BTC生态的全景分析:重塑历史或开启下一次牛市?
Original author: Fred
This article has 24,000 words and takes about 25 to 30 minutes to read.
1. Introduction: Historical development of BTC ecosystem
The recent popularity of Bitcoin Inscription has caused a craze among Crypto users. Originally considered as digital gold, Bitcoin was once more used as a store of value. Due to the emergence of the Ordinals protocol and BRC-20, people have begun to pay attention to Bitcoin again. Ecological developments and possibilities.
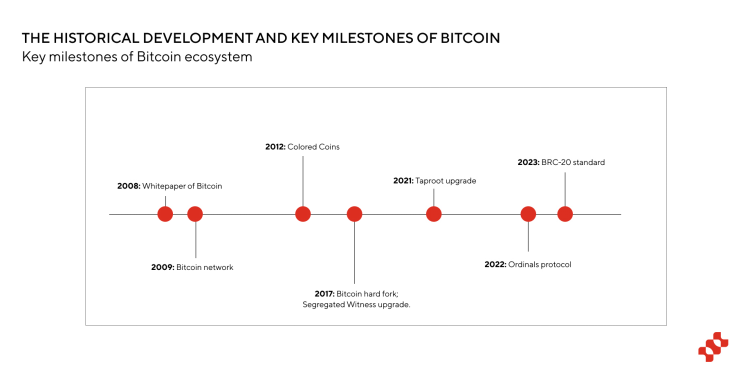
As the earliest blockchain, Bitcoin was created in 2008 by an anonymous entity named Satoshi Nakamoto, marking the birth of a decentralized digital currency that challenged the traditional financial system.
Bitcoin is an innovative solution born in response to the inherent shortcomings of the centralized financial system. It introduces the concept of a peer-to-peer electronic cash system without the involvement of a middleman, thereby achieving trustlessness and disintermediation. The underlying technology of Bitcoin, blockchain, revolutionizes the way transactions are recorded, verified and secured. The Bitcoin white paper released in 2008 laid the foundation for a financial system that emphasizes decentralization, transparency and immutability.
After its birth, Bitcoin has experienced a stage of gradual and steady growth. Early adopters were mainly tech enthusiasts and cryptography supporters who started mining and trading Bitcoin. The first recorded actual transaction occurred in 2010, when programmer Laszlo purchased 2 pizzas for 10,000 Bitcoins in Florida, marking a historical moment in cryptocurrency adoption.
As Bitcoin attracts increasing attention, related ecological infrastructure begins to take shape. Exchanges, wallets, and mining pools have emerged in large numbers to meet the needs related to Bitcoin, a new digital asset. With the development of blockchain technology and market, the ecosystem has expanded to more stakeholders, including developers, entrepreneurial teams, as well as financial institutions and regulatory agencies, promoting the diversification of the Bitcoin ecosystem.
The market has been dormant for a long time in 2023. The popularity of the Ordinals protocol and BRC-20 Token has brought about the summer of Inscriptions, which has also made people re-focus on Bitcoin, the oldest public chain, and what will be the future development of the Bitcoin ecosystem. ? Will the Bitcoin ecosystem become the engine of the next bull market? This research report will delve into the historical development of the Bitcoin ecosystem and the three core asset issuance protocols, expansion solutions and infrastructure in the ecosystem, analyze its development status, advantages and challenges, and discuss the future of the Bitcoin ecosystem. .
2. Why is the Bitcoin ecosystem needed?
1. Characteristics and development history of Bitcoin
Before discussing why we need the Bitcoin ecosystem, let’s first take a look at the basic characteristics and development history of Bitcoin.
Bitcoin is different from traditional financial accounting methods in that it has three core characteristics:
Decentralized distributed ledger: The core of the Bitcoin network is blockchain technology. It is a decentralized distributed ledger that records all transactions on the Bitcoin network. The blockchain is composed of blocks, and each block contains the hash value of the previous block, forming a chain structure to ensure the transparency and non-tamperability of transactions.
Accounting through Proof of Work (PoW): The Bitcoin network uses a Proof of Work mechanism to verify transactions and account for money. This mechanism requires network nodes to verify transactions by solving mathematical puzzles and record them on the blockchain. This ensures the security and decentralization of the network.
Mining and Bitcoin Issuance: Bitcoin issuance is accomplished through mining. Miners solve mathematical puzzles to verify transactions and create new blocks, and as a reward, miners are awarded a certain number of Bitcoins.
 It can be seen that unlike our common Paypal, Alipay and WeChat Pay, Bitcoin does not implement transfers by directly increasing or decreasing the account balance like this type of account model, but uses the UTXO (Unspent Transaction Output) model. .
It can be seen that unlike our common Paypal, Alipay and WeChat Pay, Bitcoin does not implement transfers by directly increasing or decreasing the account balance like this type of account model, but uses the UTXO (Unspent Transaction Output) model. .
Here we briefly introduce the UTXO model to help everyone understand the technical solutions of subsequent ecological projects. UTXO is a way of tracking Bitcoin ownership and transaction history. Each unspent output (UTXO) represents a transaction output in the Bitcoin network. These unspent outputs have not been used by previous transactions. They can be used to construct new transactions. Its characteristics can be summarized as the following three aspects:
Each transaction generates a new UTXO: When a Bitcoin transaction occurs, it consumes the previous UTXO and generates new UTXO, which are used as inputs for future transactions.
Transaction verification relies on UTXO: When verifying a transaction, the Bitcoin network checks whether the UTXO referenced by the transaction input exists and has not been used to ensure the validity of the transaction.
UTXO as transaction input and output: Each UTXO has a value and an owner’s address. When making a new transaction, some UTXOs will be used as transaction inputs, while others will be created as transaction outputs, possibly used by the next transaction.
The UTXO model can provide greater security and privacy because each UTXO has its own owner and value, and transactions can be tracked more granularly. Additionally, the design of the UTXO model allows for parallel processing of transactions because each UTXO can be consumed independently without resource contention.
However, due to block size limitations and non-Turing complete development languages, Bitcoin has largely played the role of digital gold and failed to host more projects.
After the birth of Bitcoin, colored coins appeared in 2012. By adding metadata to the Bitcoin blockchain, some Bitcoins can represent other assets; in 2017, a hard fork occurred due to the dispute over large and small blocks, including BCH, BSV, etc.; after the fork, BTC also began to continue to explore scalability improvement solutions. The SegWit upgrade launched in 2017 introduced extended blocks and block weights, expanding the block capacity; the Taproot upgrade starting in 2021 has improved Improve transaction privacy and efficiency. These key upgrades also laid the foundation for the subsequent development of various expansion protocols and asset issuance protocols, and also led to the popularity of the Ordinals protocol and BRC-20 Token that we are familiar with later.
It can be seen that although Bitcoin was positioned as a peer-to-peer electronic cash system when it was born, there are always many developers who do not want Bitcoin to just stay in the value of digital gold and are committed to improving Bitcoins scalability and based on The Bitcoin blockchain does more, such as having its own ecological applications.
2. Comparison between Bitcoin Ecosystem and Ethereum Smart Contracts
During the development of Bitcoin, Vitalik Buterin proposed another blockchain, Ethereum, in 2013, which was subsequently co-founded by Vitalik Buterin, Gavin Wood, Joseph Lubin and others. The core concept of Ethereum is to provide a programmable blockchain on which developers can build various applications, not just currency transactions. This feature of programmability makes Ethereum a smart contract platform that allows people to create and run blockchain-based applications that can execute automated contracts without trusting third parties.
