4D Detailed Explanation LayerZero Labs: Popularize full-chain assets and seize the core of multi-chain ecology
Original title: "Layerzero Labs: Popularize full-chain assets and seize the core of multi-chain ecology"
Original author: NCL, "overseas unicorn" analyst
This article is the public version of the Layerzero investment research memo inside Pickup.
The emergence of Layer 2 has made the new public chain track more congested, but the exorbitant valuation and many participants make it difficult for investors to choose. The cross-chain bridge will be a highly deterministic role in the multi-chain structure. It can continuously expand the business with the birth of the new chain, and it will hardly take any risk when the new chain fails. Therefore, we believe that the cross-chain bridge is a "multi-chain" "Medium risk, medium return" option.
Although the cross-chain track is still in the middle and early stages, the head cross-chain bridge has already made good income. The 2021 revenue of the cross-chain bridge leader Multichain is 17 million US dollars, which has exceeded the agreement revenue of Curve, the leader of Dex in the same period, which means that the demand and revenue space of this mid-to-early track are already at the forefront of the encryption world. However, the cross-chain track is far from mature, and there is no safe and cheap cross-chain bridge currently, and the various cross-chain solutions on the market have always been unable to solve the impossible triangle of asset cashing.
The Layerzero Labs team with a rich algorithm background accurately grasped the pain points of the market, developed the most cost-effective cross-chain communication protocol Layerzero, and the Stargate cross-chain bridge that broke the impossible triangle. Only half a year after its launch, its revenue has reached half of Multichain’s revenue at that time, and it is a player that cannot be ignored in the track.
This is just the beginning. The team will upgrade the entire chain of the industry's top Dex, stable currency and NFT, especially the cooperation with Sushiswap, Pancakeswap and Circle. In addition to optimizing the user experience, the next-generation cross-chain products should also lower the integration threshold for developers and help them reduce the cost, speed and risk of asset cross-chain, so that the cross-chain bridge can be called without the user's awareness . After successfully upgrading USDC, the fourth largest market capitalization asset in the entire network, Layerzero Labs has the ability to popularize full-chain transformation to other protocols and become the core of the multi-chain ecology.
01.Thesis
We are optimistic about Layerzero, but in the context of the current bear market, the valuation of its token STG is more reasonable than that of equity. In addition to the market level mentioned at the beginning, we are also optimistic about Layerzero Labs for the following reasons:
level of competitiveness
Layerzero provides the most cost-effective cross-chain communication
By combining the low cost of a third-party verification network and the high security of light nodes, the ultra-light nodes proposed by Layerzero provide high security at a low cost. This cost-effective solution will save a lot of learning and operating costs for developers, and these will greatly reduce the user's usage rate, making cross-chain applications built on Layerzero have a strong cost advantage.
Stargate breaks the impossible triangle of cross-chain asset redemption
Stargate broke the impossible triangle with Delta Algorithm and soft partition mechanism. Liquidity providers enjoy better capital efficiency and scalability, so that the same funds can be deployed more efficiently and bring higher returns; while users can enjoy safer and zero-slip at a lower cost Point assets cross-chain. We believe that Stargate is already the most sophisticated and competitive token cross-chain bridge on the market.
• An active builder of cross-chain ecology
Layerzero Labs is actively exploring the feasibility of cross-chain ecology, and has made great achievements in the direction of cross-chain Dex, NFT and stable currency. At present, both Sushiswap and Pancakeswap officially use Stargate for cross-chain Dex development; Gh0stly Gh0sts and Holograph are actively trying in the direction of full-chain NFT; USDC and agEUR are upgraded to full-chain stable currency assets through Layerzero technology. With the cooperation of these top teams, the full-chain concept may bring Layerzero Labs a second growth curve.
Within half a year of Stargate’s launch, cross-chain revenue has approached the leading Multichain
According to statistics, although Stargate will be launched on March 14, 2022, its cross-chain revenue in Q2 of 2022 will be nearly 1.5 million, which is 1/2 of the revenue of the current cross-chain bridge leader Multichain in the same period. This is enough to prove that Stargate has an astonishing growth rate and a certain market position.
It is believed that after cross-chain ecological projects such as SushiXSwap gradually mature, Stargate will be able to occupy more shares in this high-growth track.
team level
Layerzero Labs' team has excellent machine learning algorithms and innovative capabilities in blockchain development
Layerzero's CEO Bryan Pellegrino is one of the best Texas Hold'em players in the world, and CTO Ryan Zarick has rich experience in network optimization and blockchain security. They once founded a machine learning company that helped several Major League Baseball teams improve their performance. Later, they jointly developed the world's best heads-up robot player with researchers from Facebook AI Lab, which once again proved their extraordinary attainments in the field of machine learning algorithms.
The addition of Sushiswap Lianchuang 0xmaki will accelerate the construction of cross-chain ecology
The addition of Sushiswap's Lianchuang 0xmaki will help Layerzero's cross-chain ecological construction. SushiXSwap is a product led by 0xmaki, which will bring more application scenarios to the two protocols at the same time. 0xmaki's strong community appeal will help the expansion and maintenance of the protocol community.
02. Background
What is a cross-chain bridge
The formal definition of a cross-chain bridge is a tool for transferring assets (Token, etc.) from the source chain (Source Chain) to the destination chain (Destination Chain). In practical applications, there are also cross-chains with NFT and multi-chain activity track information, and Layerzero has been involved in these aspects, but currently does not see a good business model, so it can be regarded as a potential second in the future. growth curve.
We can split the structure of the cross-chain bridge into a cross-chain communication system and a cross-chain account system, where the cross-chain account system includes asset custody and asset cashing:

1. Cross-chain communication system
The communication system ensures that when user assets flow between different chains, the information can be accurately and truly recorded.
This is what the Layerzero protocol developed by Layerzero Labs provides - allowing developers and even users to send messages between chains.
2. Cross-chain account system
How to map the assets deposited by the user in one chain to the user's account in another chain. Due to the limitations of the current technology of the blockchain, all cross-chain bridges cannot transfer the asset itself, but the transfer of the asset value.
Because financial assets such as currencies, stocks, and bonds basically only exist in books managed by banks or exchanges. Without the ledger, it is difficult for these assets to establish the ownership of the holder. The bottom layer of the blockchain is a public account book. For example, the Bitcoin network records the balance of its native asset BTC in each address and the transfer records between addresses. How much BTC. The cross-chain bridge essentially transfers the value of user asset information in different ledgers, and needs to manage user assets through two parts: asset custody and asset cashing.
Asset custody: Cross-chain bridges need to set up addresses on each public chain to store user assets, and the custody mode of addresses determines the security of user assets.
Asset redemption: How the cross-chain bridge realizes the value transfer of assets. For example, if you send $100 from the United States to Hong Kong, you don't need to actually ship the money to Hong Kong, you just need to ensure that the customer can use the corresponding amount of money in Hong Kong.
In short, Stargate has opened accounts on each chain. When the user deposits assets in the source chain, it will use its own Layerzero communication protocol to be responsible for safely transmitting cross-chain requests to the target chain, and finally give The user's account is cashed out.
