Benfen xTX-SHIELD Privacy Payment: The first native stablecoin-driven, fully privacy-focused, regulatory-compliant, high-performance payment protocol.
- 核心观点:隐私支付应成为公链原生基础设施。
- 关键要素:
- 链层原生集成,实现性能与成本一体化。
- 内置可控隐私机制,平衡隐私与合规需求。
- 稳定币作为“一等公民”,优化支付体验。
- 市场影响:推动企业级隐私支付与合规稳定币应用。
- 时效性标注:长期影响。

This article was jointly written by Benfen and TX-SHIELD.

Privacy-preserving payments must become a native infrastructure of the blockchain layer.
In the current blockchain ecosystem, privacy is often regarded as an optional add-on feature , existing in the form of standalone DApps or Layer 2 protocols. While this "plug-in" model is flexible, it leads to performance bottlenecks, compliance ambiguity, and a fragmented user experience.
The core proposition and product positioning of this sub-chain is to completely integrate privacy payments as a native capability of the chain layer , directly built into the underlying public chain. This means that privacy is no longer an "option" that requires additional installation and multiple fees , but a basic service and platform capability that all upper-layer applications— especially the stablecoin ecosystem—can call at any time.
BenPay 's privacy payment feature will be integrated with its ecosystem application. BenPay will deeply integrate with on-chain functions such as stablecoin gas payments, sponsored transactions, and one-click RWA issuance . It will comprehensively integrate privacy capabilities across payment, transaction, and account systems, providing interface support for cross-border settlements, daily consumption, and payment scenarios, thus promoting the widespread adoption and large-scale implementation of privacy-preserving payments.
Meanwhile, this subchain collaborates with TX-SHIELD, the core infrastructure builder. The collaboration will natively embed a privacy solution based on multi-party secure computation (MPC) into the blockchain layer. This provides enterprise users with a new stablecoin settlement solution that offers high performance, compliance, and privacy .
TX-SHIELD is a technology company that develops privacy-preserving payment algorithms, providing regulatory-friendly and privacy-protecting one-stop solutions for public blockchains, stablecoin issuers, and DEXs. www.tx-shield.com 
Why must it be native to the blockchain layer? The iron triangle of performance, security, and compliance.
Embedding privacy logic into the blockchain layer is not merely a choice of technical implementation, but a profound response to performance, security, compliance, and commercialization needs.
1. Performance and cost integration: Eliminating the overhead of "plugins"
Traditional add-on methods, such as layer 2 protocols or coin mixers, often require users to pay transaction fees multiple times when transferring assets across chains, generating zero-knowledge proofs, or signing, and also incur additional delays .
- By integrating privacy-preserving computation logic with the transaction settlement mechanism, gas fees can be unified . This truly achieves "settlement once, privacy throughout," avoiding multiple fees and delays caused by breaking down proof/signature costs into cross-chain or off-chain processes.
- This native integration ensures that enterprise applications meet their essential requirements for high performance and low cost .
2. Enhanced security and "controllable privacy"
The chain layer's native capabilities allow us to deeply integrate node governance, remote proof, and auditing interfaces . This not only strengthens the decentralized trust foundation but also enables a crucial "controlled privacy" architecture.
- Privacy enforcement offers both decentralized protection and a controlled channel for "optional disclosure" when compliance is required .
- Users and organizations can use selective disclosure mechanisms to present audit credentials or regulatory information to compliance agencies when necessary, achieving a balance between privacy protection and regulatory requirements.
3. Compliance-friendly
As global financial institutions continue to raise their compliance and risk control requirements, compliance costs have become one of the key factors limiting the large-scale application of Web3.
- The chain-layer native design allows us to design compliance interfaces (selective disclosure, regulatory views, audit credentials) in tandem with privacy features.
- This compliant and user-friendly native system support can significantly reduce friction between backend integration and regulation, and substantially reduce compliance costs and access barriers for institutional users.
Architecture Comparison: Native Layer 1 vs. Layer 2 vs. Plugin
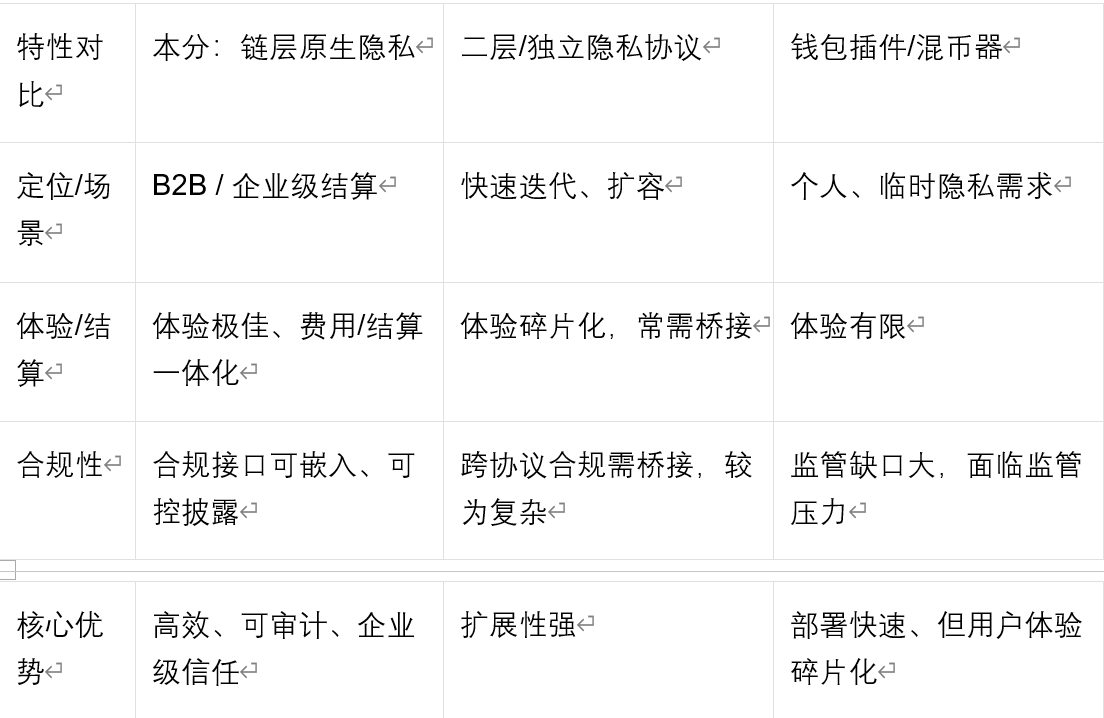
Stablecoins and privacy payments: Two sides of the same coin in the circulation of digital value and their inevitable convergence.
