order book
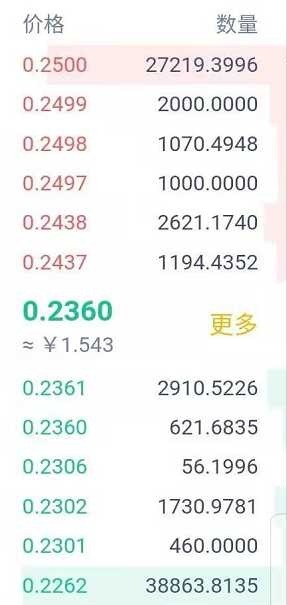
order book
The picture above is a typical order book. The orders of buyers and sellers shown in the figure are all Market Makers that provide liquidity to FC (such as selling price 0.2437 quantity 1194.4352; buying price 0.2361 quantity 2910.5226), at this time, if I place an order to buy at price 0.2437 The quantity is 100, and I eat some of FC's maker pending orders, then I am called Market Taker.
Blockchain Market Maker
The definition of a market maker is a professional institution or individual who has certain privileges on the exchange and undertakes the obligation to buy when the market is oversold and sell when the market is oversold. The English name is Market Maker, which means market creator. The market maker was originally an institutional arrangement introduced to facilitate transactions or reduce transaction costs, which can effectively make the entire market transaction active. In layman's terms, a blockchain market maker is an entity on a digital currency exchange that provides liquidity to the exchange by setting limit orders on its order book, so that transactions can be made at a range of prices.
The picture above is the FC/USDT transaction chart in Moondex. Please think about why Moondex, as a decentralized exchange, can smoothly adopt the order book model?
As we all know, mainstream centralized exchanges such as Huobi, OKEX, and Binance all adopt the order book model. So why is the order book model not prevalent in decentralized exchanges such as Uniswap, Balancer, and Curve? This is because the order book method has the following problems in decentralized exchanges:
First, the price is high! Because in a decentralized exchange, a pending order will call a smart contract once, and a transaction fee will be generated when it is uploaded to the chain. Similar to idex, which has a decentralized order book on Ethereum, the transaction fee for pending orders is very high. high.
Second, the winding speed is slow! At present, the degree of congestion of the Ethereum, a transaction on the chain, is completely different according to the different handling fees, and even the failure to go to the chain occurs due to congestion;
Third, the depth is insufficient, that is, the liquidity is insufficient. Because the price is high and the speed is slow, naturally fewer people use it, so there is no trading depth.
It's time to reveal the answer, because moondex is a decentralized trading platform on the public chain conflux, and the TPS of Conflux reaches 6000+, so the smooth and smooth throughput of the public chain is the biggest confidence for moondex to adopt the order book model. Of course, moonswap is a decentralized exchange in AMM mode on conflux. So what is an AMM automatic market maker?
AMM automatic market maker
AMM, also known as automated market maker, is one of the most critical technologies for decentralized exchanges (DEX) and has proven to be one of the most influential DeFi innovations. They can create and operate for a range of different tokens Publicly available on-chain liquidity. To put it simply, the exchange has no counterparty, and every transaction is a transaction with a liquidity pool (LP for short), which is the AMM model.
Here is an example of AMM of FC and USDT.
Question one:

Question one:Use USDT to buy FC, if you use 10 USDT to buy FC, how much FC will you get?
Here, it is known that the number of FC is 1000, the number of USDT is 250, and the constant K is 250000. Then the calculation formula for the number x worth of FC that can be exchanged for 10 USDT is:
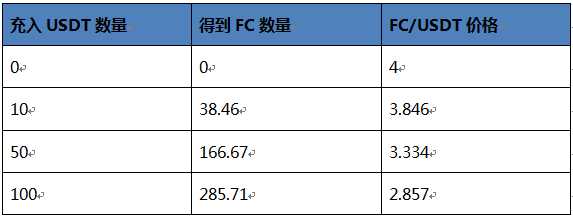
(1000-x)*(250+10)=250000 Calculate x is approximately equal to 38.46
That is to say, when exchanging USDT for FC, you can exchange 38.46 FC for 10 USDT.
