四方面对比MakerDao与Liquity在稳定币借贷过程中的优劣性
撰文:Footprint分析师Simon(simon@footprint.network)
日期:2021年11月
数据来源:Footprint MakerDao VS Liquity Dashboard (https://footprint.cool/MDL)
围绕DeFi的主要核心赛道包含了公链、借贷、DEX以及货币等,其中稳定币占据重要的组成部分。然而从8月开始监管对于稳定币的讨论逐渐增加,甚至美国的财政部、美联储、SEC等众多监管机构都瞄准了稳定币。
可以看到从2021年开始,稳定币的市值趁着DeFi繁荣的东风迅速攀升,越来越多的稳定币涉足到DeFi当中。然而人们对以USDT、USTC为首的中心化稳定币颇具微词,依靠中心化机构而生的稳定币是否与去中心化相悖。
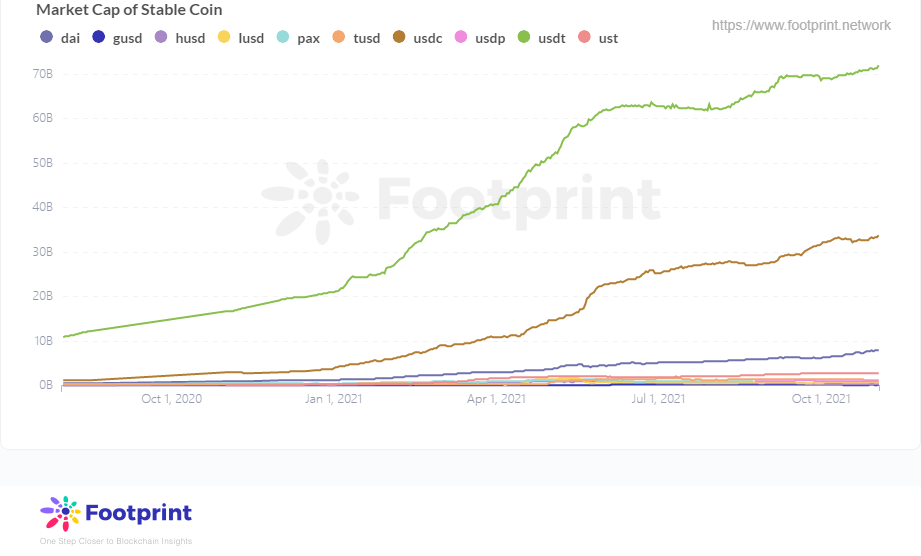
稳定币市值(自2020年8月) 数据来源:Footprint Analytics
上线于2018年的MakerDao通过抵押ETH铸造DAI带来了一个让人眼前一亮的稳定币,作为第一代去中心化稳定币,虽然在2020年3月遭遇过坏账,但由于其先发优势在去中心化稳定币中仍占据第一把交椅。
时间快速来到2021年,同样是超额抵押的稳定币LUSD也对稳定币的中心化发起质疑,称大部分稳定币都是以法币抵押而形成的中心化稳定币,要创建一个保持去中心化的协议Liquity。
同样是通过借贷协议铸造形成稳定币的MarkerDao与Liquity常常会被放在一起比较。
从Footprint Analytics上看到,MakerDao与Liquity在TVL上有着明显的差距,约是Liquity的7.6倍,DAI的市值也将近是LUSD的12倍。这主要还是由于稳定币的先发优势易守难攻,就如同USDT的问题显而易见但鉴于转移成本较高,目前USDT仍占据稳定币市值第一。
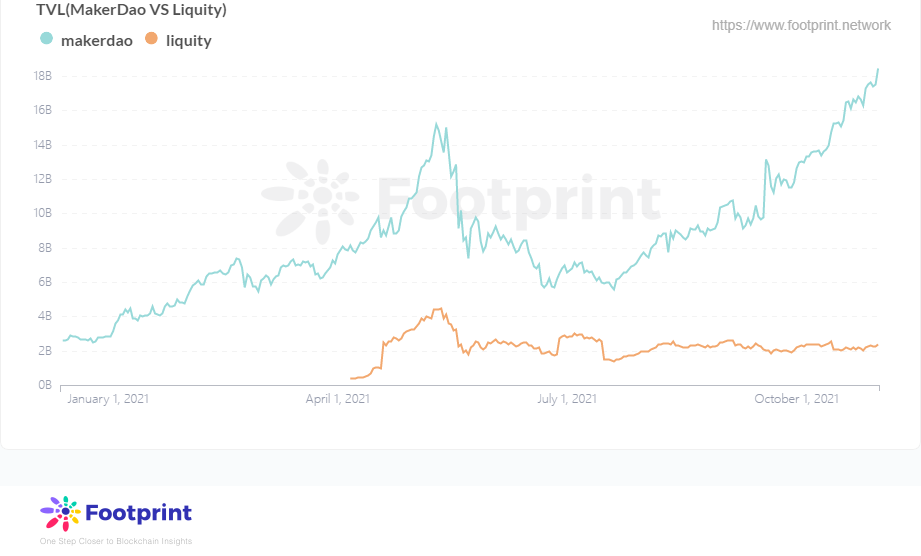
