A Review of the Development History of the NFT Market
Original author: Jake Gallen
Translation: Xunyang, SeeDAO
January 2014 - December 2022
As I slowly construct the roadmap of NFT marketplaces, I began to question why I bothered putting it together. In fact, my mind is filled with more questions than when I started.
Is the history of NFT markets important?
What will individuals gain from consuming this niche type of content?
How will this newfound knowledge impact readers?
Is it necessary in the grand scheme of things?
Will it be remembered? How will it be applied?
My contribution to the history of the NFT community started with 27 YouTube videos, covering the ecosystem of MoonCats, known as the MoonCat Tutorial Series. Subsequently, I recorded over 70 podcasts that delve into NFT history, featuring interviews with original creators, founders, teams, and collectors who are still active in the field today. Recently, I just concluded the NFT Archaeology Calendar Series (Part 1, Part 2, Part 3), which explores the culture and history of NFT archaeology.
I embarked on this journey with the vision of managing personal communities, then delved into understanding the leaders who manage these communities, and through analyzing trends and dissecting key moments that have led us to the NFT landscape we know today. As my research shifted from micro to macro, I gradually realized what the second phase meant for HNFTs: infrastructure.
At the end of spring in 2022, I really started to think about what's next for this slowly maturing "wine" market. We are moving out of the personal phase and entering the community curation phase. It was at this time that I started posting some tweets to see what kind of response I would get. Until the community saw the emergence of some websites, archives, and aggregators, but there wasn't much content about the necessary financial products.
In this situation, I felt an urge like never before, since starting my podcast in 2020 or entering the crypto rabbit hole for the first time in 2016. I knew that building a groundbreaking NFT market would be a once-in-a-lifetime opportunity. So, whenever I had free time, I started studying various materials about the NFT market on different blockchains.
After spending some time researching the NFT market, I began to notice a major trend, which was the theory I mentioned in the tweets above. Feeling right about the market is one thing, but finding a match for this theory in the world of encrypted digital entrepreneurship is another.
Therefore, I started reaching out to some trustworthy and knowledgeable leaders in the HNFT field to assess their interest. I had already made up my mind that it was time to see if this was a worthwhile adventure. After spending a few months searching for interested individuals, making phone calls, and going through some difficult negotiations, Adam McBride, myself, and the team at Emblem Vault reached an agreement to embark on the adventure of building a groundbreaking NFT market.
Now you may be wondering why I'm telling you this story. When you look at the NFT market roadmap, you will notice that it ends in 2022, which coincides with our plan to launch the groundbreaking research of the NFT market in 2023.
As the old saying goes, during the gold rush, you should sell "picks and shovels" instead of looking for gold. If NFTs are gold, then historical NFTs are Montezuma's treasure, their value far surpassing that of any glittering gem. If the NFT market is your typical jeweler, then the historical NFT market will be your world-renowned auction house. So, the next time we update this roadmap, we might celebrate it while making history.
2014 Agreement
November 2014
Counterparty, launched in January 2014, is a platform that creates derivative financial assets and tools for Bitcoin users. Its main purpose is decentralized finance (DeFi) applications and it became a gathering place for some early NFTs such as Spells of Genesis, Rare Pepes, and Sarutobi Island. The native currency of Counterparty, XCP, is created through a program called "Proof-of-Burn" in which BTC is destroyed to create XCP. Counterparty's built-in decentralized exchange (DEX) was innovative at the time, predating many common DEXes in the blockchain industry today. For a long time, Counterparty was not well-known, but in recent years, especially during the 2021 NFT boom, it has become increasingly popular. Today, it has a thriving ecosystem, and project assets can currently be purchased through XDP Dispensers and Emblem Vault.
March 2014
OneName is a pioneer in the current NFT market. OneName was created by Muneeb Ali, co-founder of Stacks, and uses the Namecoin blockchain to generate decentralized identity authentication, making Bitcoin payments and user profiles easy. With OneName, users can register their Twitter profile pictures and banners on Namecoin, enabling them to create a profile page. This makes the creation of transferable non-fungible assets efficient and is one of the earliest tokenized image projects on the blockchain.