Throughout the history of monetary development, every leap in payment paradigms, in TX-SHIELD's view, stems from the renewed fulfillment of two core demands: stable and reliable value, and free and secure transactions. This holds true from physical currency to bills of exchange, and then to electronic payments. Today, we stand on the threshold of the next generation of payment revolution, and the deep integration of stablecoins and privacy-focused payments is the key to unlocking this door. This is not a simple superposition of two technologies, but an inevitable fusion of two sides of the same coin in the digital value circulation system—stablecoins are becoming the new standard for global payments and settlements, while privacy protection meets the rigid demand for free transactions. Like two sides of the same coin, they together define the future of payments.
Historical Inevitability: Why Integration is the Ultimate Form of Digital Payments
The cornerstone of the digital economy is the ability of value to flow efficiently and frictionlessly across global networks, much like information. However, existing solutions suffer from structural flaws:
- Traditional electronic payments rely on centralized intermediaries, cross-border payment fees are expensive, and user data is monopolized by the platform, making privacy impossible.
- Stablecoins on transparent blockchains: As the on-chain representation of fiat currency value, stablecoins solve the most fundamental problems of value measurement and settlement medium in the digital economy. They make on-chain payments efficient, low-cost, and globally available. Stablecoin transaction volume has already accounted for a significant and continuously growing proportion of all on-chain transactions, particularly prominent in corporate settlements and cross-border payment scenarios. However, value stability does not guarantee complete trust . In a fully transparent and traceable on-chain ledger environment, every transaction represents a leak of trade secrets. Professional on-chain analytics tools can clearly identify a company's wallet business model, operating costs, and even strategic procurement and liquidation behaviors within a very short transaction process (even just a few key transactions), posing significant competitive risks to businesses.
- Privacy coins: They solve privacy issues, but due to their volatile prices and lack of broad anchors, they cannot function as a payment standard or medium.
Therefore, history will inevitably choose a path that leads to the native integration of stablecoins, the best payment medium, with privacy payments, which guarantee freedom of transaction. This is the necessary path for payment tools to mature .
1+1>2: How integration can give rise to new paradigms that cannot be achieved by a single technology
When stablecoins and privacy payments are deeply coupled at the underlying layer of the blockchain, the synergistic effect they produce far exceeds the functional overlap.
The shift from "compliance costs" to "compliance advantages"
TX-SHIELD argues that traditional privacy solutions often conflict with compliance requirements for financial institutions, forcing them to make difficult choices between "transparent exposure" and "privacy violations." BenFen Chain natively integrates privacy payments with stablecoins at the blockchain layer, incorporating a built-in "controlled privacy" mechanism. This means that businesses can use stablecoins for fully compliant payments while protecting transaction details by default, providing proof only through selective disclosure when required by regulatory bodies (such as audits or judicial investigations). This transforms privacy from a "compliance risk" into a "compliance and competitive advantage."
An ecological explosion from "limited scenarios" to "unlimited possibilities"
The combination of these two technologies unlocks business scenarios that were previously impossible due to privacy or payment barriers:
• A paradigm shift in global payroll and supply chain finance:
Multinational corporations can use stablecoins to pay salaries to their global employees in real time, protecting individual privacy while enabling personalized financial processing through programmability. Within the supply chain, core enterprises can build an "auditable privacy settlement network" where stablecoin transactions between upstream and downstream companies are encrypted to the public, but the compliance of the entire network can be demonstrated to regulatory agencies, significantly improving the efficiency of fund transfers and risk control.
• The “institutional-grade” upgrade of DeFi:
Traditional DeFi has been criticized by institutions for its lack of transparency in trading strategies. On this blockchain, "privacy-first" institutional-grade DeFi can emerge—such as lending based on confidential transactions and DEXs that prevent early access attacks. Large institutional funds can enter safely while protecting the privacy of their strategies, bringing unprecedented depth and liquidity to DeFi.
• Next-generation consumer applications and the data sovereignty economy:
Users can use stablecoins to pay subscription fees and purchase digital goods, while their consumption behavior patterns, identity information, and asset holdings will be effectively protected, truly achieving "payment as a service, leaving no data trace." This lays the foundation for Web3 business models built on true data sovereignty.
Stablecoins and privacy-focused payments are two core engines driving the maturity and scaling of on-chain economies. BenFen Chain 's unique positioning lies in deeply coupling these two engines to create a public chain infrastructure specifically designed for high-frequency, high-value payment scenarios . Choosing BenFen Chain means choosing a compliant, secure, and efficient stablecoin payment ecosystem, directly stepping into the next stage of digital payments.
