The convergence and evolution of AI and blockchain technologies: the restructuring of productivity and production relations under the new paradigm of the digital economy.
- 核心观点:AI与区块链互补共生,AI驱动区块链大规模落地。
- 关键要素:
- AI导致信任危机,区块链提供可信验证与确权。
- AI智能体经济需区块链实现机器间价值交换。
- 通证化是AI时代数字产权与价值流转的基石。
- 市场影响:推动Web3基础设施(支付、算力、存证)发展。
- 时效性标注:长期影响。
The Convergence and Evolution of AI and Blockchain: Reconstructing Productivity and Production Relations in the New Digital Economy Paradigm
Authors: SanTi Li, Chunfengjun, Lisa, Naxida
Abstract: Current market discussions on the relationship between artificial intelligence (AI) and blockchain & cryptocurrency often focus on a zero-sum game perspective of capital diversion. However, in-depth industry analysis and technological evolution paths reveal that they are actually complementary and symbiotic. Against the backdrop of AI driving exponential productivity growth and an almost limitless supply of digital content, the reconstruction of production relations and the establishment of rights based on blockchain are not merely "icing on the cake," but rather particularly necessary. This article aims to deeply analyze why the widespread adoption of AI will become a core driving force and accelerator for blockchain technology to move from fringe experiments to large-scale implementation, from the dimensions of trust mechanism reshaping, the establishment of rights confirmation systems, the shift in economic paradigms, the importance of tokens as value carriers, and risk control.
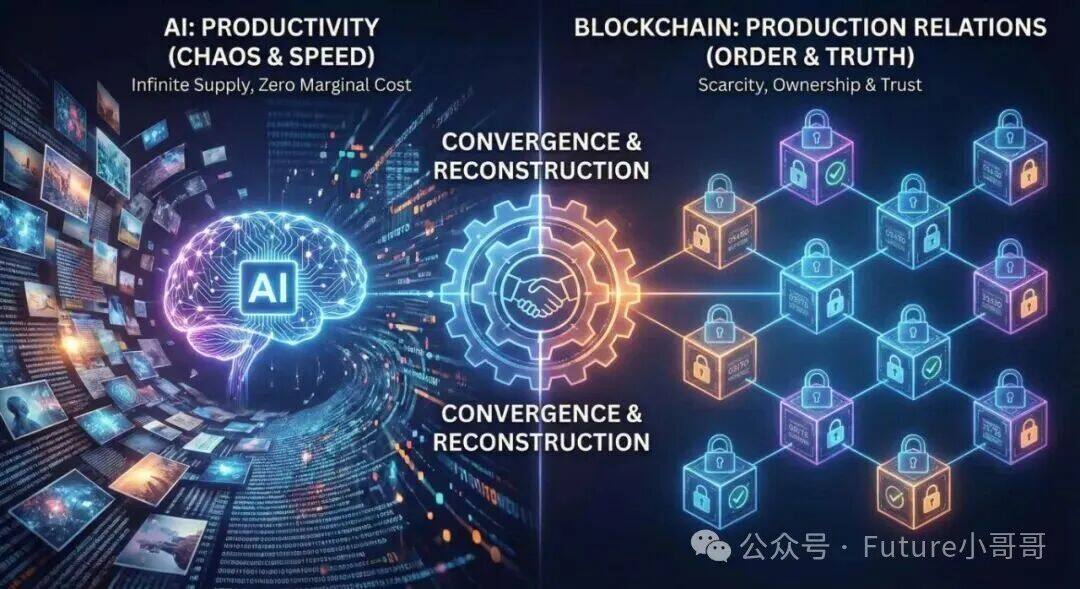
1. The Digital Trust Crisis in the Context of the AI Explosion
With the groundbreaking advancements in AI technology in recent years, especially the widespread application of Large Language Models (LLM) and Generative AI (AIGC), its core economic significance lies in reducing the marginal cost of content production to near zero. While this has greatly unleashed social creativity and productivity, it has also posed an unprecedented and severe challenge to the existing internet ecosystem, leading to drastic changes in the information environment.
- Entropy Increase and Distortion in the Digital Information Ecosystem: With the proliferation of synthetic media and deepfakes, the internet faces the risk of the "Dead Internet Theory" becoming a reality. Under this theory, most network traffic and content will be generated by bots. When the cost of forging videos, audio, and text is extremely low, and pixel-level realism is achievable, the traditional cognitive argument of "seeing is believing," which sustains society, faces the threat of complete failure in the digital realm. Political elections could be disrupted by fabricated scandal recordings, and financial fraud could be carried out against individuals through real-time face-swapping technology. These are no longer science fiction scenarios from *Black Mirror*, but imminent real threats.