Existing solutions for cross-chain communication
Cross-chain information verification is mainly responsible for transferring the information required by the cross-chain bridge. For example, a transaction that uses a Multichain cross-chain bridge to transfer 1000 USDC from Ethereum to Arbitrum will need to pass information such as the user's wallet address, USDC contract address, amount, and the transaction hash that the user deposited into the Multichain Ethereum wallet. In the future, the third-party cross-chain bridge may support more functions, such as the cross-chain governance required by DAO, which will require a larger amount of information. Before the emergence of Layerzero, cross-chain communication was mainly done through external verification or light nodes on the chain.
External validation:
External verification, also known as third-party verification, is through an intermediate chain (Intermediate Chain) or intermediate network to verify and transfer cross-chain information. The nodes of the intermediate chain or intermediate network monitor the contract address on Chain A. When they receive a cross-chain request, the verifiers vote on the cross-chain information to reach a consensus, and then send the result to the contract address of Chain B, and then Help users realize value.
If a cross-chain bridge adopts an external authentication method, additional attention should be paid to its security issues, especially the degree of decentralization.
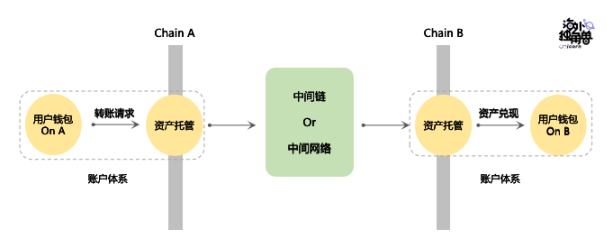
Both the Cosmos SDK and Polkadot's Substrate have provided tools for quickly developing an application chain. At present, most intermediate chains are developed using the Cosmos SDK, because the cost can be controlled when the prospects are uncertain. Just like cloud vendors or communities quickly develop Red Hat Linux or Ubuntu Linux based on the Linux kernel to meet different scenarios.
In addition to developing intermediate chains, some asset cross-chain bridges will also use multi-signature technology to allow multiple nodes to form a validator network. Commonly used technologies include MPC (multi-party secure computing) and threshold signatures, which basically allow dozens of nodes to hold a part of the wallet key on the chain, and only when the number of agreed nodes exceeds the threshold can the verifiers reach a consensus . In this way, information security can also be guaranteed in a decentralized manner.
The main difference between the validator chain and the validator network is that the chain can establish an ecology. For example, after Thorchain developed Dex and lending protocols on the chain, it increased the application scenarios of its token RUNE, increased the price of RUNE and attracted nearly a hundred nodes, thereby improving the security of the chain. Portal and Multichain, which adopt the validator network scheme, do not seem to have designed a way to allow external miners to participate. In fact, the number of nodes is only 20 to 30, and most of them are operated by official teams.
In addition, these validator chains or networks have also developed various communication formats, such as Cosmos' IBC, Polkadot's XCMP, and Portal's Wormhole. They all support rich network settings and message formats to allow other protocol developers to customize the information formats they need, hoping to become the infrastructure in the cross-chain ecology, and after users fill in the information format, the security of information transmission Still guaranteed by the validators of the chain. Of course, there are also some cross-chain bridges that do not support rich information formats, such as Multichain and most official bridges. We believe that in the long run, these rich communication formats can bring the second growth curve to the above-mentioned bridges, but from a pragmatic point of view, we must now be wary of the high bubble valuations brought about by these narratives.
On-chain light node verification:
By building a light node on the chain to verify whether the transaction information of another chain is accurate, this can inherit the security of the chain itself, so that there is no need to additionally trust an external (such as a centralized exchange or an intermediate chain) verifier, Therefore, it is also called a trustless verification method. But this method will require high computing power to verify transactions, especially setting up light nodes on Ethereum will cost hundreds of thousands of dollars to verify a transaction.
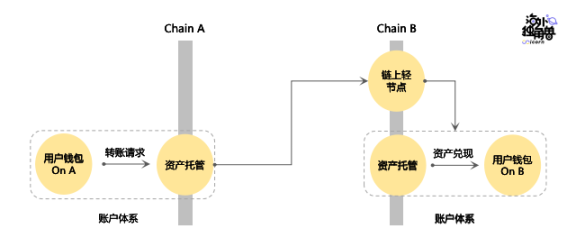
Since Layerzero refers to the verification method of light nodes, I will explain in detail how light nodes verify transaction information:
Light nodes only save all historical block headers, and do not store specific transaction information in blocks, which makes light nodes only need to store 5GB of data, while full nodes need to store about 500GB.
The block header contains Merkle Root, which is a string of abbreviations encrypted with all transaction content in the block. When the light node needs to verify the transaction content of Tx2, it needs to request Hash 0-0 and Hash 1 from the full node, and then it can quickly calculate whether the top Merkle Root is correct. In short, after the light node obtains Hash 0-0 and Hash 1 sequentially on the chain, it can calculate hash(Tx2) -> Hash 0 -> Merkle Root in sequence, and this process is called Merkle Proof.
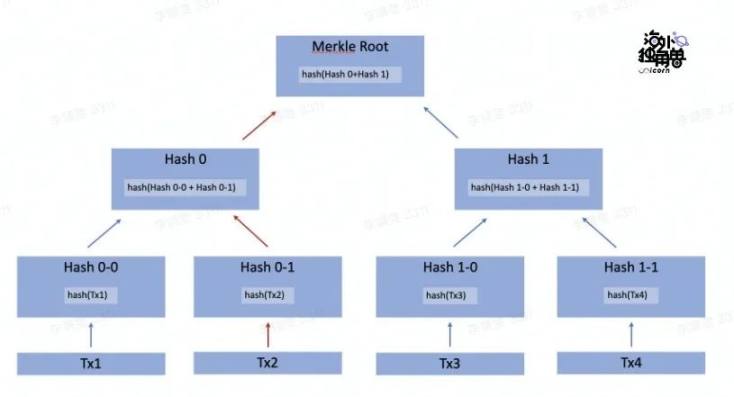
But it is worth pointing out that an Ethereum block usually has hundreds of (>200) transactions, making the above graph expand to more than 7 layers, which means more on-chain storage and computing resources are required, resulting in The light nodes on the square may need to pay tens of millions of dollars in gas a day. Therefore, the use of cross-chain bridges with light nodes should pay extra attention to cost solutions.
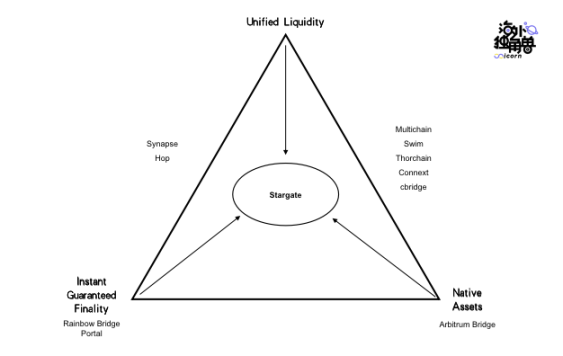
The Impossible Trinity of Asset Cashing
When the cross-chain bridge is cashing out assets, it can only meet one or two of the following three characteristics due to different asset cashing schemes
immediate finality guarantee
Guaranteed immediate settlement (finality) means that when the cross-chain request is successfully submitted, the user can obtain assets equal to the cross-chain request on the target chain.
Guaranteed immediate settlement requires high liquidity. If there is not enough liquidity, the system can reject the transaction when the user initiates a transfer request, thereby avoiding disputes. However, if multiple cross-chain transactions occur at the same time, some transactions may not be able to due to the previous transaction drying up the liquidity pool. Complete, or cause transaction disputes (such as excessive slippage).
