US Congress promotes the CLARITY Act: DeFi is expected to usher in a wave of compliance
- 核心观点:美国推进《CLARITY法案》,明确数字资产监管框架。
- 关键要素:
- 划分SEC与CFTC监管权限,明确数字商品定义。
- 引入“成熟链”标准,项目可转型为商品。
- DeFi协议获合规豁免,开发者无需注册。
- 市场影响:提升市场透明度,吸引机构资金入场。
- 时效性标注:中期影响。
I. Legislative Overview and Core Contents
In 2025, the U.S. House of Representatives overwhelmingly advanced the Digital Asset Market Clarity Act (CLARITY Act). The bill has now entered the Senate review stage. If it is passed in a subsequent Senate vote, it will mean that the United States has taken another historic step in the field of digital asset regulation.
The core content of the CLARITY Act is to plan clear definitions and regulatory rules for digital assets, especially to draw a clear line between the regulatory powers of the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) and the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC). If the bill is passed, the CFTC will be responsible for regulating exchanges, brokerages, dealers, and project parties that meet the "mature chain" standard. The SEC is responsible for securities assets and cryptocurrencies with investment contract attributes. The CLARITY Act and the GENIUS Act jointly build an upstream and downstream regulatory system for digital assets. The former focuses on blockchain infrastructure and asset attribute division, while the latter is responsible for stablecoin regulatory standards.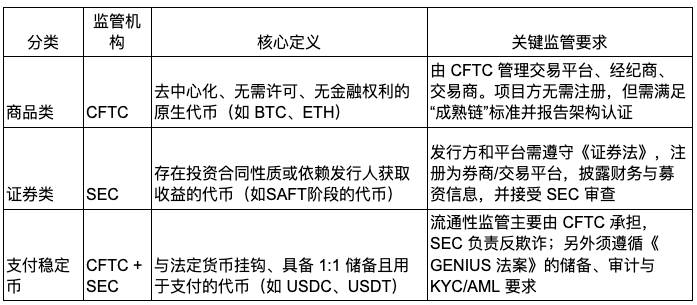
The core content includes:
1. Establish the definition of “digital goods”
Native crypto assets that have achieved decentralization and run on open blockchains (such as BTC and ETH) are clearly classified as "digital commodities" and included in the CFTC's regulatory scope, as distinct from securities assets under the jurisdiction of the SEC.
2. Mature blockchain system identification mechanism
The bill introduces the "Mature Blockchain" standard, which allows specific projects to convert their tokens from "securities" to "commodities" after reaching technical and governance thresholds such as decentralization, decentralized governance, and open source code, thereby exempting them from the onerous compliance requirements under the securities law. Securities laws apply to the initial issuance stage of such projects (such as SAFT, ICO, and IPO), and when the project completes the decentralized transformation, its tokens can be reclassified as digital commodities and transferred to CFTC supervision.
3. DeFi project compliance exemption clause
DeFi protocols that do not involve asset custody and have no centralized intermediary structure are exempted from registration obligations. At the same time, it is made clear that front-end developers and node operators do not bear financial intermediary responsibilities, thereby reducing the compliance burden.
4. Information Disclosure and Insider Trading Restrictions
Platforms operating digital commodity trading markets must register with the CFTC as "digital commodity exchanges", including over-the-counter brokers and market makers. These institutions will comply with strict federal regulatory requirements, such as minimum capital, risk management, transaction records, regulatory reporting, customer asset protection, etc. If a company is involved in both securities and digital commodity businesses, it must register with the SEC and CFTC respectively. Although the compliance burden is heavy, the bill clearly defines the regulatory boundaries of both parties.
5. Traditional institutions participate in legalization
The bill provides a legal basis for traditional financial institutions such as banks and securities firms to engage in crypto asset custody and trading, and promotes wider access of traditional capital to the digital asset market.
2. Impact on the Crypto Market
1. Improved regulatory transparency for crypto assets, boosting market confidence
The CLARITY Act provides a highly certain compliance path for the entire crypto industry, ending the long-standing chaotic situation of "replacing regulation with law enforcement". Both project parties and trading platforms can conduct business within the legal framework. Regulations increase the transparency of core market infrastructure, help prevent fraud and abuse, and enhance consumer trust. This will attract more institutional funds into the market, improve market liquidity and activity. For institutions, they can further achieve compliance to avoid risks similar to previous SEC prosecutions. For consumers, the Act requires issuers of crypto products to disclose relevant information and restrict insider trading, etc., to protect the legitimate rights and interests of consumers and reduce investment risks.
2. The US crypto asset regulatory system is moving towards “de-SEC”
For a long time, the SEC has assumed that most cryptocurrencies are securities, causing multiple projects such as XRP, SOL, ADA, and UNI to fall into regulatory disputes. The CLARITY Act builds a new regulatory framework for the vast majority of fully decentralized assets through structural allocation, and such assets no longer need to follow the SEC's regulatory system.
3. Traditional exchanges can obtain digital commodity exchange licenses
The CLARITY Act allows traditional stock exchanges to apply for a "digital commodity exchange" license, which means that in the future, traditional trading platforms such as Nasdaq and NYSE may provide stock and digital asset (such as Bitcoin, Ethereum, etc.) trading services simultaneously, and investors can seamlessly configure traditional and encrypted assets on the same platform. This not only lowers the user threshold, but also provides a compliant and reliable entry point for traditional financial mainstream funds to enter the crypto market.