- Information asymmetry and cognitive overload are exacerbating the risk of information being overwhelmed when machine-generated content far exceeds human creation by orders of magnitude. The cost of filtering massive amounts of machine-generated information, potentially biased or misleading, increases exponentially. This information overload not only reduces decision-making efficiency but can also lead to divergences in social consensus. In particular, the new generation that grew up with AI is likely to have a much higher level of trust in AI than the generation that invented AIGC, thus further increasing their likelihood of being misled or blindly following others.
- The Scarcity of Inspiration Brought by AI Convenience: It's well known that a significant difference in value between humans and robots lies in the fact that human inspiration is difficult for AI to imitate. However, human laziness is also a factor in technological progress. Due to the immense increase in convenience, reliance on AI may make inspiration an absolute "luxury" in the future. Meanwhile, the intellectual property of these creators with inspiration is being ruthlessly plundered and diluted by AI's rapid AIGC (many derivative works are currently generated without authorization through "plagiarism"). Without technological protection, humanity's original creative drive will dry up.
Against this backdrop, the first major systemic risk facing the digital society is not the awakening or rebellion of artificial intelligence, but the collapse of the foundation of social trust. Building a verification mechanism that can effectively distinguish between genuine and fake information, establish the source of information, and ensure its immutability has become a necessary condition for maintaining the healthy operation of the digital ecosystem, and this is precisely where blockchain technology can play a crucial role.
2. Blockchain-based Ownership Confirmation: From "Optional Component" to Digital Infrastructure
In the "unlimited supply" model constructed by artificial intelligence, scarcity becomes the core anchor of digital asset value. Without the constraint of scarcity, the value of digital content will approach zero as supply increases infinitely, much like the abundance of diamonds. Blockchain technology, as a decentralized distributed ledger, essentially functions to establish digital scarcity and ownership through cryptographic means, thereby re-endowing digital assets with value.
- The institutionalization of data provenance: As the barriers to content creation decrease, distinguishing between "human creation" and "AI generation" becomes crucial. In 2022, an author could commission a cartoon hand-drawn illustration to sell for hundreds of dollars, while in 2025, similar non-high-precision customized content could be completed in seconds. On-chain notarization of high-value data (such as news reports, artistic creations, legal contracts, academic papers, and identity information) will become the industry standard. Every digital file needs to be accompanied by an unforgeable "birth certificate" and "transfer record. " Digital content lacking cryptographic signatures and on-chain timestamps will face severe trust devaluation. The combination of the C2PA (Content Source and Authenticity Alliance) standard and blockchain technology will build a trusted verification layer for digital content, making the source and modification history of content transparent and visible to everyone.
- Proof of Personhood and Resistance to Sybil Attacks: In an era where bots can pass the Turing Test and permeate the internet, the economic and social value of verifying users' "real identities" is increasingly prominent. Traditional CAPTCHAs are gradually becoming ineffective and unable to stop more advanced AI agents. Identity verification systems based on a combination of biometrics and zero-knowledge proofs (ZKP) may become the key infrastructure for distinguishing human users from AI agents. This is not only to prevent the exploitation of airdrops, but also to prevent online voting and public opinion from being manipulated by botnets.
In conclusion, artificial intelligence creates an unlimited supply of productivity , while blockchain technology provides a credible constraint of scarcity and an anchor for identity . Logically, the two constitute an indispensable complementary gear in the closed loop of the digital economy: AI is responsible for making the world "faster," and blockchain is responsible for making the world "realer."
3. Restructuring the Business Paradigm: The Economics of Autonomous Intelligent Agents
The combination of artificial intelligence and blockchain heralds the potential rise of a completely new economic interaction model— the machine-to-machine (M2M) economy . This is not merely a change in payment methods, but a fundamental transformation of the nature of economic entities.
In the future, internet interactions will no longer be limited to humans; billions of autonomous AI agents will become native inhabitants of cyberspace. Traditional financial infrastructure (such as bank accounts, KYC processes, and credit card payment networks) is designed for humans and does not have the ability to serve non-human entities, nor can it meet the demands of high-frequency, micro-amount, and 24/7 machine transactions.
