andfirst articleandsecond article。
This article was published on May 17, 201944 Ways to Enhance Smart Contracts with Chainlink Oraclesdecentralized finance
decentralized finance
off-chain payment
Insurance
Insurance
utilities
supply chain
utilities
Identity and Authorization
supply chain
sustainable development
off-chain computation
supply chain
secondary title
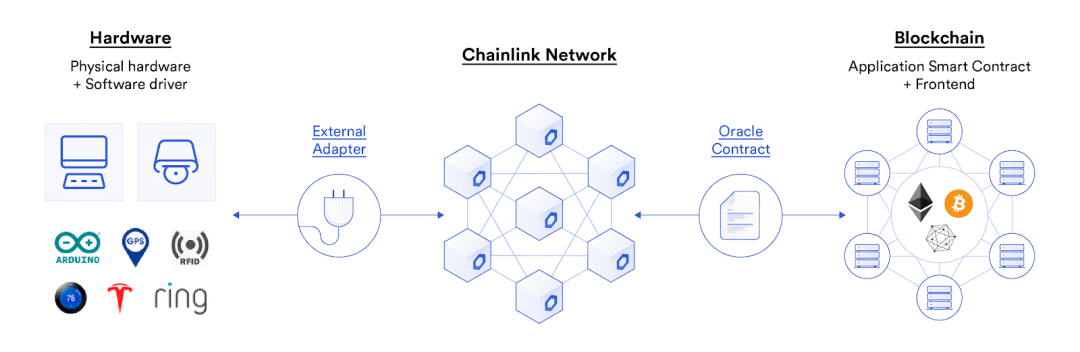
RFID tracking goods
RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) technology is increasingly used in the supply chain to track goods. The RFID system binds the goods with tags, which can be remotely identified by radio frequency. As a result, store merchandise, shipping pallets, and other common inventory management methods can be easily and efficiently tracked. With the Chainlink oracle, off-chain RFID data can be used to trigger the execution of contracts on the chain, including initiating payment after the warehouse receives the goods, or automatically triggering insurance claims when the delivery is delayed.
image description
secondary title
IoT sensor
IoT sensors can be used to ensure that goods are not damaged in transit. For example, keeping food at a certain temperature, or sealing a container, and the process cannot be manipulated. Chainlink can connect these IoT sensors with smart contracts that can trigger payments or fines based on IoT data to determine whether quality control standards meet purchase order requirements.
secondary title
Customs Clearance
secondary title
Bill of lading, invoice and insurance
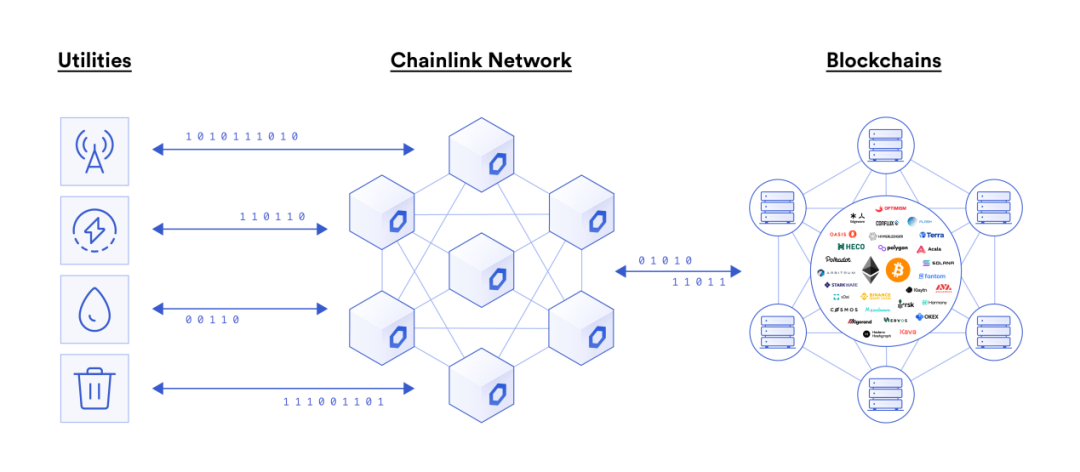
utilities
utilities
image description
secondary title
Internet, telecom and cloud services
Utilities such as internet, cable TV, and cloud services all operate on a fixed-pricing model. However, once these services fail, it can lead to serious financial losses, such as an exchange going offline due to cloud service downtime. There is often no one to take responsibility for when this happens. IoT sensors can monitor the health of the equipment, and Chainlink can transmit the performance data of the equipment to the smart contract, and calculate the price every month or compensate based on the offline time.