It can be seen that one of the most significant features of Ethereum is smart contracts, and developers can develop various applications on Ethereum. With this feature, Ethereum has gradually become the leader of the entire Crypto. Various Layer 2 applications, as well as various asset types such as ERC 20 and ERC 721 have appeared, and many developers have gathered to build and enrich the city-state of Ethereum. .
So since Ethereum can already realize the development of smart contracts and various Dapps, why do people still need to go back to BTC to expand and develop applications? The core reasons can be summarized in the following three aspects:
Market consensus: Bitcoin is the earliest blockchain and cryptocurrency and has the highest visibility and trust in the minds of the public and investors. Therefore, it has a unique advantage in acceptance and recognition. The current market value of Bitcoin has reached 800 billion US dollars, accounting for about half of the market value of the entire crypto market.
Bitcoin has a high degree of decentralization: Among mainstream blockchains, Bitcoin has the highest degree of decentralization. The founder Satoshi Nakamoto has disappeared, and the entire chain is promoted by the community; while Ethereum still has vitalik and ether. The Fang Foundation is controlling the development.
Retail investors’ demand for Fair Launch: The demand for Web3 is inseparable from the way new assets are issued. In traditional project Token issuance, whether it is FT or NFT, the project party is basically the issuer, and the income of retail investors strongly depends on the market making of the project party and the VC behind it; in the Bitcoin ecosystem, inscriptions have appeared This type of innovative Fair Launch venue gives retail investors more say, and thus gathers more money and wealth in the BTC ecosystem. The renewed attention of the Bitcoin ecosystem this time is largely inseparable from the characteristics of Inscription Fair Launch.
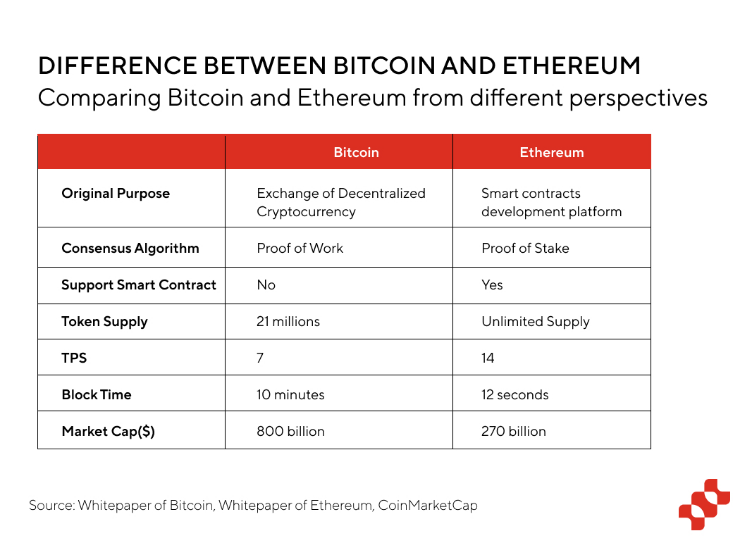
This is why although BTC is weaker than Ethereum in terms of TPS and block time, and its original purpose was to be used in the context of cryptocurrency transactions, there are still a large number of developers who hope to introduce smart contracts on it for application development.
In summary, just as the rise of BTC stems from value consensus - people generally agree that Bitcoin is a valuable digital asset and medium of exchange, the innovation in the Crypto world is also closely related to the properties of assets. The current popularity of the BTC ecosystem is mainly driven by inscribed asset types such as the Ordinals protocol and BRC-20. This popularity has also fed back to the entire Bitcoin ecosystem, causing more people to begin to return their attention to the Bitcoin ecosystem.
Different from previous bull markets, the influence of retail investors in this round of market is increasing. Traditionally, VCs and project parties have dominated the crypto market, investing in and promoting the development of many blockchain projects. However, as retail interest in crypto assets continues to increase, they want to play a larger role in the market and participate in the development and decision-making of projects. To some extent, retail investors have also driven this round of development and renewed prosperity of the Bitcoin ecosystem.
So although the Ethereum ecosystem is more flexible in terms of smart contracts and decentralized applications, the Bitcoin ecosystem as digital gold and stable value storage, as well as its leading position and market consensus, make it still unparalleled in the entire cryptocurrency field. important position. Therefore, people continue to pay attention to and work hard to develop the Bitcoin ecosystem to continue to tap its potential and possibilities.
3. Analysis of the development status of Bitcoin ecological projects
In the process of developing the Bitcoin ecosystem, it can be seen that Bitcoin currently has two main difficulties:
The Bitcoin network has low scalability. If you want to build applications on it, you need a better expansion solution;
There are few applications in the Bitcoin ecosystem. The development of the Bitcoin ecosystem requires some popular applications/projects to gather more developers and produce more innovations.
Around these two dilemmas, the Bitcoin ecosystem is mainly constructed from three aspects:
Related agreements surrounding asset issuance
Expansion plan: on-chain expansion and Layer 2
Infrastructure projects such as wallets and cross-chain bridges
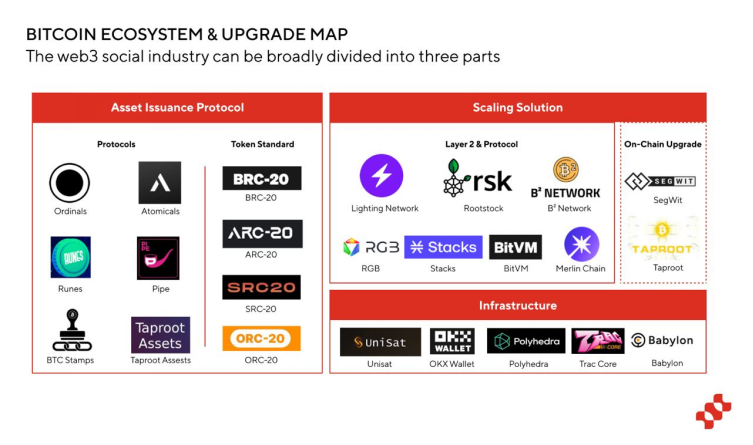
Since the development of the entire Bitcoin ecosystem is still in its early stages, and application scenarios such as defi are still in their infancy, this article will focus on analyzing the development of the Bitcoin ecosystem from four aspects: asset issuance, on-chain expansion, Layer 2 and infrastructure. .
1. Asset issuance agreement
The popularity of the Bitcoin ecosystem starting in 2023 is inseparable from the promotion of the Ordinals protocol and BRC-20, which allows Bitcoin, which was originally only used as a store and exchange of value, to also be used as a place for asset issuance, greatly broadening the use of Bitcoin. Scenes.
In terms of asset issuance protocols, after Ordinals, various different types of protocols have been born, such as Atomics, Runes, PIPE, etc. to help users and project parties issue assets in BTC.
1)Ordinals & BRC-20
First lets look at the Ordinals protocol. Simply put, Ordinals is a protocol that allows people to mint NFTs on Bitcoin similar to Ethereum. The Bitcoin Punks and Ordinal punks that initially attracted attention were minted based on this protocol; and later, they are still popular today. The BRC-20 standard also appeared based on the Ordinals protocol, which started the subsequent Summer of Inscriptions.
The birth of the Ordinals protocol dates back to early 2023 and was launched by Casey Rodarmor. He has been working in technology since 2010 and has worked at Google, Chaincode Labs, Bitcoin core, and now serves as co-moderator of SF Bitcoin BitDevs (Bitcoin discussion community).
Casey started to be interested in NFT in 2017 and was inspired to use Solidity to develop Ethereum smart contracts. However, he did not like building NFT on Ethereum because he thought it was a Goldberg machine (implementing simple things in an overly complicated way). , so we gave up building NFT on Ethereum. In early 2022, he once again came up with the idea of implementing NFT on Bitcoin. In the course of his research on Ordinals, he said he was inspired by Bitcoin founder Satoshi Nakamotos reference to something called an atom in the original Bitcoin codebase, which gives some sense of Caseys motivations. The hope was that Bitcoin would become interesting again, so Ordinals was born.