May 2014
Monegraph was created by long-time entrepreneurs Anil Dash and Kevin McCoy during a 24-hour competition at the Seven on Seven conference on May 3, 2024. In the 5th edition of the annual collaboration between artists and technologists, the team presented an idea on how to "authenticate" digital artworks and protect digital property. Just a day later, they introduced a method that successfully utilized the Namecoin blockchain to achieve digital ownership. Through a live demonstration, they registered a car GIF image, and then Anil directly purchased this newborn tokenized artwork for $4. This presentation will go down in history and is likely the first "live minting" and also regarded as the first tokenized artwork at that time. Thus, the Monegraph protocol was born. However, in 2021, 7 years later, Anil Dash published a blog post denying this experience.
August 2014
Dogeparty is a fork version of Counterparty, launched by Adam B. Levine and others at the end of 2014. It uses the same "burnt proof" as Counterparty to mint its native token XDP, which requires users to destroy Dogecoin to obtain XDP. The infinite inflation protocol of Dogecoin is an attractive choice for users who want to offset the increase in Dogecoin supply. Dogeparty was active for about a year and then gradually disappeared in mid-2015. But in 2021, the Dogeparty Foundation was established, and subsequently the project was relaunched. XDP assets can be purchased through XDP Dispensers and Emblem Vault.
April 2015
Ascribe is a Bitcoin-based non-fungible token (NFT) protocol that operated from 2014 to 2018 and even had its own language called SPOOL! It hosted 31,900 tokens for 13,500 users. This protocol and platform achieved success early on and built multiple token markets on top of it. In early 2018, the Ethereum blockchain introduced the ERC-721 NFT standard, allowing artists to directly register their art on Ethereum. This led to a large number of users migrating from Ascribe to Ethereum, and Ascribe decided to shut down their platform. When it closed, all the NFTs on the platform were lost and could not be claimed by anyone. However, one of the founders of Ascribe said that there may be hope to recover these "ancient" NFTs in the future.
Birth of the NFT Market (2015-present)
January 2016
Cointemporary is the first marketplace built on Ascribe and powered by SPOOL's infrastructure, launched in March 2015. Every ten days, a new digital artwork is released on its website and can be purchased directly with Bitcoin, marking the first time in blockchain history that a tokenized digital artwork can be bought with digital currency (Bitcoin). Ten days later, a new artwork will be launched on the website, repeating the cycle. Trent McConaghy, one of the founders of Ascribe, recounts his historic experience of presenting at MAK in Vienna.
December 2015
There was a market that emerged in 2015 using Ascribe, aiming to sell non-fungible assets in the form of recorded brainwaves. These brainwaves were collected using the Emotiv Insight wireless headset. The recordings were sold as limited digital editions of "Thoughts and Dreams". This market was called N^3uro and was developed by Greg McMullen and Ascribe co-founder Trent McConaghy at the Ascribe CONSTRUCT hackathon in September 2015. However, N^3uro was denied cooperation with Emotiv, which led to the experiment being shut down shortly after.
April 2016
In May 2014, Kevin McCoy and Anil Dash publicly showcased Monegraph (protocol), and 18 months later, on September 28, 2015, Monegraph (market) was officially launched. Prior to the market launch, Monegraph was used to create the coveted namecoin asset Quantum, which was sold at Sotheby's for $1.2 million. However, Kevin and Sotheby's were subsequently sued because they were selling re-minted tokens on Ethereum instead of the original "ownership chain" on Namecoin, which was touted in a live presentation a year prior. Through some public tweets, we know that some transactions were conducted on the Quantum market, but we may never know the specifics of those transactions as the platform closed down a few years later.
March 2016
EtherID is an identity protocol launched on November 29, 2015, at around the same time Ethereum proposed the ERC20 standard for fungible tokens. It is similar to Namecoin Identities launched in 2012 and Ethereum Name Service (ENS) launched in 2017. One notable feature of EtherID is that it has a built-in marketplace that allows users to buy, sell, and transfer identity records. This may be the first NFT marketplace on Ethereum. Wrapped EtherIDs can now be purchased on OpenSea.
