Learn about Lookup Arguments in one article
TL;DR
As mentioned in the previous article Hello, OlaVM!, the vision of OlaVM is to build a high-performance ZKVM. This article will focus on one of the tools that enable OlaVM to achieve high performance, Lookup argument. Lookup argument plays an important role in reducing the size of the circuit to improve the efficiency of ZK. It is widely used in the circuit design of ZKVM. Through this article, you can learn:
1. What role will Lookup argument play in ZKVM?
2. Plookup protocol principle.
3. Halo 2's Lookup argument protocol principle.
first level title
The roles in ZKVM
The so-called ZKVM actually uses ZK to constrain all the execution process of the VM. The execution process of the VM can generally be divided into: instruction execution, memory access, built-in function execution, etc. It seems a bit impractical to implement the constraints on these operations in a trace. First, the constraints of different operation types correspond to different trace widths. If the trace width corresponding to one of the constraints is particularly large, it will cause the remaining constraints to correspond to trace widths. waste; then, if there are too many different operation types in a trace, more selectors will be introduced, which will not only increase the number of polynomials, but also increase the order of constraints; finally, due to the order limit of the group, the line of trace The number cannot exceed the order of this group, therefore, the number of trace lines occupied by certain types of operations should be minimized.
So, for simplicity, we need:
a. Divide different operation types into multiple sub-traces, and then prove separately that a Lookup argument is required between the main trace and the sub-traces to ensure data consistency.
b. For some ZK-unfriendly calculations, we can use Lookup argument technology to reduce the size of the trace, such as bit operations.
secondary title
Lookup between trace tables
image description

Figure 1. Lookup between traces
secondary title
Lookup for ZK-unfriendly operations
As mentioned earlier, the proof of each sub-trace is independent, so obtaining a trace as small as possible will improve the efficiency of the prover. Take bitwise as an example, bitwise operations include AND, XOR, NOT three operations. If you want to simply implement constraints on bitwise operations through circuits, what you need to do may be to split each op into multiple binary limbs. If these ops are 3 2bit wide, they will be split into 32 limbs. Then, you need to constrain:
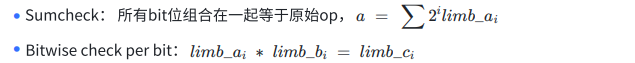
A total of 3 + 32 * 3 = 99 trace cells are occupied, and the number of constraints is 3 sumcheck + 32 bitwise = 35.
image description

Figure 2. Lookup in Arithmetic operations
first level title
secondary title
secondary title

secondary title

secondary title

secondary title

first level title




secondary title
secondary title

secondary title

first level title

Extend - 1 : Vector Lookup

Extend - 2 : Multi-tables

Links between Plookup and Lookup
Both the Plookup protocol and the Halo 2 lookup protocol can prove f⊂t, but the ideas of the two protocols are different, and the differences are as follows:
Plookup needs to use f and t to build a new sequence s, the elements in f and t appear at least once in s, and then prove that s⊂t by comparing the non-zero distance sets of elements in s and t are equal, and finally f⊂s⊂t→f⊂t.
Halo 2's lookup directly proves f⊂t without constructing a new sequence, which is more concise than plookup.
first level title
refer to
1.Hello, OlaVM!:https://hackmd.io/@sin 7 y/H 1 yPj_J 8 i
2.OlaVM:https://olavm.org/
3. Plookup protocol:https://eprint.iacr.org/2020/315.pdf
about Ushttps://zcash.github.io/halo 2/design/proving-system/lookup.html
about Us
Community: http://t.me/sin 7 y_labs
Official website: https://sin 7 y.org/
White Paper: https://olavm.org/
Community: http://t.me/sin 7 y_labs
WeChat public account: Sin 7 y
WeChat public account: Sin 7 y
E-mail: contact@sin 7 y.org
Research Article (EN): https://hackmd.io/@sin 7 y
Github:Sin 7 y