secondary title
electricity
Electric service providers are responsible for ensuring that all infrastructure around the world can receive electric energy to maintain the global economy. To improve the efficiency of electricity supply, Chainlink oracles can be used to transmit electricity consumption rate data to smart contracts, trigger excess fines, collect carbon emissions taxes, and provide current electricity prices, fair pricing and accept payments in different types of currencies. Smart contracts can read data from smart meters, trade electricity, track consumption and make payments.
secondary title
tap water
secondary title
Emissions and Waste Management
first level title
Identity and Authorization
electronic signature
electronic signature
Adding electronic signatures to documents is an increasingly accepted way of signing. Electronic signatures are a more advanced way of signing because the cost of obtaining handwritten signatures is very high. Signature is the most common way to authorize contracts, so Chainlink oracles must connect smart contracts to top electronic signature companies like DocuSign to ensure the reliability of signatures.
secondary title
biometric identification
image description
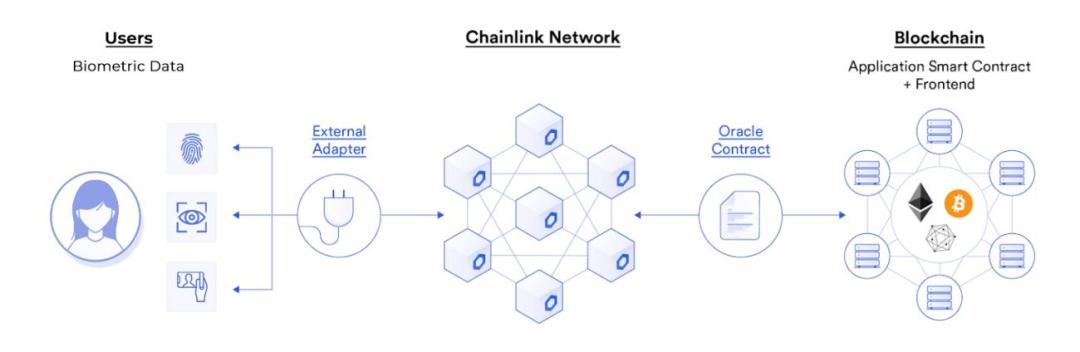
prove
prove
secondary title
KYC/AML
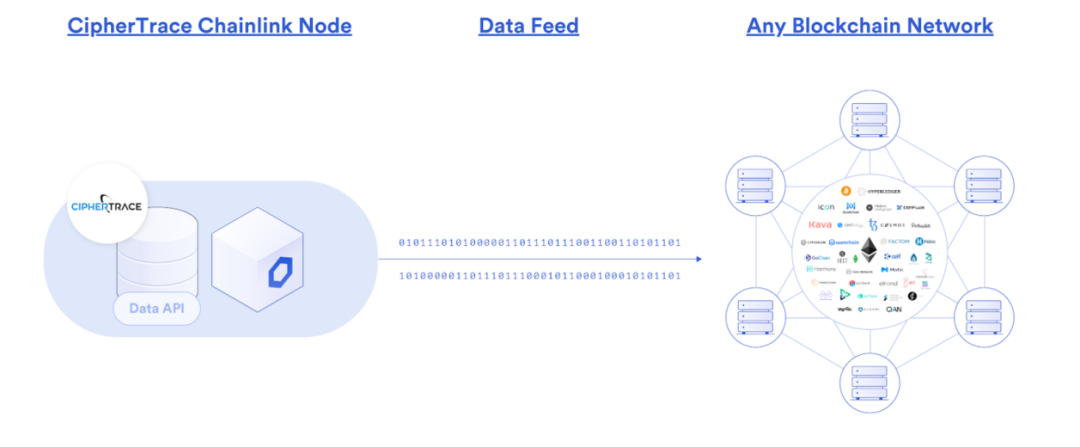
Institutions applying blockchain and smart contract technology often require additional infrastructure to ensure full compliance with KYC and AML-related laws and regulations. Therefore, it is necessary to access the oracle to provide identity information and complete historical data of funds.