Therefore, if the cross-chain bridge has no way to guarantee the depth of the agreement, the solution to the immediate finality guarantee is to sacrifice the original assets and complete the asset redemption after issuing a deposit certificate to the user on the target chain. More details will be explained below.
Native Assets/ Synthetic Assets - Native / Synthetic Assets
In the cross-chain transaction, only the original assets on the source chain and the target chain are involved, that is, the assets that the user really wants, such as USDC, which is officially certified on ETH, Solana, and BSC.
It corresponds to synthetic assets, such as Wormhole's USDCet. Users transfer USDC from Ethereum to Solana through Wormhole. What users get is USDCet (a synthetic asset) not Solana’s native USDC. Users need to go to Dex to trade into native USDC (liquidity is unknown) before they can participate in other DeFi protocols. Cause bad user experience and extra trouble between ecology. So essentially Wormhole's solution is to issue deposit certificates to users on the target chain, and set up an AMM to allow users to exchange for native assets. But the AMM scheme means that half of the assets are destined to be unable to be effectively utilized, which means extremely poor capital efficiency.
In addition, synthetic assets cannot provide good composability, because the project party also needs to consider the ecology of the synthetic assets minted around its agreement, resulting in the composability of the agreement from the composability of project party and investor resources, not The advantages of the protocol itself, such as its ease of use, attract developers to build an ecosystem on it.
Therefore, cross-chain protocols using synthetic assets should pay extra attention to the composability of synthetic assets and capital efficiency issues.
Unified Liquidity - Unified Liquidity
Unified liquidity means that the same (/equivalent) assets on the same chain can be deposited and withdrawn in a unified pool, which makes capital utilization more efficient.
Corresponding to this is the liquidity of the split. That is to say, the cross-chain of the same asset is completed through the paired liquidity pool. For example, for the same asset (such as USDC), two one-to-one paired liquidity pools of Ethereum-BSC and Ethereum-Solana are formed. Such a paired liquidity pool can guarantee instant settlement, because the liquidity pool of the target chain does not need to consider requests from multiple liquidity pools.
As shown in the figure below, for example, when cross-chaining USDC on BSC and Solana to Ethereum, the corresponding liquidity pools are independent of each other and have different depths. Therefore, even if a total of 300 USD can be withdrawn on Ethereum, the overall amount can just meet the cross-chain request of $150 from BSC and $150 from Solana, but because the pools of BSC-Ethereum and Solana-Ethereum are not Shared liquidity, so BSC's request is denied.
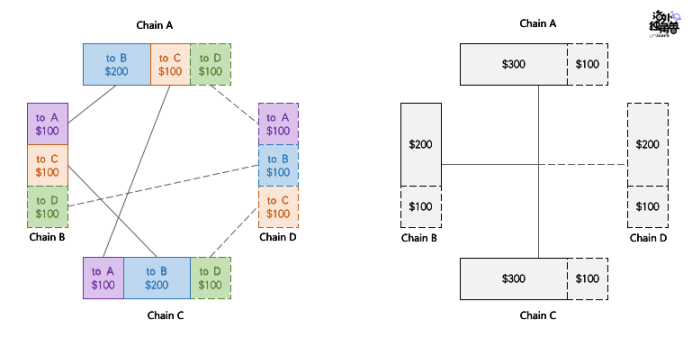
Split liquidity will also encounter the problem of poor scalability, because a protocol that supports cross-N chains will have liquidity pools, and adding a new chain will require additional N-1 liquidity pools.
This will not only reduce the use efficiency of funds and deteriorate the depth of the pool, but also cause additional troubles for the liquidity provider, because he needs to track the yield of more liquidity pools to optimize his strategy. Therefore, cross-chain protocols using split liquidity pools should pay extra attention to capital efficiency and scalability issues.
To ensure unified liquidity and original assets, the current mainstream solution is to set up wallets on each chain and attract liquidity. When users deposit original assets (such as USDC) in the source chain, they will directly transfer from the wallet of the target chain. Transfer money to the user's wallet. However, if multiple transactions occur at the same time, some transactions may not be completed due to the previous transaction drying up the liquidity pool, or transaction disputes (such as particularly large slippage).
To ensure final and immediate settlement and native assets, the current mainstream solution is a paired cross-chain pool, such as USDC(ETH)-USDC(BNB) or USDC(ETH)-USDC(SOL). In this way, the liquidity pool will not dry up quickly due to multiple chains requesting assets from one chain at the same time. However, this will result in split liquidity, because the more supported chains, the worse the liquidity will be, which will reduce the scalability and capital efficiency of the bridge. This is why the current mainstream cross-chain bridges do not adopt a paired cross-chain pool solution, because the poor capital efficiency makes the project almost unable to survive the early stage.
If you want to ensure final and immediate settlement and unified liquidity, the current mainstream solution is to obtain a deposit certificate to ensure immediate settlement after the user deposits assets in a certain chain, and the deposit certificate will allow users to withdraw funds to any supported chain. But obviously this would require the use of synthetic assets.
In other words, these three features are interlocking and cannot be taken into account, which is also known as the impossible triangle of cross-chain. The figure below shows the characteristics of the asset redemption link of the current mainstream asset cross-chain bridge, and none of them except Stargate can meet the three conditions at the same time.
Asset cross-chain bridge market size
The market size of the asset cross-chain bridge can be seen from two parts: one part is the L1-L1 cross-chain in the relatively mature underlying public chain scenario, and the other part is the L1-L2 between L2, which is more imaginative. cross-chain.
The TVL of each official bridge on the Ethereum address is the most intuitive display of the volume of Ethereum outflow assets. We have summarized the data of April, when the market was still at a high point of concern for the new public chain, and July, when the market completely entered a bear market. In the table below, these official bridges account for 80-90% of Ethereum's overflow liquidity:
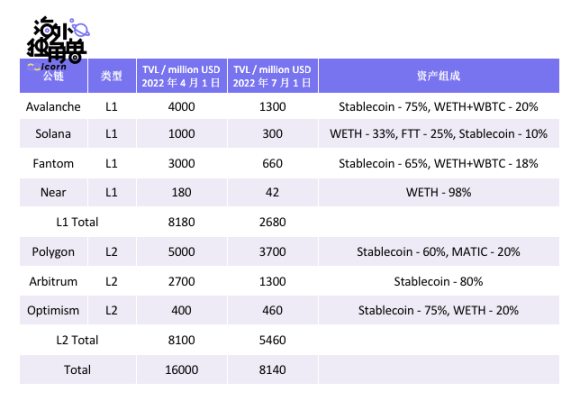
From the statistics in the table above, we can see that:
The TVL volume of L2 is already comparable to that of L1;
Among the cross-chain assets, 60-80% of the assets entering L2 are stable coins, and only 30-50% of the assets entering other L1 are stable coins, and the rest are mainly WETH and WBTC.
Due to the above characteristics and the current market hotspot switching to L2, etc., the TVL of L2 is less affected by the bear market. Because what is received is the overflowing liquidity of Ethereum, which needs to flow back to deleverage in a bear market, so the TVL of the L1 bridge shrinks sharply.