BenfenChain : A "Highway" Built for Privacy-Focused Payments
Building a blockchain network capable of supporting large-scale commercial-grade privacy payments requires overcoming the performance overhead and economic friction caused by privacy computing at the underlying architecture level. The full-stack system co-developed by this sub-chain and TX-SHIELD, encompassing programming languages, consensus mechanisms, and economic models, is designed to systematically dismantle these barriers, constructing a secure, efficient, and usable triple foundation for institutional-level privacy payments.
3.1 Move Language: "Mathematical-Level Trust" Built for the Security of Privacy Assets
The core of privacy payments lies in protecting the security of on-chain assets and ensuring correct operational logic. This subchain uses the Move programming language , specifically designed for digital assets, providing far superior security guarantees for privacy payments from the ground up.
• Inherent security safeguards: Move's rigorous type system and unique resource management mechanism eliminate common fatal vulnerabilities in smart contracts, such as reentrancy attacks and resource exhaustion , during compile time. This ensures that the core contract logic involving the flow of privacy assets is rigorous and that the asset status is clear and unambiguous.
• Reliability Guarantee: Move uses its unique Move Specification Language (MSL) to define preconditions, postconditions, and invariants for smart contracts, describing from the source "how the program should run correctly." During the compilation phase, these specifications are translated into Boogie language expressions and logically verified by an automated theorem prover. This process allows contracts to be mathematically verified for security and correctness before being added to the blockchain, minimizing runtime errors and vulnerabilities, thereby achieving a verifiable, predictable, and trustworthy on-chain execution environment.

3.2 High-Performance Consensus: The Powerful Computing Power to Overcome the "Performance Tax" of Privacy Computing
Privacy-preserving computation inherently involves computational overhead and latency; top-tier performance is essential for its application in high-frequency commercial scenarios. This subchain's innovative DAG-based hybrid consensus mechanism successfully addresses this challenge.
• Sub-second latency and tens of thousands of transactions per second: By differentiating transaction types and employing a "fast path" for transactions that do not involve shared objects, this subchain achieves a transaction processing time of less than 0.5 seconds and a consistently high throughput of tens of thousands of transactions per second (TPS). This performance enables computationally intensive privacy transactions to achieve an "instant completion" experience, fully meeting the real-time requirements of commercial settlement.
• Exceptional robustness and availability: This consensus mechanism is highly fault-tolerant (the network can still operate stably even if some validator nodes fail). This 24/7 uninterrupted high availability is key to the reliability of privacy payment services comparable to traditional financial infrastructure.
3.3 Stablecoins as "First Citizens": Eliminating Economic Friction
One of the most revolutionary designs of this blockchain is elevating stablecoins to the status of "first citizen" at the public blockchain level. This is the economic cornerstone for eliminating barriers to user adoption and enabling mass adoption.
• Native integration, payments equal privacy: Privacy payments operate directly on the native stablecoin of this subchain, without the need for complex cross-chain bridges or encapsulated assets . This achieves an atomic-level combination of payments and privacy protection at the chain layer, completely eliminating intermediate steps that introduce additional security risks and friction costs.
• Web2-level smoothness: Users can directly pay transaction fees with stablecoins without having to acquire and hold native tokens as gas in advance. This design minimizes the barrier to privacy payments, providing a user experience as smooth and natural as using Web2 tools, and is key to driving large-scale commercial adoption.
3.4 Modularity and Universality: Flexibility for a Future Privacy-Focused Payment Ecosystem
BenFen Chain leverages the modular design and high-level abstraction capabilities of the Move language to provide great flexibility and reusability for the development of upper-layer applications for privacy payments.
• Secure modular reuse: Developers can reuse formally validated security modules like building blocks to quickly build complex privacy payment logic.
• Universality and Future Compatibility: Although this subchain is centered around stablecoins, its underlying architecture and Move module possess universal privacy payment capabilities , compatible with any asset. This flexibility ensures that the infrastructure not only meets current stablecoin payment needs but also adapts to future evolving business scenarios and innovation requirements.
This subchain is not a public chain that adds privacy features after the fact, but rather an infrastructure deeply customized for privacy payments . Its full-stack technology selection—from secure Move and high-performance DAG consensus to frictionless stablecoin native integration —together constitutes a top-tier infrastructure that provides comprehensive support for next-generation privacy payments in terms of security, performance, usability, and user experience.
How does this subchain enable privacy payments?
This subchain's privacy payment function, through its partnership with TX-SHIELD, aims to provide users with a smooth experience while ensuring the confidentiality of critical information. Our design implements a complete closed loop—from the privacy-preserving creation of assets to secure value transfer and controlled viewing and redemption . Through technological integration with TX-SHIELD, privacy protection becomes a fundamental feature of the payment system, rather than an add-on function.
Creating Privacy Assets: A One-Step Privacy Solution Starting with Top-Up
This blockchain features an improved architecture that prioritizes privacy options. Users can decide whether to deposit tokens in a privacy-preserving format during the deposit process , eliminating the need for multiple steps and providing a smoother experience.
Specific procedures:
1. Initiate privacy top-up or privacy token conversion :
When users select to deposit tokens in their wallet, they can check the "Deposit as Privacy Tokens" option. Additionally, users can initiate an "Asset Encryption" transaction through their wallet, specifying the tokens and amount they wish to convert to a privacy-oriented form.
2. Asset Lock-up :
Once the transaction is confirmed online, a special smart contract will automatically lock the tokens converted by the user as the value backing for the privacy asset that will be created.
3. Value Sharding :
After receiving the value, the network verification node uses its internal shared key and encryption algorithm to convert the value into a unique set of random data fragments.
