Why is the crypto market continuing its downward spiral despite the Federal Reserve's continuous interest rate cuts?
- 核心观点:加密市场总市值增长但币价普遍下跌。
- 关键要素:
- 美联储温和降息,买压不足。
- 新资产发行与代币解锁卖压大。
- 美中韩股市上涨分流资金。
- 市场影响:短期资金竞争加剧,投资者体感熊市。
- 时效性标注:中期影响。
Original author: Yuuki, TechFlow
TL;DR
The recent market downturn is attributed to a combination of factors: short-term macroeconomic headwinds, the industry black swan event of October 11th, and competition for funds among the stock markets of the US, South Korea, and China. In the long term, the Fed's preventative interest rate cuts and the resulting mild liquidity injections have not generated as much buying pressure as the new issuance of crypto assets and the unlocking of tokens have generated selling pressure. This has resulted in an increase in the total market capitalization of cryptocurrencies, but a decline in the prices of most cryptocurrencies, creating a perceived bear market for secondary market investors.
In the short term, pay attention to when the US government reopens and when the Federal Reserve's balance sheet reduction ends (December 1st); in the long term, pay attention to the pace of interest rate cuts and the competition for funds between the crypto market and other risk markets.
I. The total market capitalization of the crypto market has grown in tandem with the easing of liquidity, but the massive supply of assets has resulted in poor price performance.
1. Over the long term, the growth of the total market capitalization of the crypto market is highly correlated with the growth of the global risk market capitalization.
The release of macro liquidity will affect mainstream risk assets globally. By comparing the changes in the total market capitalization of the crypto market with that of the US stock market, it is not difficult to find that the two are highly correlated in terms of the pace of their rise and fall over a long period.
The following chart shows the situation over the past year:
Red line: Total market capitalization of the crypto market;
Green line: Total market capitalization of altcoins excluding BTC and ETH;
Blue line: The trend of the S&P 500 index;
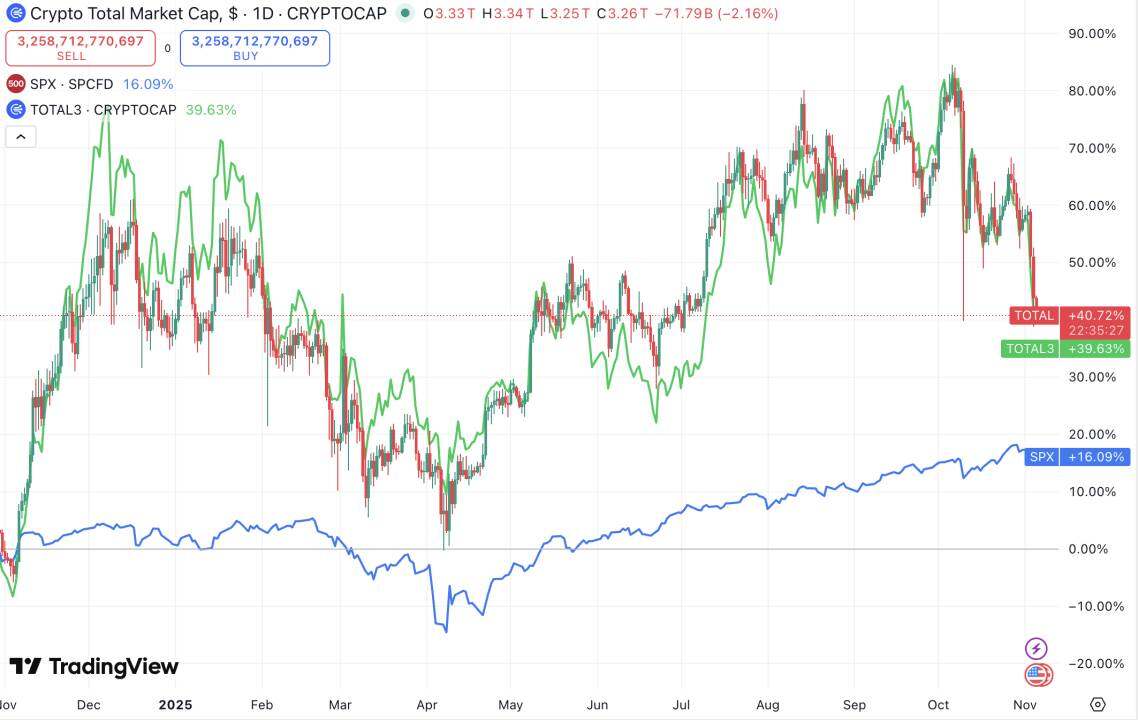
2024.11-2025.11 Total,Total3&SPX
Data source: TradingView
Several phenomena can be clearly observed:
1. Crypto market capitalization growth surpasses that of US stocks.
2. The three generally fluctuated, bottomed out, and resumed their upward trend in sync (the recent cryptocurrency black swan event on October 11th caused asynchronous price movements, which will not be discussed further in this article).
2. The massive supply of assets has led to an increase in the total market capitalization of altcoins, but a decrease in token prices.
The growth in total market capitalization does not equate to investor profits. The large number of new asset issuances in the crypto market over the past year, along with the peak unlocking periods for numerous projects (especially public chains, DeFi, and AI tokens launched in the 2021-2023 cycle), has created continuous supply pressure. According to Tokenmist data, the market capitalization of newly unlocked tokens in the past three months is approximately 30 billion.
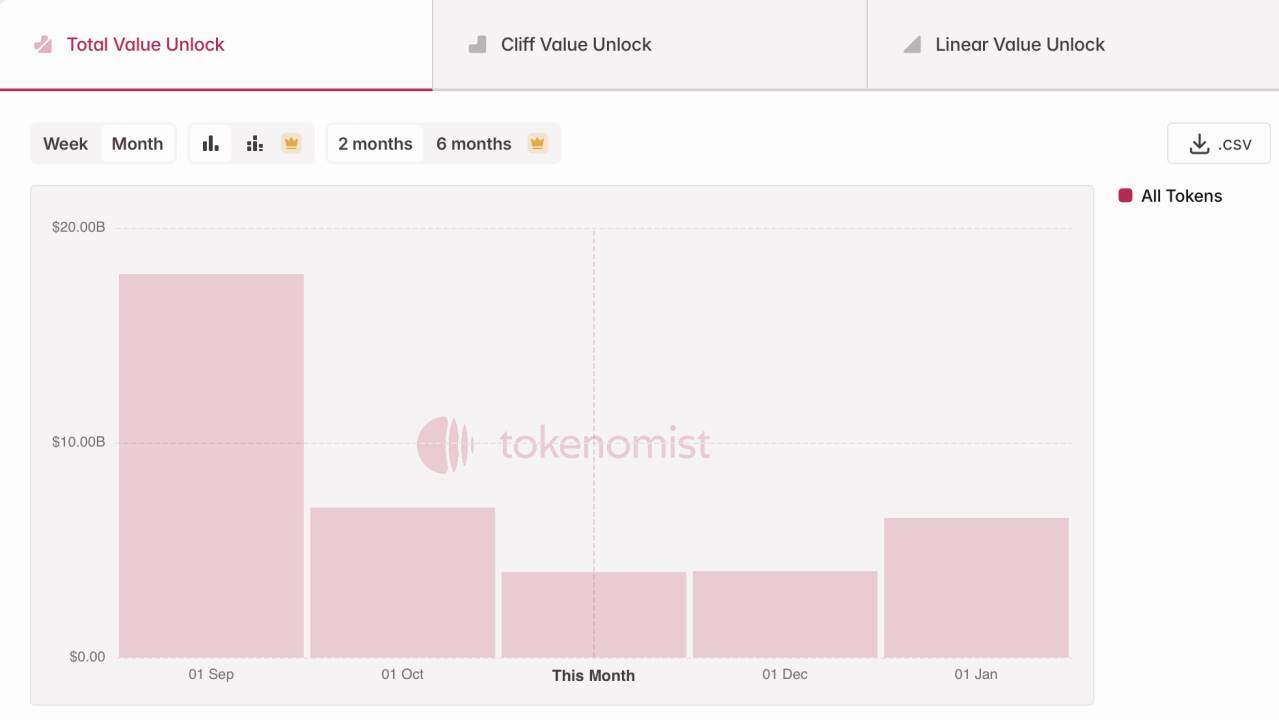
Nearly $30 billion in token unlocks in the past three months
Data source: Tokenmist
In summary, the Fed's current preventative, moderate interest rate cuts and mild liquidity injections have not generated more buying pressure than the selling pressure from newly issued Crypto assets and token unlocks. This is reflected in the total market capitalization of the crypto market, but the prices of most cryptocurrencies have fallen, creating a perceived bear market for secondary market investors.