- Machine-native monetary systems: Cryptocurrency is a value exchange medium naturally adapted to machine logic. AI agents cannot open bank accounts at a counter, but they can instantly generate wallet addresses and manage private keys through code. They can use stablecoins (such as USDC) or specific utility tokens for data procurement, API calls, or computing power leasing. This type of payment is not subject to the intermediary barriers, business hour restrictions, or high cross-border fees of traditional finance.
- Agent-to-Agent (A2A) Economic Networks: The future business landscape will transcend B2B and B2C models, evolving towards an A2A (AI Agent-to-AI Agent) model. For example, an AI Agent responsible for itinerary planning might need to purchase real-time data from another agent responsible for weather forecasting and pay a deposit to a third agent responsible for ticket booking. These service exchanges involving micropayments and high-frequency transactions are economically feasible only with a high-performance, low-friction blockchain network. Smart contracts will automatically execute these complex business logics without human intervention.
- Collaboration through Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Networks (DePIN): AI operations require significant computing power (GPUs) and data. Through DePIN networks (such as io.net and Render), AI agents can directly rent idle computing power from individuals or businesses globally and settle payments in real-time using tokens. This breaks the monopoly of centralized cloud service providers (AWS, Google Cloud) to some extent, reducing the operating costs of AI and providing real-world utility scenarios for blockchain (although the initial computing power source for projects and participants is likely still from the original giants; subsequent rentals can be chosen independently to dismantle absolute monopolies).

4. Cryptocurrency: A Value Carrier and Symbiotic Engine for Rights Confirmation in the AI Era
Blockchain is more than just a database; it's a value network. Having clarified the technical aspects of anti-counterfeiting and evidence preservation (point 2) and the business aspects of intelligent agent interaction (point 3), we must delve into the core of assets and finance . Property rights are the prerequisite for transactions and pricing. In the "unlimited supply" model built by artificial intelligence, relying solely on technical means for "anti-counterfeiting and evidence preservation" is far from sufficient. We can use crypto to truly tokenize and financialize these rights, which also gives rise to the concept of RWA (Real World Asset).
Tokens, as the smallest granular carrier of rights confirmation and the lifeblood of rights transfer, constitute an indispensable cornerstone of digital property rights in the AI era. This has upgraded AI and crypto from a simple "tool superposition" to a deep "symbiotic evolution".
- Tokenization: Transforming abstract rights into programmable digital assets. Crypto uses NFT (non-fungible token) and SFT (semi-fungible token) technologies to transform abstract intellectual property (IP), ownership, copyright, and other unique datasets, fine-tuned model parameters, or even the ownership of an AI agent into unique and immutable on-chain assets.
- IP-NFTs serve as a value anchor: every human creator's unique style or original work can be minted as an NFT. When AI needs to use these works for training or style transfer, it's no longer a seamless appropriation, but rather requires authorization from the NFT through on-chain protocols. Here, the token is not only a copyright certificate, but also proof of revenue rights. For example, RWA music projects like Opulous and Audius tokenize artists' album rights, establishing revenue-sharing agreements with fans in advance.
- Data tokenization: High-quality personal or corporate data is no longer static files, but assets that can be encapsulated into tokens for trading. Every time an AI model accesses this data, it is essentially consuming the rights represented by that token, thus generating refined returns and rights protection.
- Crypto: Realizing the instant settlement and transfer of ownership rights is meaningless if it is not linked to value distribution. Digital currency provides the only execution layer for the confirmation of rights in the AI era.
- Micropayments and Streaming Payments: In the high-speed operation of AI, rights confirmation often occurs within milliseconds (e.g., AI quoting a sentence or generating an image). Traditional fiat currency systems cannot handle such extremely small amounts (US$0.0001) and extremely high frequency of copyright revenue sharing. Cryptocurrencies enable smart contracts to automatically "flow" revenue to token holders the instant rights confirmation occurs, achieving a closed loop of usage equals rights confirmation, and rights confirmation equals settlement.
- The construction of the incentive layer: Why are humans willing to expend effort to verify the authenticity of AI content? Why are nodes willing to contribute computing power to maintain network consensus? Because of the incentive of cryptocurrencies. Token economics rewards participants who maintain the ownership system with digital currency, thereby building a self-operating, AI-attack-resistant trust network. This is also the core value of public blockchain systems and corresponding projects. The internal or partial circulation models of consortium blockchains and private blockchains are difficult to promote on a larger scale.