To sum up, the L1-L1 bridge enjoys the liquidity spillover effect of Ethereum in the bull market, but in the bear market, it will face the cool situation after the return of capital to Ethereum. There is a high ceiling, especially when the security of ZK Rollup is verified (or trusted by large users), it is expected to obtain a large amount of Ethereum assets, so the L2 bridge will capture a larger market space than the L1 bridge.
It is worth pointing out that the chains with the most transfer requests on Stargate in April were Avalanche and Fantom, and the chain with the most transfer requests in July was Arbitrum. This shows that Stargate has a good user base and usage scenarios between L1 and L2, and will be able to eat the Beta of the entire multi-chain structure in the future.
The business model and revenue capability of the cross-chain bridge are relatively clear.
The main business model of the third-party cross-chain bridge is to charge fees from the cross-chain amount, and the market average Take Rate is 0.05%. But the official bridge does not charge this part of the fee, which can bring more liquidity to the chain. In the future, the third-party bridge will be able to attract these funds from the official bridge through advantages such as lower fees, better user experience and a more complete ecology.
Multichain and Synapse are currently the two most profitable third-party bridges:
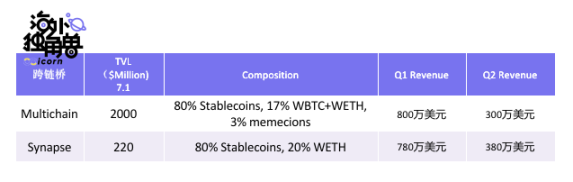
Multichain earned USD 8 million in agreement revenue in Q1 this year, and in Q2 under the current bear market background, it still has USD 3 million. As for the Synapse protocol with smaller cross-chain amount and TVL, because more charging links are set up, the protocol revenue is on par with Multichain.
When the multi-chain ecology is prosperous, the revenue limit of the cross-chain bridge is extremely high. Multichain said in its 2021 annual report that its full-year revenue was $17 million. For comparison, the Curve protocol (an on-chain Dex protocol with profitability at the head) has protocol revenue of $12 million in 2021. It can be seen that the demand and profitability of cross-chain bridges cannot be underestimated in the encryption world.
To sum up, cross-chain is one of the important investment varieties under the multi-chain structure, and has already achieved high revenue in the immature stage of the market. The products in the current track either have high operating costs, or centralization leads to insecurity, and it is impossible to satisfy the impossible triangle of asset cashing. The Layerzero Labs team relies on years of experience in algorithm development to solve the pain points of this industry, and also relies on top team and investor resources to build the next generation of multi-chain ecology and look for the second growth curve.
03. Products and business models
LayerZero cross-chain communication protocol
Moving data between two chains is expensive, tedious and insecure.
——From Poker to Protocols
LayerZero is a trustless cross-chain communication protocol. Its essence is to use the technical principle of light nodes to divide the trust link of the intermediate chain into two, so as to exchange for better security with lower costs. In short, it is the most cost-effective cross-chain communication solution on the market. It not only greatly reduces the developer's learning and operating costs, but also reduces the user's usage rate, making applications built on Layerzero have a security cost advantage.

The Layerzero protocol consists of two parts:
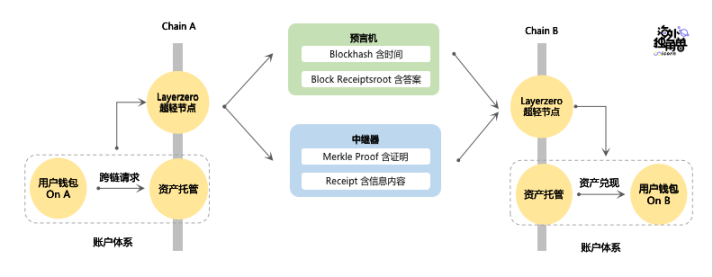
1. Ultra-Light Node -- responsible for sending, receiving, and verifying information
Ultra-light nodes can be quickly deployed on each chain to achieve standardized multi-chain deployment. This will allow developers of other cross-chain protocols to greatly reduce development time on the basis of a high degree of freedom.
2. Oracles and repeaters -- responsible for information transmission
Simply put, the main function of the oracle is to let the contract on the target chain know when to verify and what the answer to the verification is. The relayer is responsible for providing the proof process required to verify the transaction and the specific content of the cross-chain information.
Specifically, the function of the oracle machine is mainly to transfer the Blockhash and Block Receiptsroot where the cross-chain request on the source chain is located to the target chain.
Blockhash is mainly to inform the contract on the target chain which block has the user's cross-chain request, so as to facilitate the target chain contract to query.
Block Receiptsroot is used to verify transactions, and only when the message transmitted by the relayer can calculate the same answer, the cross-chain information transmitted by the relayer is believed.
The role of the repeater is to pass the path information required by the Receipt and Merkle Proof where the cross-chain message is located to the contract on the target chain for verification.
Receipt is a transaction receipt, which mainly contains the transaction execution result, transaction hash and transaction event log.
The result of transaction execution is to ensure that the transaction has indeed been completed, so that the contract of the target chain will perform subsequent cross-chain operations.
The transaction hash is a string that can fully represent the transaction content, but because it does not contain specific transaction content, it saves storage and computing resources.
The transaction event log describes events in the transaction process, such as token transfers. The event log records some results during the processing of the source chain contract, so that the target chain contract does not need to re-run the contract content, but can directly use the results on the source chain. Therefore, the transaction event log can be understood as the specific content of cross-chain information.
The path information required by Merkle Proof refers to the calculation path and required path from a specific Receipt to ReceiptRoot.
For example, after telling the information of Receipt 2 -> Hash 0-0 -> Hash 1 to the nodes on the chain in turn, the Receipt Root can be calculated according to the red path.
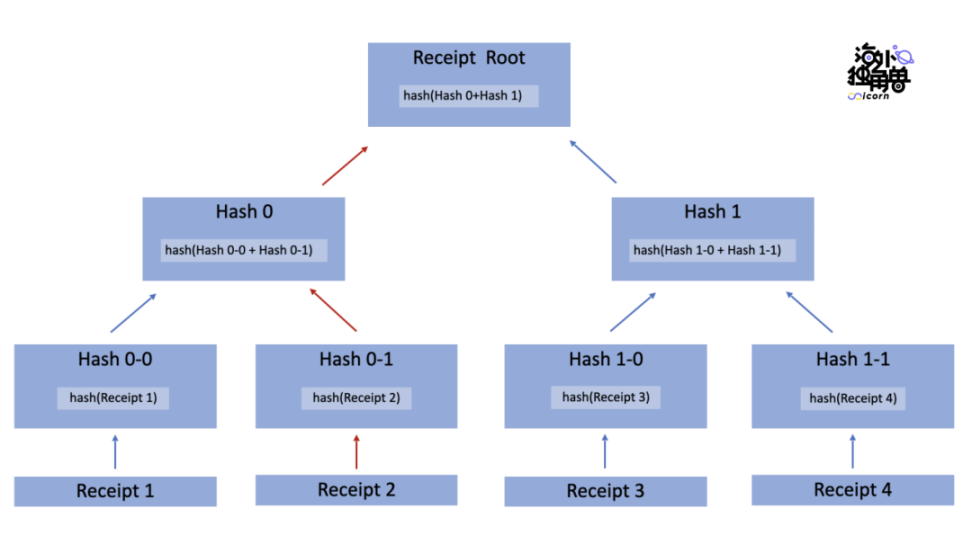
Finally, compare the Receipt Root calculated by the repeater and the Receipt Root given by the oracle machine with the on-chain contract to confirm that the transaction has indeed occurred, and then use the event log in the Receipt as the cross-chain information content, which is the cross-chain agreement. The rest of the process provides information, such as the user's wallet address, the ERC20 contract address of the token, the quantity, etc.