Question two:
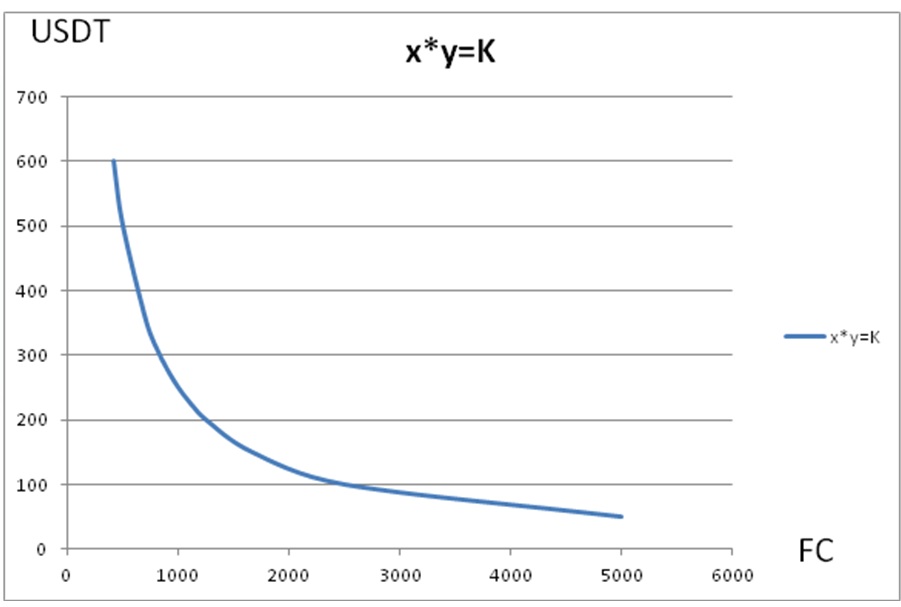
Question two:How many FCs can be obtained by depositing 10 USDT, 50 USDT and 100 USDT respectively?
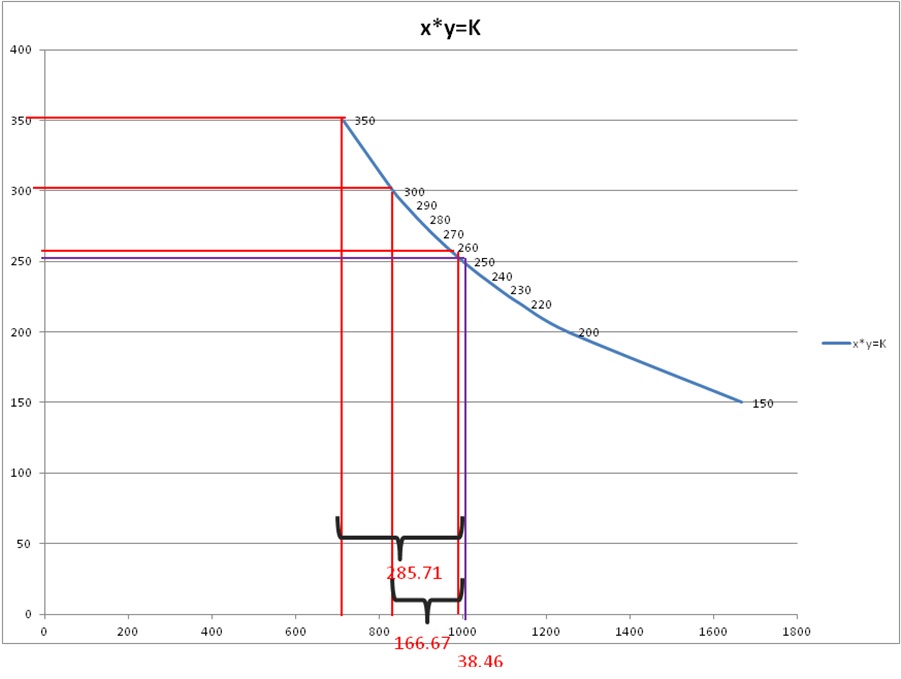
With 10 USDT charged, 50 USDT charged and 100 USDT charged, the horizontal and vertical axis coordinates are drawn (as shown in the figure below), and the number of FC obtained respectively is shown in the figure below.
Question three:
Question three:After providing liquidity for the LP pool, deposit 10 USDT in the same way, how much FC will you get? Is there a lot of FC obtained by depositing 10 USDT in the previous liquidity pool?
Let's take a look at the changes in LP after retail investors fill in liquidity.
Initially, 1000FC and 250USDT
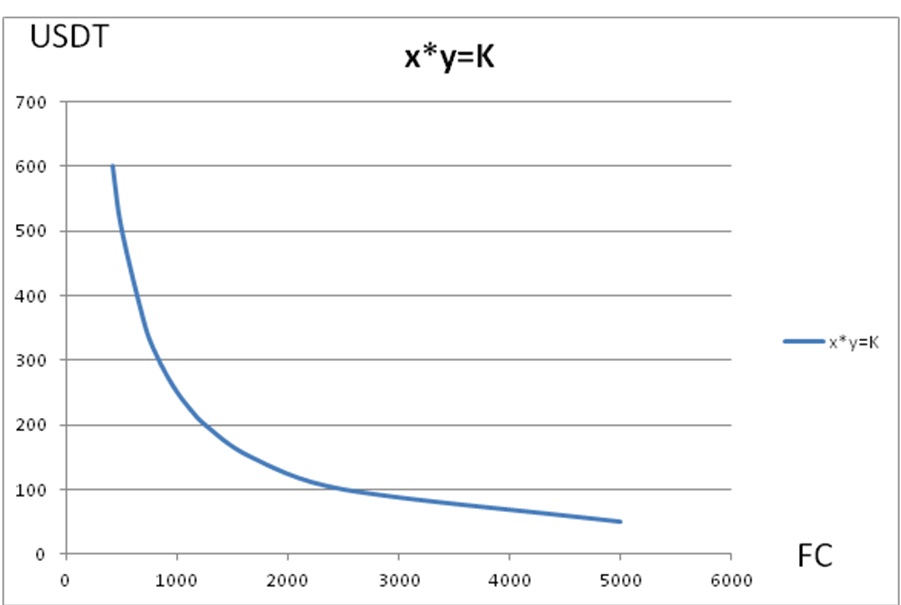
Assuming that the amount charged into the liquidity pool is also 1000FC and 250USDT, the assets in the liquidity pool after charging are 2000FC and 500USDT, and the constant k is 2000*500=1000000. The inverse proportional function after charging is as follows. It can be seen that the function graph is consistent with that before charging, but the coordinate value has changed.
