A detailed explanation of the Federal Byzantine Agreement
Author: Shaan Ray
Original title: "Federated Byzantine Agreement"
Original translator: Tan.Z |H.Forest Ventures
Recommended reason: Byzantine agreement is the basis for understanding the blockchain. This question was raised by Lamport, the winner of the Turing Award and the key founder of the distributed system. For explaining and solving decentralized consensus problems.
As blockchain technology grows in popularity, developers are increasingly tweaking and experimenting with consensus mechanisms.
first level title
Federated Byzantine Agreement
first level title
quorum slice
A quorum is the number of nodes required to reach consensus within the system. FBA uses "quorum slices" instead. A quorum slice is a subset of the quorum that can convince another specific node to agree.
A node can depend on many slices, and node selection may depend on external criteria. For example, "Node X" can say: "In order to achieve consensus, we must buy from three nodes out of the five banks we have chosen". Three of the five banks can now determine whether node X agrees. Adding another layer of complexity Node X may be part of another node's quorum slice.
image description
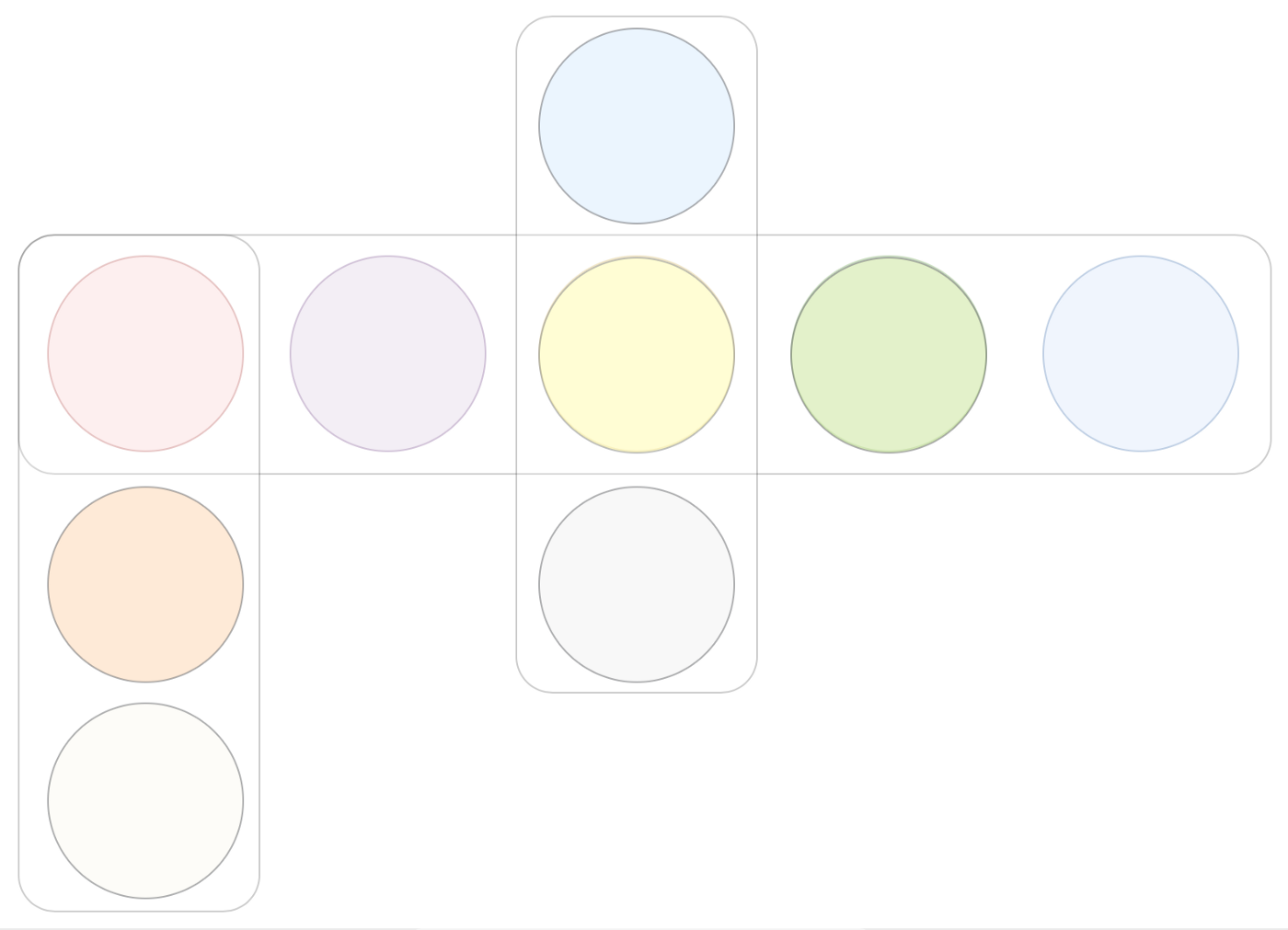
quorum slice
quorum intersection
Trust is set in the node's configuration file. Since nodes may have different profiles, slices and quorums in the network may form dynamically. A good quorum shares nodes, resulting in overlapping quorums. This overlap is called "population crossover". When quorums are disjoint, the system ends up with a "disjoint quorum". Disjoint quorums are undesirable because each of them can independently and simultaneously agree on contradictory transactions, undermining the overall consensus.
quorum intersection
Blocked state and divergent state
Blockchain should be fast and secure. If nodes are "blocked" in the process of reaching agreement, the blockchain will slow down. A system is "divergent" when nodes on the blockchain assume different values than other nodes. A diverging system is more dangerous than a blocking system: a blocking system is just slow, but a diverging system starts showing conflicting data.