Coinfirm is a blockchain analysis company that accesses Chainlink oracles to transmit data from AML solutions to the chain. This provides users with a plug-and-play solution for real-time authentication through the oracle network to ensure blockchain application compliance. in addition,CipherTracePublished on ChainlinkDeFi compliance oracle serviceimage description
secondary title
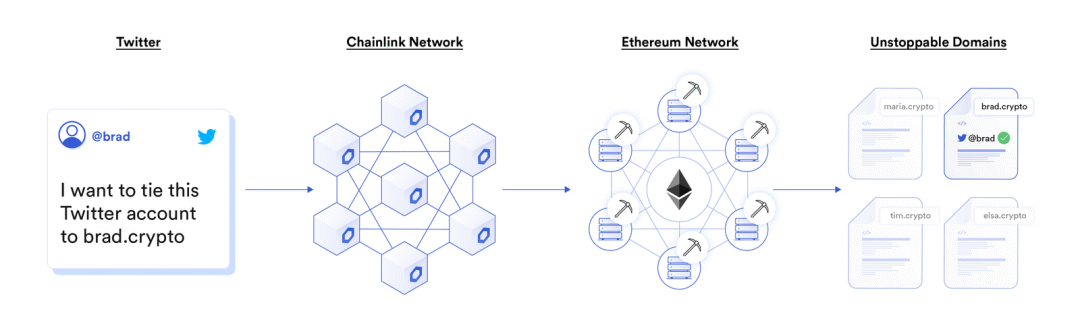
Social media identities and domain names
Blockchain is still a very new concept to many, especially sixteen-digit blockchain wallet addresses are often daunting. To further improve the user experience, an oracle can be used to convert the sixteen-digit address into a human-readable domain name, such as "chad.crpto".
image description
secondary title
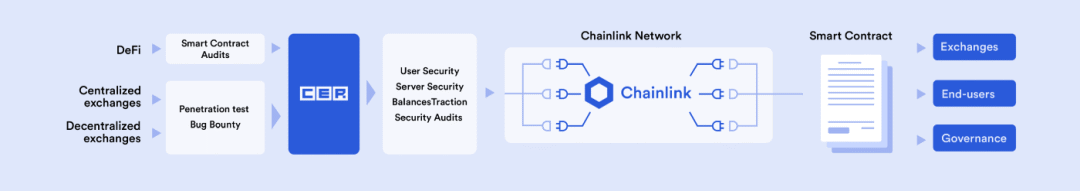
Smart Contract Audit Results
In order to ensure the security and normal functions of smart contract applications, developers may need to verify whether the protocol has passed one or more rounds of security audits before transferring funds. Users can use oracles to verify audit results directly on-chain, which will enable a whole new range of use cases, including automated reviews before conducting high-value transactions or escrowing other people’s funds.
