连接Web2与Web3:探索Attestation历史和其相关项目
Attestation is not a new concept, especially if you understand the Ethereum PoS consensus, some of the steps are called Attestation. In addition, EAS, Smart Layer, EthSign, Verax and PADO Labs also emphasize that their protocol layer is related to the concept of Attestation. So what exactly does Attestation mean? What is the difference between Verification and Verification?
Attestation History and Definition
Start withetymologyIt seems that Attestation originated in the mid-15th century and means testimony (testimony) or a declaration in support of a fact (a statement in support of a fact). Verification has slightly earlier origins and means confirmation or corroboration. According to the word frequency statistics of literature in the past two hundred years, the frequency of use of Verification has increased year by year, while the opposite is true for Attestation, and the word frequency of Verification is more than ten times that of Attestation. It can be seen that Attestation is a relatively niche word.
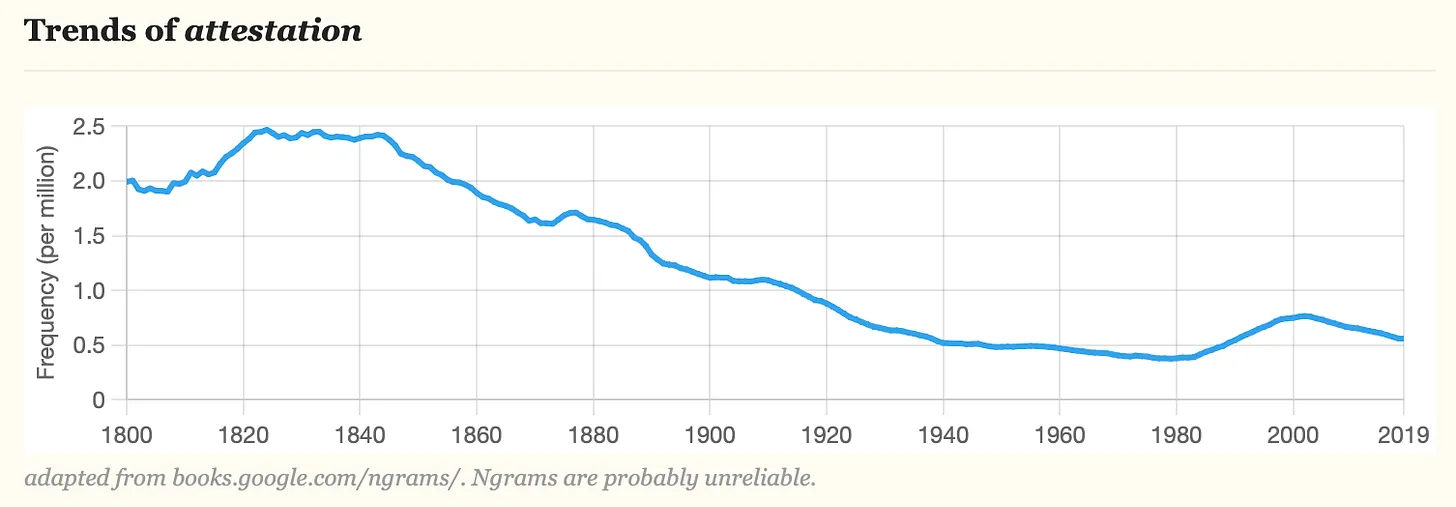
In the consensus process of Ethereum, Attestation refers to the validators recognition of the final status of the current block, which is similar to a voting process. In addition, if the validator does malicious behavior during this process (Surround Vote), or the validator passively participates (or goes offline), it will be punished by the consensus algorithm (Slashing/Inactivity Leak). This also means that there is some subjectivity in the verifiers participation in Attestation.
And according to Cornell Law SchooldictionaryIt seems that the meaning of Attestation is similar to testimony (testimony). Usually when signing a contract, making a will or signing other written documents, a witness needs to be present, and the witness must also sign to attest (attest) the content of the document. authenticity and the authenticity of the parties’ signatures.” This process can also be summarized as “witnessing”.
Therefore, based on the above information, Attestation is more similar to the meaning of witness, testimony, and statement. It is also recognized by the Attestor with a certain degree of subjectivity, and others cannot verify its accuracy through other methods. The meaning of Verification is too common, and it is repeatable and verifiable based on a certain method.