So how does the Ordinals protocol implement Ordinal Inscriptions, commonly known as BTC NFT? There are two core elements:
The first element is to assign a serial number to each Satoshis (Satoshi), which implements the labeling of the smallest unit of Bitcoin, and tracks these Satoshis when transactions are spent, thus allowing Satoshi to achieve non-fungibility, which is a very creative way of doing.
The second element is the support for attaching arbitrary content to individual Satoshis, including text, images, videos, audio, etc., thereby creating unique Bitcoin-native digital items - inscriptions (also commonly known as NFTs).
By numbering Satoshi’s and appending content, Ordinals allow people to own Ethereum-like NFTs on Bitcoin.
Next, let’s dive into the technical details to better understand how Ordinals is implemented. In the first element sequence number allocation, new sequence numbers can only be born in Coinbase Transaction (the first transaction in each block). Through the transfer of UTXO, we can trace it back to the corresponding Coinbase transaction and be able to determine the Satoshi number in this UTXO. However, it should be noted that this numbering system does not come from the Bitcoin chain, but is numbered by the indexer off the chain. So essentially the off-chain community developed a numbering system for Satoshi on the chain.
After the birth of the Ordinals protocol, many interesting NFTs appeared, such as Ordinal punks, TwelveFold, etc. As of now, the number of Bitcoin inscriptions has exceeded 54 million. On the basis of the Oridinals protocol, BRC-20 was also born, which opened the summer of BRC-20.

(Source: Dune - Ordinals total number of inscriptions)
The BRC-20 protocol is based on the Ordinals protocol and writes functions similar to ERC-20 Token into script data to realize the process of Token deployment, minting and trading.
Deploy tokens: Specify deploy in the script data, and indicate the token name, total issuance amount, and quantity limit for each token. After the indexer identifies the token deployment information, it can start recording the minting and transactions of the corresponding Token.
Mint tokens: Specify mint in the script data, specifying the name and quantity of the mint token. After identification, the indexer adds the balance of the payees corresponding token in the ledger.
Trading tokens: Specify transfer in the script data, indicating the name and amount of the token. The indexer deducts the corresponding number of tokens from the senders balance on the ledger and adds it to the balance of the payees address.
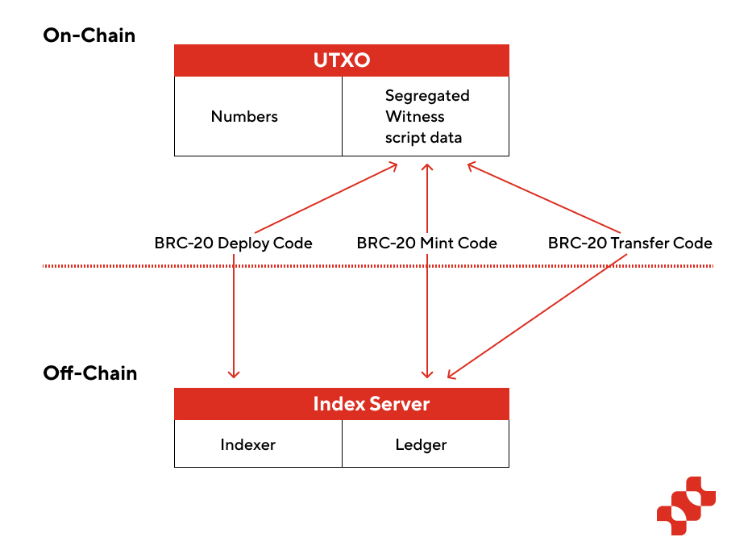
It can be seen from the technical principle of minting that since the balance of BRC-20 tokens is engraved in the script data of Segregated Witness and cannot be recognized and recorded by the Bitcoin network, an indexer is required to record BRC-20 locally. ledger. In essence, Ordinals just uses the Bitcoin network as a storage space, recording metadata and operation instructions on the chain, but the actual calculations and status updates of all operations are processed off-chain.
After the birth of BRC-20, it detonated the entire inscription market. BRC-20 accounts for the vast majority of Ordinals asset types. As of January 2024, BRC-20 assets account for more than 70% of all Ordinals asset types. In addition, from a market value perspective, the current market value of BRC-20 tokens has reached US$2.6 billion, of which the leading token Ordi has a market value of US$1.1 billion, and the market value of Sats is also around US$1 billion. The emergence of BRC-20 tokens has brought a new boost to the Bitcoin ecosystem and even the Crypto world.
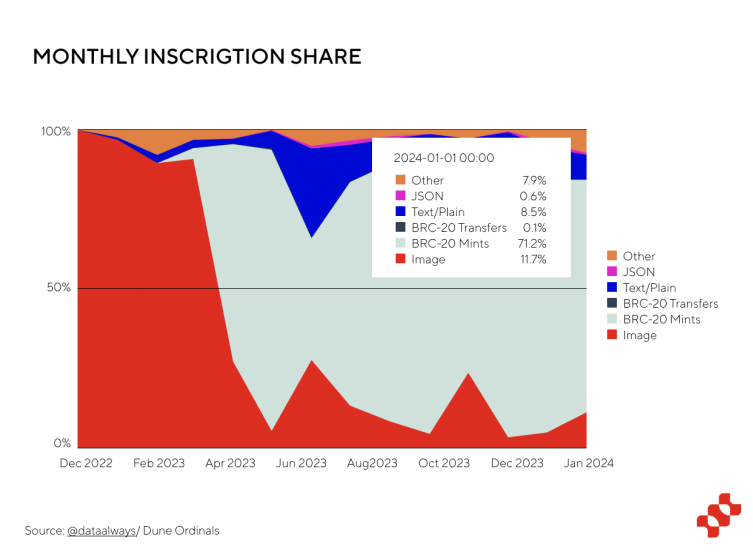
(Source: Dune - Ordinals Proportion of different asset types)
There are many reasons behind the popularity of BRC-20. The core ones can be summarized as the following two aspects:
Wealth creation effect: The popularity of Web3 protocols and projects is inseparable from the wealth creation effect, and BRC-20, as a new asset class on the BTC chain, has natural appeal and can attract a large number of users attention and occupy their minds.
Fair Launch: The BRC-20 Inscription features a fair launch where no one is the natural banker. Compared with traditional Web3 projects, Fair Launch allows retail investors to be on the same starting line as VCs in Token investment, making retail investors more willing to participate in Fair Launch projects; even some scientists want to maliciously raise a large number of BRC -20 Token, there is also a casting cost.
In general, although the Ordinals protocol has been subject to considerable controversy from the Bitcoin community since its inception, it is believed that Bitcoin NFT and BRC-20 will cause the block size to increase rapidly, resulting in higher requirements and fewer node operating equipment. , thereby reducing the degree of decentralization; but from a positive perspective, the Ordinals protocol and BRC-20 have demonstrated a new value use case for Bitcoin (in addition to digital gold), bringing new vitality to the ecosystem , attracted many developers to start paying attention to and developing the Bitcoin ecosystem again, and work on expansion, asset issuance and infrastructure.
2)Atomicals & ARC-20
The Atomiclas protocol was released by an anonymous developer in the Bitcoin community in September 2023. Essentially, it hopes to realize the issuance, minting and trading of assets without the need for external indexing mechanisms, and build a more native and complete protocol than the Ordinals protocol. Asset Release Agreement.