Second, in the short term, macro liquidity is currently facing a temporary headwind.
In the long term, we are still in a historical process of dual easing of monetary and fiscal policies; however, in the short term, the fiscal liquidity headwinds caused by the US government shutdown and the TGA account's inflows without outflows, as well as the monetary liquidity headwinds caused by the Fed's slower-than-expected pace of interest rate cuts, cannot be ignored; at the same time, the decline in global risk appetite due to the Sino-US confrontation is also continuing to affect the market.
(Note from Deep Tide: The TGA account stands for Treasury General Account. It can be understood as the bank account of the U.S. Treasury Department. The Treasury deposits funds from the issuance of national debt and tax revenue into this account for fiscal expenditures, such as paying salaries or infrastructure projects. Therefore, an increase in the TGA balance means that fiscal funds are locked in the account and have not flowed into the economic system, resulting in a short-term tightening of fiscal liquidity. This situation was amplified by the recent U.S. government shutdown.)
1. Finance side: The TGA account's "only deposits and no withdrawals" resulted in funds being locked.
The prolonged deadlock in Congress over budget appropriations and the record-breaking US government shutdown led to a situation where fiscal funds were flowing in but not out, resulting in a temporary liquidity withdrawal. As of October 29, 2025, the TGA account balance had grown to $957.8 billion, and on November 4, the US government conducted another auction of $274 billion in short-term debt.
