ArkStream Capital: Modular Blockchain - Infrastructure to Promote Web3 Ecological Evolution
Summary
Summary
There is no doubt that the modular blockchain will become the new narrative of infrastructure in the next cycle, but this does not mean that the monolithic blockchain will be replaced. On the contrary, the development of modular blockchain will become an important boost to promote the evolution and progress of single blockchain. The two will complement each other to lead and support the next Web3 ecosystem with 1 billion users;
Compared with the accurate definition of modular blockchain, feeling and understanding the execution layer, data availability layer, consensus layer and settlement layer of modular blockchain through transaction and block data will produce a more intuitive understanding;
The execution layer acts as a practical pioneer in the expansion of single blockchain transactions and computing outsourcing. The data availability layer not only reduces the cost and increases the efficiency of blockchain data storage, but also realizes the availability after data verification under the guarantee of the consensus layer. The consensus layer is committed to reusing the power of decentralization to create a new decentralized construction framework. The core of the settlement layer is to optimize and improve the matching of account assets and transaction flow, so as to achieve the correct correlation between the two;
Definition, development, advantages and disadvantages and solutions of monolithic blockchain
The birth of Bitcoin marked the arrival of a decentralized electronic cash system through which people realized the concept of blockchain technology and the consensus mechanism of proof-of-work. Subsequently, the emergence of Ethereum, as a world computer and smart contract platform, its powerful programmability has shown broad prospects in the fields of finance, social networking and games. Although the blockchain is in its infancy in terms of popularity and technology accumulation during the development of more than ten years, there is no doubt that its potential is still huge and infinite.
Under normal circumstances, the public chains we are in contact with now can be collectively referred to as monolithic blockchains. They use each transaction as a carrier, store legal and valid transaction records through blocks, and realize a decentralized, trustless, and non-tamperable distributed ledger network through a specific consensus mechanism.
The characteristic of a single blockchain is that it can independently establish a complete ecosystem from wallets, applications, middleware to infrastructure, and maintain a close relationship between all parties. However, with the development and prosperity of the ecosystem, It will also have problems such as transaction congestion, rising transaction costs, high threshold for network participation, and increased cost of maintaining the state of the entire network. When encountering high concurrent usage, monolithic blockchains often become expensive and difficult to use due to transaction throughput limitations, and user experience suffers greatly. In addition, as the blockchain continues to grow, the state of the entire network will explode, and the threshold for maintaining the network will not only increase, but also the cost will continue to increase.In order to solve the problems existing in the single blockchain, industry insiders have conducted extensive research and exploration in terms of capacity expansion and state pruning over the years, including but not limited toState Channel, Side Chain, Rollup, Light Node, Fragmentation, Modularization
and other technologies. The research and development of these technologies continuously optimize the blockchain technology stack and increase the popularity of blockchain technology.
Definition and products of modular blockchain:
In essence, the modular blockchain is to redefine and divide the layered architecture of the blockchain through the idea of aggregation and combination, and divide it into different modules. These modules are independent of each other, can be modified and expanded according to requirements, and can be combined with each other. This combined modular blockchain can not only improve performance in all aspects, but also meet diverse application scenarios.In the past, thinking from the standpoint of the architecture of a single blockchain, we used to split the results as follows:
The application layer that carries the decentralized application is responsible for executing the execution layer of the smart contract logic of the decentralized application, the consensus layer that deals with transaction validity, transaction order and block composition, maintains and stores the data layer of transactions and blocks, and conducts peer-to-peer The network layer for broadcast communication.It can be known that the transaction submitted by the user no longer directly interacts with the first-tier network, but is transferred to the sequencer of the second-tier network for collection and batch processing. The sequencer compresses the raw data of multiple transactions processed in batches and sends them to the first-tier network , at the same time, it also sorts the batch-processed transactions, calculates user and network state transitions, and then sends the state results to the layer-1 network for settlement.