4. Voucher generation :
The system creates a new "privacy asset" object for the user and stores the newly generated data fragments into it.
5. Completed :
Once the transaction is recorded on the blockchain, the user's public tokens are locked, and they receive an equivalent privacy asset in the form of encrypted shards. The true value of this asset is no longer visible on the blockchain.
This "recharge equals privacy" mechanism eliminates the barrier for users to acquire privacy assets, making privacy protection the default option for on-chain operations, rather than a complicated additional process.
Privacy payment
Once users hold privacy assets, they can complete payments without exposing transaction details.
The following example, using user A paying user B, illustrates the core process of privacy-preserving payments:
1. Transaction Construction :
A's wallet creates a transaction, specifying B as the recipient and setting the payment amount. It then sends an authorization request to a trusted verification node, requesting that the payment amount be processed into temporary cryptographic fragments.
2. Submit to the network :
The wallet packages the necessary information for executing the transaction into a single transaction and submits it to the network. The transaction will include a shard of A's current balance, a shard of B's current balance, and a cryptographic shard representing the transaction amount obtained in the previous step.
3. Background processing :
After receiving the transaction, the network verification node will use the shared key to decrypt and process the three fragments, and then re-encrypt the results into new encrypted fragments.
4. Status Update :
The calculation generates two new sets of data shards—one representing the new balance after A's decrease, and the other representing the new balance after B's increase. The system then updates these two new shards into the privacy asset objects of A and B, respectively.
5. Transaction completed :
Once the transaction is recorded on the blockchain, the transfer of value is complete. For any other on-chain user, they can only see that the data in A and B's privacy asset objects has changed, but they have no way of knowing the specific transaction amount.
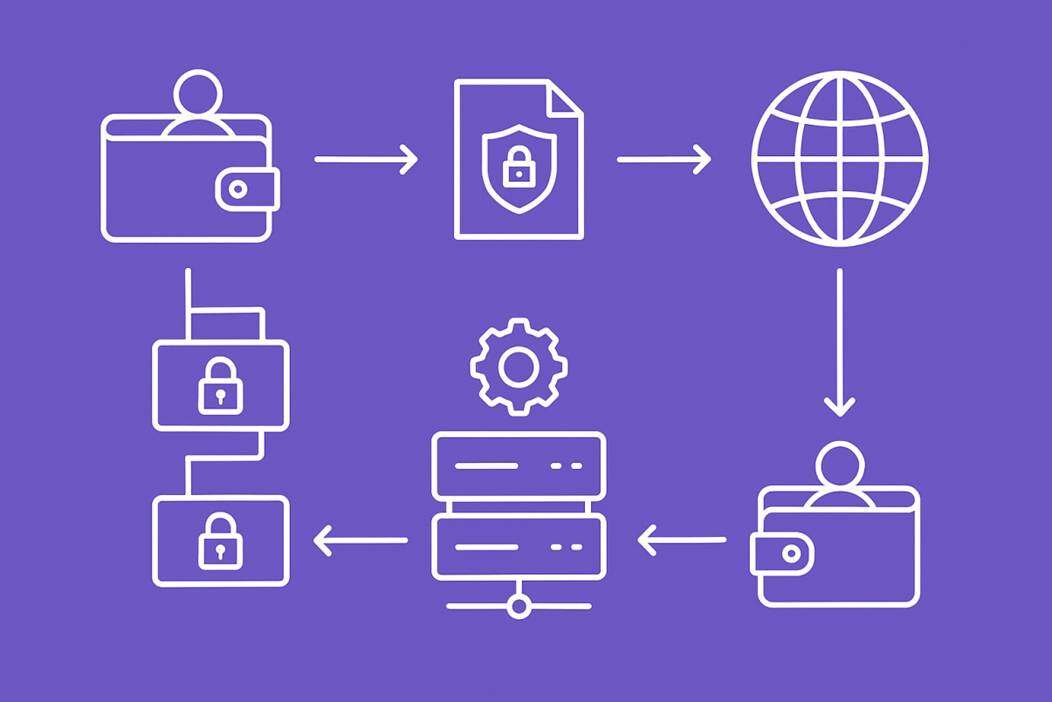
Viewing and redeeming privacy assets
1. Initiate a request and sign it :
The user sends a request to a trusted network node via their wallet. This request includes a digital signature generated from the user's wallet private key to prove ownership.
2. Authentication :
Upon receiving a request, the node verifies the validity of the signature, confirming that the requester is the legitimate owner of the privacy asset recorded on the blockchain. Authentication is primarily used to prevent unauthorized access by other users.
3. Off-chain restoration :
Once the verification is successful, the trusted node will read the user's encrypted shards from the chain and, in its local memory, use a shared key to restore these shards into a real balance value that the user can read.
4. Safe return or redemption :
View : The actual balance will be sent back to the user's wallet front end for display through a secure encrypted channel.
Redemption : Users can authorize this transaction to destroy their privacy asset credentials on-chain. Once the network confirms the destruction, the initially locked equivalent amount of public tokens will be automatically released and returned to the user.
This subchain's privacy payment system constructs a complete, verifiable, and regulated closed loop through three stages: privacy-preserving deposits, sharded encrypted transfers, and controllable transparent redemptions . This system is not an external plugin or an added feature of the protocol layer, but rather a native capability of the public chain's underlying layer. It makes privacy protection the default option, ensures the inherent confidentiality of stablecoin settlements, and enables businesses and individuals to achieve truly private payments while remaining compliant. On this subchain, privacy is no longer "additional protection," but rather an integral part of the payment process itself.
