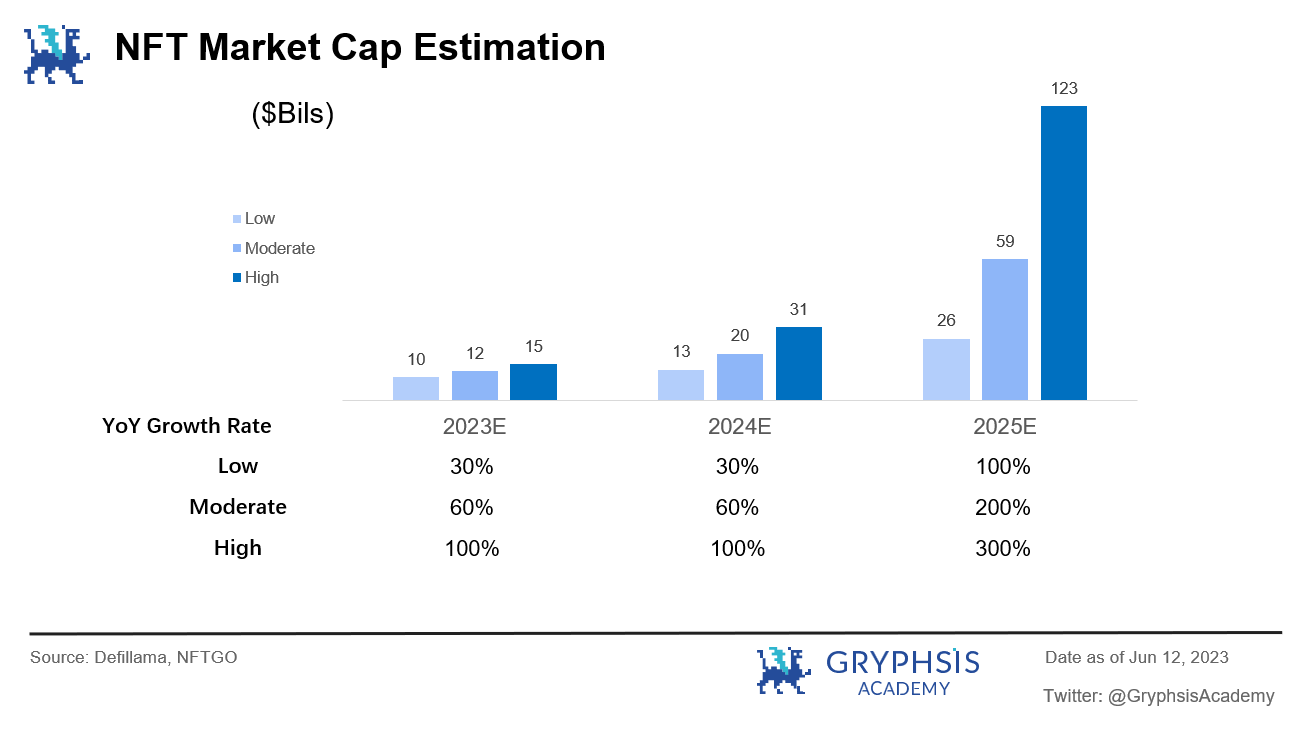
Based on the above assumptions, it is expected that within 3 years, the overall market value of NFT can reach about $60 billion, with NFT lending TVL reaching about $18 billion, and able to meet lending demand of about $9 billion (estimated based on an average 50% LTV). The projected revenue of the overall NFT lending industry is expected to reach $1.3 billion, equivalent to nearly 10 billion RMB (estimated based on an average annualized lending rate of 15%).
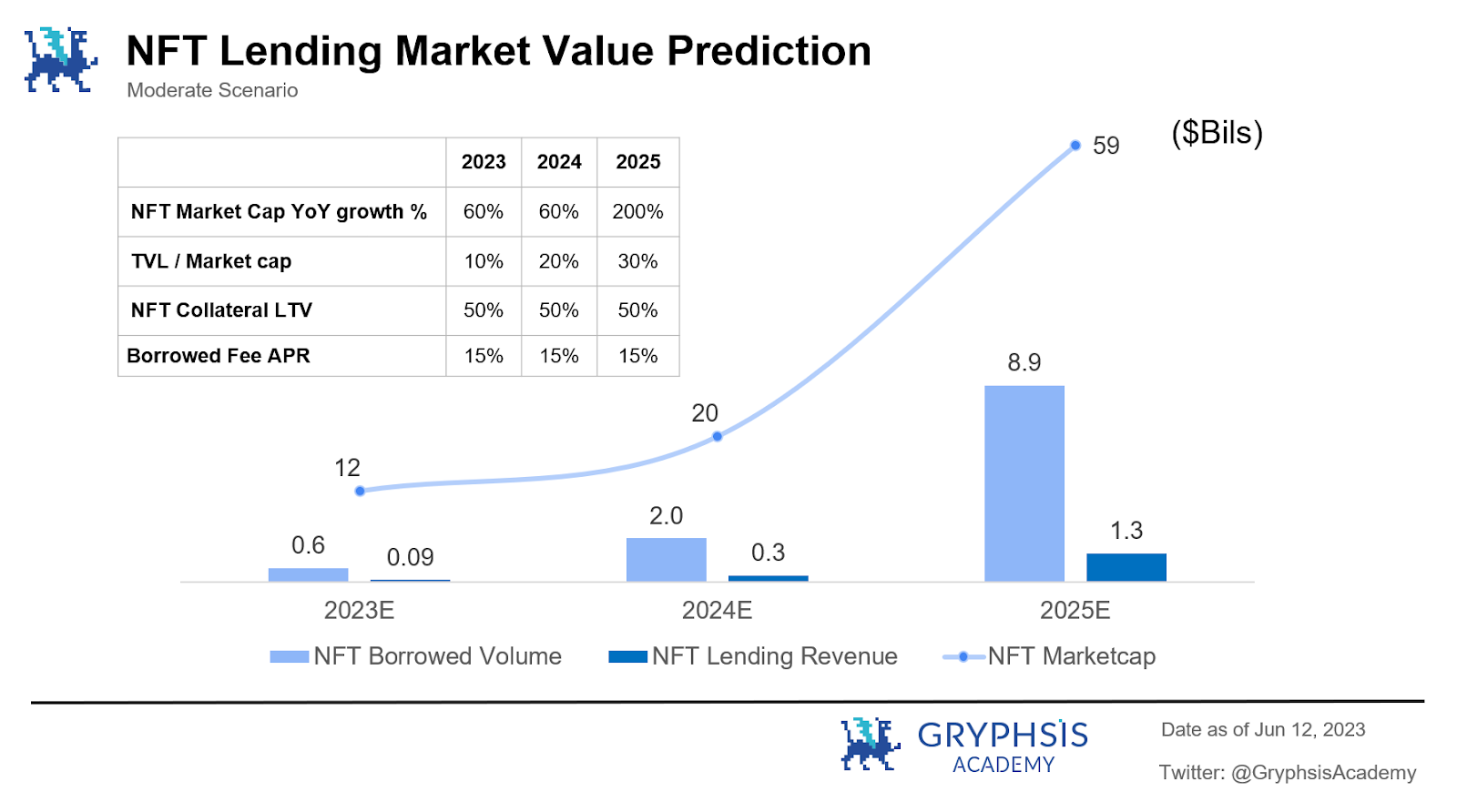
Note: The revenue mentioned here only considers the interest income from lending, which is the majority in the industry, referring to historical lending data from major NFT lending platforms (with interest rates usually ranging from 15% to 30%) and considering the trend of Defi lending rates. A 15% annualized lending rate is assumed as the average rate for NFT lending.