Such a design trades for greater security at a lower cost. Specifically, there are two points
Double security: This will require the attacker to control both the relay and the oracle to do evil, so the worst case is as safe as a bridge that only uses a single validator chain or network. In the future, if the repeater can be decentralized (such as a validator network similar to Multichain), it will greatly increase the difficulty of attack;
Security isolation: The development team of each application can modify the repeater code provided by Layerzero and graft it to the application's own server or validator network. And they can choose a trusted oracle (such as Chainlink or Band) by themselves, so that if the repeater or oracle of a certain application is attacked, it will not affect the security of other applications. This design is also called security isolation.
In the long run, this will greatly affect the narratives of The Internet of Blockchain, such as Cosmos and Polkadot. Because they try to use a chain and nodes on the chain to complete various cross-chain operations, the main business model is to sell the tokens of the chain or participate in the ecology.
But now that Layerzero has open-sourced the code, it does not need a chain in the middle, and uses cheaper oracle machines and validator networks to reduce costs. In the future, Layerzero can earn fees by developing and maintaining repeater services for different protocols, or it can learn from Polkadot to develop a Layerzero-led decentralized repeater main network to complete commercialization.
Stargate cross-chain bridge
Stargate is a token cross-chain bridge made by Layerzero Labs based on its excellent communication protocol. Its biggest highlight is breaking the impossible triangle of cross-chain asset cashing, so that
Users complete more composable cross-chain requests at lower rates (no slippage). For example, the cross-chain Swap function in cooperation with Sushiswap will be mentioned later.
The funds of liquidity providers (depositors) can be used more efficiently to obtain higher rewards (interest), which will eventually bring better depth and application scenarios.
First, Stargate now attracts tokens from liquidity providers (depositors) on each chain, and these tokens are hosted in wallets bridged on each chain. After the user deposits in the wallet of the bridge on the source chain, the bridge will transfer money from the wallet of the target chain to the user to complete the cross-chain request. For example, after a user deposits 1,000 USDT in the source chain to Stargate's wallet, and after the information is cross-chained to the target chain, Stargate's contract on the target chain will use the liquidity provider's money to transfer 994 USDT to the user's wallet. And the protocol itself can earn 5 USDT and give 1 USDT to the liquidity provider. It can be seen that Stargate has chosen the asset cashing path of native assets and unified liquidity. Because there is no casting of synthetic assets in the process, and the same asset can be taken out in a unified pool.
In addition, it regards USDT and USDC as 1:1 assets, that is to say, a user who deposits 1,000 USDC on Ethereum can withdraw 994 USDT on Arbitrum. In this way, if the stock of USDC on Arbritrum is not enough, the user can exchange the remaining demand for basically equivalent USDT, so that the user can experience a better depth and the protocol obtains a higher cross-chain amount.
However, adopting native assets and unified liquidity will cause huge troubles in ensuring instant settlement. Because, as explained in the background introduction, when multiple transactions are concurrent, the liquidity pool on the popular target chain will dry up, making the remaining transactions impossible, causing transaction disputes. For example, Multichain, the largest cross-chain bridge, also uses native assets and unified liquidity, but if the USDT pool on Arbitrum dries up, Multichain will only open an anyUSDC for the user on the target chain as a deposit certificate, and wait for others to deposit more USDC can be used to cash out native assets for users.
However, users can also manually burn anyUSDC in advance and then go to the source chain to retrieve their deposits, but this will require payment of additional Gas Fee during the burning and redemption process. In other words, Multichain can only guarantee instant settlement in the case of high liquidity (high TVL), while low liquidity assets often fail. But a better cross-chain bridge should reject cross-chain requests as soon as possible when liquidity is insufficient, so as to avoid the waste of redemption Gas Fee and reject combined cross-chain transactions (such as cross-chain Swap) as early as possible.
The Delta Algorithm proposed in Stargate's white paper solves this problem. Specifically, the algorithm contains soft-partitions (Soft-partitions) and redistribution (Redistribution) mechanisms.
soft partition
Soft partition means to set up credit partition between chains, and credit is the credit liquidity set between chains according to the size of historical transaction volume. For example, taking Ethereum, BSC and Solana as examples, Stargate’s liquidity pool on BSC has a total of 100 USDT. Because the transaction volume from Ethereum to BSC is relatively large, it allows a maximum of 60 USDT to be requested from Ethereum. taken out.
If there is high concurrency on the same chain, and there are two transactions that want to withdraw 50 USDT at the same time, Stargate will reject the second transaction that is slightly slower;
If there is high concurrency in different chains, such as a 50 USDT from Ethereum and a 50 USDT from Solana, Stargate will reject Solana's request because 50 > 40.
This is the soft partition mechanism to ensure immediate settlement, so that there will be no transaction conflicts or failures.
But the soft partition essentially automatically allocates liquidity, so that the split liquidity is formed between the chains, so as to ensure the original assets and immediate settlement. And automatically means that the low capital efficiency and liquidity provider troubles brought about by the split liquidity mentioned above can be solved. In addition, the ratio of this soft partition is allocated through the team's tuning parameters, and team members have previous experience in a large number of data analysis to ensure the optimization of this ratio.
Specifically, the low capital efficiency is because supporting more chains will require the establishment of more one-to-one liquidity pools, resulting in liquidity fragmentation and even mismatch in extreme cases. Liquidity providers also need to keep track of the information of each pool, and then switch assets to the one with the highest yield or the one with the greatest demand. This kind of mismatch requires high-frequency coordination between LPs who do not know each other, which is almost impossible. impossible. This is why there is currently no bridge with a split liquidity pool solution, because it is too troublesome for liquidity providers, and users often encounter mismatched liquidity pools.
The soft partition automatically splits all liquidity according to the ratio set by the team. For example, the above-mentioned 100 USDT on BSC will be divided into 40:60 according to the ratio of 4:6 set by the team. When there are 200 USDT on BSC The time is divided into 80:120, thus avoiding liquidity providers to adjust themselves. When the total amount of the pool changes, algorithms are needed to dynamically balance these changes, so as to solve the mismatched liquidity and maximize capital efficiency. This is the redistribution link to be discussed below.
redistribute
Redistribution means that when new liquidity is injected, Delta Algorithm will redistribute new liquidity to soft partitions. Its strategy can be summarized as filling the valley first and then flattening the peak
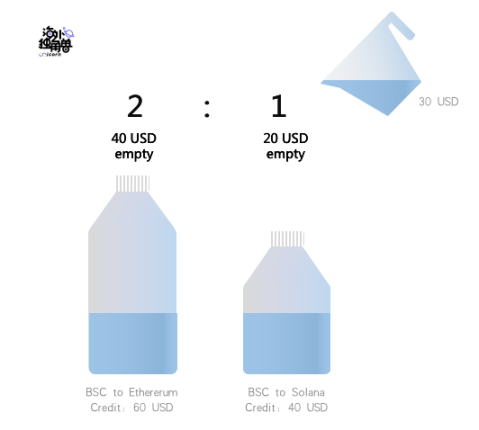
fill the valley
Filling the valley means that when the user deposits assets in the source chain, Stargate will give priority to this part of the liquidity to fill the chain whose credit is about to be exhausted. For example, the BSC mentioned above will only have 10 USDT left after 50 USDT is withdrawn, and if a user wants to go to another chain from BSC, they will also deposit assets. When the deposited assets are not enough to fill the valley, this part of the assets will be distributed to each soft partition after calculating the weight according to the difference. For example, when the credit pool difference between BSC and Ethereum and Solana is 20 USDT and 40 USDT respectively, the user's newly deposited 30 USDT will deposit 10 USDT and 20 USDT into the two credit pools respectively.