3. Impact on DeFi projects
1. Clarify the exemption mechanism to protect protocol developers
As long as DeFi projects do not engage in intermediary business, DeFi developers and operators do not need to register with the SEC or CFTC. Writing code, running nodes, or providing front-end interfaces are generally not considered financial service providers.
- No custody ≠ intermediary: If the protocol does not custody user assets and does not provide traditional financial services, its developers, node operators, and front-end maintainers are not considered financial intermediaries and do not need to bear registration or licensing obligations.
- No risk in code and operation: The self-release of smart contracts or wallet software does not constitute a securities issuer. Its behavior is similar to technology release and is not covered by financial supervision.
2. Introducing autonomous custody rights to protect the property rights of DeFi users
Sec. 105 and related provisions of the Act protect the right of users to manage digital assets independently, confirming that users can freely conduct peer-to-peer transactions through non-custodial wallets and legally enjoy control over funds. This right provides legal protection for DeFi users, so that they do not have to worry about policy penalties for choosing self-custody.
- Legal custody freedom: Users manage their assets with hardware or software wallets without relying on banks or third parties (financial institutions) to intervene.
- Autonomous trading rights: Users can independently initiate on-chain transfers, participate in DeFi protocol governance and liquidity mining without registering KYC intermediaries to participate.
- Establish the concept of sovereign digital rights in the United States: Incorporate "control of private keys means control of assets" into the legislative framework to ensure that actions on private chains are not considered illegal or require permission.
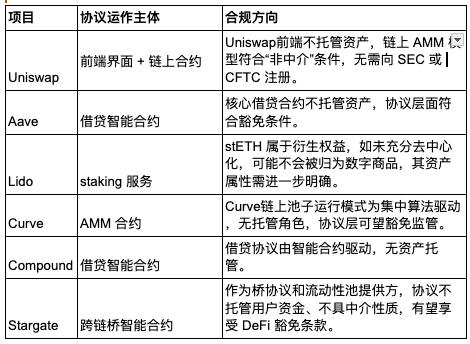
3. Impact on representative DeFi projects:
For most DeFi projects, the operation of their protocols usually meets the definition of "non-intermediary" roles in the CLARITY Act. Therefore, after the passage of the bill, they are expected to obtain clear registration and intermediary exemption qualifications, and will usher in significant compliance benefits in the short term. However, this does not mean that DeFi has achieved full compliance. It is worth noting that there is still legal uncertainty in the official tokens issued by many platforms. Whether they constitute securities still depends on whether they have the characteristics of "investment contracts", such as whether the investor's returns depend on the behavior of the project party. Therefore, although the CLARITY Act provides regulatory clarity at the protocol level, it does not solve the compliance issues at the token level once and for all. In order to reduce the risk of platform tokens being identified as securities, project parties still need to continue to promote the transparency of governance structures, strengthen community-led governance mechanisms, and gradually disperse control rights to improve the compliance of tokens and build a more robust legal firewall.
IV. Future Development
As of July 23, 2025, the CLARITY Act has successfully entered the review stage of the U.S. Senate, marking a key step in the legislation of digital asset regulation. The biggest controversial focus of the current legislative process is whether the Senate version can retain the key provisions on DeFi and token classification in the version passed by the House of Representatives. This decision will depend on the hearing procedures of the relevant Senate committees and the subsequent revision of the provisions.
From the overall trend, the CLARITY Act is expected to push the United States to establish a clearer and more layered regulatory framework for crypto assets in the coming months: security tokens are regulated by the SEC, and commodity tokens are under the jurisdiction of the CFTC. This framework will provide a clear compliance path for blockchain developers, DeFi protocols, trading platforms, etc., which will not only help reduce legal uncertainty, but also stimulate compliance innovation, attract institutional funds to enter the market, and further consolidate the United States' leadership in global digital asset policy making.
In addition, the linkage between the CLARITY Act and the GENIUS Act, which has been officially signed by President Trump, has laid a two-pillar foundation for the compliance system of the US crypto market. The former focuses on asset classification and market structure, while the latter provides a safe harbor and registration exemption path for the issuance of stablecoins. The two together build a complete compliance closed loop of "exemption first, transformation later, and final classification". Once the CLARITY Act is also officially passed and signed into law, it will mark the entry of the US crypto asset legislative system into the full implementation stage, significantly enhancing the legitimacy and strategic position of crypto assets in the mainstream financial system of the United States.
Risk Warning:
The information provided is for informational purposes only and should not be considered a recommendation to buy, sell or hold any financial asset. All information is provided in good faith. However, we make no representations or warranties, express or implied, as to the accuracy, adequacy, validity, reliability, availability or completeness of such information.
All cryptocurrency investments (including returns) are highly speculative in nature and involve significant risk of loss. Past, hypothetical or simulated performance is not necessarily indicative of future results. The value of digital currencies may rise or fall, and there may be significant risks in buying, selling, holding or trading digital currencies. You should carefully consider whether trading or holding digital currencies is suitable for you based on your personal investment objectives, financial situation and risk tolerance. BitMart does not provide any investment, legal or tax advice.