8. Major Companies / Protocols Introduction
This section introduces the main company products under the collateral lending model.
8.1 Peer-to-Peer
8.1.1 NFTfi
NFTfi.com is a mature P2P NFT lending platform in the form of an auction, where the bidding, interest calculation, and duration are determined jointly by the funding provider and the NFT collateral provider. It is a leading platform in the P2P lending business.
Since 2020, more than 45,000 loans have been issued, with a total loan amount of about $450 million (as of the end of May 2023). Since April 2022, the monthly ETH loan volume has remained above 10,000 coins, reaching a peak of nearly 18,000 coins in January 2023. From March to May 2022, monthly revenue exceeded $1 million, with a peak in May exceeding $1.5 million.
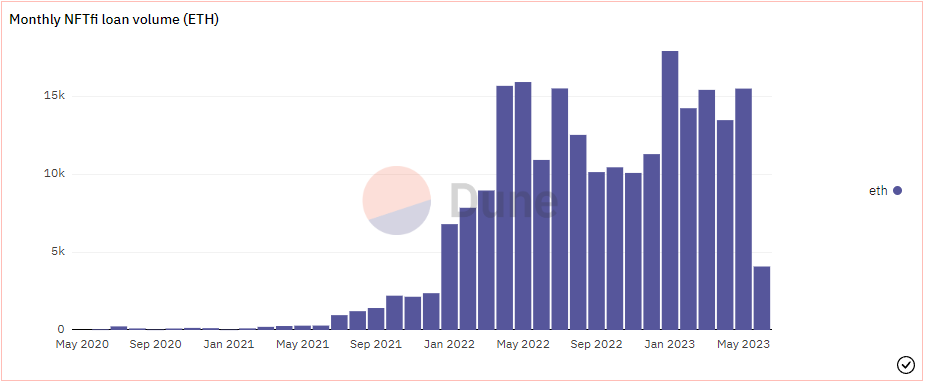
Source: Dune Analytics@rchen 8 (June 12, 2023)
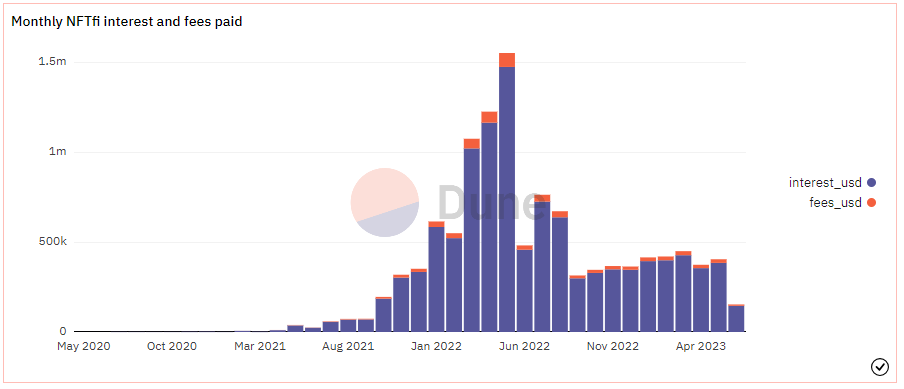
Source: Dune Analytics@rchen 8 (June 12, 2023)
8.1.2 Arcade
Arcade is also a peer-to-peer platform that provides liquidity borrowing market for NFTs. It was formerly known as Pawn.fi. The project is built on top of the Pawn protocol, which is an infrastructure layer for NFT liquidity. It includes a set of smart contracts deployed on the Ethereum blockchain to enable the securitization of non-fungible assets. NFT holders can apply for loans by using one or more of their assets as collateral through the Arcade application. Then, specific loan terms are required.
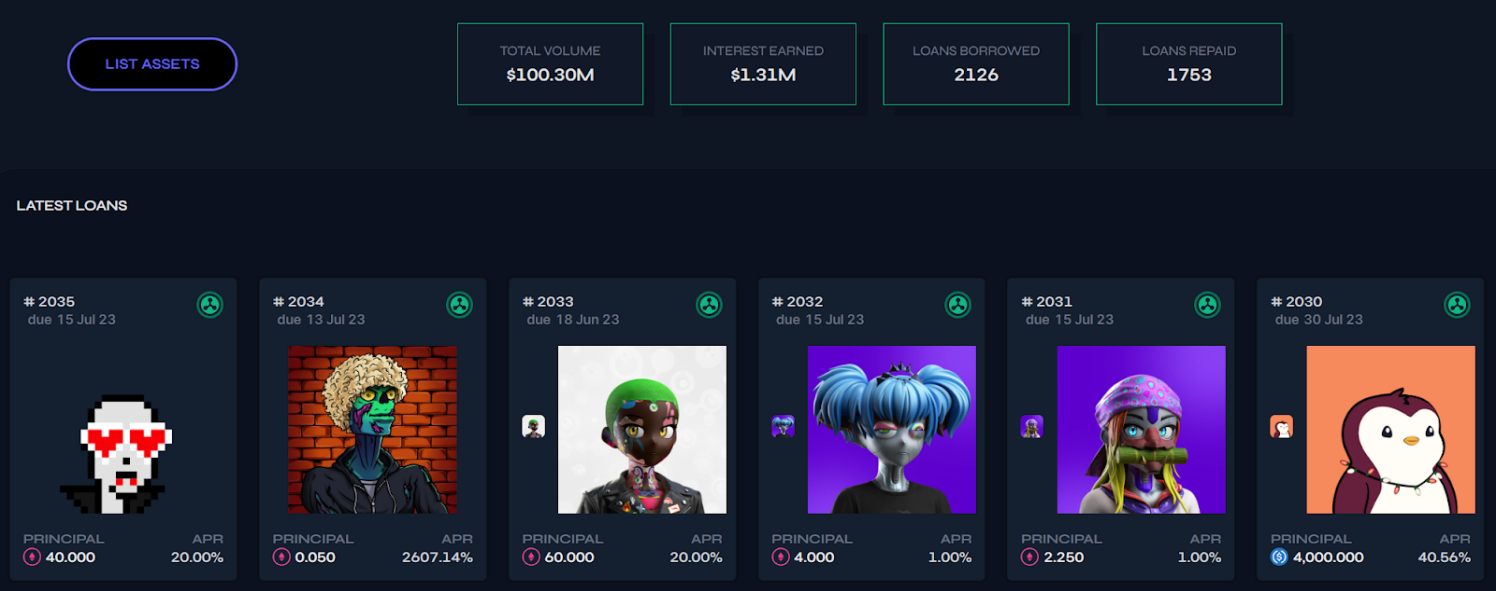
Source: Arcade ( 2023.6.12)
This platform uses smart contracts to create a packaged NFT (also known as wNFT) that represents the collateral for borrowers when applying for loans. wNFT is locked in a custody smart contract, which records when the principal is sent to the borrower and repaid to the lender.