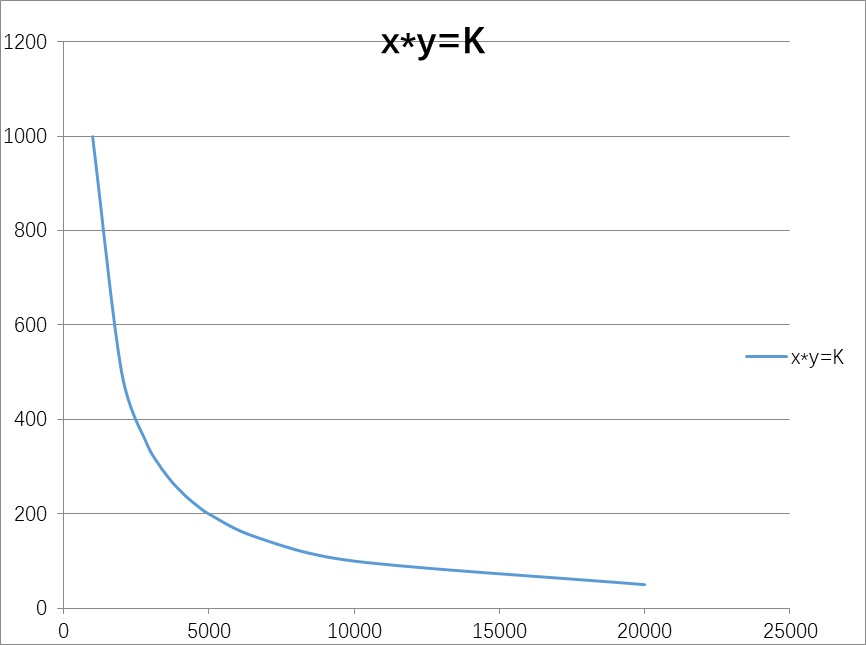
Let's take a look at the change in the asset pool, that is, after the liquidity is increased, and then deposit 10 USDT, how much FC will be obtained. Here, it is known that the number of FC is 2000, the number of USDT is 500, and the constant K is 100000. Then the calculation formula for the number x worth of FC that can be exchanged for 10 USDT is:
(2000-x)*(500+10)=1000000 Calculated x is approximately equal to 39.22
That is to say, when exchanging USDT for FC, you can exchange 39.22 FC for 10 USDT.
Then the actual exchange price is 39.22FC/10USDT, which is 3.922FC/USDT.
It can be seen here that by depositing 10 USDT in the same way, the number of FCs obtained when the liquidity is low is 3.846; when the liquidity is high, the number of FCs obtained is 3.922. Therefore, the more assets in the liquidity pool, the more FC you will get when exchanging FC. Therefore, the more assets in the liquidity pool of the exchange, the deeper the depth and the more stable the price.
Finally, let’s briefly review the advantages and disadvantages of AMM:
Advantages of AMM
1. Liquidity will not drop to 0
It can be seen from the inverse proportional function graph that the larger the value of the horizontal axis or the vertical axis, the closer the horizontal axis and the vertical axis will be, but there will be no intersection point. This allows the liquidity pool to never dry up.
2. Very friendly to retail investors
The threshold is low, and retail investors can deposit liquidity and enjoy a share of liquidity fees.
3. For some currencies, trading venues are concentrated
In fact, it is also the benefit of decentralized exchanges. For some small currencies, it saves the fee for listing on centralized exchanges, and can "issue coins with one click" on decentralized exchanges. Of course, the risks of these coins also need to be carefully screened.
Disadvantages of AMMs
1. Compared with the order book, it is not possible to place pending orders for transactions, but only for exchange transactions. In this way, if you want to buy at the price of the location, you can only keep an eye on the market, which will be tiring;
2. It is not conducive to small-amount transactions. Most AMMs are on Ethereum, and the gas fee is a few dollars, which is not friendly to small-amount funds;
3. There may be slippage, and the slippage tolerance needs to be set. Because there will be a delay in the block confirmation on the chain, and large transactions or liquidity withdrawals may occur during this period, so the price fluctuation may already be relatively large when your block transaction is confirmed.