After understanding these differences, you can understand why so many projects use Attestation as the core concept to explain, because it is not solving a technical and algorithmic problem, but a social consensus problem, how to make these witnessable and visible. The declared events are defined according to a certain standard, and then these data are stored through the blockchain, smart contracts are used to implement more combinable logic, generate liquidity, etc.

Attestation application scenarios in Web2:
Account Verification: Verify user accounts via email or phone number.
Employment certificate: A certificate of employment provided by the employer, including the employees basic information, employment period, position, etc., usually provided by the companys human resources department.
Educational certificate: An official academic certificate issued by the school, confirming that the individual has completed specific studies through Xuexin.com, etc.
Proof of Identity: An identification document issued by a government agency, such as a driver’s license, passport, etc.
Web3 introduces a paradigm shift in proof capabilities. Trust no longer relies on a single centralized entity, but is dispersed in a network composed of multiple nodes, using cryptography technology and consensus algorithms to protect and ensure the security and credibility of information.
Attestation application scenarios in Web3:
Proof of Digital Asset Ownership: A digital signature certificate is generated on the blockchain to prove that a specific address owns a specific number or type of digital assets, such as NFT.
Identity verification: Obtain individual identity certification on the blockchain through a decentralized identity system.
Smart contract execution proof: The smart contract issues an Attestation to prove that it has been executed as expected and certain conditions or events have been triggered.
Data integrity and traceability: By generating a digital signature on the blockchain, the integrity and non-tamperability of the data are ensured. The signature will be successfully verified only if the data has not been tampered with.
The imagination of Attestation combined with Web3 and Web2 is very large. Attestation serves as a bridge between the digital and the real world, and can provide proof mechanisms in various scenarios such as verification, endorsement, voting, certification, and guarantees. For example:
Event tickets: Event organizers use blockchain technology to issue ticket Attestation to prevent counterfeiting or reuse of tickets.
Proof of Attendance: Using on-chain Attestation, it not only proves that users attended a specific event, but also provides digital souvenirs.
Email: Users can use email Attestation to associate their identities in Web3 and Web2, simplifying the authentication process.
Medical record verification: Medical information such as patient health information, diagnosis, treatment process, etc. is recorded on the blockchain. The doctor can generate a digitally signed Attestation to prove the integrity of the record.
……
Attestation concept projects worthy of attention
Although the Attestation concept is still in the early stages of development, there are some projects that have attracted widespread market attention.
1.Ethereum Attestation Service(EAS): Universal Attestation
EAS is an open source infrastructure project for attesting on or off the chain. Utilizes digital signature Attestation of structured information as a means to verify facts, prove authenticity, and establish trust in various online and on-chain interactions. EAS operates through two smart contracts, the Schema Registry Contract for registering the attestation schema and the Attestation Contract for performing attestations.
The main function of Schema Registry Contract is to allow users to register proof templates and define the structure and format of proof data. The user first defines a schema, which is submitted to the schema registration contract for registration. After the pattern is registered, the contract assigns a unique identifier (UID) to the pattern so that it can be referenced in subsequent proofs.
The Attestation Contract mainly manages the attestation cycle. Users create a certificate using a previously registered template, fill in the specific content according to the previously defined format, and digitally sign it either on-chain or off-chain. This signed data, along with the schemas UID, is submitted to the attestation contract. The contract verifies the signature and UID, and if the verification passes, the proof is recorded on the blockchain and anyone can verify its authenticity. If the status of a certificate needs to change, the certificate can be revoked. Revocation does not edit the certificate itself but makes it no longer considered valid.
Proofs can be made on-chain or off-chain, with on-chain proofs stored directly on the Ethereum blockchain, providing immutability and security. Off-chain proofs are stored outside of the blockchain, typically in a decentralized storage solution (IPFS), and can be used to share privately on demand.
2.Samrt Layer:Authentication
Smart Layer is a programmable blockchain service network that provides support for executing token logic to enable complex interactions with various systems and tokens in a decentralized, scalable and secure manner. Smart Layer creates Executable Token based on TokenScript technology. Executable Token is an NFT or Token with built-in runnable code. It is not just a static digital asset, but can also perform various functions.
Smart Layer and the Ethereum Foundation Devcon team collaborated to develop ticket certification based on Executable Token, and 20,000 Ethereum builders participating in Devcon 6 Bogotá, EFDevconnect Amsterdam and EDCON 2023 events have all conducted NFT ticket certification. People with tickets to these events can generate proof via the same email address to receive a special pass called a Smart Pass to earn additional Smart Layer Points.