As of June 12th, Arcade has issued over 2,000 loans, lending out approximately $100 million in loan funds. The monthly lending volume has remained above 5,000 ETH for the past six months. The accumulated interest income from loans exceeds $1.3 million.
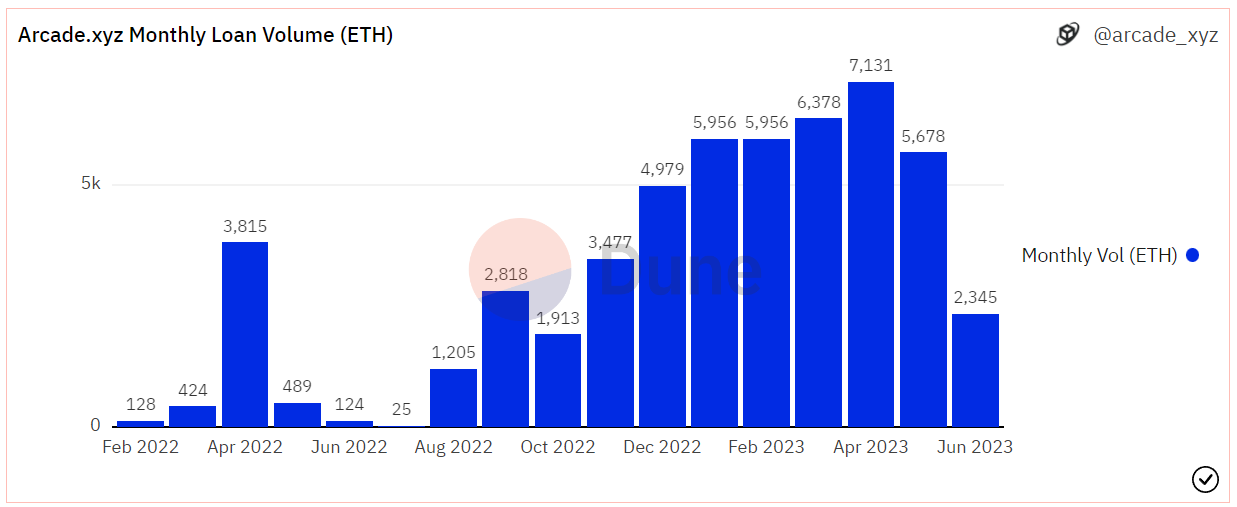
Source: Dune Analytics@arcade_xyz ( 2023.6.12)
8.1.3 Blur (Blend)
NFT trading platform Blur, in collaboration with Paradigm, launched Blend, a P2P NFT lending protocol, and the ability to purchase NFTs with loans.
The core features of Blend are:
P2P perpetual lending with no expiration date and no need for oracles
Lenders set loanable amounts and APY to create offers, borrowers choose offers
Lenders can exit, borrowers need to repay within 30 hours or refinance, otherwise liquidation occurs
Borrowers can repay at any time
Supports buying NFTs with down payment + loan

Source: Blur
Blend's core advantage is to unify non-essential elements, reduce system complexity, achieve flexible migration of lending relationships within the system, price risks and returns through market games, and maximize user satisfaction.
Compared to the traditional point-to-point model, Blend unifies the term element in the three elements of loan-to-value ratio, interest rate, and term into a perpetual flexible mode, greatly improving the liquidity problem for the lender.
Blend unifies the exit and liquidation of the lender, and the oracle is responsible for deciding the timing of liquidation. Blend gives the lender the flexibility to handle exit choices.
Blend improves efficiency by unifying non-essential elements in the traditional point-to-point lending model and fully integrating with the Blur trading module, resulting in significant improvements at the product level. After its launch, it quickly gained market recognition, with lending volumes surpassing NFTfi in early May.