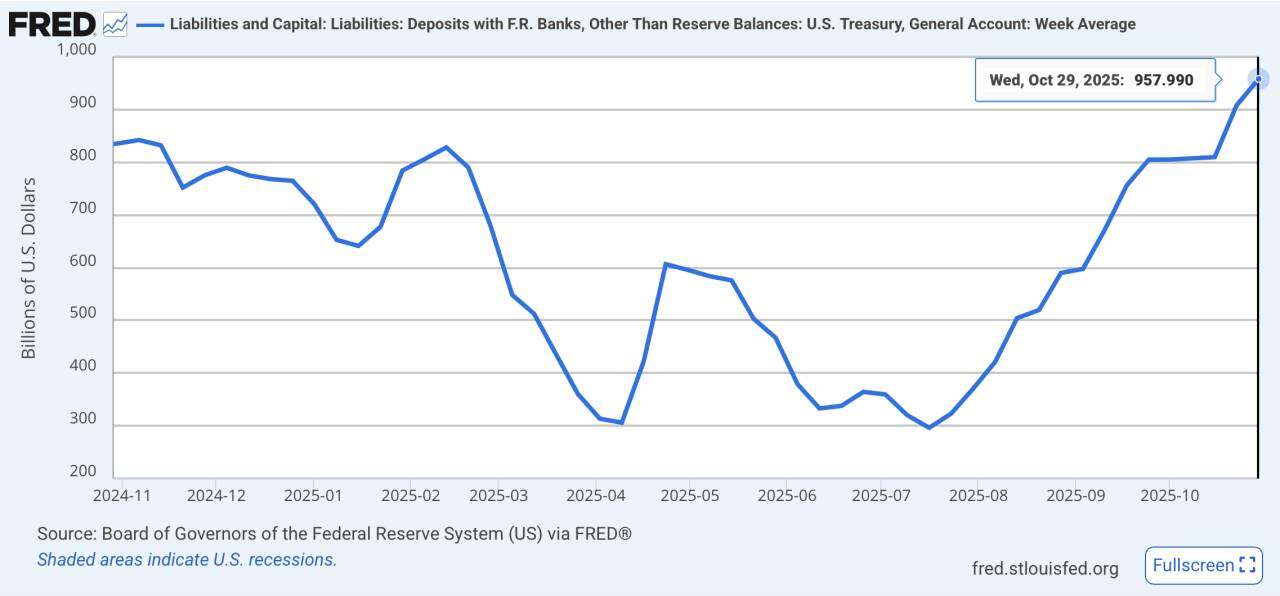
TGA balance climbs to a one-year high
Data source: FRED
2. Monetary policy: The pace of interest rate cuts is slower than expected.
Although we are currently in a rate-cutting cycle by the Federal Reserve, the pace of these cuts is far slower than the market expected; real interest rates remain relatively high. In particular, Powell's recent remarks at the FOMC meeting, which did not commit to a rate cut in December, have further dampened market confidence; at the same time, this preemptive rate cut also reflects underlying concerns about a recession.
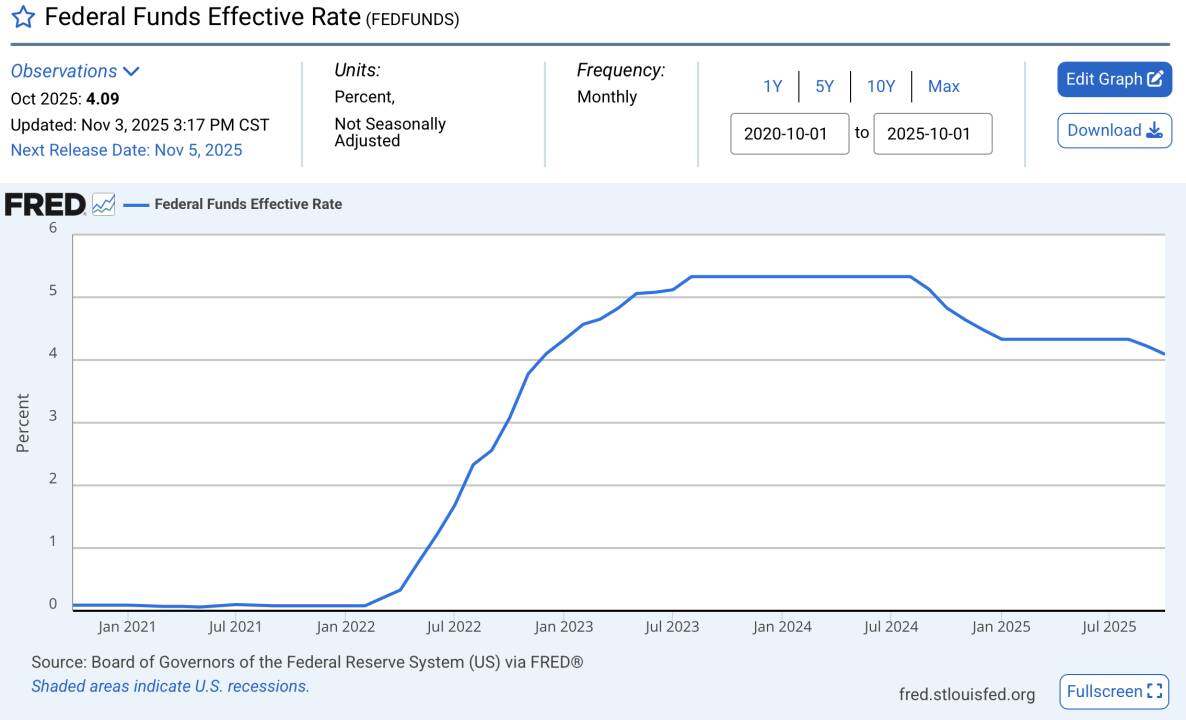
Interest rates remain at historically high levels.
Data source: FRED
3. US-China frictions have led to a decline in risk appetite, suppressing the prices of risky assets.
Recent events such as China's rare earth export restrictions and the US's reimposition of tariffs have increased risk aversion, leading to a simultaneous rise in the US dollar index and the US stock volatility index, reflecting a global surge in risk aversion.