So what are the differences between the Atomics protocol and the Ordinals protocol? The core technical differences can be summarized in the following two aspects:
In terms of indexing, the Atomics protocol does not adopt the mechanism of numbering Satoshi off-chain, but chooses to index in UXTO.
In terms of appending or engraving content, the Atomics protocol does not append content to the Segwit script data of individual Satoshis, but rather engraves it in UXTO.
In addition, the Atomics protocol also introduces a PoW mechanism to control the difficulty of mining by adjusting the length of the prefix characters. Minters need to use the CPU to calculate the matching hash value, thus achieving a fairer distribution method.
Under the Atomics protocol, 3 asset types are created: NFTs, ARC-20 Tokens, and Realm Names. Realm is an innovative domain name system based on the Atomicals protocol. Unlike traditional domain names that add suffixes, Realm uses domain names as prefixes.
Next, we will focus on analyzing ARC-20. Unlike BRC-20, which is based on the Ordinals protocol, ARC-20 is a token standard officially supported by the Atomics protocol. Different from BRC-20, which writes Token into the script data of Segregated Witness, ARC-20 is a mechanism for dyeing coins. The registration information of the token is recorded on UXTO, and the transaction is completely processed by the BTC network, so it is different from the BTC network. BRC-20 is different in many aspects, see the table below for details:
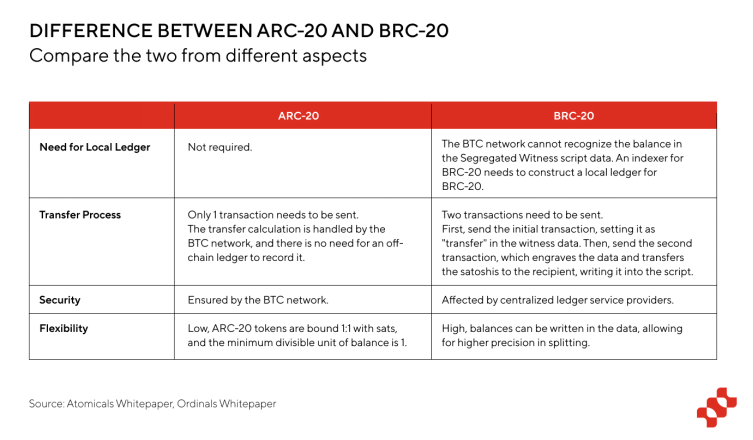
In general, the transactions of the Atomics protocol rely on the BTC network, do not repeatedly create a large number of meaningless transactions, and have less impact on the transaction cost of the network; and do not rely on off-chain ledgers to record transaction information, making it more decentralized; in addition, The transfer process only requires one transaction (while BRC-20 requires two), so the transfer performance of ARC-20 is significantly higher than BRC-20.
However, on the other hand, unlike retail investors participating in fair launch, the mechanism of ARC-20 mining will cause the market to pay for miners to a certain extent, so the advantage of inscription fair launch will be weakened. In addition, the difficulty in preventing users from mis-spending ARC-20 tokens is also a challenge that needs to be faced.
3)Runes & Pipe
As mentioned above, the emergence of BRC-20 resulted in the generation of many meaningless UTXOs. Casey, the developer of Ordinals, was also very dissatisfied with this, so he proposed Runes, a token protocol based on the UTXO model, in September 2023.
Overall, the standards of Runes protocol and ARC-20 are relatively similar. Token data is also engraved in UTXO scripts. Token transactions also rely on the BTC network. The difference is that the number of Runes can be defined, unlike ARC-20. The minimum precision is 1.
However, the Rune protocol is currently only in the conceptual stage. One month after the Runes protocol was proposed, Benny, the founder of Trac, launched the Pipe protocol. The principle is basically the same as Rune. In addition, according to founder Benny’s remarks in the official Discord, he also hopes to support more asset types (similar to Ethereum). ERC-721, ERC 1155 type assets)
4)BTC Stamps & SRC-20
BTC Stamps is a completely different asset issuance protocol from Ordinals. Since Ordinals data is stored in Segregated Witness script data, it may be pruned by full nodes and will be erased once the network hard forks. To address this risk, Twitter user @mikeinspace created the BTC Stamps protocol to embed data in an indivisible way in the blockchain by storing it in BTC’s UTXOs.
This integration ensures that data remains permanently on-chain, protected from deletion or modification, making it more secure and immutable. Once data is embedded as a Bitcoin Stamp, it remains on the blockchain forever. This feature is invaluable for ensuring the security and integrity of your data. It provides a powerful solution for applications that require immutable records, such as legal documents, digital art authentication, and historical archives.
Judging from the specific technical details, the Stamps protocol uses the method of embedding the transaction output into base 64 format image data, encoding the binary content of the image into a base 64 string, and placing the string as the suffix of STAMP: in the transaction description password. key and then broadcast it to the Bitcoin ledger using the Counterparty protocol. This type of transaction splits the data and embeds it into multiple transaction outputs and cannot be deleted by the full node, thus achieving storage permanence.
Under the Stamps protocol, the SRC-20 token standard also emerged, benchmarking the BRC-20 token standard.
In the BRC-20 standard, the protocol stores all transaction data in Segregated Witness data. Since the adoption rate of Segwit is not 100%, there is a risk of being pruned.
In the SRC-20 standard, data is stored in UTXO, making it a permanent part of the blockchain and cannot be deleted.
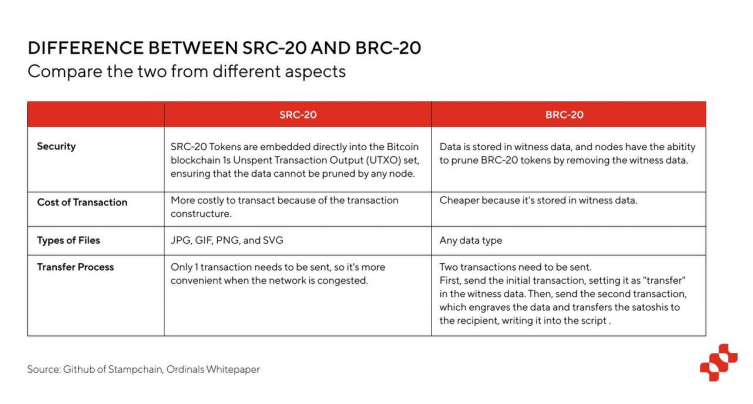
Among them, BTC Stamps supports multiple types of assets, including NFT, FT, etc. SRC-20 Token is one of the FT standards. It has the characteristics of more secure data storage and difficulty in tampering. However, the disadvantage is that the cost of casting is very expensive. The initial mint fee of SRC-20 is around 80 U, which is BRC-20 casting. Many times the cost. However, on May 17 last year, after the SRC-21 standard upgrade, the cost of a single Mint dropped to 30 U, which is similar to the Mint cost of ARC-20. However, after the decrease, the fee is still relatively expensive, about 6 times that of the BRC-20 token (the recent BRC-20 Mint fee is 4-5 U).
Although the Mint fee of SRC-20 is more expensive, like ARC-20, SRC-20 only requires one transaction during the Mint process; in contrast, the Mint and transfer of BRC-20 tokens require two transactions. A transaction can be completed. When the network is smooth, the number of transactions has little impact, but once the network is congested, the time cost required to initiate two transactions will increase significantly, and users will need to pay more gas to speed up transactions. In addition, it is worth mentioning that SRC-20 Token supports 4 types of BTC addresses, including Legacy, Taproot, Nested SegWit and Native Segwit addresses, while BRC-20 only supports Taproot addresses.