Since its launch in early May, Blend has achieved nearly 50,000 lending transactions and a loan amount exceeding $700 million in just over a month. The cumulative number of users is nearly 20,000. In June, the business has further grown compared to May, with daily lending transactions averaging around 2,000 and daily loan amounts steadily surpassing $20 million, reaching a peak of $34 million on June 6.
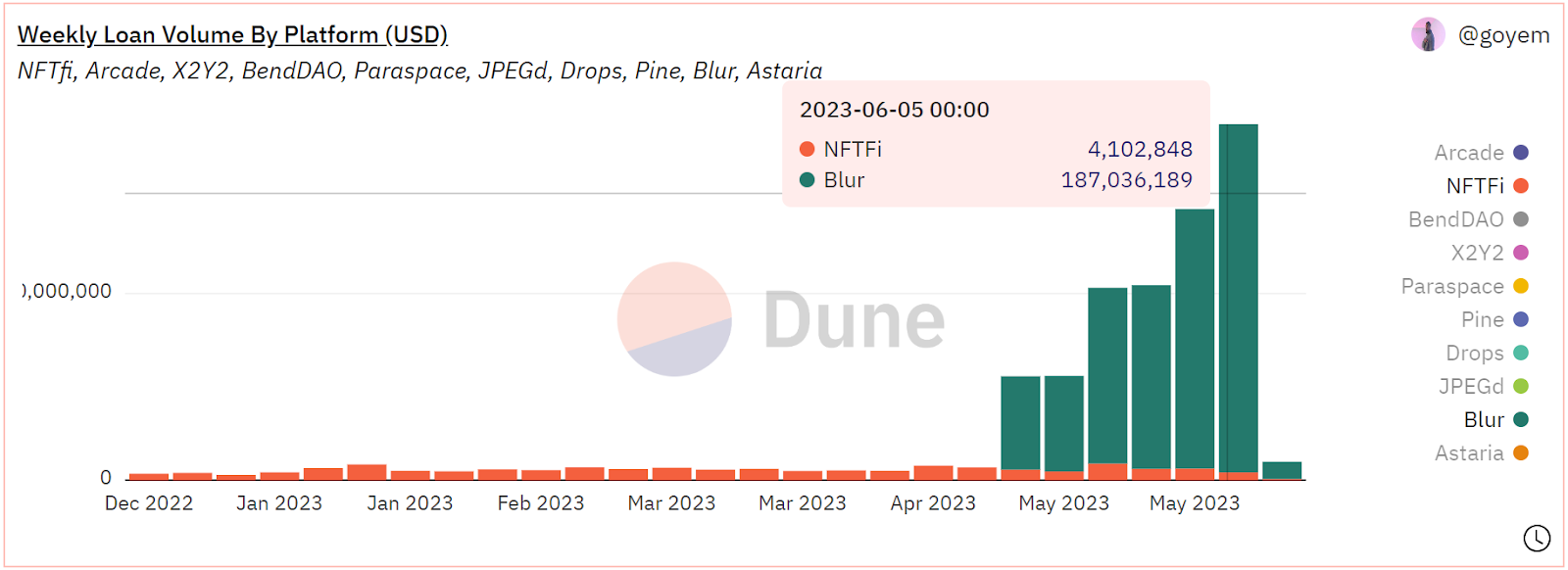
Source: Dune Analytics@goyem (2023.6.12)
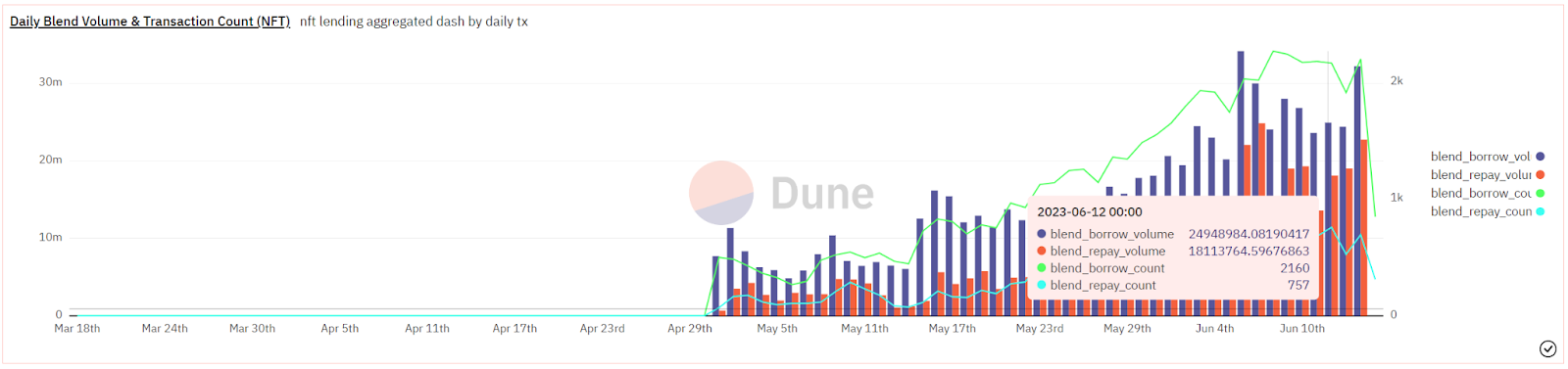
Source: Dune Analytics@impossiblefinance (June 12, 2023)
8.2 Spot-to-Pool
8.2.1 BendDAO
The spot-to-pool model is led by BendDAO, the industry's first NFT lending protocol based on the "Spot-to-Pool" model (Peer-to-Pool). It mainly serves blue-chip NFT holders. Borrowers (spotters) can quickly borrow funds by collateralizing blue-chip NFTs in the protocol pool (pool) and receive ETH from the pool. Depositors (spotters) provide Ethereum to the funding pool (pool) and earn interest based on the valuation of ETH. Both borrowers and lenders will receive BEND mining rewards. When the price of the collateralized NFT drops to a certain level, liquidation will be triggered. Currently, BendDAO supports the collateralization of mainstream 10 types of blue-chip NFTs.

Source: BendDAO
BendDAO interface:
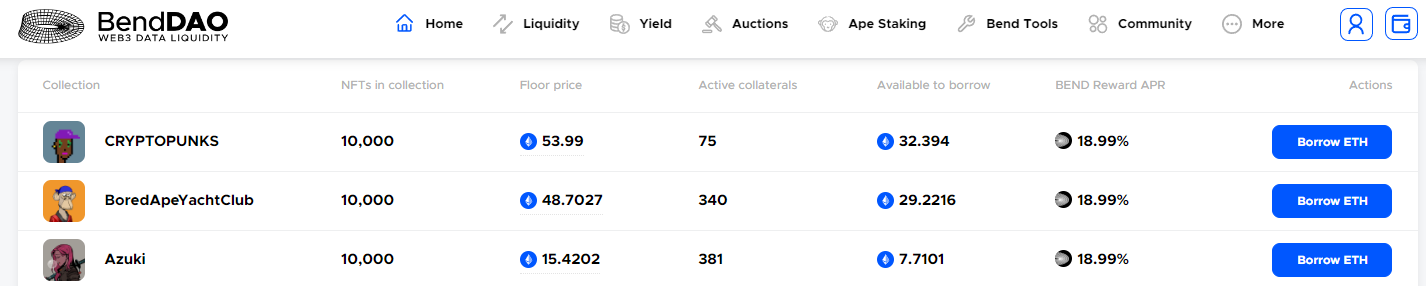
Source: BendDAO
BendDAO blue-chip NFT collateral quantity:
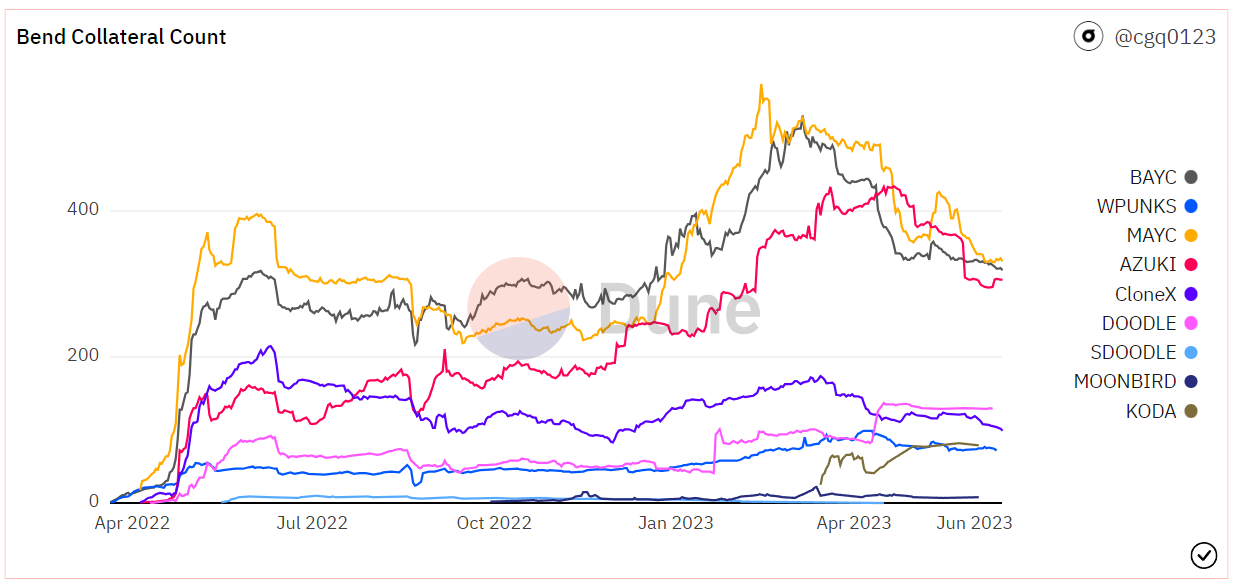
Source: Dune Analytics@cgq 0123 (2023.6.12)
The floor price data of NFT is obtained through the Bend Oracle, which is developed by the BendDAO team in collaboration with Chainlink. The original data of the oracle comes from the floor prices of Opensea, X 2 Y 2, and LooksRare, and the original data is filtered and the low price is calculated based on the trading volume of each platform. The Time-Weighted Average Price (TWAP) is used to ensure that the data is not manipulated.