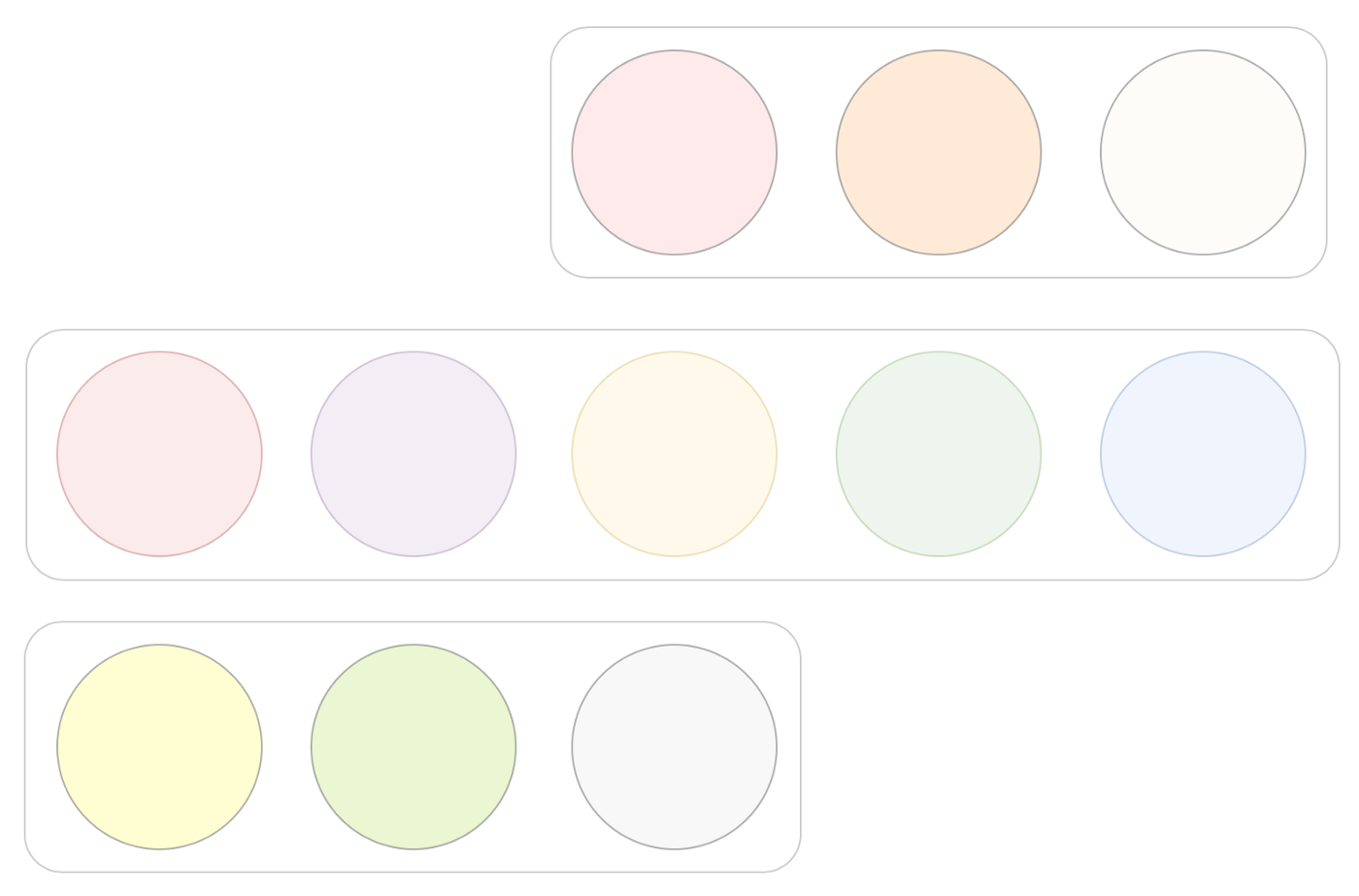
3 sets of disjoint quorum
Advantages of FBA
Open Membership and Decentralized Control
No gatekeepers or central authority - individual nodes can decide who they trust for information
The ability to choose who each node trusts makes the network decentralized
Nodes can have multiple slices
Low barriers to entry (anyone can join)
Resilience in the face of failures (one node can go down and the rest of the system will remain intact)
Nodes can be programmed to trust quorum slices or external sources, depending on their performance over time
in conclusion
in conclusion
The FBA ledger can be up-to-date and accurate without all its nodes agreeing. Instead, a quorum emerges from the selection of each node.
Arbitration slices can convince individual nodes to agree, while arbitration slices can convince the entire system to agree. If a node finds that a particular quorum is completely trustworthy, it can agree to follow whatever that quorum agrees to.
The traditional Byzantine agreement system differs from the FBA system in that in the latter each node chooses its own quorum slice.
translator notes:
In PBFT (Byzantine Fault Tolerance Algorithm), each sub-node needs to be synchronized with other nodes for P2P consensus, so if the number of nodes increases, the performance of changing the chain will decrease. However, blockchains with fewer nodes can still have good performance, and have a very low probability of difference. Therefore, alliance chain or Si chain will have more applications, such as ant chain and Fabric.
Our mirrors:
Follow us:
Our Twitter: @Forest_Ventures
Our mirrors:H.Forest
Official account: H Forest