In general, SRC-20 tokens have obvious advantages over BRC-20 in terms of security and transaction convenience. The non-cuttable feature is in line with the needs of the security-focused Bitcoin community, and it can be split freely. Compared with the limitation of ARC-20, each Satoshi represents 1 token, which is more flexible. On the other hand, transfer costs, file size, and type restrictions are challenges currently faced by SRC-20. We also look forward to the future exploration and further development of SRC-20.
5)ORC-20
The ORC-20 standard aims to improve the usage scenarios of BRC-20 tokens and optimize existing problems of BRC-20. On the one hand, the current BRC-20 tokens can only be sold in the secondary market, and the total amount of tokens cannot be changed. There is no way to activate the entire system like ERC-20, which can be pledged, issued, etc.
BRC-20 tokens, on the other hand, rely heavily on external indexers for indexing and accounting. In addition, there may also be a double-spending attack. For example, if a certain BRC-20 Token has been minted, then according to the BRC-20 token standard, it is invalid to use the mint function to mint additional identical tokens. However, since the transaction is paid in Bitcoin Network fees, so this casting will still be recorded. Therefore, it completely relies on external indexers to determine which inscription is valid or invalid. For example, in April 2023, a hacker carried out a double-spend attack in the early stages of Unisat development. Fortunately, it was repaired in time and the impact was not expanded. .
In order to solve the dilemma of BRC-20, the ORC-20 standard came into being. ORC-20 is compatible with the BRC-20 standard and improves adaptability, scalability and security, as well as eliminating the possibility of double spending.
In terms of technical logic, ORC-20 is the same as the BRC-20 token, which is also a JSON file added to the Bitcoin blockchain. The difference is:
ORC-20 has no restrictions on names and namespaces, and has flexible keys. In addition, ORC-20 supports a wider range of JSON-formatted data formats, and all ORC-20 data is not case-sensitive.
BRC-20 has a maximum mint value and an immutable supply after initial deployment, while the ORC-20 protocol allows for changes in the initial value and maximum mint value of the issuance.
ORC-20 transactions use the UTXO model. The sender must specify the amount received by the receiver and the remaining balance to be sent to itself. For example, if you have 3333 ORC-20 tokens and want to send 2222 tokens to someone, then at the same time will also send 1111 to itself as new"enter". The entire model process is the same as the Bitcoin UTXO process. If the two steps are not completed, the transaction can be canceled midway; since UTXO can only be used once in the UTXO model, double spending is fundamentally prevented.
ORC-20 tokens add ID identification when deployed, and even tokens with the same name can be distinguished by ID.
Simply put, ORC-20 can be seen as an upgraded version of BRC-20, giving BRC-20 Token higher flexibility and richer economic models. Since ORC-20 is compatible with BRC-20, it is also easy to Wrap BRC-20 Token into ORC-20 Token.
6)Taproot assets
Taproot assets is an asset issuance protocol launched by Lightning Labs, Bitcoin’s second-layer network development team. It is also a protocol directly integrated with the Lightning Network. Its core characteristics and current situation can be summarized into the following three aspects:
Being completely based on UTXO means that it can be well integrated with Bitcoin native technologies such as RGB and Lightning.
Unlike Atomics, Taproot assets, like the Runes protocol, allow users to customize the number of token transactions and can create or transfer multiple tokens in a single transaction.
Directly integrated with the Lightning Network, users can use Taproot transactions to launch Lightning channels and deposit Bitcoin and Taproot Assets into Lightning channels in a single Bitcoin transaction, thereby reducing transaction costs.
However, it should be noted that there are currently some disadvantages:
There is a risk of evil: Taproot Assets metadata is not stored on the chain, but relies on off-chain indexers to maintain state, which requires additional trust assumptions. Data is stored locally or in a universe (a collection of servers containing historical data and verification information for a specific asset) to maintain token ownership.
It is not a fair launch: users cannot mint tokens on the Bitcoin network, but the project party issues all tokens and transfers them to the Lightning Network. The issuance and distribution are controlled by the project party, which essentially loses fairness. Launch characteristics.
Elizabeth Stark, co-founder of Lightning Labs, is committed to leading the Bitcoin renaissance with Taproot Assets while promoting the Lightning Network as a multi-asset network. Due to the native integration of Taproot Assets and Lightning, users do not need to cross-chain assets to side chains or other Layer 2, and can directly store Taproot Assets into Lightning channels for transactions, making transactions more convenient.
7) Summary of current situation analysis
In summary, the birth of the Oridinals protocol and the BRC-20 token standard has brought about the craze of inscriptions, and has also made people turn their attention to the asset issuance protocol on Bitcoin again, with the emergence of Atomics, Runes, BTC Stamps, Taproot Diversified asset issuance protocols such as Assets have also produced ARC-20, SRC-20, ORC-20, etc.
In addition to the mainstream asset issuance protocols introduced above, there are many asset protocols that are also being conceived and developed. For example, BRC-100 is a decentralized computing protocol based on Ordinals theory. It is hoped that it can enrich the use scenarios of assets and support the development of similar For applications such as DeFi and GameFi; the BRC-420 standard is similar to ERC-1155 and can combine multiple inscriptions into a complex asset, thus having many application scenarios in games and metaverses (for example, the ERC-1155 protocol is suitable for The game scenario of the combination of NFT and FT.); Even some memecoin communities have begun to launch new asset protocols on BTC (for example, the Dogecoin community launched DRC-20), showing a situation where a hundred flowers are blooming.
Judging from the current status of the project, the current asset issuance protocols can be divided into BRC-20 faction and UTXO faction. The former includes BRC-20, and the upgraded and expanded version of BRC 20, ORC-20, which engraves data in the script data of Segregated Witness and relies on off-chain indexers for indexing and accounting; the latter mainly includes ARC-20, SRC -20. The asset types that Runes and Pipe want to implement and Taproot Assets.
The two factions of BRC-20 and ARC-20 also symbolize the two ideas of the BTC ecological asset protocol:
One is a very simple solution like BRC-20. Although the function is not complicated, the whole idea and code are very simple and elegant. Just a few lines of innovation meet the smallest unit of demand. It is a very good solution. MVP version.
The other is a protocol like ARC-20, where problems are solved as they arise. During the development process of ARC-20, there were many bugs and areas that needed to be optimized. However, we only solve problems when we encounter them, and we prefer a bottom-up development path.
At present, BRC-20 has occupied the first place in the asset agreement due to its first-mover advantage. In the future, let us wait and see who can occupy the second place in standards such as SRC-20 and ARC-20 or even overtake BRC-20 in corners.
Returning to the essence, on the one hand, the Inscription track has brought a new model of fair launch to retail investors and brought huge attention to the Bitcoin ecosystem; on the other hand, according to OKLink data, the income of Bitcoin miners increased in December last year. So far this month, the revenue from handling fees has accounted for more than 10%, which has also brought tangible benefits to miners. It is believed that driven by the Bitcoin ecological community of interests, the inscription ecology and asset issuance protocols on Bitcoin will enter a new period of exploration and development.
2. On-chain expansion
The asset issuance protocol has attracted renewed attention to the Bitcoin ecosystem. Due to the difficulties of Bitcoins scalability and transaction confirmation time, if the ecosystem is to develop for a long time, Bitcoin expansion is also an area that needs to be faced directly and attracts much attention.
In terms of improving the scalability of Bitcoin, there are currently two main development routes. One is on-chain expansion, which is optimized on Bitcoin Layer 1; the other is off-chain expansion, which is commonly understood as Layer 2. In this section and the next section, we will talk about the development of the Bitcoin ecosystem from the aspects of on-chain expansion and Layer 2 respectively. In terms of on-chain expansion, on-chain expansion wants to improve TPS through block size and data structure, such as BSV and BCH. However, there is currently no consensus from the mainstream BTC community. In the current on-chain expansion upgrade plan with mainstream consensus, The most noteworthy ones are SegWit upgrade and Taproot upgrade.