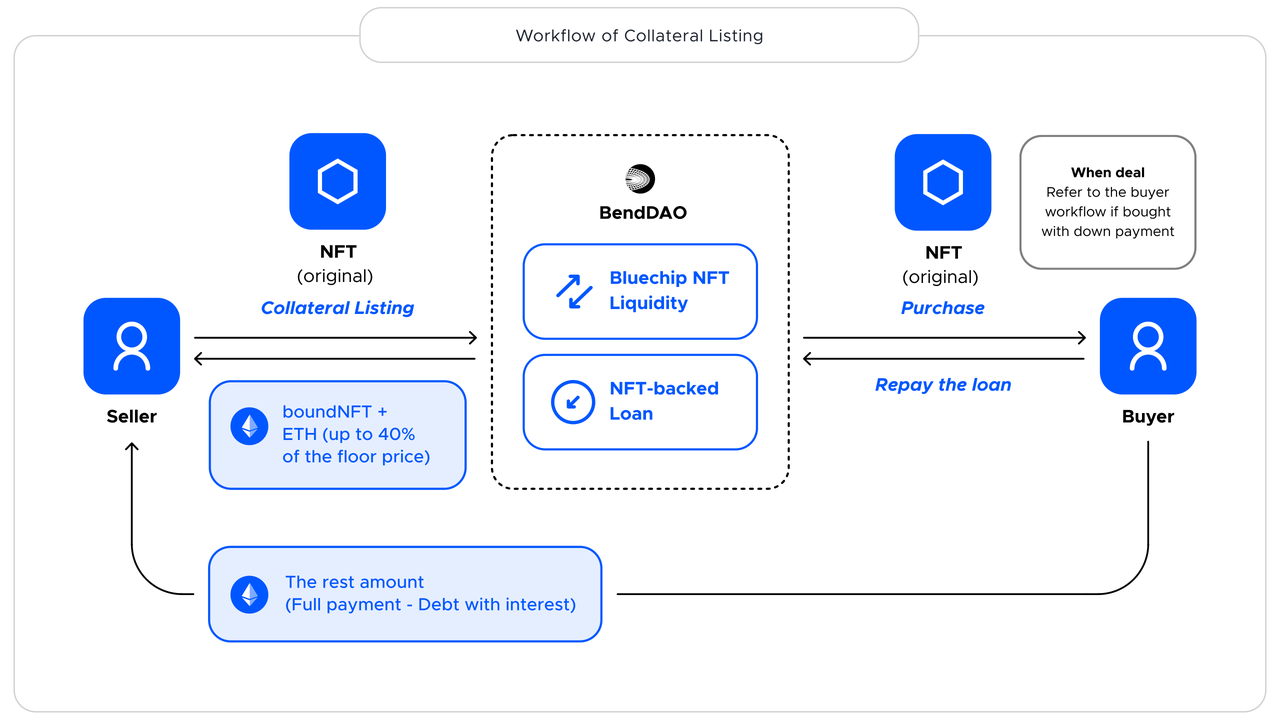
Source: BendDAO
Since its launch in March 2022, the protocol has been continuously updated and iterated, and the team has been continuously expanding new businesses to serve market demand. Currently, in addition to the main lending business, BendDAO has also launched a built-in trading market, supporting new features such as "Flash Loans" and "Collateralized Listings", as well as "Peer-to-Peer" lending and asset pairing for Yuga Labs' staking function "Bend Ape Staking".
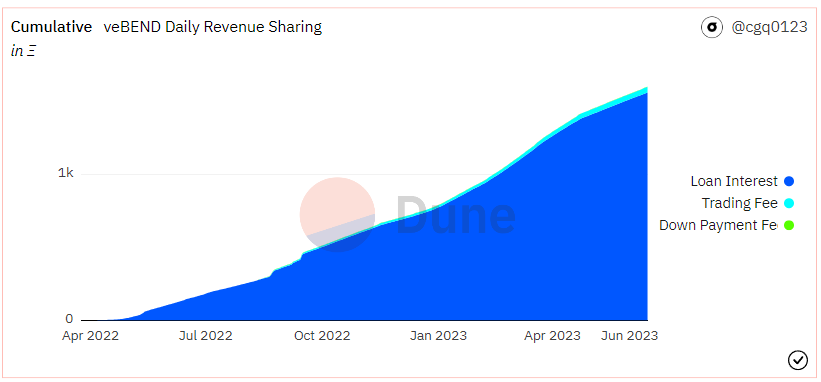
Source: Dune Analytics@cgq 0123 (2023.6.12)
BendDAO protocol fees from lending-related activities include (1) loan interest and (2) lightning loan transaction fees (paid by the buyer, at a rate of 1%). There are also transaction market fees (paid by the seller, at a rate of 2%), but these are unrelated to lending business. Among them, 30% of the interest paid by the borrower and 50% of the lightning loan fees are allocated to the national treasury.