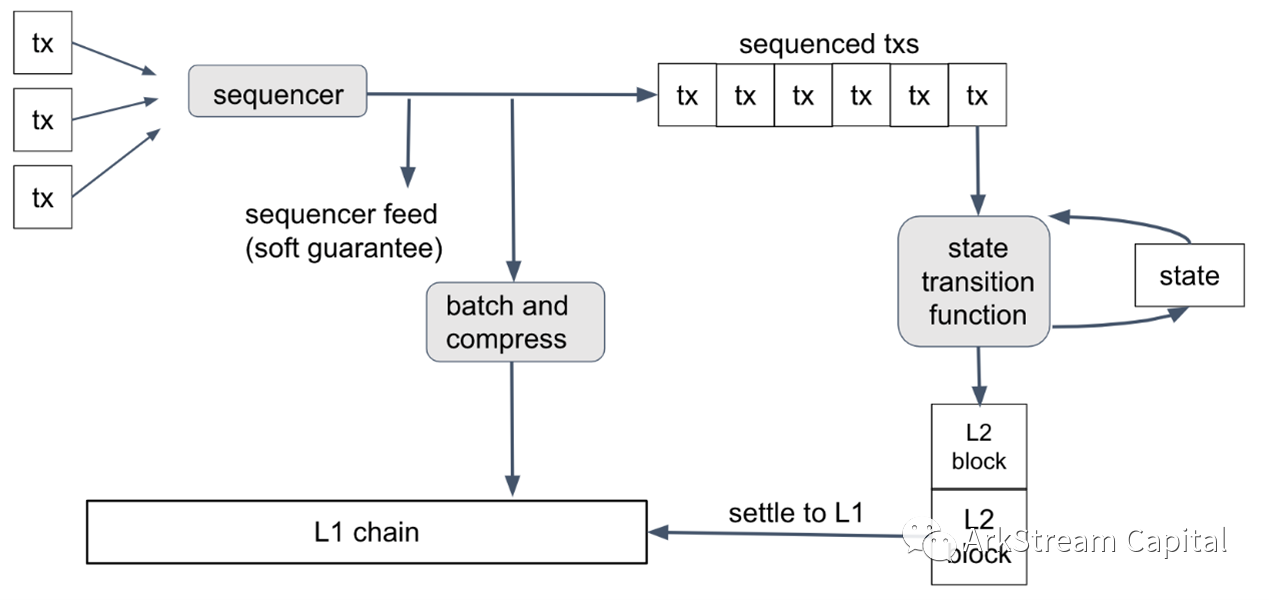
The sequencer of the two-tier network collects and batches transactions (execution layer)
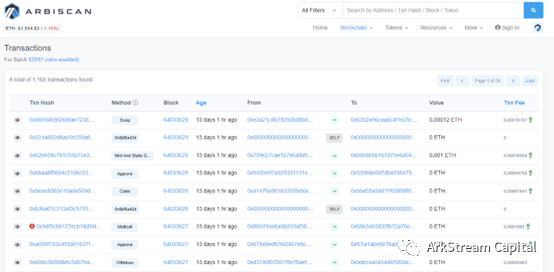
image description
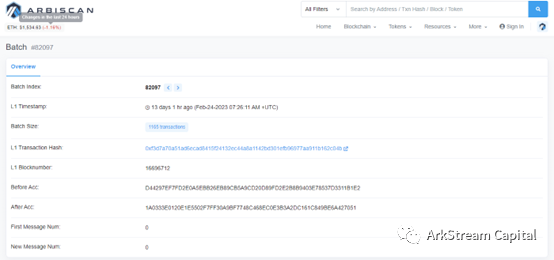
The second-tier network compresses and processes transactions and sends them to the first-tier network (data availability layer)
As for the settlement transactions, Arbitrum’s block browser does not do a good one-by-one coupling. Here we directly start with the smart contracts deployed on the Ethereum official website on Arbitrum’s official website, and analyze the settlement-related functions involved in the Delayed Inbox contract: send L1 FundedContractTransaction , called when there is a disagreement in the settlement; call updateSendRoot of the Outbox contract when there is no disagreement in the settlement. For relevant contract addresses, please refer to: https://developer.arbitrum.io/useful-addresses.
Now, we have a clear and intuitive understanding of the respective functions and roles of the execution layer, data availability layer, consensus layer and settlement layer. The execution layer is the batch processing of transactions by the sequencer, including raw transaction data compression and state transition calculation. The settlement layer is responsible for confirming the finality of state transitions. The data availability layer is a layer of network that stores and maintains the compressed transaction data collected by the execution layer. As for the consensus layer, what is guaranteed is the security that the execution layer relies on in terms of data availability layer and settlement layer.