The core technology of this blockchain privacy payment
Confidential transaction system architecture based on FAST MPC and regulatory intervention
This blockchain-based privacy payment system, in collaboration with TX-SHIELD, systematically innovates by integrating blockchain technology (Block Node), Fast Multi-Party Computation (FAST MPC), and regulatory compliance mechanisms (Regulator) to achieve "data usable but invisible" asset transfers in a distributed network.

I. Core System Objectives
The main goal of this system is to resolve two core contradictions in traditional blockchain transactions: privacy protection and regulatory compliance. Privacy protection means that when user A transfers assets to user B, sensitive information such as the transaction amount and the identities of the participants will not be publicly exposed on the chain in plaintext, ensuring the confidentiality of the transaction content. Regulatory compliance means that while protecting privacy, the system can reserve necessary mechanisms to allow authorized regulatory agencies to securely and controllably disclose and audit transaction details under specific needs. Specific details on how to implement this function using FAST MPC will be described later. Furthermore, in the currently released version, all privacy payments on this subchain are implemented using MPC; however, a more complex and feature-rich new version combining MPC and FHE will be gradually released in subsequent iterations.
II. Key Technology Components
This system has several core components: Block Node, Fast Multi-Party Computation (FAST MPC), and Key Sharding. These will be introduced below:
1. Block Node
Block nodes are the core of a distributed ledger system, responsible for transaction verification, consensus, and storage. All transactions (whether Plain TX or Confidential TX) must be processed by these nodes.
2. Fast Multi-Party Computation (FAST MPC)
FAST MPC is the core technology for privacy protection in this system. MPC allows participants to collaboratively compute a predetermined function without revealing their individual input data. "FAST" emphasizes the performance and efficiency optimizations of this MPC scheme to meet the high throughput requirements of blockchain. The MPC module runs internally within the Block Node, primarily responsible for handling Key shards and User Private Meta Data for generating or verifying confidential transactions. In the initial version of this subchain, FAST MPC had relatively limited functionality. However, through research by STL, a more advanced MPC version was developed that can be integrated with other cryptographic protocols such as HE, adding more functionality and enabling participation in transactions. This improves transaction privacy and security under regulatory oversight and provides a faster and more convenient batch operation version.
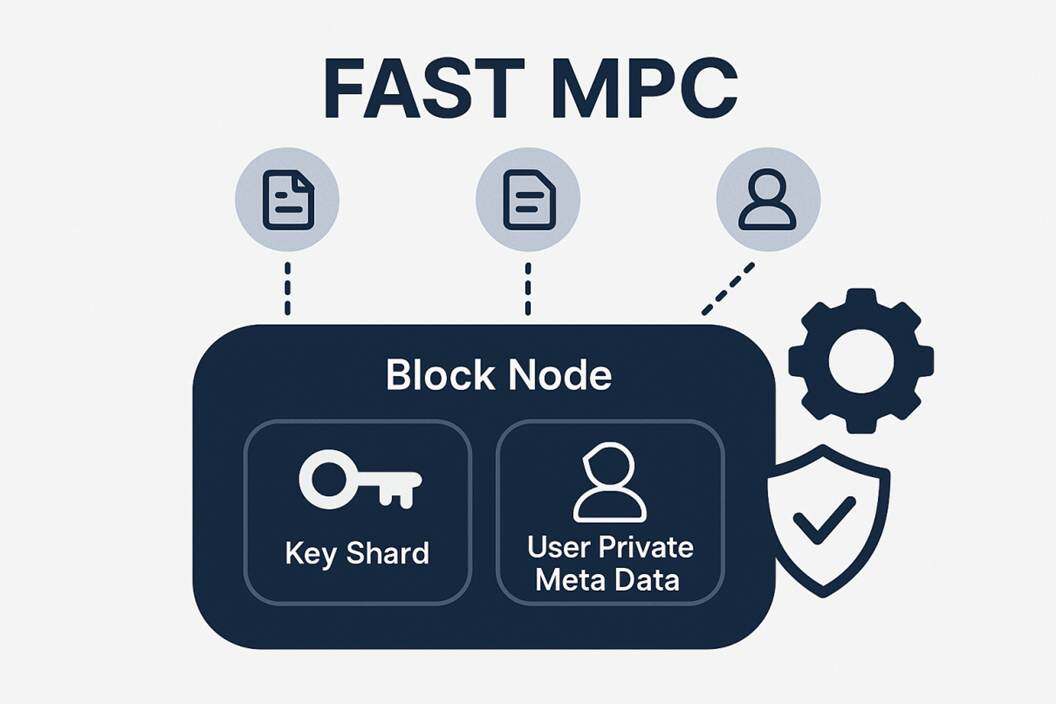
3. Key sharding
This is a key element for achieving data security and regulatory intervention, generated by the FAST MPC module.
User private metadata is encrypted or fragmented into multiple key shards, held by different entities (such as Block Nodes and Regulators). Only by aggregating key shards from different sources (such as shards from Block Nodes and shards from Regulators) can the core User Private Meta Data be accessed or decrypted.