1) Segwit upgrade
In July 2017, Bitcoin underwent a Segregated Witness (Segwit) upgrade, which greatly improved scalability. It was a soft fork.
The main goal of SegWit is to solve the problem of transaction processing capacity limitations and high transaction fees faced by the Bitcoin network. Before SegWit, the size of Bitcoin transactions was limited to 1 MB blocks, which led to transaction congestion and high fees. SegWit separates the transactions witness data (including signatures and scripts) by reorganizing the transaction data structure and storing it in a new section called the witness area by separating the transaction signature data from the transaction data. , thereby effectively increasing the capacity of the block.
SegWit introduces a new unit of measurement for block sizes called weight units (wu). A block without SegWit has 1 million wu, while a block with SegWit has 4 million wu. This change allows the block size to exceed the 1 MB limit, effectively expanding the capacity of the block, thereby increasing the number of Bitcoins. The throughput of the network enables each block to accommodate more transaction data, and due to the increase in block capacity, SegWit enables more transactions to enter each block, reducing transaction congestion and the increase in transaction fees.
In addition, the importance of Segwit upgrade is not limited to this, but also promoted the occurrence of many major events later, including the subsequent Taproot upgrade, which was also developed on the basis of Segwit upgrade to a large extent, such as the Ordinals protocol that exploded in 2023. And the operations of BRC-20 token are also carried out in isolated data. To a certain extent, the Segwit upgrade has also become the booster and founder of this summer of inscriptions.
2) Taproot upgrade
The Taproot upgrade is another important upgrade to the Bitcoin network, taking place in November 2021 and combining three different related proposals, BIP 340, BIP 341, and BIP 342, designed to improve Bitcoin’s scalability. The goal of the Taproot upgrade is to improve the privacy, security, and functionality of the Bitcoin network. It makes Bitcoin transactions more flexible, secure and has better privacy protection by introducing new smart contract rules and cryptographic signature schemes.
The core advantages of its upgrade can be summarized into the following three aspects:
Schnorr multi-signature aggregation: Schnorr signatures are proposed in BIP 340, which allow multiple public keys and signatures to be aggregated into a single public key and signature, thereby reducing the size of transaction data. By aggregating signatures, the network can process more transactions, making overall operations faster and cheaper, thus maximizing block space savings.
Greater privacy: P2TR in BIP 341 uses a new script type that combines the functions of the previous two scripts P2PK and P2SH, introduces another privacy element, and provides a better transaction authorization mechanism. P 2 TR also makes all Taproot outputs look similar so that there are no more differences between multi-signature and single-signature transactions. In this way, it becomes more difficult to identify the transaction inputs of each participant storing private data.
Makes more complex smart contracts possible: Previously, Bitcoin’s smart contract capabilities were limited, but after the upgrade, Taproot allowed multiple parties to sign a single transaction using a Merkle tree. Taproot introduced a new script type called"Tapscript", allowing developers to write more complex smart contracts, including conditional payment, multi-party consensus and other functions, giving Bitcoin more possibilities for its future development.
Overall, through SegWit and Taproot upgrades, the Bitcoin network has been able to improve scalability, transaction efficiency, privacy, and functionality, laying a solid foundation for future innovation and development.
3. Off-chain expansion: Layer 2
Due to the structural limitations of Bitcoins own chain, coupled with the decentralized nature of Bitcoins community consensus, on-chain expansion plans are often questioned by the community. Therefore, many builders have begun to try off-chain expansion and build off-chain expansion protocols or so-called off-chain expansion protocols. Layer 2, to build a second layer network on top of the Bitcoin network.
Among them, Bitcoin’s current Layer 2 types can be roughly divided into: state channel, side chain, Rollup, etc. based on data availability and consensus mechanism.
Among them, the status channel allows users to build communication channels off the chain, conduct high-frequency transactions off the chain, and then record the final results on the chain. The scenarios are mainly limited to transaction scenarios. The core difference between Rollup and side chain is the inheritance of security. The consensus of Rollup is formed on the main network and cannot operate once the main network fails. The consensus of side chain is independent, so once the consensus of side chain itself fails, it cannot run. run.
In addition, in addition to the Layer 2 mentioned above, there are also expansion protocols like RGB for off-chain expansion to improve network scalability.
1) Status channel
A state channel is a temporary communication channel created on the blockchain for efficient interactions and transactions outside the chain. It allows participants to interact multiple times with each other and ultimately record the final results on the blockchain. State channels can increase the speed and throughput of transactions and reduce associated transaction fees.
When it comes to Layer 2 such as state channels, the most important thing to mention is the Lightning Network. The earliest state channel project in the blockchain is the Lightning Network on Bitcoin. The concept of Lightning Network was first proposed in 2015, and then Lightning Labs implemented Lightning Network in 2018.
The Lightning Network is a state channel network built on the Bitcoin blockchain that allows users to conduct fast transactions off-chain by opening payment channels. The successful launch of the Lightning Network marked the first implementation of state channel technology and laid the foundation for subsequent state channel projects and development.
Next, let us focus on the implementation technology of Lightning Network. As a Layer 2 payment protocol based on the Bitcoin blockchain, the Lightning Network aims to achieve fast transactions between participating nodes and is considered an effective solution to the Bitcoin scalability problem. The core of the Lightning Network is that a large number of transactions occur off-chain. Only when all transactions are completed and the final status is confirmed, will they be recorded on the chain.
First, the transaction party uses the Lightning Network to open a payment channel and transfer funds to Bitcoin as a pledge according to the smart contract. Parties can then conduct any number of transactions via the Lightning Network off-chain to update the temporary allocation of channel funds, a process that does not need to be recorded on-chain. When parties complete a transaction, they close the payment channel and the smart contract distributes the committed funds based on the transaction record.
Next to shut down the Lightning Network, a node first broadcasts the current transaction record status to the Bitcoin network, including settlement proposals and allocation of committed funds. If both parties confirm the proposal, the funds are immediately disbursed on-chain and the transaction is completed.
Another situation is a shutdown exception, such as a node exiting the network or broadcasting an incorrect transaction status. In this case, settlement is delayed until the dispute period, and nodes may dispute settlement and fund distribution. At this time, if the questioning node broadcasts an updated timestamp, including some transactions missed in the first proposal, then the subsequent correct results will be recorded, and the commitment of the first evil node will be confiscated. , reward the other party’s node.
From the core logic of the Lightning Network, we can see that it has the following four advantages:
Real-time payments eliminate the need to create a transaction for each payment on the blockchain, and payment speeds can reach milliseconds to seconds.
High scalability. The entire network can handle millions to billions of transactions per second, its payment capabilities far exceed those of traditional payment systems, and operations and payments can be made without relying on intermediaries.
low cost. By conducting transactions and settlements outside the blockchain, Lightning Network fees are extremely low, making emerging applications such as instant micropayments possible.
Cross-chain capabilities. Perform off-chain atomic swaps through heterogeneous blockchain consensus rules. As long as the blockchains support the same cryptographic hash function, cross-blockchain transactions can be made without trusting a third-party custodian.
Although the Lightning Network also faces some difficulties, such as users need to learn and understand the use, opening and closing of the Lightning Network, in general, the Lightning Network allows a large number of transactions to be carried out on Bitcoin by establishing a Layer 2 transaction protocol. It is carried out off-chain, which reduces the burden on the Bitcoin main network. The current TVL is close to 200 million US dollars.
However, since Layer 2 of the state channel is limited to transactions, it cannot support more types of applications and scenarios like Layer 2 of Ethereum. This has also led many Bitcoin developers to think about Bitcoin Layer with a wider range of scenarios. 2 solutions.