- The symbiotic relationship between AI and Crypto: a double helix of growth
- AI needs blockchain crypto: Without the rights confirmation and payment facilities provided by blockchain systems, AI creators and users will easily fall into a dead end of rampant piracy, data depletion, and inability to monetize. The more intelligent AI becomes, the more it needs clear property rights boundaries to avoid disputes. The current freshness of AI creation stems from decades of accumulated data and creative sharing; however, as this accumulation nears depletion, whether new creative ideas can fill the gap will heavily depend on meticulous protection of rights.
- Crypto also needs AI: AI has created massive amounts of digital assets and high-frequency trading scenarios, providing crypto with unprecedented utility and liquidity. This symbiotic relationship indicates that crypto is the "physical law" and "economic system" of the AI era. The combination of the two will restructure the production relations of the digital world, allowing the productivity dividends of AI to be fairly returned to every participant through a rights confirmation mechanism.
5. Risk Governance: A Paradigm Shift from "Moral Self-Discipline" to "Technological Constraints"

Current AI development is highly concentrated in the hands of a few tech giants (such as OpenAI, Google, and Meta), perpetuating the centralized, black-box logic of the Web 2.0 era. Under this model, the public can only hope that companies maintain a "Don't be evil" moral compass. However, historical experience shows that centralized power is often accompanied by risks of monopolies, data misuse, and algorithmic bias.
Blockchain technology introduces a "do no evil" governance logic, using open-source code, cryptographic proofs, and mathematical contracts to rigidly constrain system behavior.
- Zero-Knowledge Machine Learning (ZKML): As an important branch of privacy-preserving computation, ZKML allows for mathematical proof to verify that the AI model's reasoning process is executed according to a predetermined algorithm and has not been tampered with, without disclosing underlying sensitive data (such as medical records and financial transactions) and the model's core parameters. This ensures the transparency and auditability of algorithmic decisions, which is crucial for AI applications in high-risk fields such as medical diagnosis and credit assessment, solving the "black box trust" problem.
- Public chains that have weathered multiple bull and bear market cycles possess a higher degree of credibility. NEAR has fully transitioned to AI, becoming the first AI public chain, while Render and others have shifted from game rendering to AI computing power. ETH, BSC, Solana, Cardano, Avalanche, Algorand, Hbar, Conflux, and others each have their own unique strengths, technical characteristics, and weaknesses. Emerging public chains like Monad are also facing a new round of challenges in token economics. Regarding the VC long-cliff model that has plagued the primary market in the past two years —where institutional holdings are locked up, but this has ironically led to excessive selling pressure due to premature and unintentional circulation of project incentives and airdrops—the market still needs 1-2 years to verify the balance between token release curves and ecosystem value capture.
- Data sovereignty and value distribution: Addressing the widespread issues of data infringement and "data harvesting" in large-scale model training, blockchain projects can return data ownership to users, allowing them to selectively authorize data for training and receive rewards. This restructures production relations, enabling data contributors to obtain reasonable value returns through a token economic model, thereby incentivizing higher-quality data supply and preventing the tragedy of data depletion.
6. Conclusion: Embracing the balance of "entropy reduction," reshaping the future within the order of digital civilization.
The essence of AI tends towards entropy increase —that is, the explosive generation and accelerated spread of information, as well as the increase in future uncertainty; while the essence of blockchain tends towards entropy reduction —that is, establishing an immutable order through consensus mechanisms, anchoring a unique factual truth, and solidifying execution rules.
A robust digital world cannot be composed of either chaos (though vibrant) or order (though stable) alone. The deep integration of artificial intelligence and blockchain is essentially an inevitable result of the digital ecosystem seeking a dynamic balance. AI provides the driving force, while blockchain provides the compass and the foundation for security. This, in turn, will further accelerate the development of large-scale applications.
For investors and industry practitioners, a deep understanding of this convergence trend means grasping the core dividends of the digital economy's development over the next five to ten years. The focus should not be limited to the AI concept itself, but should also extend to the Web3 infrastructure layer that provides payment settlement, computing power scheduling, data storage, and rights confirmation services for the AI ecosystem. The development and regulation of blockchain and digital currencies have also reached a necessary stage; the future is here, and this wave of technological convergence is on the eve of its explosion.
Risk Warning: This article is for educational purposes only. The projects mentioned are described in a relatively objective manner and are not investment advice. Please refrain from making any investment decisions based on the information provided.
Author: Future Little Brother
PNU Master of Engineering, long-term institutional investor; contributing writer for mainstream media and securities firms; winner of the Korean BK21 prize; CFT leader for new energy product R&D cooperation projects with Tesla, GM, FF, etc. Extensive experience across multiple blockchain fields.