image description
secondary title
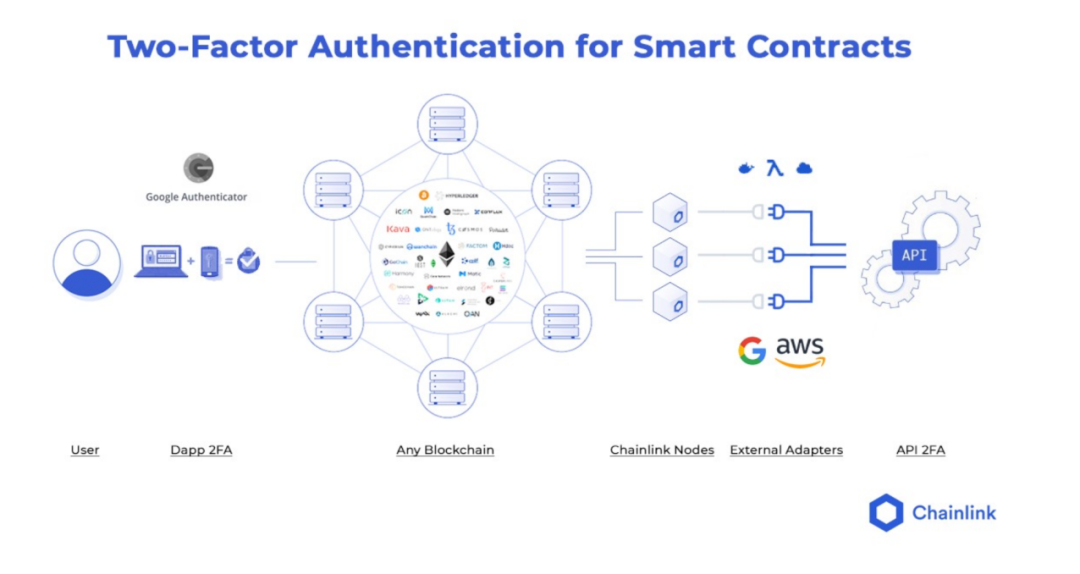
accounting security
Users can also secure online accounts using two-factor authentication (2FA), which requires another layer of verification in addition to a username and password. After the security is improved, the leakage of private information can be prevented, and multiple authentications are required to transfer money successfully. After the smart contract is connected to the Chainlink oracle machine, it can realize the 2FA function and directly protect the security of the user's cryptocurrency funds.
image description
intellectual property
intellectual property
secondary title
Bounty Programs for Open Source Communities
first level title
government
secondary title
Regulations
When enterprises apply smart contracts, they need to change the traditional compliance mode and realize automatic compliance. Some regulations can be coded into smart contracts, but governments still need access to oracles to obtain metadata from smart contracts, or require approval from government-run oracles before broadcasting transactions.
vote
vote
secondary title
Title deeds, permits and certificates
secondary title
sustainable development
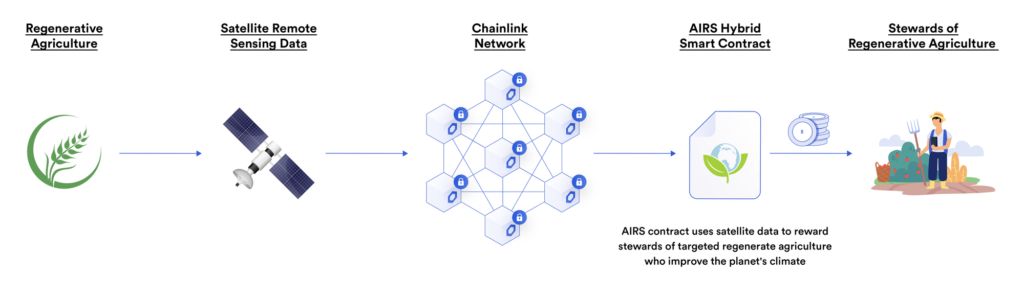
regenerative agriculture
Hybrid smart contracts combine on-chain code and off-chain sensor and satellite data, which can be used to create fully traceable, transparent and automated incentive mechanisms that directly reward individuals, businesses and governments that contribute to sustainable development, and encourage All to tackle climate change and its negative impacts. Sustainability initiatives include creating carbon-neutral tokens, regenerative agriculture, and monitoring resource consumption and rewarding behaviors that address resources.