After the birth of the Lightning Network, Elizabeth Stark was committed to developing the Lightning Network into a multi-asset network, and asset protocols such as Taproot Assets also emerged to enrich and broaden the usage scenarios of the Lightning Network; in addition, some subsequent expansion plans were also implemented through and Lightning Network integration for greater scope of use. The Lightning Network is not only a state channel, but also a soil for basic services, giving birth to and stimulating the flowers of a more diverse BTC ecosystem.
2) Side chain
The concept of sidechains was first mentioned by Adam Back, the inventor of Hashcash, and others in the paper Enabling Blockchain Innovations with Pegged Sidechains published in 2014. It was mentioned that if Bitcoin wants to provide better services, there are still many ways Room for improvement. Therefore, the technology of sidechain was proposed to allow Bitcoin and other blockchain assets to be transferred between multiple blockchains.
Simply put, a sidechain is an independent blockchain network that runs in parallel with the main chain, with customizable rules and functions, allowing for greater scalability and flexibility. From a security perspective, these side chains need to maintain their own set of security mechanisms and consensus protocols, so their security depends on the design of the side chain. Sidechains typically have greater autonomy and customization, but may have less interoperability with the main chain. In addition, a key element of side chains is the ability to transfer assets from the main chain to the side chain for use, which usually involves operations such as cross-chain transfers and locking assets.
For example, Rootstock uses merged mining to ensure the security of the side chain network, and Stacks uses the Proof of Transfer (PoX) consensus mechanism. The following two cases will be used to help everyone understand the current status of BTC side chain solutions.
First let’s take a look at Rootstock. Rootstock (RSK) is a sidechain solution for Bitcoin that aims to provide more functionality and scalability to the Bitcoin ecosystem. RSKs goal is to provide a more powerful decentralized application (DApp) development platform and more advanced smart contract functions by introducing smart contract functions into the Bitcoin network. The current TVL has reached $130 million.
The core design idea of RSK is to connect Bitcoin to the RSK network through side chain technology. A sidechain is an independent blockchain that can interact with the Bitcoin blockchain in both directions. This makes it possible to create and execute smart contracts on the RSK network while leveraging Bitcoin’s security and decentralized properties.
The core advantages of RSK include Ethereum language friendliness and merged mining:
Ethereum Development Language Friendly: One of the main advantages of RSK compared to other smart contract platforms like Ethereum is its compatibility with Bitcoin. RSKs Virtual Machine (RSK Virtual Machine) is an improved version based on the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM), allowing developers to use Ethereum smart contract development tools and languages to build and deploy smart contracts. This provides developers with a familiar development environment and the ability to take advantage of Bitcoin’s strong security.
Merged Mining Boosts Miner Participation: RSK has also introduced a consensus algorithm called “merged mining” that is integrated with Bitcoin’s mining process. This means that Bitcoin miners can mine RSK while mining Bitcoin, providing security for the RSK network. This merged mining mechanism is designed to increase the security of the RSK network and provide an incentive mechanism for Bitcoin miners to participate in the operation of the RSK network. And since both blockchains use the same consensus, Bitcoin and RSK consume the same mining power, so miners can contribute hash rate to mine blocks on RSK. Ultimately, merged mining can increase miner profitability without requiring additional resources.
RSK attempts to solve the problems of long transaction confirmation time and network congestion of Bitcoin layer 1 by placing smart contracts on the side chain. It provides developers with a powerful platform to build decentralized applications and adds to the Bitcoin ecosystem. Provides more functionality and scalability, promoting greater adoption and innovation.
RSK creates a new block approximately every 30 seconds, which is significantly faster than Bitcoin’s 10-minute block time. In terms of TPS, RSK is 10-20, which is significantly faster than the Bitcoin network, but compared to the high performance of Ethereum Layer 2. It seems insufficient, and there are still some challenges in supporting high-concurrency applications.
Next let’s take a look at Stacks, a Bitcoin-based sidechain with its own consensus mechanism and smart contract functionality. The Stacks blockchain enables security and decentralization by interacting with the Bitcoin blockchain, and is incentivized through Stacks coins (STX).
Stacks was originally called Blockstack and the project started in 2013. The Stacks testnet was launched in 2018, and its mainnet was released in October 2018. In January 2020, with the release of the Stacks 2.0 mainnet, the network ushered in a major update. This update natively connects and anchors Stacks to Bitcoin, allowing developers to build decentralized applications.
Among them, Stacks deserves attention for its consensus mechanism - Proof of Transfer (PoX). Proof-of-transfer is a variant of Proof-of-Burn (PoB). Proof-of-burn was originally proposed as a consensus mechanism for the Stacks blockchain. exist"burn proof"In the mechanism, miners participating in the consensus algorithm will send Bitcoin to the burn address, in this way proving that they have paid for the new block. In Proof of Transfer, this mechanism has all the changes: the cryptocurrency used is not destroyed, but distributed to a group of participants who help secure the new chain.
Therefore, in the Stacks consensus mechanism, miners who want to mine the Stacks token STX and participate in the consensus need to send a Bitcoin transaction to a predefined random Bitcoin address in order to generate a block in the Stacks blockchain. Which miner can generate a block is ultimately determined by sorting. However, the probability of being selected increases with the number of Bitcoins a miner transfers to a list of Bitcoin addresses, and the Stacks protocol rewards them with STX.
In a sense, Stacks’ consensus mechanism is modeled after Bitcoin’s proof-of-work mechanism. But instead of consuming energy to mine to generate new blocks, Stacks miners use Bitcoin to maintain the Stacks blockchain. Proof-of-transfer is also a very sustainable solution for Bitcoin’s programmability and scalability. Since Clarity, the development language of Stacks, is relatively niche, the number of active developers has not been particularly high, and ecological construction has been relatively slow. The current TVL is only US$50 million. Although the official claim is that it is Layer 2, it is currently more of a side chain.
It won’t become a true Layer 2 until its Nakamoto upgrade, scheduled for the second quarter of this year. Nakamoto Release is an upcoming hard fork on the Stacks network that increases transaction throughput and 100% Bitcoin transaction confirmation finality.
One of the most significant changes in the Nakamoto upgrade is to speed up the block confirmation time, shortening the transaction confirmation time from Bitcoins 10 minutes to a few seconds. By increasing the block productivity and producing a new block approximately every 5 seconds, transactions It may be confirmed within a minute, which is very beneficial to the development of Defi projects.
In terms of security, the Nakamoto upgrade will bring the security of Stacks transactions in line with the security of the Bitcoin network. The integrity of the network has also been improved and its ability to handle Bitcoin reorganizations has been enhanced. Even in the event of a Bitcoin reorganization, most Stacks transactions will remain valid, ensuring the reliability of the network.
In addition to the Nakamoto upgrade, Stacks will also launch sBTC. sBTC is a decentralized programmable 1:1 Bitcoin-backed asset that enables the deployment and transfer of BTC between Bitcoin and Stacks (L2). sBTC enables smart contracts to write transactions to the Bitcoin blockchain, while in terms of security, transfers are secured by the entire Bitcoin hashing power.
In addition to Rootstock and Stacks, there are different sidechain solutions such as Liquid Network that use different consensus mechanisms to improve the scalability of the Bitcoin network.
3)Rollup
Rollup is a two-layer solution built on the main chain that improves throughput by offloading most of the computation and data storage from the main chain to the Rollup layer. In terms of security, Rollup relies on the security of the main chain. Usually the transaction data on the chain will be submitted to the main chain in batches for verification. Moreover, Rollup often does not require direct transfer of assets. The assets still remain on the main chain, and only the verification results are submitted to the main chain.