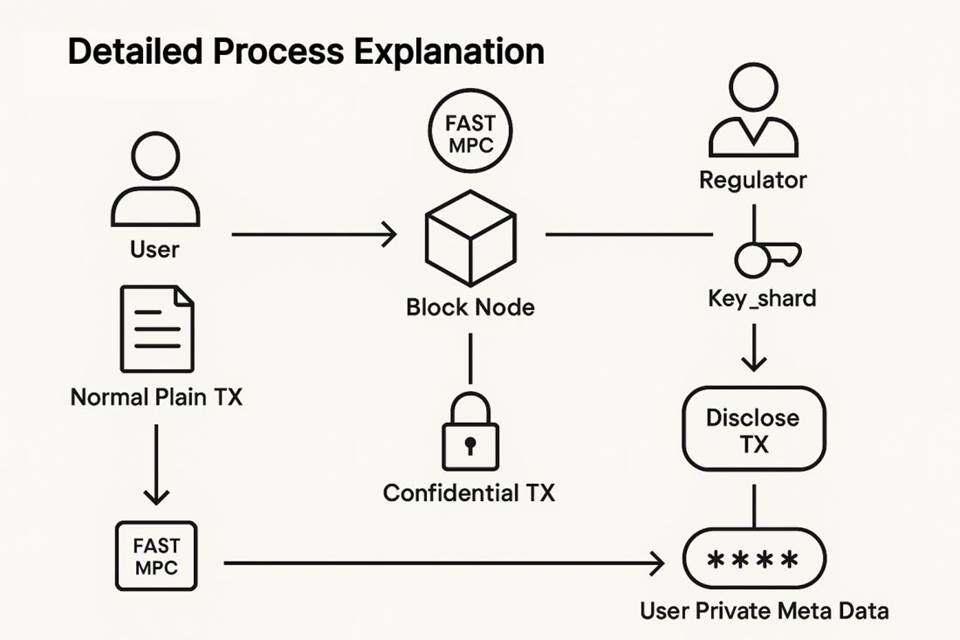
III. Detailed Process Explanation
1. Initiate a normal transaction: A user initiates a Normal Plain TX (transaction in plain text) to transfer assets.
2. Generate a Confidential Transaction: The transaction enters the Block Node. The system's FAST MPC module uses its held key to shard and process the User Private Meta Data, generating an encrypted Confidential TX. This confidential transaction is then sent back to the Block Node for on-chain processing.
3. Regulatory Intervention Point: The Regulator is a special participant in the system that holds the Key_shard.
4. Transaction Disclosure: When a transaction needs to be monitored or audited, the Regulator initiates a Disclose TX request. This request, along with the Key_shard held by the Regulator, flows to the User Private Meta Data. This means:
a. The key sharding of the Regulator is combined with the sharding of the Block Node to restore or access User Private Meta Data.
b. Only after the regulatory process is triggered and the Regulator's permissions are verified can the contents of Confidential TX be disclosed conditionally and in a controlled manner through MPC or decryption mechanisms.
Highlights and differentiating advantages of this blockchain-based privacy payment system
On the road to mainstream blockchain applications, privacy and user experience are often mutually exclusive. BenfenChain elevates privacy-preserving payments from an "optional feature" to a native chain-layer capability. Through several protocol-level and product-level innovations, it significantly lowers the barrier to entry and meets institutional compliance requirements. The following are the core highlights and differentiating advantages of Benfen's privacy-preserving payments.
Comprehensive privacy protection
Privacy protection is no longer limited to the amount of assets, but extends to all sensitive dimensions of transactions, and provides different levels of protection through cryptographic primitives.
- Complete transaction data concealment
Core Technology: Deeply integrated MPC protocol and zero-knowledge proofs. The transaction initiator collaborates with participants off-chain via the MPC protocol to generate the transaction. During this process, all key fields such as the transaction's input amount, output amount, sender address, receiver address, and asset type are converted into encrypted states or commitments, with only the final valid state change result synchronized to the blockchain. Network nodes can only verify the correctness of the state transition and cannot infer any original transaction information, fundamentally cutting off the possibility of on-chain data analysis.
- Bulk privacy transactions and group settlement
Core Technology: MPC batch processing based on verifiable encryption and aggregated signatures. By embedding a verifiable random function into the MPC protocol, a batch of transactions is assigned a batch-verifiable anonymous identifier. This allows verifiers to perform a one-time validation of the entire batch of transactions, rather than processing them one by one.
- Private asset transfer
Core Technology: Key Encryption and Access Control. Each encrypted transaction record is associated with one or more symmetric/asymmetric keys. Only the party holding the corresponding decryption key can decrypt and view the transaction details. This achieves a return to data ownership, ensuring that transaction records become a private diary accessible only to the relevant parties, rather than a public ledger.
- Temporary visibility authorization
Core Technology: Attribute-based encryption or proxy re-encryption. When transaction information needs to be provided to auditors, regulatory agencies, or judicial authorities, key owners do not need to expose all their private data. They can authorize a third party to decrypt specified transaction records within a specific time period by generating a time-limited, scope-specific access token or performing a proxy re-encryption operation. Access rights automatically expire after the authorization period.
Built-in and programmable manageability
Regulatory compliance is not an external feature added after the fact, but is designed as a core feature at the protocol layer to achieve a balance between "privacy protection" and "regulatory compliance".
- Selective disclosure
Core Technology: Zero-knowledge proofs and a hierarchical key system. Different attributes of a transaction are encrypted and controlled by different keys or zero-knowledge proof systems. Users can selectively disclose specific information without exposing all data, based on regulatory or business needs. For example, they can prove to tax authorities that a transaction amount meets a certain threshold without revealing the counterparty.
- Enterprise-level audit node authorization
Core Technology: Threshold Signatures and Dynamic Access Control. Enterprises can preset audit policies and distribute access keys for certain transaction data to designated audit nodes in a threshold manner through smart contracts or off-chain protocols. Only when preset conditions are met can the key be reconstructed and data accessed, ensuring both internal governance needs are met and preventing single-point abuse of power.
- Protocol layer embedded compliance interface
Core Technology: Modular cryptographic suite and standardized regulatory API. Cryptographic components such as MPC, FHE, and ZKP are not invoked as add-on APIs, but rather are integral parts of the consensus mechanism and state transition functions. Regulatory rules can be executed through verifiable computation in the offline phase of MPC or in on-chain smart contracts, ensuring that compliance checks are completed automatically without compromising privacy.