image description
secondary title
Satellite Imagery and Drones
Although this application scenario sounds more sci-fi, it is not difficult to imagine that in the future, satellite imagery, the Internet of Things and drones can be combined to collect off-chain event data (such as: construction projects). The data can be analyzed and cross-contrasted with previous projects through artificial intelligence technology to determine the project completion rate. The Chainlink oracle machine can transmit data to the smart contract on the chain, and automatically pay the construction company after completion, which solves the problem of serious payment delays for large-scale projects.
secondary title
off-chain computation
Verifiable Random Function (VRF)
Due to the highly deterministic nature of blockchain networks, on-chain applications often do not have access to secure random number generators. Using on-chain block hashes to generate random numbers can potentially be manipulated by blockchain miners/validators, who can discard blocks that are not good for them and re-roll the dice to manipulate the random numbers. However, off-chain random numbers lack transparency, and it is impossible to verify whether the random numbers are fair and not manipulated by data sources or nodes. Chainlink's verifiable random function can solve the above problems, providing smart contracts with secure random numbers with cryptographic proofs, which cannot be tampered with by oracle nodes, users or development teams.
image description
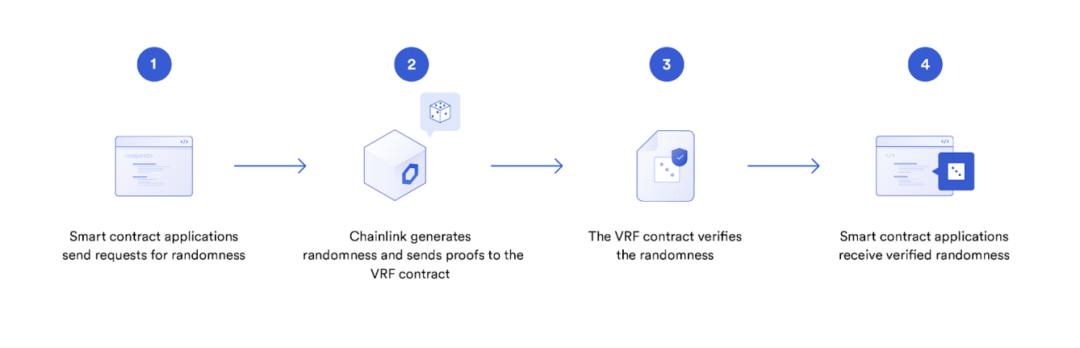
secondary title
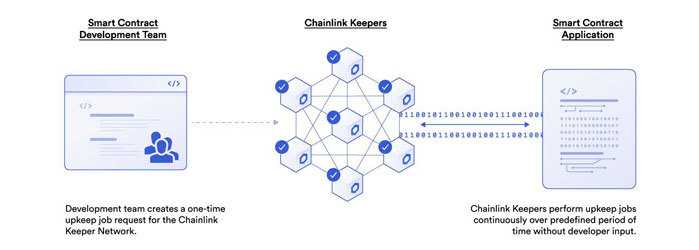
Keepers
Smart contracts are composed of code that can run on the blockchain with a high degree of certainty. However, the default state of a smart contract is "sleeping" and must be "woke up" by an external party in order to perform on-chain functions and change the contract state. Chainlink Keepers provides a solution for smart contract developers, decentralized applications, and decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs) to automatically execute any smart contract function through a reliable and cost-effective decentralized network of nodes, and maintain it regularly .