MakerDao与LiquityTVL(自2021年) 数据来源:Footprint Analytics
DAI目前的市值已经是仅次于USDT和USDC的第三名,在去中心化稳定币中一直稳居第一。而LUSD目前在稳定币中仅排第7,与DAI的体量相差甚远。
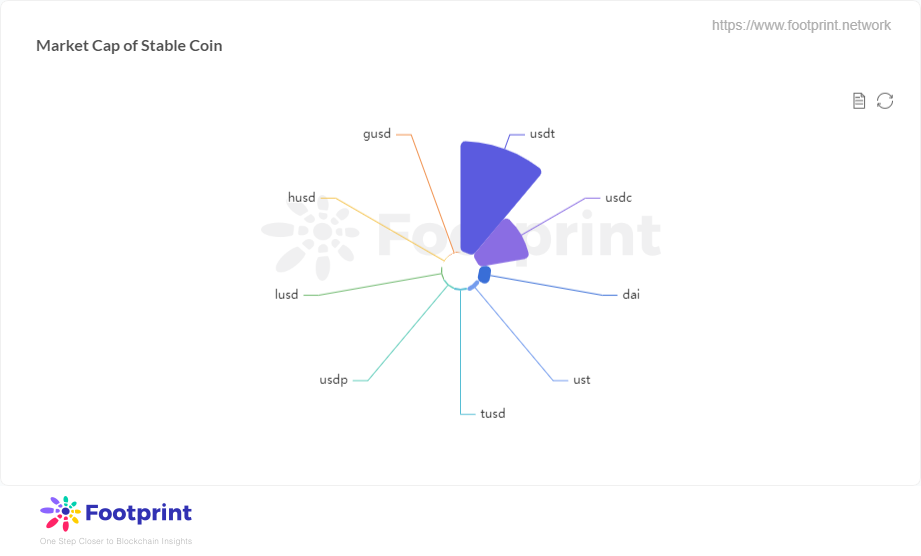
稳定币市值分布(2021年11月) 数据来源:Footprint Analytics
但Liquity作为超额抵押稳定币市场的后来者,自然要吸取了前车之鉴,Liquity很多机制都是针对MarkerDao的痛点而设定的。Footprint Analytics已在《Liquity的机制真的能实现后来居上?》中对Liquity的特点进行剖析, 本文将主要从1)借贷过程、2)稳定币机制、3)代币模式、4)清算机制这四方面对Liquity和MakerDao进行对比。
对比1:借贷流程
抵押物
用户借款的第一步便是要抵押资产,与Liquity只能抵押ETH相比,MakerDao允许有多种抵押物。目前MakerDao还支持USDC、USDT、TUSD等中心化稳定币,LINK、YFI、COMP等平台代币,以及Uniswap的LP token。
Liquity认为LUSD作为去中心化稳定币,以ETH作为抵押物才是真正的去中心化。而如USDT等背后是中心化机构,由此生产的稳定币实则仍是中心化。
MakerDao在2020年3月前也曾只支持ETH做为抵押物,但2020年3月ETH币价的大跌加速了MakerDao对支持多抵押物决策的上线,在危机时刻开放了USDC使得DAI恢复了流动性。
多抵押物是一把双刃剑,一方面通过USDT等稳定币可以分散平台风险,调整DAI的供需。另一方面以USDT作为抵押的稳定币也有众多风险,如被SEC起诉或储备金监管不足,同时其他平台代币的涨跌也与ETH的涨跌相关性很高。
站在平台的安全性出发,无法给出到底是MakerDao还是Liquity更安全的定论,但作为用户的可选择性来说,MakerDao给出的选项会更加多样化。
利息和最低抵押率