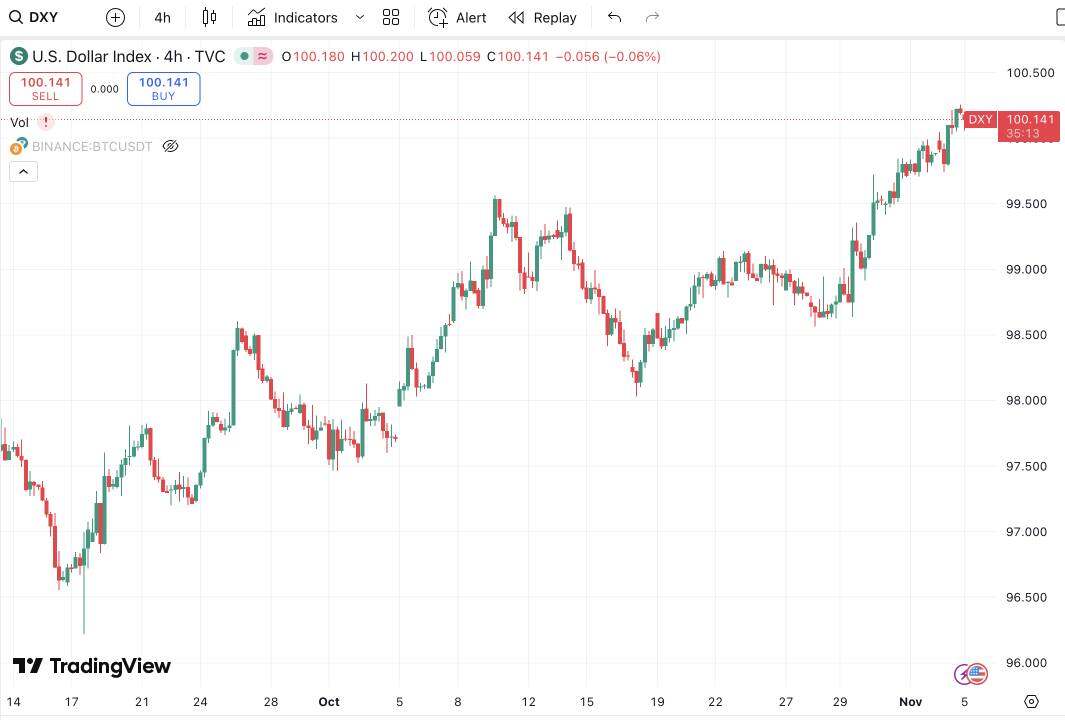
The US dollar index continued to climb.
Data source: TradingView
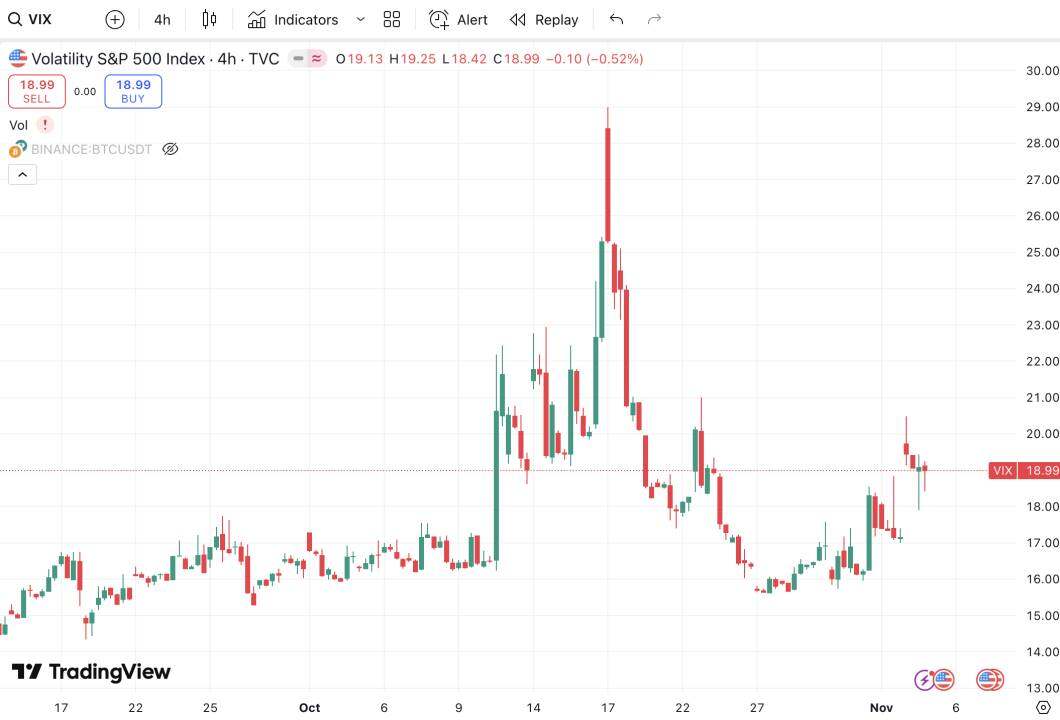
Increased volatility in US stocks
Data source: TradingView
Third, the continued rise in the stock markets of the United States, China, and South Korea has exerted a strong attraction on risk capital, siphoning funds from the crypto market.