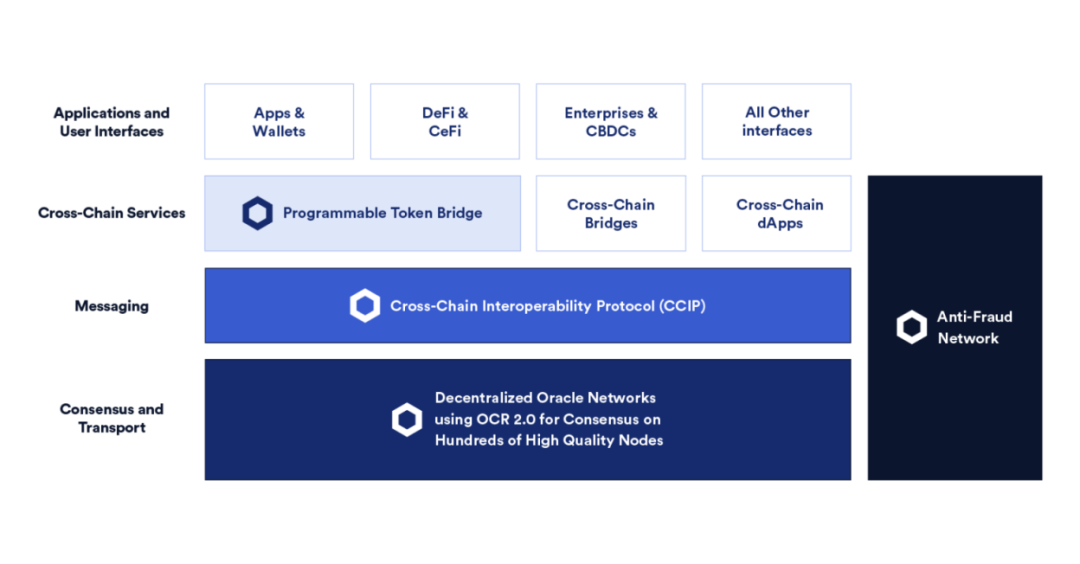
Cross-Chain Interoperability Protocol (CCIP)
Cross-Chain Interoperability Protocol (CCIP)
Cross-chain Interoperability Protocol
Cross-chain Interoperability Protocolimage description
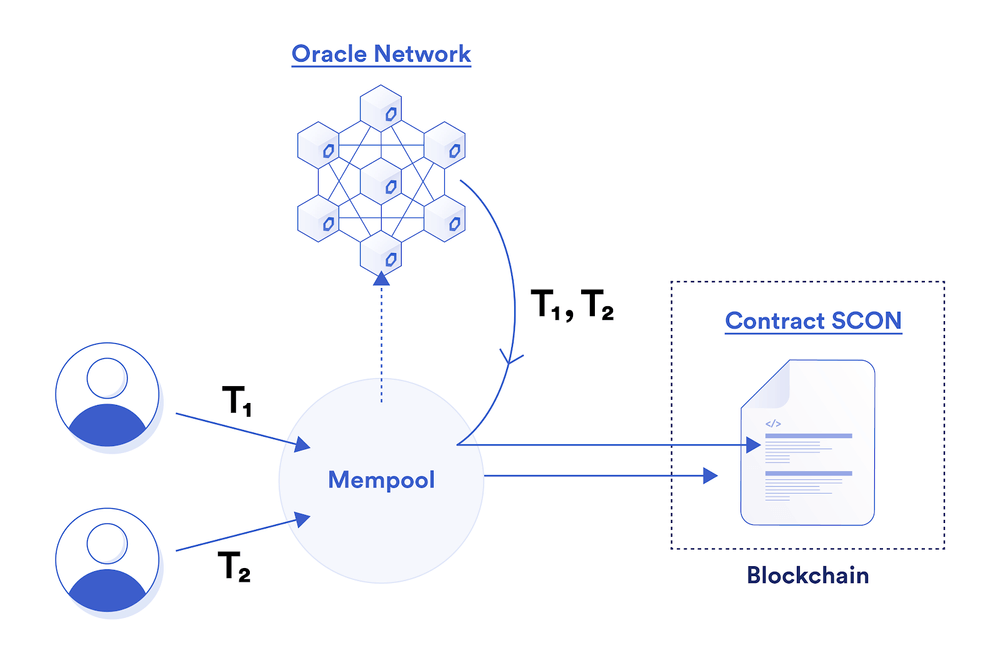
Fair Sequencing Service (FSS)
Fair Sequencing Service (FSS)
image description
secondary title
Blockchain gas price
In order to avoid spam hiding attacks, transactions on the smart contract blockchain need to use native tokens to pay gas fees to miners to verify transactions. However, the gas pricing market is often off-chain, so the smart contract needs to access the oracle to obtain the current gas price.