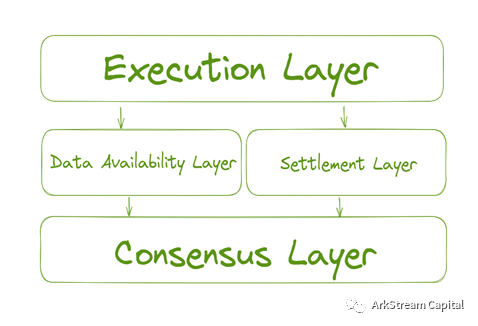
According to the definition from top to bottom, the hierarchical structure of the modular blockchain is as follows:
Since the settlement layer involves the design of transaction validity proofs at different execution layers, such as optimistic fraud proofs and zero-knowledge proofs, we will not further understand this for now. Below, we will directly understand the three modules of the modular blockchain, the execution layer, the data availability layer, and the consensus layer, focusing on the background of their development, the problems they solve, and their current development and challenges.
Executive level products and projects
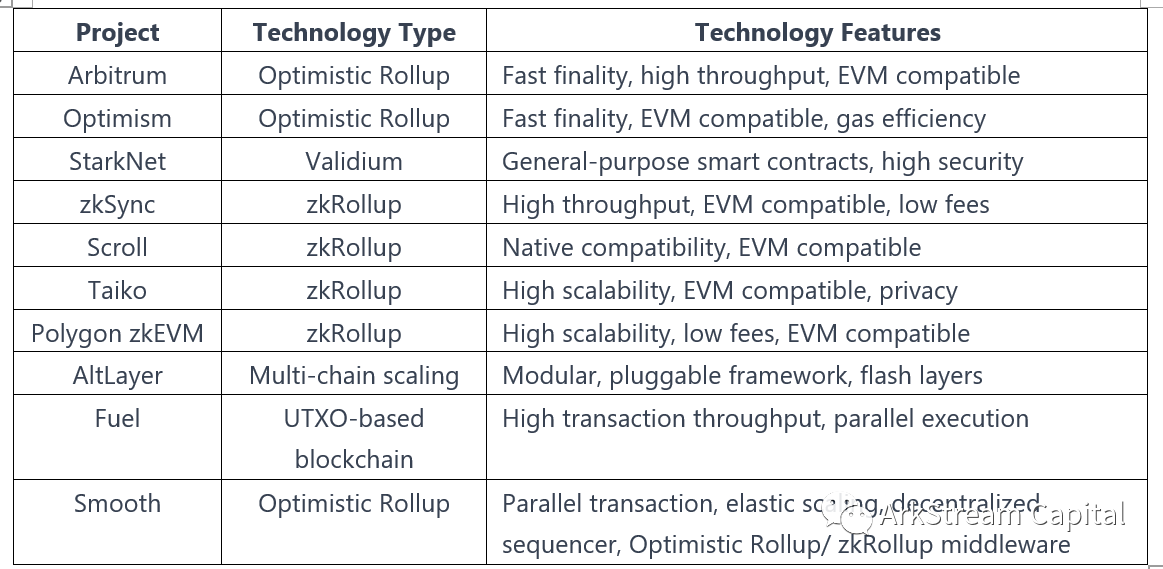
Before actually coming up with an executive layer product, we often hear a word: Ethereum Killer. This shows that there is an obvious mismatch between the performance requirements of blockchain users in terms of transaction throughput, transaction speed, and transaction costs and the status quo provided by Ethereum. For this reason, many new public chains try to explore and research from the transaction structure, block design, consensus mechanism and network broadcasting mechanism of the single block chain itself, and construct a new high-performance public chain to achieve massive transaction throughput, Fast transaction speed and cheap transaction costs. At the same time, the ecology of Ethereum is exploring and developing various technologies and product solutions. Today, the Layer 2 route with Rollup as the main solution dominates, among which Optimism and Arbitrum of Optimism and Arbitrum, which are optimistic about the fraud proof, have surpassed other EVM-compatible new public chains in terms of project construction, user attraction and retention. In addition, with zero Knowledge proof-based ZKRollup (Starknet, Hermez, zkSync, Scroll, Taiko, etc.), parallel transaction-based Fuel, AltLayer, Smooth, etc. are also advancing in their respective solution areas.With the vigorous development of Layer 2 such as Rollup, the concept of execution layer, which generally refers to these Rollup and parallel trading products, was formally proposed. Of course, not only Ethereum, but also public chains such as Solana, BNB Chain, Cosmos, and Aptos that have optimized TPS and transaction costs, each official or community has proposed its own Rollup and execution layer products.As a result, we have not only entered an era where multiple chains coexist, but also entered a scenario where multiple types of execution layers coexist.