MakerDao在借款时收取固定利息(Stability Fee),费率会根据不同资产及不同最小抵押率而变化。
例如ETH有3个池子,最低抵押率从低到高分别是130%、145%、170%,对应的固定利息分别是5%、2%、0.5%。除部分稳定币和LP Token的最低抵押率较低,其他代币的池子最低的抵押率均在130%以上,越高的抵押率会使资金利用率变得越低。
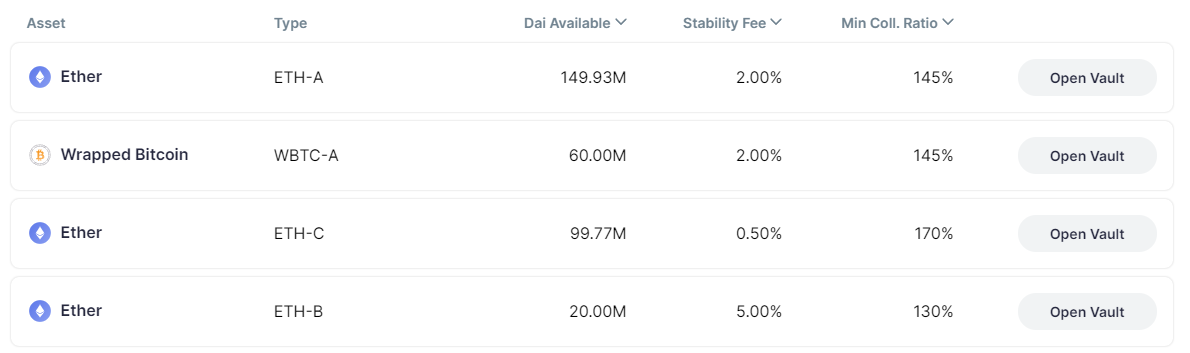
数据来源:https://oasis.app/
对于在Liquity的用户最低抵押率仅需要110%,且没有随着时间不断增长的借款利率。虽然Liquity仍有一个0.5%-5%的借款费用,但这个费用为一次性费用不会随着时间不断增加。这就使Liquity的用户更偏向于长期使用借款,并不急于还款,从而帮助Liquity的TVL保持相对稳定。并且持有LUSD的用户也将长期持有,进而提高了LUSD的供应量。
而MakerDao的用户看着每日不断增加的应偿还费用,需要不断地提醒自己寻找更高利率的投资渠道覆盖借款费用,否则他需要尽早还款以便停止借款的不断生息。
对比2:稳定币用途
MakerDao和Liquity通过抵押铸造的稳定币分别是DAI和LUSD,两者在用途上有着明显的区别。
MakerDao平台本身支持让Dai 的持有者可以通过将其存入储蓄账户中来获得持有 Dai 的存款利息(Dai Saving Rate,简称DSR)。当DSR上升时,会刺激更多持有者将DAI存入,增加DAI的需求。
MakerDao通过固定利息(Stability Fee)和存款利息(DSR)调控DAI的供需,但这些调整的依据是 MakerDAO 成员的判断,又回到了MakerDao是否足够去中心化的问题。
Liquity平台为LUSD的持有者提供一个稳定池(Stability Pool),允许用户将LUSD投进池子赚取因他人被清算而获得的抵押物ETH和平台代币LQTY奖励。收益的多少取决于有多少人会被清算,当市场越不稳定,ETH的价格急速下跌反而会使稳定池的收入增加。