secondary title
fair selection of participants
With the popularity of the public sale model on the blockchain, many projects hope to select participants in a fairer way, rather than adopting a "first-come, first-served" model, which is easy to be manipulated by humans. More and more projects now randomly select participants, a model that was originally developed by centralized exchanges.
image description
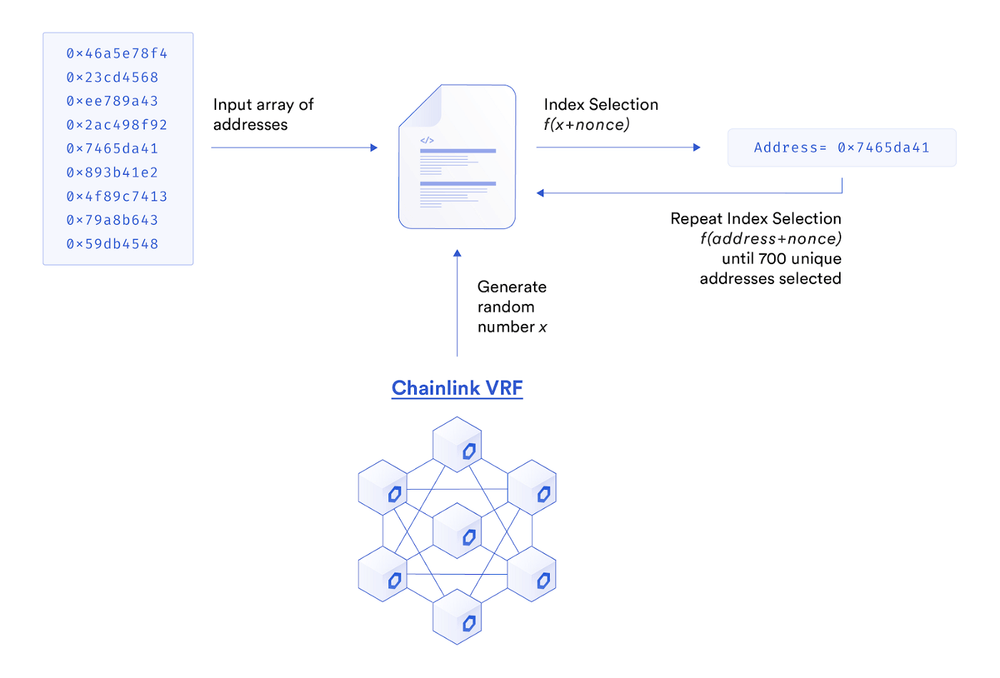
Cantaur uses Chainlink VRF to select users who participate in the public sale on the chain to ensure the fairness of the process.
secondary title
random node selection
Summarize
Summarize
Chainlink is a general-purpose decentralized oracle network development framework that provides developers with the tools they need to connect smart contract applications to any off-chain data or event. The application scenarios listed above are just some of them, and there are countless potential application scenarios of Chainlink oracles in smart contracts. We hope to serve as a catalyst for developers to develop more innovative decentralized applications.
developer documentationdeveloper documentation, and join us in theDiscordcontact us.herecontact us.