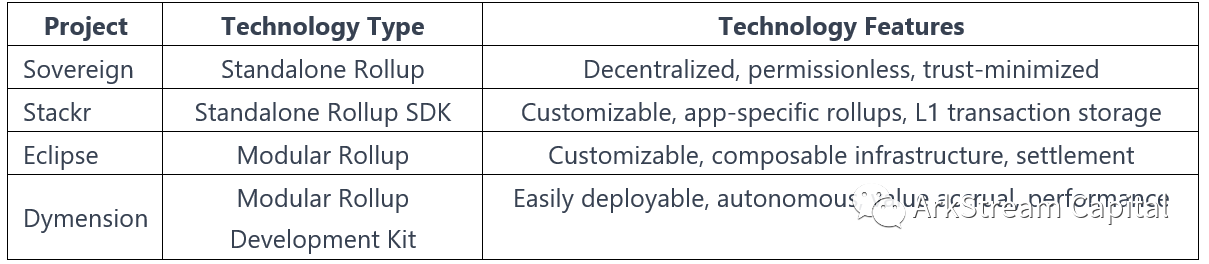
This also brings different problems to developers, users, and the ecology: the respective execution layer products are independent and closed, the ecology is difficult to share, the operation costs for users are heavy, and the time period and cost for developers to build and operate are expensive. For this reason, products that use Rollup as a service are also available. Such as Sovereigen Labs, Stackr Labs, Eclipse Builders, Dymension, etc. These products are analogous to the Hub in the execution layer, transforming the Rollup that was originally located in the two-layer network into Layer 3, thereby constructing a tree-type execution layer with a single Hub and multiple Rollups.
Due to the historical needs of expansion scenarios, the implementation layer has been exploring and developing products for many years, and their respective solutions have achieved major breakthroughs over the years. In the future cycle, there are still many products in the execution layer that have not yet solved the problems being explored: such as decentralized sequencer, zkEVM and parallel transactions.
Data availability layer products and projectsWith the advent of the era of big data and the era of cloud, data, as the basic resource of modern society, can provide help and support in various decision-making scenarios, and its strategic position is like oil in the past.These data storage methods are different from traditional databases. From a certain perspective, the data storage method of the blockchain is distributed, that is, each node must store a complete copy of the data. At present, with the active transaction data of users on the chain and the prosperity of smart contracts, blockchain data shows signs of exponential growth on the basis of linear growth. The Bitcoin network has been growing at an annual rate of 50 G from 55 G in 2016. However, starting in 2020, the annual growth rate of its network size has jumped to 60 G. As of February 2023, the data size of the entire network will be It is 459G.
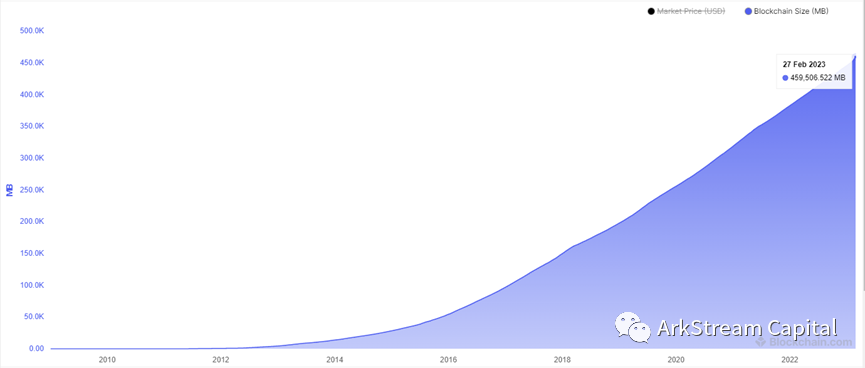
https://www.blockchain.com/explorer/charts/blocks-size
image description
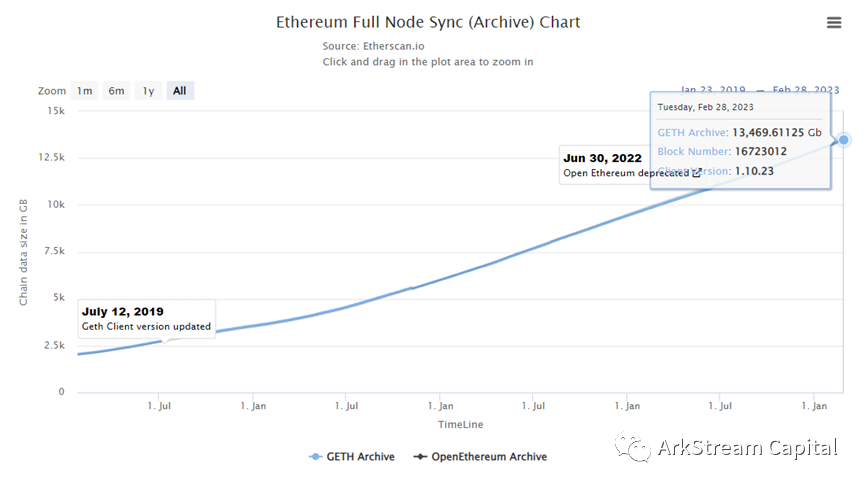
As the world's computer and smart contract platform, Ethereum's entire network data is much larger than Bitcoin, which focuses on the payment field. It can be seen from Etherscan that at least 800 G space is required to become the default full node of Ethereum, and at least 13000 G storage space is required to become the full node of Ethereum Archive.Not only is the overall data volume huge, but most of the data is stored in unformatted form, which makes it extremely difficult to process, index, and query blockchain data. to this end,
From the perspective of a single blockchain, how to efficiently and cheaply store, quickly process and support massive access to blockchain data has become an extremely important research direction.