flat peak
And if the newly deposited assets are enough to fill the valley, the remaining money will be divided into two soft partitions according to the weight of 4:6 set by the system, thereby deepening liquidity. This prevents one chain from having a particularly deep credit pool, while other chains cannot benefit from an overall better depth.
business model
business model
Stargate is currently the company's main source of income, and users will need to pay a 0.06% handling fee for each use. in
0.01% is paid to liquidity providers as a reward, which can be understood as the interest that banks give to depositors, and it is also considered a cost.
0.01% is given to the holders of the pledged token veSTG, which can be understood as the bank's dividends to shareholders.
0.04% belongs to the national treasury and ecological construction expenses.
In addition, there is a special design in STG's token economic model, which can be referred to as liquidity premium for short. Specifically, STG itself is a multi-chain token, and there is no fee for using Stargate cross-chain STG. This innovation refers to the design of Throchain's RUNE (introduced in the appendix). Assuming that a user wants to exchange ETH on Ethereum for AVAX on Avalanche, he can choose to exchange ETH for USDC and then use Stargate to cross-chain to Avalanche to exchange for AVAX, and will be charged 0.06% as a cross-chain fee. But it is also possible to switch to STG (assuming the price is stable and the depth is sufficient), thus saving this 0.06%. This will attract liquidity providers to generate STG-related transaction pools (such as ETH-STG) on each chain. More transaction pools mean that STG has better in-depth support, bringing more people to use the second path, thus bringing higher returns to the liquidity providers of the ETH-STG pool, encouraging them to continue to hold or increase their positions. In short, this will bring a liquidity premium to STG, and this liquidity can enhance the user experience of the protocol and the benefits of protocol supporters. When a token has better depth and good application scenarios, its value will naturally rise.
Of course, the liquidity premium advantage has not yet been reflected, but when the market value and ecology of STG are improved, it will be able to bring better opportunities for token holders to exit.
04. Agreement performance and valuation
Agreement performance
From the official website, you can check the cumulative cross-chain amount. You can see that since Stargate went online on March 14, as of September 1, the cumulative cross-chain amount has been about 2.4 billion US dollars. Considering the background of the bear market, it is estimated that in the next six months there will be 1.5 billion, 2 billion, and 2.5 billion US dollars of cross-chain value, corresponding to Bear, Base, and Bull Case respectively.
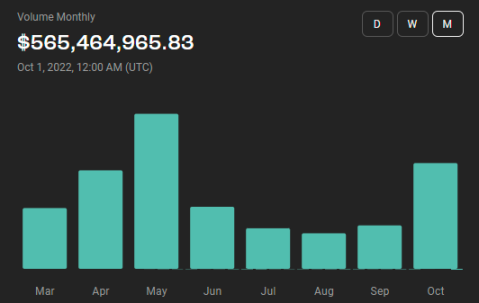
Stargate's current accumulated cross-chain amount
Stargate draws 0.06% from each cross-chain transaction as a fee, of which 0.01% is equivalent to the cost of capital use and returned to liquidity providers (depositors), and the rest enters the agreement treasury or rewards token holders. Simply put, Stargate is now a company with the performance in the table below.
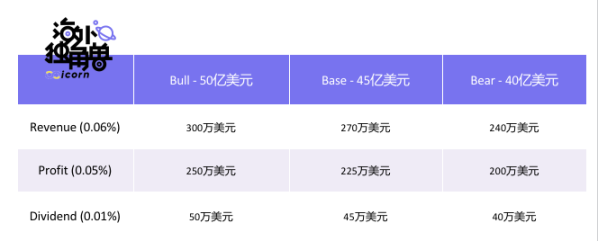
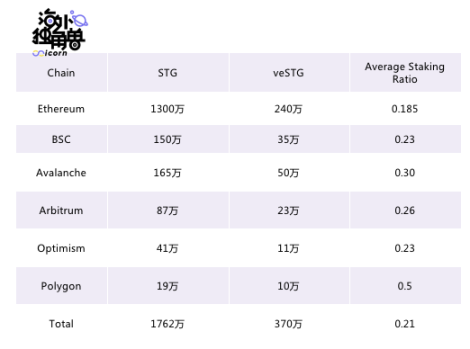
It is worth pointing out that the dividend (Dividend) does not share the income with all token holders, but after the tokens are pledged, the corresponding dividends can be obtained every week according to the share of veSTG. stgscan does not contain the specific number of vestg, we made this link after crawling historical pledge data using Dune. Since Dune does not support Fantom and some special transactions, there may be an error of about 10% in the data, but overall it is worth referring to. As of August 20,
Agreement Valuation
The following discussion is deduced under the assumption of Base Case, and readers can make changes according to their own judgment on the market.
Price-to-sales ratio PS
Layerzero Labs is currently a $3 million annual revenue company. But according to its latest round of valuation of 1 billion US dollars, this is a company with an ultra-high valuation of nearly 300 times PS. Although it may develop more businesses in the future, no other commercialization plans have been seen so far. And if you look at the current STG's full circulation market value of 300 million (0.3 US dollars), a rapidly growing agreement with a PS valuation of 100 times is difficult to accept, but considering that its profit margin is above 60% (deducting the inestimable After the Equilibrium Fee), the market usually gives a higher valuation multiple.
Of course, Layerzero Labs is also a high-growth company. In less than half a year, its Q2 revenue in 2022 has reached 1/3 of the cross-chain revenue of the industry leader Multichain in the same period. It is believed that the current high valuation will be digested as the multi-chain ecosystem gradually matures and maintains high growth.
Price-to-earnings ratio PE
Similar to PS, based on the valuation of the primary market, the current PE of Layerzero Labs is nearly 300 times. However, when the market value of STG's full circulation is 300 million US dollars, 100 times PE can be quickly digested by the high growth rate of the market. On the whole, investing in STG will have a better safety cushion than the primary equity of Layerzero Labs itself.
dividend yield
According to the current STG price of $0.35 (August 15), the dividend rate of a veSTG is 45/370/0.35 = 35%. That is to say, the user can buy $10,000 of STG and pledge it for three years, and at the same time open a perpetual short order of the equivalent amount of $10,000, and can obtain a rate of return of 30%/2=15% or more after one year with low risk (net of perpetual contract costs, transaction costs, and funding costs).
Although this is a very attractive number, other users will pledge STG at any time to dilute the dividend rate later, and the STG locked by the user for 3 years will endure extremely low yields in the follow-up time, so this operation is not recommended. The current inflated dividend rate is because most users in the market cannot clearly know the performance of Stargate and the number of veSTG, and the existence of this information gap makes the rate of return of veSTG seriously underestimated.