- Decryption threshold mechanism based on legal procedures
Core Technology: Distributed Key Generation and Threshold Decryption. The system pre-defines a supervisory public key jointly controlled by multiple parties. Corresponding private keys are held in fragmented, threshold-based arrangements. Only upon obtaining a legitimate legal order can these independent parties collaboratively execute the threshold decryption protocol to recover the master key and decrypt the transaction history of a specific address. This process is transparent, auditable, and requires multi-party collaboration, preventing unilateral monitoring.
High-performance architecture and implementation
Through cryptographic innovation and system architecture optimization, the bottleneck of low performance in traditional privacy technologies has been overcome.
- An improved architecture integrating MPC and advanced cryptography (expected implementation)
○ Core Technology: FHE-MPC Hybrid Model and Recursive Combinatorial Proof. We plan to adopt a layered cryptographic architecture. At the bottom layer, fully homomorphic encryption is used for encrypted computation of data, ensuring that the data is never decrypted during computation. At the upper layer, the MPC protocol is responsible for coordinating the computation of FHE and handling complex logical judgments. In addition, recursive zero-knowledge proofs are used to aggregate multiple transactions or state updates into a single, small-volume proof, greatly reducing the overhead of on-chain data storage and verification, and achieving "fully encrypted sharding and recovery".
- Second-level privacy confirmation time
Core Technology: Currently, all processing is done online, but future plans include a two-stage offline/online computation and pipeline optimization. The vast majority of computationally intensive operations are pre-completed offline. The online stage only requires lightweight verification, signing, and consensus protocols. This design decouples on-chain confirmation time from transaction complexity, ensuring second-level on-chain confirmation regardless of the complexity of the backend logic. Our benchmark tests show that on standard commercial hardware, the system can conservatively handle 1,000+ privacy transactions per second, and with algorithm optimization and hardware acceleration, performance has the potential for orders of magnitude improvement, fully meeting the needs of future high-frequency financial transactions.
Ultimate User Experience
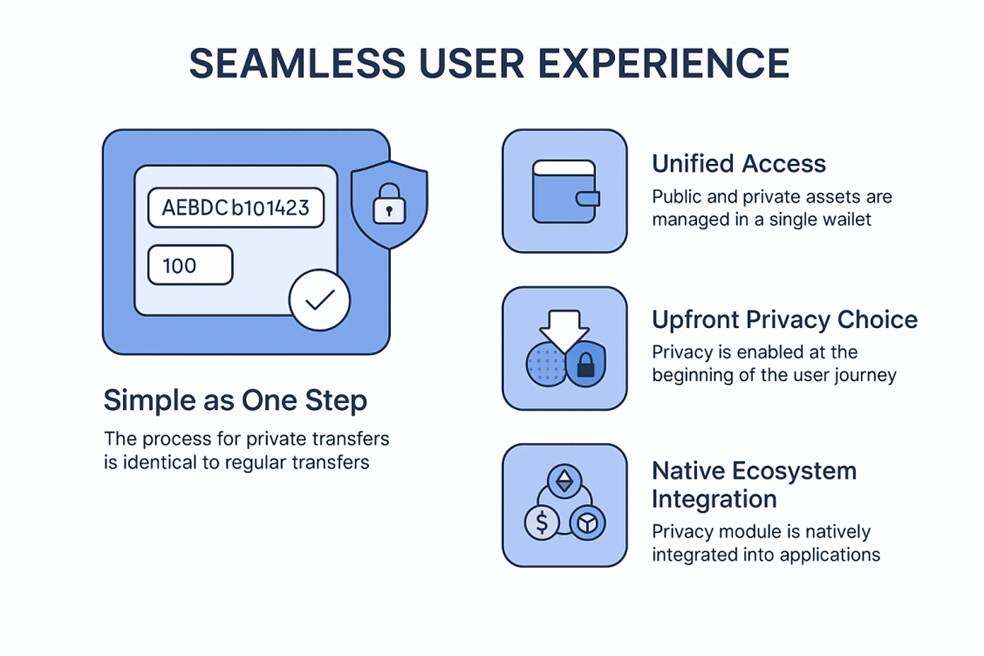
Traditional blockchain privacy features are usually "plug-in," requiring users to learn the operation process separately. This blockchain, however, aims to make privacy protection a seamless, default experience for users.
The process is as simple as a regular transfer: users complete the same privacy-protected transfer as any other. Simply enter the address and amount in the wallet and confirm; privacy protection is then automatically handled in the background, eliminating any additional learning curve. This design philosophy aligns with the industry's exploration of ways to improve blockchain usability.
Unified access management: Users can seamlessly manage public and private assets under a single wallet address without needing to install multiple wallets or plugins, and can view the corresponding balances at any time. This unification greatly simplifies asset management for users.
Pre-payment privacy selection: By designing features such as "privacy-based payment", privacy selection is brought forward to the payment process, making privacy protection the starting point of the user journey, rather than an additional option for remediation afterward.
Native Ecosystem Collaboration: Upper-layer applications such as the BenPay ecosystem, RWA issuance, and DeFi protocols can natively call the privacy module for a seamless integration experience. Taking BenPay DeFi Earn and BenPay Card as examples, when users participate in earning strategies, processes such as deposits, share changes, and redemptions are encrypted using BenFen's native privacy module. The protocol can verify the validity of operations, but external parties cannot see the user's position, profit scale, or portfolio adjustments, making BenPay DeFi Earn a privacy-protected DeFi entry point. When users use BenPay Card... When making online payments or offline purchases, the amount, payment path, and account information are encrypted, and merchants cannot see the user's on-chain assets. Observers cannot build a consumption profile, thus achieving a privacy-preserving stablecoin payment experience and a truly usable Web3 consumption experience. Relying on Layer 1's native privacy design, the entire ecosystem maintains a consistent and seamless privacy experience across payments, transactions, consumption, and asset allocation.