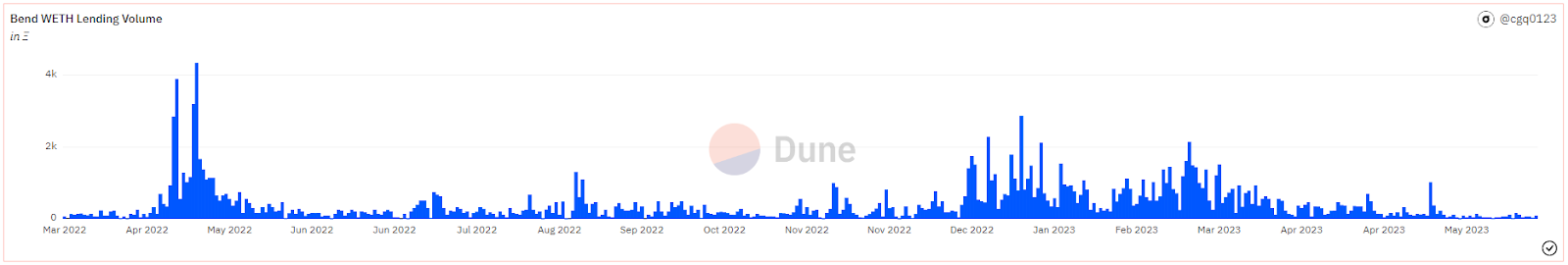
Source: Dune Analytics@cgq 0123 (2023.6.12)
As of June 12, BendDAO has cumulatively lent over 170,000 ETH, with a peak daily lending of 4,340 ETH in May 2022. The total project revenue reached 1,669 ETH, with lending interest income accounting for approximately 94%. As a point-to-pool project, BAYC/MAYC/Cryptopunks are the three main collateral assets, accounting for over 70% of the collateral quantity. Since the beginning of this year, the project's loan annual percentage rate (APR) has remained in the range of 25% to 30%, with daily interest income of approximately 3 to 6 ETH.
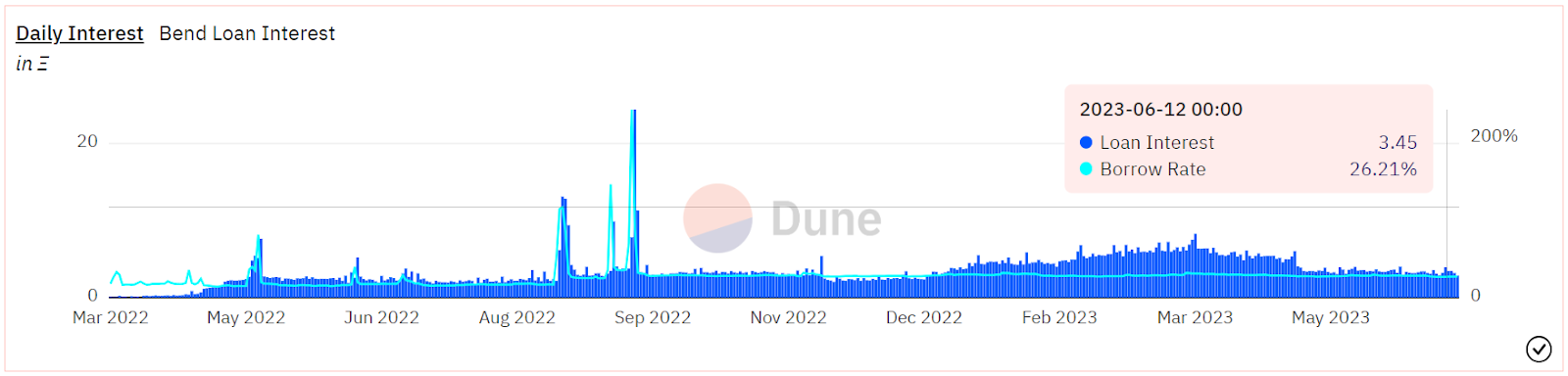
Source: Dune Analytics@cgq 0123 (2023.6.12)
8.2.2 DROPS
DROPS operates a currency market similar to Compound, where users can collateralize their NFT portfolios to obtain loans in USDC and ETH. The pricing of NFTs is determined by the Chainlink oracle, which adjusts based on outliers and average values over a period of time.
Like Compound and Aave, DROPS uses a segmented interest function that targets a specific utilization rate. When there is not enough funds for withdrawal, the interest rate paid by the borrower will significantly increase.
To limit the risk for liquidity providers, DROPS separates the protocol into isolated pools, each with its own NFT collection. This is similar to how Fuse operates on Rari Capital, ensuring borrowers can select the collection they are satisfied with.
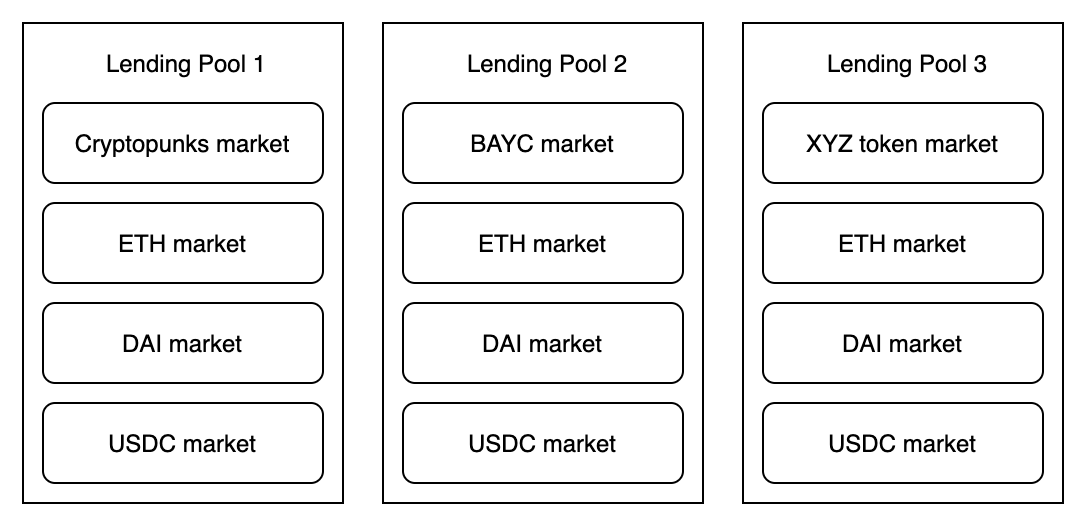
Source: DROPS
DROPS currently has accumulated lending funds exceeding 11 million US dollars (as of 6.12).
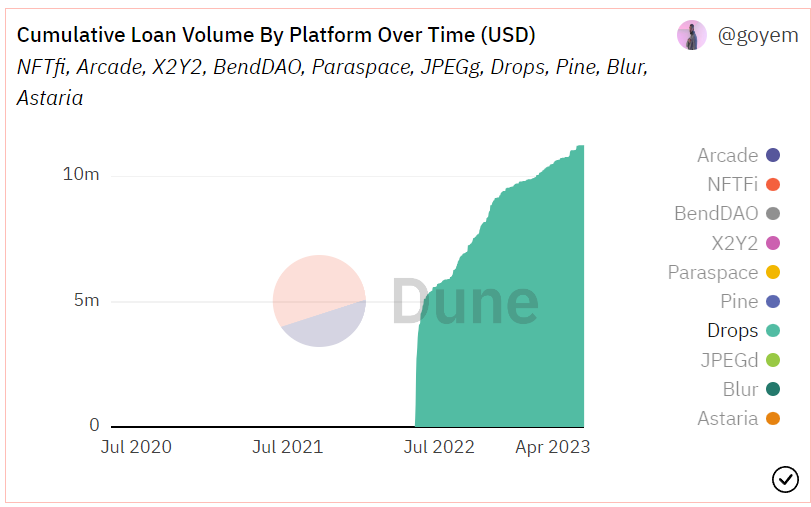
Source: Dune Analytics@metastreet / @goyem ( 2023.6.12)
8.3 Hybrid Type
8.3.1 ParaSpace
ParaSpace is an NFT lending protocol that utilizes the pool-to-pool model. It allows users to collateralize and borrow NFTs and fungible tokens. ParaSpace allows users to bundle assets of ERC-721 tokens or ERC-20 tokens, collateralize the bundled assets, borrow against them, and utilize underutilized funds for further investment, addressing the issue of low capital efficiency for users' on-chain assets and earning profits from it.