05. Team
05. Team
On the whole, both the CEO and CTO have years of experience in machine learning algorithms and blockchain development, and their excellent innovation capabilities can also be seen from Layerzero and Stargate. The company's BD Director is 0xmaki, one of the veterans of DeFi, and will be able to bring the most crypto native resources and an active community atmosphere.
CEO - Bryan Pellegrino
He used to be the world's top poker player, and won the top few World Poker Championships many times during the period from 2009 to 2014. Later, I quit the circle because I wanted to create some value-providing tools after reaching the top.
「I was just trying to be the best. Once I got there, I realized, hey—there’s no leverage. There’s no anything. I hadn’t realized until then, you need to focus on the utility payoff of what you’re doing.」
Then go to help several MLB (Major League Baseball) teams (such as Oakland Athletics) conduct data analysis to help them improve their performance. He also founded one or two blockchain security companies and accumulated some experience in blockchain engineering. Around 2020, it cooperated with Facebook AI Lab researcher Noam Brown to develop the world's strongest heads-up poker robot.
To sum up, Bryan Pellegrino is an engineer who covers a wide range of fields, is proficient in algorithms and has a high degree of self-motivation. His many successful entrepreneurial experiences have proved his excellent algorithm skills and innovative ability, and he brings his dominance in Poker to Blockchain protocol.
CTO - Ryan Zarick
He is a senior engineer with rich experience in machine learning algorithms and smart contract development, and also a friend of the CEO in college.
He once jointly invented a network optimization algorithm to improve the fairness in the transmission process of network packets, thus promoting the development of gateway technology related to Cisco high-frequency trading.
Later, he also founded the smart contract service company 80Trill (responsible for smart contract writing, auditing, consulting) and the machine learning consulting and development company Minimal AI, and helped the CEO optimize his Poker robot during the period.
BD Director - 0xmaki
0xmaki was the core developer of the former Sushiswap, and was forced to quit in September 2021 due to the internal struggle within Sushi.
Then went to Aura Finance, a Convex-like income amplifier, currently specializing in opportunities on Balancer.
In March 2022, he also joined Layerzero Labs, mainly responsible for ecological development. Layerzero's AMA is now held multiple times with Sushiswap, which will bring better exposure and community atmosphere to both protocols at the same time. In addition, Sushi's cross-chain Swap project SushiXSwap was completed under the leadership of 0xmaki, adding application scenarios to the two protocols.
06. Funding history
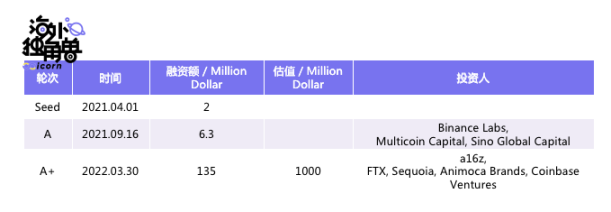
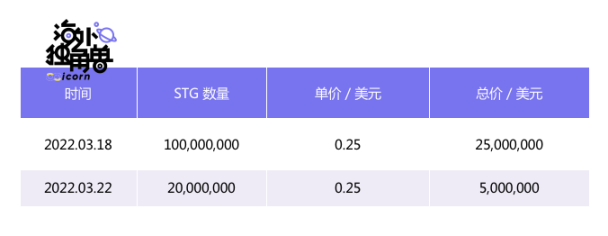
STG public sale records.
💡Note: The total amount of STG is 1 billion
public chain
public chain
Currently Stargate and Layerzero already support the 7 largest public chains, and actively support new public chains. For example, Layerzero will deeply support 7 protocols on the chain, including Econia and Martain, on the first day of the Aptos mainnet launch.

Dex
At present, Stargate announced to jointly develop multi-chain Dex with Sushiswap, Pancakeswap and other Dex.

Take SushiXswap as an example: Sushi, as the first multi-chain AMM Dex, has already deployed the protocol on 16 chains. However, these liquidity pools are scattered on various chains, and the TVL of 500 million US dollars in Ethereum does not allow Sushiswap on Fantom to obtain more application scenarios. In other words, the previous Sushi was only multi-chain, not cross-chain.
But if Sushi becomes a cross-chain Dex, when users want to participate in the ecology of the new chain, they will first use Sushiswap to exchange their ETH on Ethereum for AVAX on Avalanche. This will increase the application scenarios of Sushiswap on the two chains, resulting in more handling fees and better depth. This also allows users to save tens of minutes of waiting time for the official cross-chain bridge and seven or eight operation interfaces.
stable currency

stable currency
Circle
On September 28, 2022, Layerzero announced that it helped Circle develop USDC's native cross-chain facility. The large amount of USDC cross-chain that originally needed to be completed through off-chain or exchanges can now be easily completed with the official bridge. For example, Whale Alert usually reported that 100 million USDC was burned on BSC, and 100 million USDC was minted on Ethereum a few minutes later. This situation may be that some large users want to carry out a huge amount of cross-chain, but the current cross-chain bridge does not have enough After the depth or a good rate can bear this volume, the big players will go to Circle for the cross-chain method.
But with the help of Layerzero, USDC can perform native cross-chain on-chain faster and cheaper, which means that USDC has become a full-chain asset. Full-chain assets mean that the cost, speed and risk of cross-chain assets are greatly reduced, and assets will be able to flow freely on multiple chains.
I believe that good cooperation with Circle will effectively promote the concept of full-chain assets, and more protocols are willing to cooperate with Layerzero to jointly develop full-chain assets.

Angle
The partnership between Layerzero and Angle Protocol has upgraded agEUR to a multi-chain Euro stablecoin. In return, Angle announced that the depth of Layerzero's cross-chain pool will become the deepest pool on the market.
NFT
Gh0stly Gh0sts
Gh0stly Gh0sts is the first full-chain NFT (omnichain NFT), built using the Layerzero cross-chain communication protocol, which can realize cross-chain operations between 7 chains.
The total number of NFTs in this set is 7710, and the total historical transaction volume is 5500 ETH. This is already a good score for a free casting exploration project.
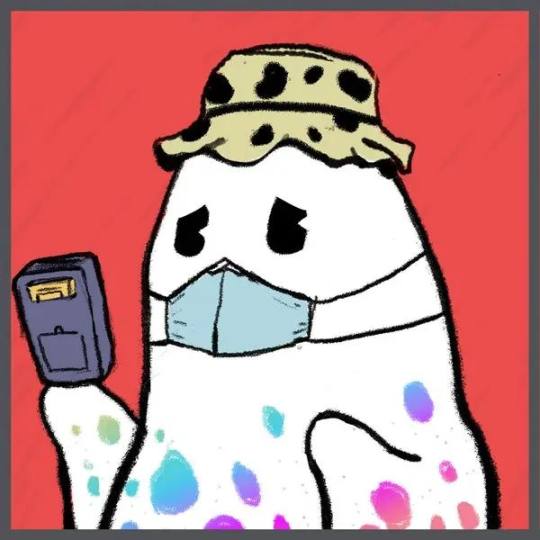

The red background means that this NFT was minted on Avalanche, and the gray border means that this NFT was crossed to Ethereum.
08. Market competition
Cross-chain communication protocol
Chainlink's CCIP
The emergence of Layerzero made Chainlink discover more application scenarios, so it immediately developed its own on-chain nodes, so as to seize the market of cross-chain communication protocols.
The business model of CCIP is to help the protocol develop cross-chain dAPP, which is not completely open source. These dAPPs then drive higher usage and empower Link.