Zero Gas Fee Experience
Gas fees are one of the main barriers preventing ordinary users from entering the Web3 world, especially from using computationally complex privacy features. This subchain reshapes the transaction cost structure through protocol-layer innovation.
Sponsored Transactions: This subchain natively separates the roles of "transaction initiator" and "gas payer" at the protocol level. This allows project teams or merchants to directly pay gas fees for users in a simple, secure, and efficient process. For users, this means they can completely ignore and pay gas fees when using privacy payments.
Stablecoin Gas Payment: Users can also use the system's native stablecoin to pay gas fees directly without holding additional tokens, simplifying asset allocation.
Native stablecoin architecture
Unlike stablecoins that rely on smart contracts for issuance, this subchain builds multi-currency stablecoins as "first-class citizens" at the chain layer, which provides a more solid and reliable underlying support for privacy payments.
Chain-native, security paramount: As the native asset of the public chain's underlying layer, stablecoins do not rely on the logic of smart contracts, fundamentally avoiding the risk of contract vulnerabilities and thus offering higher security.
Ecosystem scalability
The value of a technology depends on the prosperity of its ecosystem. This subchain lowers the barriers to entry for developers and merchants through its open design.
Standardized integration: Provides fully functional and clearly documented SDKs and APIs, facilitating the rapid integration of privacy payment functionality into third-party wallets, merchant systems, and cross-chain bridges, significantly reducing development costs.
Support for decentralized commerce: Whether it's a centralized e-commerce platform or a decentralized DApp, both can quickly deploy privacy-preserving payment modules using the tools provided by BenPay, offering users more diverse payment options. BenPay's integration also validates the feasibility of this capability in real-world payment scenarios, providing a template for future commercial applications.
Bulk Privacy Payments
For high-frequency, multi-target payment needs such as corporate salary payments, project airdrops, and community rewards, this chain's batch privacy payment function perfectly combines efficiency and privacy.
Increased efficiency: Users can accurately distribute their privacy assets to hundreds or even thousands of addresses in a single operation by selecting groups or uploading Excel templates, completely eliminating tedious single operations.
Privacy and compliance protection: All bulk transactions are completed in a privacy computing environment, ensuring that the amount and recipient information of each transaction are kept completely confidential, protecting both the privacy of the recipient and the confidentiality of the financial information of the sender.
Privacy payment in any currency
Oracle Support: This subchain's privacy payment mechanism does not rely on any specific asset type. As long as the asset has the system's supported settlement and accounting capabilities, it can be integrated into the privacy payment system. Users can freely choose to convert tokens into privacy-preserving forms to achieve one-click privacy transfers and receipts.
This blockchain's privacy payment system, through native innovation, encapsulates complex privacy technologies within a simple user experience; its revolutionary zero-gas-fee model removes the barrier to entry for users; its underlying integration with native stablecoins lays the foundation for security and globalization; and through an open ecosystem and efficient batch processing capabilities, it extends its capabilities to various scenarios from individuals to enterprises. This marks the maturity of a truly complete solution that balances privacy, usability, and scalability. It is not only a technological breakthrough but also a crucial step towards mainstream blockchain privacy payments.
This subchain's privacy execution capabilities are natively integrated at the chain layer based on TX-SHIELD's underlying cryptographic structure, together forming the infrastructure for stablecoin privacy settlement. As the system evolves, we will continue to deepen our capabilities in cryptographic execution, regulatory architecture, and institutional-grade payment scenarios, promoting the large-scale implementation of privacy settlement in the financial and commercial sectors.
About BenFen
BenFen is a high-performance public blockchain built specifically for stablecoin payments. Based on the Move programming language, we have created a secure, low-cost, and highly scalable underlying network. Its core feature is the ability for users to directly pay gas fees with stablecoins, significantly lowering the barrier to entry and paving the way for large-scale applications. Building upon powerful cross-chain and multi-currency settlement capabilities, BenFen covers diverse payment scenarios through a rich ecosystem of applications. More importantly, we provide enterprise users with crucial privacy payment options, ensuring they can enjoy the efficiency advantages of blockchain while protecting their core business data from leakage.
Benfen is committed to becoming a global stablecoin circulation network serving corporate payroll, cross-border payments, e-commerce, and offline merchants—a next-generation financial infrastructure that balances efficiency, cost, and security.
Regarding TX-SHIELD
TX-SHIELD is a regulatory on-chain privacy settlement infrastructure that provides stablecoins and blockchain applications with privacy-preserving and regulatory-visible payment and settlement capabilities.
Core Solution:
- Tx-SHIELD: A privacy infrastructure for blockchain applications, enabling confidential transactions, dark pools, and a privacy-centric protocol layer.
Our innovations:
We not only protect transaction privacy, but also reshape asset ownership and security through distributed cryptography. TX-SHIELD's solution enables enterprises and financial institutions to achieve joint asset custody, privacy-based clearing, and regulatory compliance auditing without disclosing trade secrets.
We are building an infrastructure layer that will prevent privacy from becoming an obstacle to regulation and institutional adoption, and instead serve as a protective layer for financial flows.
TX-SHIELD — The private and regulatable settlement base-layer for stablecoin, blockchain and enterprise.