When discussing bull markets, comparisons are invariably made with 2021. In the 2021 bull market, while quantitative easing led to a rapid expansion of liquidity, the stock market suffered severe damage to EPS due to the pandemic (meaning company revenue declined significantly due to the pandemic, and the extremely deteriorated stock market fundamentals at the time did not support secondary market buying). The abundant liquidity, with nowhere else to go, fueled a frenzied bull run in the crypto market. The entire crypto market capitalization jumped from $300 billion to over $3 trillion within a year, with altcoins outperforming Bitcoin, and small-cap stocks increasing by hundreds of times their initial value springing up like mushrooms after rain.
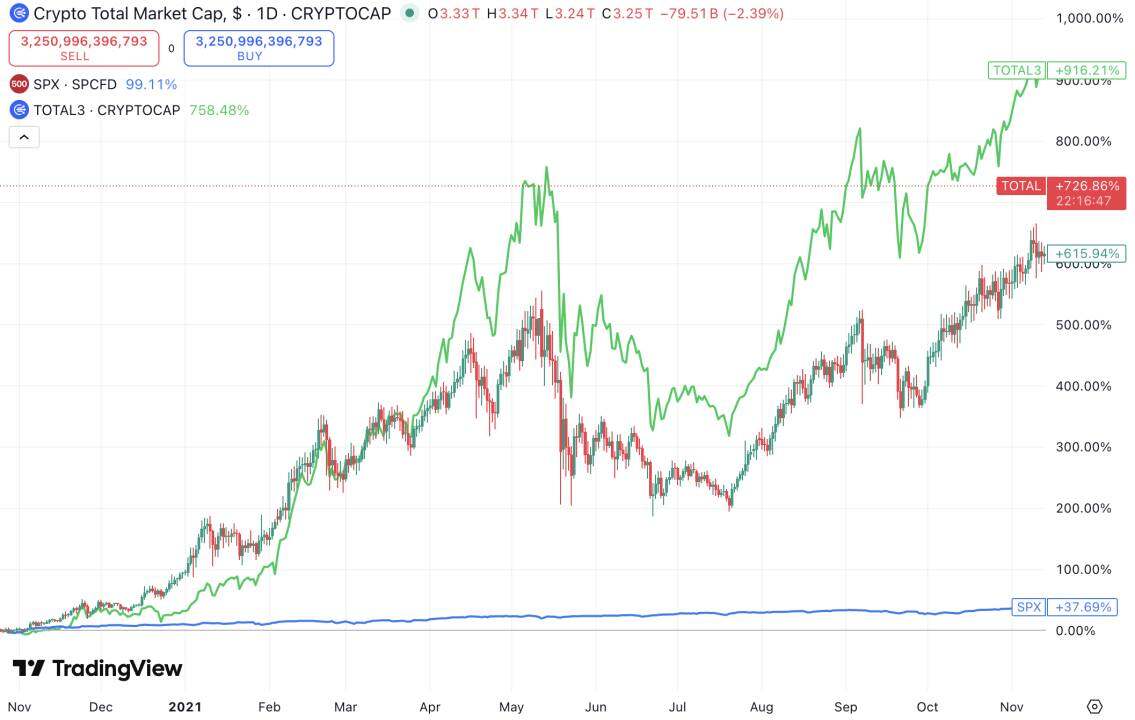
2020.11-2021.11 Total,Total3&SPX
Data source: TradingView
Meanwhile, the stock markets in the US, China, and South Korea, which are most closely related to the crypto market, are rising steadily. US stocks have repeatedly hit new highs driven by AI, while A-shares have broken through 4,000 points with policy support and expectations of improved liquidity. South Korea has also shown a strong trend due to the recovery of semiconductor exports. The KOSPI index has risen by nearly 70% so far this year, making it the best-performing major stock index in 2025.