The security of CCIP should not be as good as Layerzero, because it is equivalent to using Chainlink as a verification chain, and there is no double security mechanism.
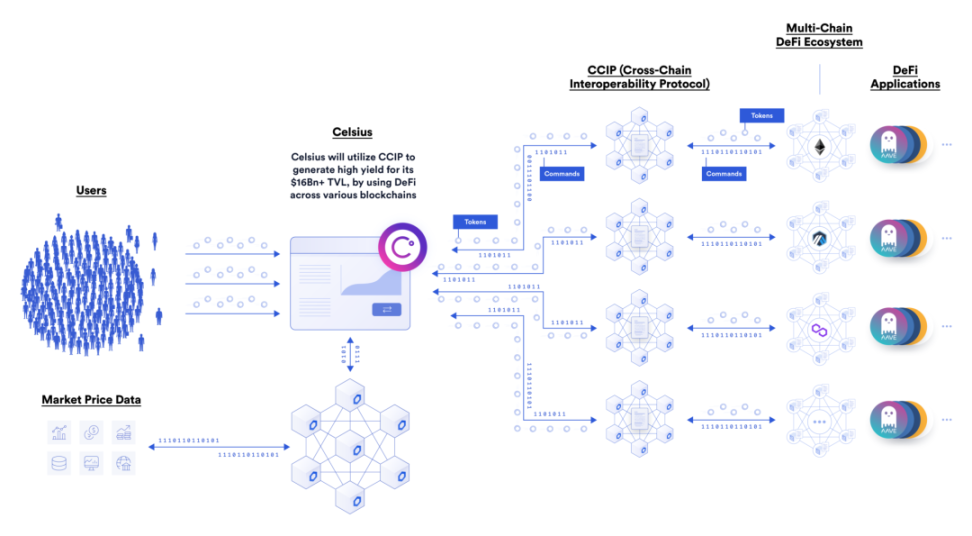
Currently the only application is to help Celsius to obtain DeFi interest rate information, but Celsius is bankrupt.
Cosmos
The biggest narrative of Cosmos is that a set of open source code (Cosmos SDK) for PoS chains and nodes on the chain has been written for many developers, and then developers can develop application chains, including cross-chain communication verification chains of course. For example, Thorchain, a cross-chain Swap invested by Multicoin, currently has an average daily transaction volume of 1.5 million US dollars, but Cosmos tokens cannot benefit from it.
But the biggest problem of Cosmos is that its token ATOM is difficult to capture the value of these application chains, so it also opened its own main network Cosmos Hub. Then I hope that in the future, more application chains can rent security from the nodes of the Cosmos Hub, which is safer for a new chain than attracting verifiers from scratch.
Polkadot
The narrative of Polkadot is basically similar to that of Cosmos, and it also has its own open source code (Substrate) for developing new chains. The new application chain needs to participate in Polkadot's card slot auction (tens of millions of dollars a year), and then it can use the nodes of the Polkadot main network to verify transactions.
On the whole, Cosmos is a bit like Android. You can choose to build your own distribution channel, or let the official store distribute it and get a commission. Polkadot is a bit like IOS, usually only distributed through the official store and can be drawn, but it can also bypass the official store after making some changes.
Layerzero also provides such a cross-chain communication system, which will affect the market of Cosmos and Polkadot in cross-chain narrative as a whole, because most of the current cross-chain applications (transactions, lending and NFT, etc.) can be developed using Layerzero, Security at an affordable cost.
Asset cross-chain bridge
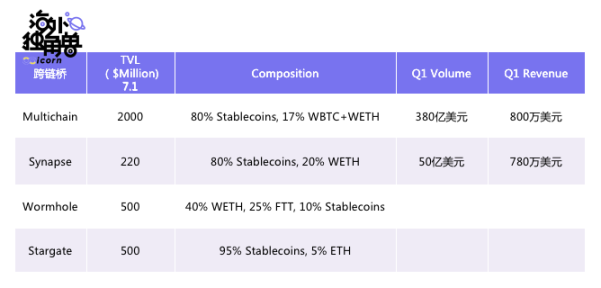
Multichain
Multichain is currently the overlord of third-party asset cross-chain bridges. Its total cross-chain cross-chain in Q1 of 2022 is 38 billion U.S. dollars, and it earned 8 million U.S. dollars from it. But compared to Stargate
Multichain uses an external verification network operated by the official team, which has poor security.
In addition, Multichain does not support a variety of communication content, so it cannot support NFT like Layerzero.
Multichain can only guarantee instant settlement when the TVL is high.
So there are still more opportunities for Layerzero to compete.
Synapse
Synapse is the best bridge for commercialization, and has obtained similar revenue when the cross-chain amount and TVL are only 1/10 of Multichain. But compared to Stargate,
Synapse uses an external verification network operated by the official team, which has poor security.
Although a multi-asset AMM pool has been adopted to improve the low capital efficiency brought by AMM, it is still lower than Stargate as a whole.
Wormhole
Wormhole is Solana's official bridge and has the most secure external authentication network. Because its nodes are all Solana's big miners, they have more professional management experience. Wormhole supports rich information formats, so it can also meet cross-chain needs such as NFT. But compared to Stargate
Wormhole uses a lot of synthetic assets and is extremely capital inefficient.
Wormhole is not a direct competitor of Stargate as it is an official bridge. But it will serve as the bottom layer of some other cross-chain bridges, such as Swim Protocol, and will become one of the powerful players in the asset cross-chain track.
09. Risk
Contract permission loopholes lead to loss of user assets
Cross-chain bridges are a high-incidence area for hacker attacks, and the largest asset losses in history have come from cross-chain bridges
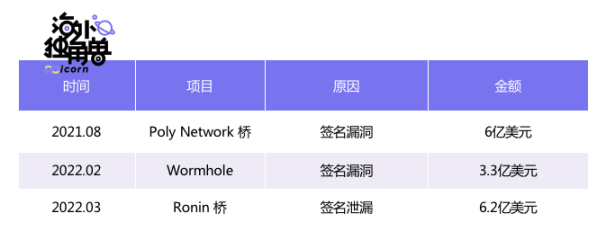
As the cross-chain bridge supports more and more functions, various loopholes may appear during the upgrade process, which may cause the loss of user assets.
The multi-chain pattern cannot be sustained
Regarding the current multi-chain structure, one of the more popular criticisms is that the same protocols (AMM, lending, GameFi, etc.) are constantly copied to the new public chain to reopen the game. When the circle gradually gets tired of this kind of gameplay, it will reduce the user's demand for cross-chain.
However, the current cost performance problem of Ethereum still cannot be solved, and after the popularity of this round of new public chains has cultivated a large number of new users to participate in multi-chain habits, we believe that the flameout of the multi-chain structure may occur in the foreseeable future Sex is still relatively small.
10. Conclusion
We believe that the Layerzero Labs team exchanged lower costs for considerable security in the cross-chain communication solution, and solved the impossible triangle of asset redemption in the asset redemption link. This is inseparable from the team's understanding and innovation capabilities of blockchain security and mathematics, providing users with more cost-effective security solutions and more capital-efficient cross-chain asset cashing. These two advantages have helped Stargate gain a considerable share and revenue in the cross-chain bridge market. It is believed that Stargate will become an important player in the multi-chain structure.
Original link