As early as when the Bitcoin white paper was proposed, Satoshi Nakamoto made advance solutions to the state explosion of the network: Reclaiming Disk Space and Simple Payment Verification (SPV). Reclaiming Disk Space allows nodes to trim the consumed historical data to reduce the data size of the entire network. This solution can reduce maintenance costs and participation thresholds to a certain extent. However, due to the huge amount of data in the entire network and the single area of the account model Block chains, such as Ethereum, maintain data dimensions that are different from the UTXO model, and the degree of direct application will be relatively limited. However, based on the idea of Reclaiming Disk Space, the solution extended and pursued by the Ethereum community is to separate the account status from the blockchain Go out Stateless Ethereum program,. SPV mainly advocates the scheme of light node Merkle tree to verify blockchain transaction data, in addition to realizing the low participation threshold of the network, it ensures the validity of transaction data. Since SPV's light nodes simply download block header information for verification, they may receive fraudulent proof attacks. To this end, Mustafa Al-Bassam of Celestia, Alberto Sonnino and Vitalik of Mysten Labs published "Fraud and Data Availability Proofs: Maximising Light Client Security and Scaling Blockchains with Dishonest Majorities" in 2018 to propose solutions to fraudulent proof attacks Solution, here, the data availability of the single block chain can be understood as the validity verification of the transaction data by the light node only through the transaction Merkle tree on the premise of not completely synchronizing the block data.For the execution layer of the modular blockchain, the data of the single blockchain is transformed into on-chain data, and the transaction data of the execution layer is compressed and stored as on-chain data and off-chain data on it. The data on the chain not only has direct requirements on the performance and cost of conventional storage and query for the data on the chain, but also relies on the consensus mechanism accompanying the data on the chain for security guarantee.
In this way, it is the development of the execution layer product that enriches the data availability of the single blockchain and expands the context corresponding to the concept of the data availability layer.
Before proceeding, we must understand that the data availability layer and the data storage layer are concepts that cannot be confused. The data availability layer emphasizes availability and thinks from the perspective of data validity. The data storage layer is more about defining the storage and usage performance of data from the perspective of computer memory, and more attention is paid to the cost of on-chain storage, read and write efficiency, etc. Data availability must be based on the concept extended from the data storage layer, and what is extended here is the availability brought about by the consensus mechanism. In other words, Don't Trust, Verify, where Verify corresponds to data availability.
Ethereum, as the preferred data availability layer for current execution layer products, has the following obvious disadvantages due to its own Gas model and Calldata structure: 1. High data operation and storage costs; 2. Data storage capacity is limited; 3. Unequal distribution of network resources. To this end, Ethereum proposes its own data fragmentation and state expansion schemes through EIP-4844's Proto-Danksharding, Data Availability Sampling (DAS), Erasure Coding, and Proposer/Builder Separation. In the future, Ethereum will introduce new Blob transaction types and additional data layers to reduce the dynamic storage cost on the current chain under the premise of ensuring data availability. As for other specialized DA products, they not only explore technical solutions such as data availability sampling and Erasure Coding, but also increase their research breakthroughs in the field of data availability, such as Polygon Avail's Fast Sync technology and Celestia's sovereignty and interoperability. In addition to the products of the data availability layer, in terms of the existing data storage layer, we can also see the newly launched storage side chain Greenfield of the BNB ecosystem, as well as combined products such as Kvye and Arweave.