Source: ParaSpace
ParaSpace's innovative mortgage lending model is the first to adopt a cross-margin credit system instead of the isolated margin pool design used by existing platforms. This will allow users to provide loans against all collateral with a single credit limit.

Source: ParaSpace
By mortgaging your NFT assets through ParaSpace, you will generate a credit limit and a health factor for your entire collateral portfolio. As long as the health factor of your entire collateral portfolio remains above 1, none of your NFTs will ever trigger a liquidation auction.
This credit system is similar to a valuation system that assesses the value of all your collateral and automatically approves loans based on that assessment. You can borrow against their total value as long as they are supported collateral types by ParaSpace.
This is the full-collateral leverage model that adopts cross-margin.
In addition, ParaSpace has also designed features such as "Hybrid Dutch Auction" liquidation mechanism, "Buy Now, Pay Later" under the credit system, high-rarity NFT lending with high limits, and borrowing to short sell, to meet the needs of the current NFT market.
Since its official launch in December 2022, ParaSpace has seen rapid growth in its business scale, with growth rates significantly higher than the overall NFT lending market data. In the past six months, its lending data has surpassed BendDAO across the board. Currently, the accumulated loan funds of the project have reached nearly $300 million (data as of June 12, 2023), with over 13,000 users. In April of this year, the weekly loan peak exceeded $20 million, and in the past month, the loan capital scale has remained at around $5 million per week.
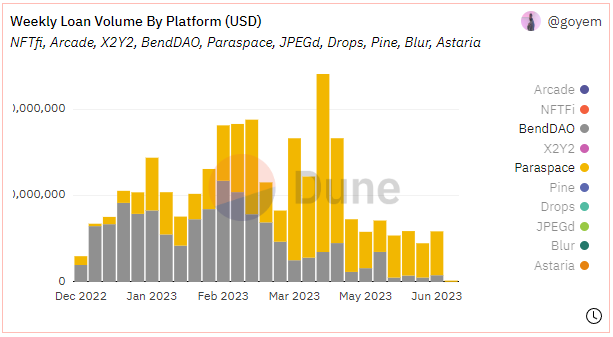
Source: Dune Analytics@goyem ( 2023.6.12)
8.4 Collateralized Debt Position (CDP)
8.4.1 JPEG'd
JPEG'd is an improved lending protocol on the NFT P 2 P ool, which adopts the CDP (Collateralized Debt Position) model from MakerDAO for its borrowing mechanism. Users of the protocol pledge NFTs into the protocol and borrow stablecoin PUSd against the collateralized NFTs, with a maximum borrowing amount of 32% of the floor price of PUSd. The first NFT allowed to be used as collateral in JPEG'd is CryptoPunks. The initial loan interest rate is set at 2% with a one-time loan fee of 0.5%. JPEG'd sets the Loan-to-Value (LTV) ratio, which is the borrowing value divided by the collateral floor price, to 32%. Liquidation is triggered when the LTV reaches 33%.

Source: JPEG'd
Due to the large fluctuations in the floor price of NFTs, JPEG'd adopts Chainlink as its data source, with a focus on time-weighted average price. It is worth mentioning that JPEG'd has designed a novel insurance mechanism where users can choose to pay 5% of the loan fee for insurance. Once the user is liquidated, they can repurchase the NFT after repaying the debt, accrued interest, and a 25% liquidation penalty. However, they must repay the debt within 72 hours, otherwise the NFT will be owned by JPEG'd DAO.
JPEG'd also innovates by providing a platform-defined weighted valuation for specified blue-chip NFTs (CryptoPunks, BAYC, Azuki). For each specific attribute, the valuation will receive a corresponding weight boost reward after being weighted differently. Currently, there are few platforms in the market that provide valuation for rarity attributes.
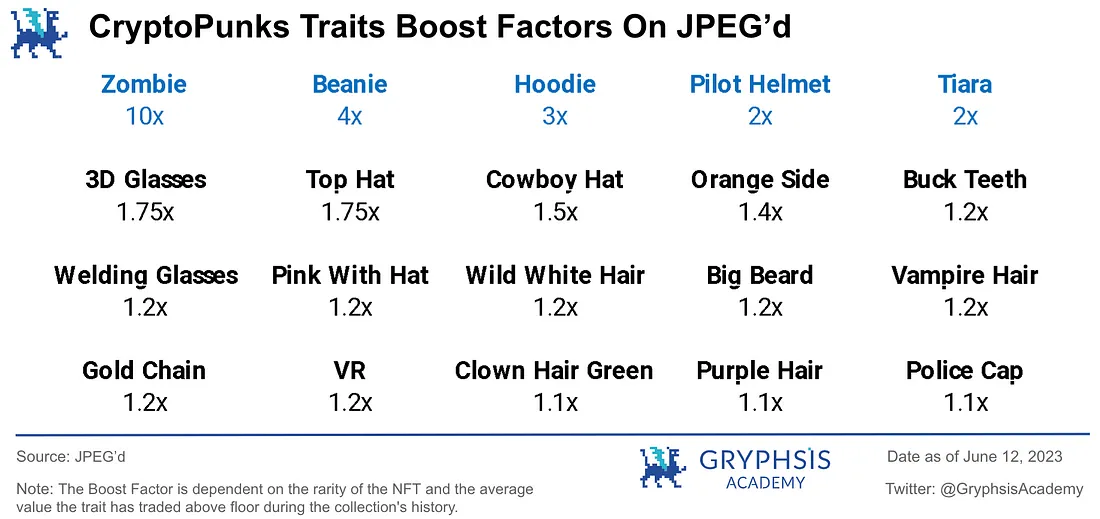
In addition, pETH generated from JPEG'd has relatively good yields when staked on ETH-pETH assets on Convex, reaching a peak of around 30 ~ 45% in early 2023.
The project currently has accumulated loan funds exceeding 36 million US dollars (as of 2023.6.12). In January and February of this year, the weekly loan peak reached around 770,000 US dollars. NFT lending protocols of the CDP type have relatively small market share.