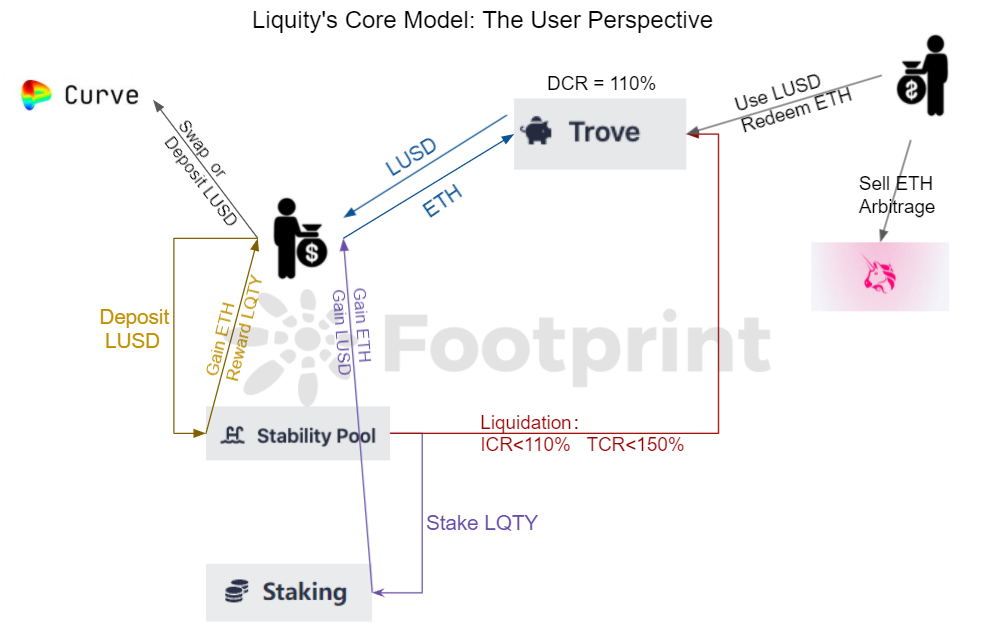
Liquity核心模式 图片来源:Footprint Analytics
从外部用例的角度来看,目前有众多协议均支持DAI。而LUSD的持有者有60%以上始终在Liquity的稳定池中,并未实际走出Liquity平台本身。虽然LUSD在Curve、SushiSwap和OlympusDao中的比例在不断增多,但距离DAI还有一段距离。
对比3:代币机制
MakerDao和Liquity的平台代币分布为MKR和LQTY,两者的主要区别在于发行量及用途不同。
从代币发行来说,MKR的供应量并无固定数量,主要取决于整个MarkerDao的债务情况。如在2020年3月全球加密货币市场暴跌时,MakerDao的抵押物ETH发生530万美元的缺口,MakerDao通过发行和拍卖新铸造的MKR补充DAI,从而通过销毁DAI偿还发生的不良债务。反之,当协议的盈余超过某个阈值时,MKR将被销毁。
而LQTY并不会参与到清算债务中,且它的供应量仅1亿。LQTY的主要来源于在其稳定池中投入LUSD而获得奖励,用户还可再把获得的LQTY进行质押从而分得其他用户借款和赎回的费用。LQTY主要用于激励用户把借出的LUSD投入到它的稳定池中完善清算机制,这也解释了为什么目前有60%以上的LUSD还都在Liquity自己体系中。
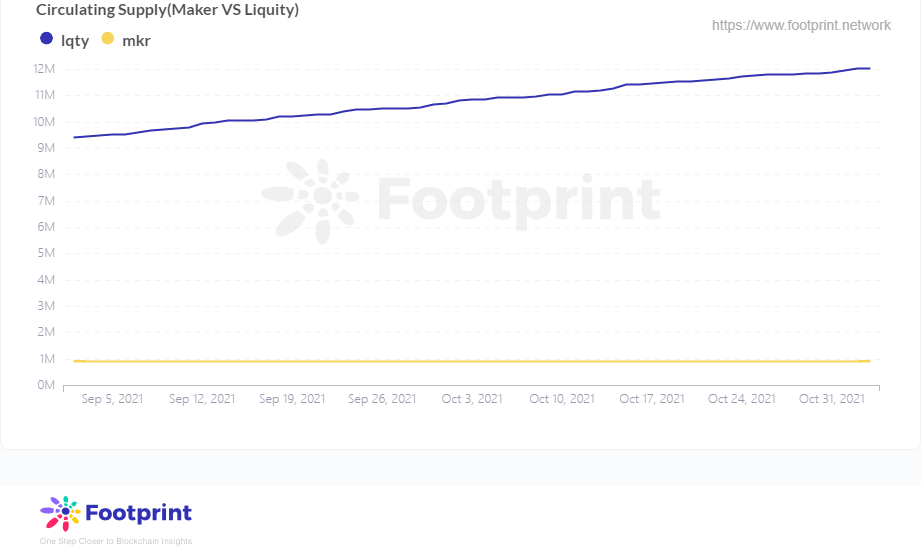
代币流通量(自2021年9月) 数据来源:Footprint Analytics
从代币的用途上来说,MKR是一个治理代币,使用MKR可以对协议参数(例如稳定费、债务上限、最低抵押比率)以及重要的生态系统事物(如资助工作组、赠款等)进行投票。但大部分MKR由早期投资者及大户持有,这又使得MakerDao陷入了中心化的漩涡。
而LQTY并不是治理代币,它的用例仅为帮助持有者捕获收益,因此从两者的币价可以看出相差400倍之多。代币LQTY的流通供应量在未完全释放前仍是稳步上升的,而MKR的流通供应量在市场稳定时基本会保持稳定。
对比4:清算机制