Not your keys,Consensus layer products and projectsnot your crypto. In the blockchain network, the secret key represents the ownership of digital assets. In order to ensure the ownership of secret keys and digital assets, the blockchain network must implement a strong consensus mechanism to ensure sufficient decentralization and security.
The consensus mechanism guarantees data that conforms to the single blockchain transaction format. For example, Bitcoin guarantees the transactions on it and the script logic built into the transaction, and Ethereum guarantees the transactions that EVM can execute and verify. Not only that, because there are two types of consensus mechanisms (PoW and PoS) with obvious differences in the blockchain world, it is difficult to combine and use different consensuses between different single blockchains. In addition, even single blockchains that natively support multi-chain interoperability, such as Cosmos and Polkadot, although compatible in terms of transaction formats or consensus mechanisms, there are still situations where consensus mechanisms are difficult to share and use.
Before entering the consensus layer products, let us first understand and be familiar with the development and current status of PoW and PoS.PoW can be roughly understood as using the computing power of the physical world to ensure the security of the blockchain network. The most common attacks it faces are 51% computing power attacks and double-spending attacks. Therefore,Only when the computing power of the network is large enough can the security of the network be guaranteed.
For many new PoW public chains, in the cold start stage, due to insufficient computing power in the early stage, the network is prone to security problems. For this reason, they either accumulate computing power at high cost for a long time, or consider using the same PoW algorithm for joint mining with the mining computing power of traditional PoW networks such as Bitcoin. Since the nature of the computing power of the blockchain gradually increases with the increase of the block height, joint mining/merged mining rents computing power through an encryption economic incentive mechanism. When the interests of the two public chains overlap and match, the joint mining Mining/merged mining is attractive to miners. However, when there is a conflict of interest between the new PoW public chain and the Bitcoin network, since the Bitcoin network has no way to sanction miners at the protocol level, miners generally Will take actions that are not conducive to other new PoW public chains. For example, a long time ago, Namecoin conducted joint mining with the computing power of the Bitcoin network. Because the joint mining scheme would cause the interests of the two networks to mismatch in some scenarios, it caused potential risks for Namecoin. For the Bitcoin sidechain RSK that implements the smart contract function, although RSK has been optimized in terms of interests with the Bitcoin network, its own iterative development is limited by the non-Turing completeness of the Bitcoin network. Breakthroughs in merged mining are limited. In addition, for the Quai Network, from the beginning of the design, the multi-chain joint PoW was originally proposed to keep warm at the computing power level. Even so, Quai Network only amortizes the cold start cost of the consensus, and cannot achieve the reuse and combination of the PoW consensus mechanism.The core of the PoS consensus mechanism is to use rights and interests to protect the network. The value of rights and interests will determine the overall value of the network. Only sufficiently high-value rights and interests can guarantee a high-value network.The current popular PoS mechanism is improved based on PBFT, and its essence is still proof of rights and interests. Common PoS networks include the well-known Cosmos and Polkadot. Adhering to the mechanism of minimizing trust, Cosmos, as a Hub, is a consensus mechanism that will not actively interfere with the ecological application chain. The Cosmos ecological application chain can reuse the entire ecologically sound development stack. However, when maintaining the corresponding application chain network, the establishment and maintenance of the network verifier set requires a very high threshold and cost, which is also the cost of trust and security. . Many application chains generally use airdrops to attract Cosmos validators, and provide high inflation rewards to encourage validators to pledge to protect the network. In order to reduce the establishment cost of the consensus mechanism and improve the security of the application chain, Cosmos 2.0 proposes various improvement schemes. For example, Cosmos can be used to implementShare ICS securelySpace Mesh, which can be shared by consensus for the application chain
first level title
epilogue
epilogue
Service-oriented micro-service architecture is popular in modern software development. By splitting applications into services with independent functions and characteristics, each service can be independently developed, deployed and run, and various services can be flexibly communicated and shared through data sharing. Combination to achieve higher scalability, flexibility and maintainability. The development of the microservice architecture is gradually maturing and perfecting. Although there are still some challenges and problems in practice, such as distributed transactions, service governance, security, etc., with the further maturity of technology and the accumulation of experience, these problems will be solved. gradually resolved.