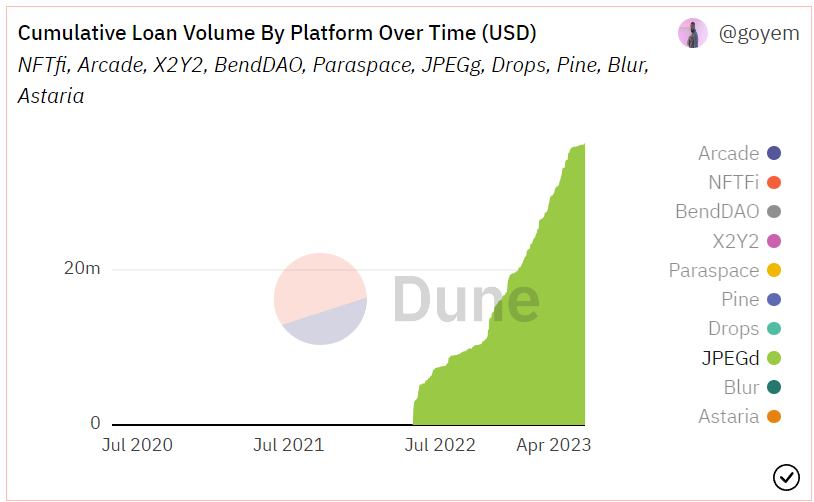
Source: Dune Analytics@goyem (2023.6.12)
9. Risks and Prospects
Although the NFT lending track is developing rapidly, some key risks should not be overlooked:
1) NFT Collateral Valuation Volatility Risk (Bad Debt Risk)
For lending projects, the worst-case scenario is the depletion of liquidity in the funding pool, where borrowers using collateral assets cannot repay their debts.
For NFT lending protocols, it is particularly important to define high-quality NFT collateral targets. When the floor price of the collateralized NFT series drops sharply, many borrowers may choose to abandon their NFT assets and default on their loans, and in this case, the NFTs that have experienced price collapses are likely to have no bidders.
(Historical Event Review - BendDAO Liquidity Crisis: In August and September 2022, the floor prices of blue-chip NFTs dropped significantly, triggering liquidation of multiple collateral assets with no bidders, causing panic in the market and a massive withdrawal of ETH from the liquidity pool. This led to the depletion of liquidity in the pool, skyrocketing loan and deposit interest rates, and a potential collapse crisis in the BendDAO protocol. To address the crisis, the team proposed modifications to certain parameters. Over the next few days, funds in the protocol pool gradually recovered, market sentiment eased, and utilization and borrowing rates returned to normal levels.)
2) High Concentration of Target Users
The audience for NFT lending itself is not very broad. Although the industry is developing rapidly as a whole, data from certain projects show that the top users account for a large proportion of the business, and the projects rely on the transaction volume of the target key customer group.
Example:
BendDAO Protocol: As of June 12, 2023, the cumulative loan amount is 178820 ETH. Franklinisbored.eth, the user with the highest cumulative loan amount, has borrowed a total of 45447 ETH, accounting for more than 25% of the total business volume.
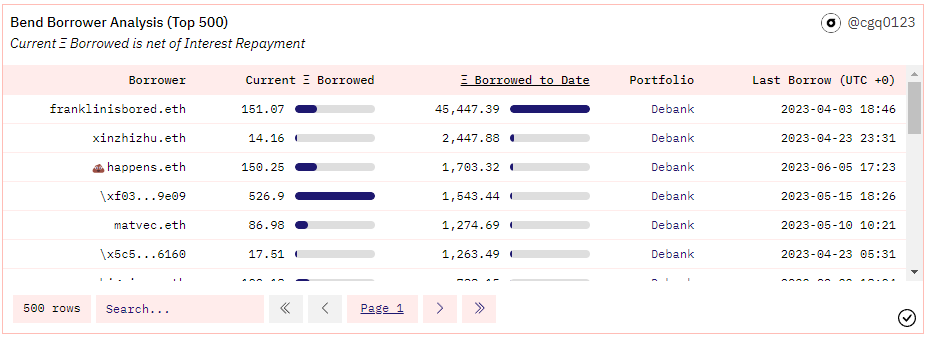
Source: Dune Analytics@cgq 0123 (2023.6.12)
3) Limited Growth Potential in the Market
In order to ensure healthy business development, NFT lending projects often focus on selecting high-quality blue-chip NFTs as collateral assets with strong pricing consensus and risk resistance. However, the number of blue-chip NFTs meeting these criteria is limited, and each project has a fixed issuance quantity of NFTs. In the current market environment, the inclusion of high-quality NFT collateral assets requires extensive market validation and is difficult to predict in advance. This poses certain limitations on the overall market size and business growth potential of NFT lending, and it may be a potential risk point.
For the development of the NFT market as a whole, currently, subcategories including blue-chip PFP (Profile Picture), high-quality GameFi assets, and NFT assets with unique project capabilities will be important components of future industry development. As the industry matures, more and more users will embrace and invest in the field of NFTs. The connection between NFTs and real-life will become more diverse, and the influence of NFTs will continue to expand through various derivatives. As the overall market size of NFTs grows, opportunities in various subfields of NFTs will also increase. For NFT lending, the diversity of protocols can meet the needs of different users. If overall lending protocols can achieve high activity and wide adoption, they will be able to provide better bidirectional liquidity solutions for NFT and DeFi users.
10. Conclusion
In the current NFT market, most users still concentrate on the markets and aggregators with the lowest entry barriers. However, these two areas have not fully demonstrated the maximum capital efficiency. As more and more users join the NFT space, how to use the financialization of NFTs to improve market capital efficiency and attract user attention may be a continuing breakthrough for Web 3 businesses.
NFT lending, as an important part of the financialization of NFTs, benefits from the improvement of oracle and liquidation mechanisms, gradually showing the efficiency advantage over peer-to-peer pooling. The iterative updates among different products also make the product forms in this market increasingly mature. The key issues for enhancing customer experience are how to independently rate different NFTs, accurately price them, and establish liquidity.
It is believed that an NFT liquidity solution with a reasonable and accurate pricing mechanism, smooth user experience, sustainable trading model and profit model, and comprehensive risk control mechanisms will become an important cornerstone for the progress of the NFT-Fi industry.
11. References
- Official information from various NFT lending protocols
- BAYC Price Drops Again: A Comprehensive Analysis of BendDAO, the Leading Player in NFT Lending
- An In-depth Explanation of How NFT Lending Works and Lending Platforms
-Project research report | BendDAO: NFT collateralized lending protocol using the peer-to-pool model!
-In-depth analysis of NFTFi: Looking at the future development of NFTFi from the current market
-Is fully collateralized leveraged NFT lending protocol ParaSpace the "BendDAO killer"?
-Introducing ParaSpace Pt.1 — Universal Liquidity, Instantly Unlocked
-Overview of NFT lending platform ParaSpace
-Road to Financialization of NFTs
-Dune Analytics (@metastreet @goyem)
-Dune Analytics (@impossiblefinance)
Published on 2023.06.22 , original article link:
NFT Lending: An In-depth Analysis of Market Dynamics, Risk Landscape, and Future Prospects