Limited high-risk funds in the market are being absorbed by assets with higher certainty, significantly diverting some of the funds that could have been injected into the crypto market.
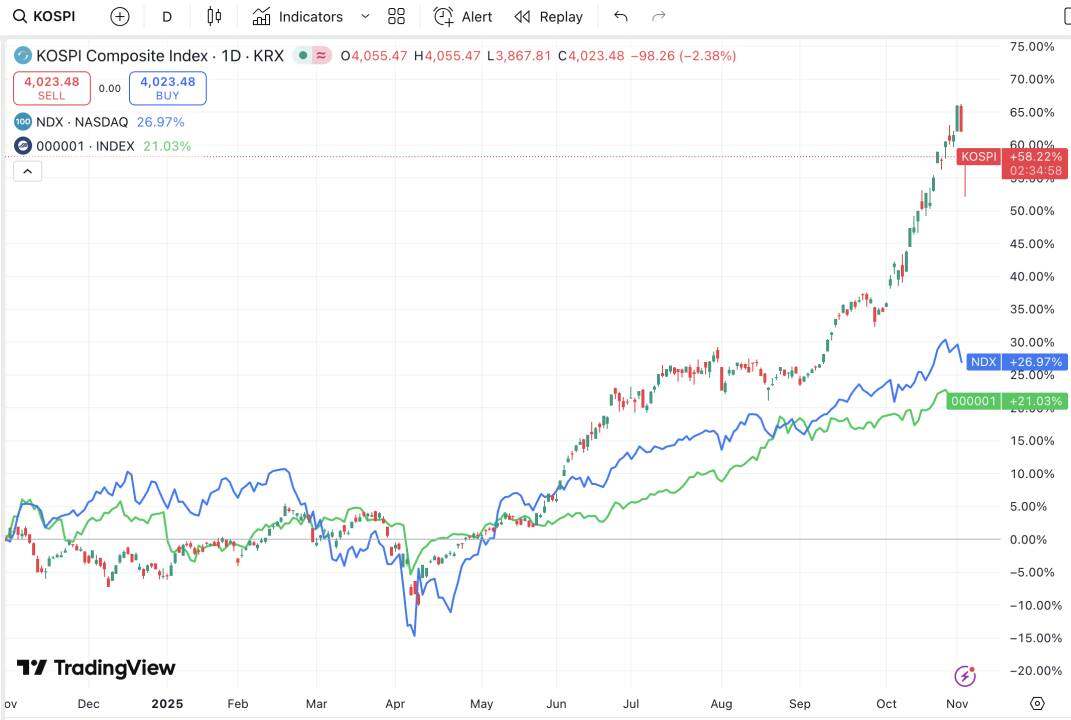
The stock market gains of South Korea, the United States, and China over the past year
Data source: TradingView
Therefore, in the long run, if the global stock market continues its upward trend and the Federal Reserve's liquidity injection remains moderate, the crypto market may still be in a "marginalized funding" stage, generally characterized by a growth in total market capitalization but weak price performance due to a large issuance of assets. In the short term, the key focus is on the marginal liquidity improvement brought about by the reopening of the US government and the effective date of the end of the Federal Reserve's balance sheet reduction (December 1).