Although Rollup is often regarded as the most orthodox Layer 2, it has wider usage scenarios than state channels, and it inherits the security of Bitcoin more than side chains. However, the current development is in a very early stage. Here is a brief introduction. Merlin Chain, B² Network and BitVM.
Merlin Chain is Layer 2 launched by Bitmap and BRC-420 development team Bitmap Tech, which uses ZK-Rollup to improve the scalability of Bitcoin. It is worth mentioning that Bitmap is a fully on-chain, decentralized and fairly launched Metaverse project. The number of users holding its asset Bitmap has reached 33,000, surpassing Sandbox and becoming the largest holder of the Metaverse project. s project.
Merlin Chain has recently launched its testnet, which can freely cross-chain assets between Layer 1 and Layer 2, and supports Bitcoin’s native wallet Unisat. In the future, it will also support native Bitcoin asset types such as BRC-20, Bitmap, BRC-420, Atomics, SRC 20 and Pipe.
In terms of implementation, the sequencer on Merlin Chain batches transactions, generates compressed transaction data, ZK state roots and proofs. The compressed transaction data and ZK proof are uploaded to the Taproot of the BTC network through the decentralized Oracle, thus ensuring the security of the network. In terms of Oracles decentralization, each node needs to pledge BTC as a penalty. Users can challenge ZK-Rollup based on compressed data, ZK state root and ZK proof. If the challenge is successful, the BTC of the pledged node will be confiscated, thus preventing Oracle does evil. The network is currently still in the test network stage, and it is said that it will be launched on the main network within two weeks. We are looking forward to its performance after the main network is launched.
In addition to Merlin Chain, Bitcoin Layer 2 Rollup solutions include B² Network, which hopes to increase transaction speed and expand application diversity without sacrificing security. Its core features can be summarized as the following two aspects:
Rollup solution: B² Network provides an off-chain trading platform that supports Turing-complete smart contracts, which improves transaction efficiency and reduces costs. At the same time, unlike side chains and expansion solutions, Rollup better inherits the advantages of the Bitcoin blockchain. safety.
Combining ZKP and Fraud-Proof: Ensure enhanced privacy and security of transactions by combining Zero-Knowledge Proof (ZKP) technology and Fraud-Proof’s challenge response protocol with Bitcoin’s Taproot.
Regarding how B² Network implements the BTC Layer 2 Rollup solution, we look at its core Rollup Layer and DA Layer (data availability layer). In terms of the Rollup layer, B² Network uses ZK-Rollup as the Rollup layer, which is responsible for the execution of user transactions within the Layer 2 network and the output of relevant certificates. In terms of the DA layer, it includes three parts: decentralized storage, B² nodes and the Bitcoin network. This layer is responsible for permanently storing a copy of the rollup data, verifying the rollup zk proof, and ultimately finalizing it via Bitcoin.
In addition, BitVM also implements Rollup by processing complex calculations such as Turing-complete smart contracts off-chain, reducing congestion on the Bitcoin blockchain. In October 2023, Robin Linus released the BitVM white paper, hoping to improve Bitcoins scalability and privacy by developing a zero-knowledge proof (ZKP) solution. BitVM uses Bitcoins existing scripting language to develop a method of representing NAND logic gates on Bitcoin, thereby enabling Turing-complete smart contracts.
Among them, there are two main roles in BitVM: prover and verifier. The prover is responsible for initiating a computation or assertion, essentially presenting a program and asserting its expected results. The role of the verifier is to verify this claim, ensuring that the calculation results are accurate and trustworthy.
In the event of a dispute, such as a validator challenging the accuracy of a provers statement, the BitVM system uses a challenge-response protocol based on fraud proofs. If the provers claims are untrue, the verifier can send a proof of fraud to the Bitcoin blockchains immutable ledger, which will prove the fraud and maintain the overall trustworthiness of the system.
However, BitVM is still in the white paper and construction stage, and it is still some time away from actual use. In general, the entire BTC Rollup track is currently in a very early stage. The future performance of these networks, whether it is support for Dapp or TPS and other performance, still needs to wait for market testing after the network is officially launched. .
4) Others
In addition to the state channels, side chains and rollups mentioned above, there are also some off-chain expansion solutions that use client verification, the most representative of which is the RGB protocol.
RGB is a private and scalable client-verified smart contract system developed by the LNP/BP Standards Association on Bitcoin and the Lightning Network. Originally proposed by Giacomo Zucco and Peter Todd in 2016, the name RGB was chosen because the original intention of the project was to become"Better version of colored coins"。
RGB solves the scalability and transparency issues of the Bitcoin main chain through the use of smart contracts, in which an agreement is reached in advance between two users and is automatically completed once the conditions of the agreement are met. And because RGB is integrated with Lightning, there is no need for KYC, thus maintaining anonymity and privacy since there is actually no need to interact with the Bitcoin main chain at all.
RGB Protocol hopes that Bitcoin will open up a new world of scalability, including the issuance of NFTs, Tokens, fungible assets, implementation of DEX functions and smart contracts, etc. Bitcoin Layer 1 serves as the base layer for final settlement, and Layer 2 such as Lightning Network and RGB are used for faster anonymous transactions.
RGB has two core features, client verification mode and one-time sealing:
Client verification mode: RGB operates in client verification mode and implements smart contracts. In RGB, data is stored off-chain, and smart contracts are only responsible for verifying the validity of the data and executing related logic. Bitcoin transactions or Lightning channels only serve as an anchor point for validating data, while the actual data and logic are verified by the client. This design enables RGB to build smart contract systems on top of Bitcoin or Lightning Network protocols without modifying them.
One-time seal: RGB tokens need to be associated with a specific UTXO. When spending UTXO, the Bitcoin transaction will include a message commitment, indicating that the message contains the input of RGB, the destination UTXO, the ID and amount of the asset, etc. Although the transfer of RGB Token must require a Bitcoin transaction, the UTXO output by RGB transfer and the UTXO output by Bitcoin do not need to be the same, which means that the Token on RGB can be output to another party that has nothing to do with this UTXO transaction. A UTXO without leaving a trace on Bitcoin, once you send the asset via RGB you cannot see where it went, and even if you receive the asset its history is difficult to decipher, thus providing users for greater privacy protection.
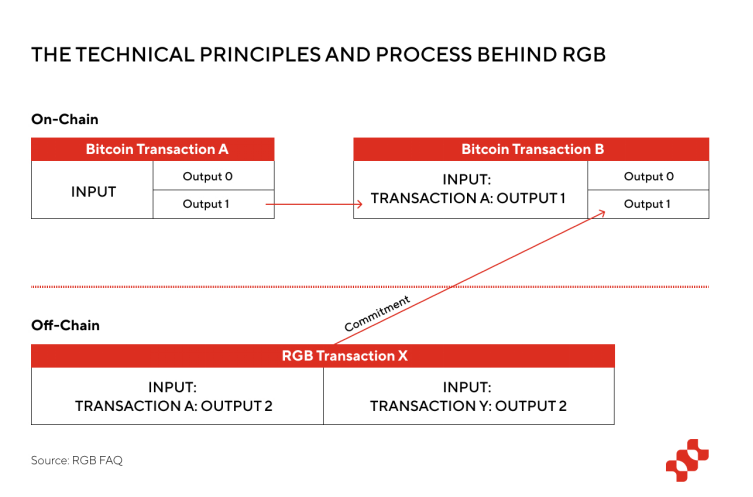
As can be seen from the one-time seal above, each contract state in RGB is associated with a specific UTXO, and access to and use of that UTXO is restricted through Bitcoin scripts. This design ensures that the contract state is unique because each