3.EthSign:Contract signing
EthSign is a blockchain-based document signing protocol whose main purpose is to allow users to sign, encrypt and permanently store files in a decentralized, secure and verifiable environment. EthSign allows users from different blockchain systems to digitally sign and encrypt files using their encryption keys. This means that Bitcoin users can collaborate with Ethereum users and users of other blockchain ecosystems to sign contracts, etc. EthSign utilizes the Arweave blockchain for permanent storage at no cost to users.
EthSign provides a variety of contract samples, and the overall operation process is similar to DocuSign. First, users can log in with a blockchain wallet, or choose an email or Twitter account to log in. EthSign uses Particle Networks authentication scheme to support web2 authentication. Then create a new contract through the template or upload an unsigned file, add signature and date fields or text content, fill in the address or account number of the signer, and finally select the contract pre-date, after which signature will not be possible. Considering file privacy, users can choose to encrypt documents and enable the EthSign contract password manager, which uses asymmetric encryption principles to host user contract passwords, so users do not need to remember contract passwords.
In addition, EthSign also offers contract verification, from the initial user can verify on the Verification page that the original content of their completed document is consistent with the copy on Arweave. It is now possible to verify the validity of a digital signature and whether it was created by an EthSign Certified signing address, and will support offline verification in the future.
EthSign’s next step is to evolve from a contract signing application to a full-chain attestation protocol.Sign Protocol, which aims to be able to sign everything on-chain. For example, Coinbase Verifications currently leverages EAS to enable users to prove their KYC status on the Base network. If a user wants to prove that they have passed Coinbases verification to gain admission to other projects, they can use Sign Protocols zkAttestations to capture data from the Coinbase server through a browser extension, and then generate an encrypted certificate proving that the user has passed the verification. .
4.Verax: Developer Tools
Verax is a shared on-chain proof registry that provides a centralized place to store on-chain proofs and provides developers with a general, extensible tool to help them manage and utilize on-chain proofs that can prove The identity of an entity, the right to own digital assets, trust in a wallet, etc. These proofs can be used to build digital identities, trust systems, reputation protocols, and more.
One of Veraxs design goals is interoperability, helping developers publish attestations that are compatible with other standards. Similar to a channel, different projects are allowed to store and retrieve on-chain proofs on this channel, and other protocols, dapps or users can easily use and combine these proofs without worrying about compatibility between different standards.
5.PADO Labs:privacy protection
PADO is a cryptography-based infrastructure designed to allow users to prove their off-chain data in an authentic and privacy-preserving manner. For example, prove to the GameFi protocol that you are an experienced player in Web2 games without revealing your personal details. What is unique about PADO is the use of advanced cryptographic technologies, including MPC-TLS (Secure Multi-Party Computing Transport Layer Security) and IZK (Interactive Zero-Knowledge Proof), to enable the prover to prove the data blindly, that is, the prover cannot see the original data , including public and private user information, but still ensuring the origin of the transmitted data through cryptographic methods.
PADO achieves its goals by guaranteeing two key security properties:
Authenticity: By protecting the origin of the data, ensure that user data comes from a specific source and remains unchanged during the sharing process.
Privacy: Follow the principle of data minimization when handling private information. When performing data calculations, PADO uses zero-knowledge proofs to protect privacy and ensure that no original data, including public and private user information, is leaked.
None of the above projects have yet issued coins, and the economic models are yet to be further considered by the team. Those who are interested can experience the products first and look forward to possible airdrops in the future.
future outlook
As one of the most important long-term narratives in the Web3 field, RWA has attracted capital attention. Many well-known DeFi protocols, such as MakerDAO, Synthetix, Compound, etc., have also begun to deploy in this field.Boston Consulting Group estimates, the RWA market may grow to US$16 trillion by 2030. However, introducing off-chain assets onto the chain is a complex task and will inevitably face a series of issues such as transparency audits, legal compliance, and supervision.
In this context, Attestation plays an important role in promoting Mass Adoption. Attestation can provide verification of the correlation between assets on the chain and actual assets off the chain, enhance transparency, and provide confidence to investors and participants. This not only satisfies compliance review and regulatory requirements, but also helps establish a bond of trust between Web2 and Web3. Through Attestation, traditional financial institutions and enterprises can more smoothly access the blockchain ecosystem and achieve seamless integration of digital assets.