清算机制是任何借贷类系统稳定性的核心,MakerDao和Liquity的清算机制有着显而易见的差别。
经历了2020年3月份考验的MakerDao对清算机制进行了完善,由原来的英式拍卖模式切换到初始要价从高到低的荷兰式拍卖,但它仍为拍卖模式,时效需6小时。并且MakerDao在发生清算时需要有足够持有DAI的用户主动参与进来。虽然MakerDao已经通过引入稳定币抵押和发行MRK来加强对DAI流通量的调控。
Liquity创新了一种自动化的清算机制,降低MakerDao清算机制的风险。当有用户低于最低抵押率时,任何人都可以发起清算的操作。为了弥补发起者支出的Gas费,发起者将获得借款人借款时存入的200LUSD清算准备金(Liquidation Reserve)外加0.5%的清算抵押物作为奖励。而清算的LUSD来自于Liquity的稳定池,作为回报稳定池的持有者将按比例获得清算的抵押物ETH。
这种模式不论对于清算发起人还是稳定池中持有LUSD的清算人来说都是有利可图的,并且清算的发生无需等待6小时,一旦触及110%的抵押率将立即执行。
即使是有大规模资产需要被清算,当稳定池中的LUSD被消耗殆尽时,将进被称作”重新分配“的二级清算机制:对于需清算的借款人,系统会将他金库(Trove)中的债务和抵押物重新分配到所有其他借款人的金库中,此时抵押率越高的借款人将分得越多的债务和抵押物,作为额外的收入,即使他的抵押率有所降低。
此外,Liquity为了保证有足够抵押率应对风险设置了复原模式(Recovery Mode),当系统总抵押率(Total Collatral Rate, TCR)低于150%时将启动对全部抵押率小于150%的金库的清算。复原模式的设置对有较低抵押率的用户起到了震慑作用,使Liquity的总抵押率目前保持在280%左右。
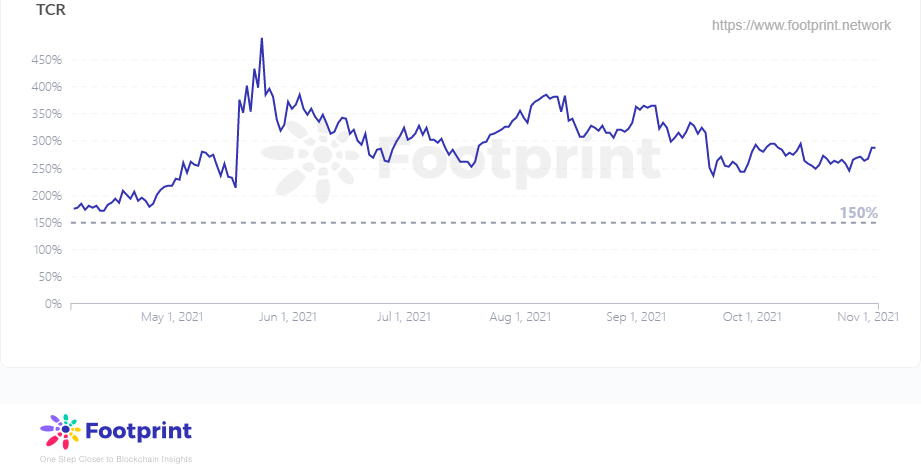
Liquity总抵押率(自2021年4月) 数据来源:Footprint Analytics
结论
Footprint对这两个协议的区别对比汇总如下:
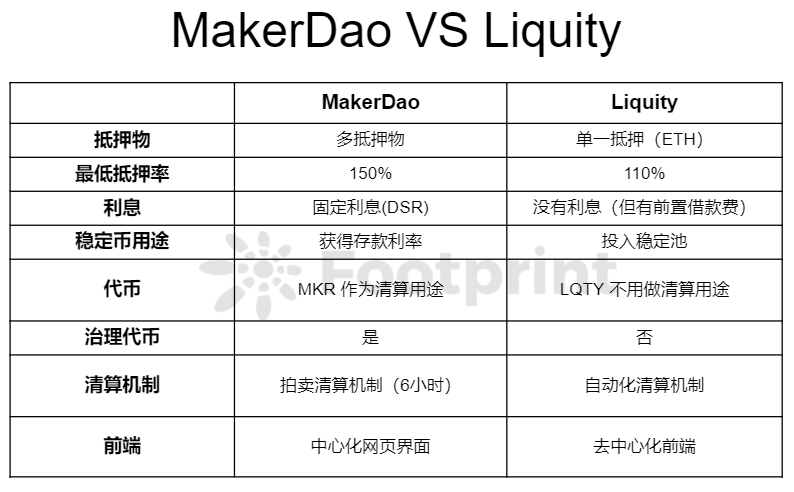
MakerDao与Liquity模式对比 图片来源:Footprint Analytics
Liquity可谓是站在了巨人的肩膀上,设置的机制处处针对MakerDao的痛点。但不能定论Liquity的机制就能战胜MakerDao,两者都是处于不同时期根据市场不断优化的产物。MakerDao作为最早的稳定币借贷协议,利用先发优势已经在市场中站稳了根基。
Liquity在追逐MakerDao的道路上还有相当一段距离,主要在于DAI的流通性和使用范围更大,这使新用户也会更优先考虑使用DAI。近期MakerDao也仍在坚持不懈的扩展它的用例,提出让DAI成为清洁货币(Clean Money),不断拓展与现实世界资产的结合,去解决更高维度的人类问题——环保和绿色金融。
作为去中心化稳定币的前驱者,MakerDao虽然因为涉及中心化问题而屡遭诟病,但它具有的前瞻性和更宏大的战略视角是不容否定的。Liquity更像是不断跟随“带头大哥”脚步并努力青出于蓝的“后浪”,想要动摇MakerDao的根基还需要等待一个可以“趁虚而入”的时机。在那之前Liquity还需要在拓展LUSD的用例方面继续打稳根基,或在稳定币的细分市场继续形成更多的差异化,例如Liquity更加鼓励长期借款。
以上内容仅为个人观点,仅供参考、交流,不构成投资建议。如存在明显的理解或数据错误,欢迎反馈。
关于Footprint Analytics:
Footprint Analytics是一个一站式可视化区块链数据分析平台。Footprint协助解决了链上数据清理整合的问题,让用户免费享受0门槛的区块链数据分析体验。提供千余种制表模板和拖拽式的作图体验,任何人都可以在10秒内建立自己的个性化数据图表,轻松洞察链上数据,了解数据背后的故事。
Footprint Analytics官网:https://www.footprint.network/
Discord社群:https://discord.gg/3HYaR6USM7