March 2016
Pells of Genesis (SOG) is the first-known blockchain game with collectibles, created by Shaban Shaame and EverdreamSoft. Originally planned as "Spells of Orbital," it is a mobile game that combines trading card game (TCG), arcade game, and fantasy adventure elements. SOG raised funds through an initial coin offering (ICO) with its native token BITCRYSTALS and Bitcoin. In a unique way, the first card of the collectible series FDCARD was given away for free through proof-of-work mechanism by offering computational power to assist in the development of important drugs. These cards can be traded on the SOG marketplace and later on other trading platforms, including Rare Pepes and Janssen's JPJA. SOG can be purchased through XCP Dispensers or Emblem Vault.
January 2023
Left Gallery was originally launched in December 2015. In May 2016, it found its first group of artists to promote on the platform, including founder Harm van den Dorpel. Initially, Ascribe provided the driving force for Left Gallery's development, but they closed in 2018. LG then turned to Ethereum where they offered a variety of art selections until 2022. The team is committed to maintaining the continuous operation of the website and seeding IPFS Hashes to ensure the artwork can exist forever. Left Gallery is considered a historical platform in the digital art and blockchain history world.
2016 NFT Market

November 2016
PixelMap is a non-fungible token (NFT) project created by Ken Erwin in 2016. It was launched before the first "compartment store" NFT trading market, OpenSea, came online. A year later, the ERC-20 standard was introduced to Ethereum. During this time, many pre-ERC-721 NFT projects like PixelMap had to create their own trading markets, which is different from the typical trading markets we see now. However, these projects played an important role in the development of the NFT industry. Wrapped PixelMap can now be purchased on OpenSea.
2017 NFT Market
January 1, 2017
Rare Pepes are often regarded as the "birth of the crypto art movement" because their origins are decentralized. They started out as a joke in a Telegram group and evolved into a multi-year collection with over 300 artists and 1774 unique tokens. In September 2016, after RAREPEPE was minted on Counterparty, the community realized they needed a place to store and trade these small images. So, Joe Looney launched RarePepeWallet, which has become a gathering place for Rare Pepe collectors. Rare Pepes can be purchased on pepe.wtf, Scarce City, XCP Dispensers, and Emblem Vault.
April 4, 2018
Curio Cards was launched in May 2017 and is considered the first "NFT art collection" on Ethereum. Unlike Rare Pepes, which were created by a group of "Rare Pepe scientists," artists anonymously submitted their works to the Curio Cards team, who then submitted the works to the community for voting. Curio Cards used a unique method to distribute their NFTs, using "vending machines" on their website, each with specific cards set by the artists. A total of 31 cards were issued as part of the collection (including 17 printing errors), and the series sold out completely in 2021 when it was rediscovered. Wrapped Curio Cards can now be purchased on OpenSea.
June 10, 2017
CryptoPunks is widely regarded as having contributed to the development of non-fungible tokens (NFTs), including the profile picture movement (PFP), the ERC-721 standard, and the use of a standardized supply of 10,000 units. In addition to these innovations, the CryptoPunks marketplace was pioneering and continues to be used today, in part because it is embedded in the V2 code. However, the market has changed over time. In the V1 version of CryptoPunks, there was a loophole that allowed buyers to purchase a CryptoPunk and then have the ETH used for the purchase refunded to their wallet. Larva Labs made a series of improvements to the market, resulting in the iconic brand of CryptoPunks we see today. Wrapped CryptoPunks V1 can be purchased on OpenSea, and CryptoPunks V2 can be purchased on CryptoPunks.app.
December, 2017
MoonCatRescue is one of the earliest generative non-fungible token (NFT) projects, launched by ponderware in August 2017. It allows users to randomly generate over 4 billion possible cat outcomes, and as of 2021, there are a total of 25,440 different options produced. The functionality of the MoonCatRescue marketplace is similar to CryptoPunks, where bidders need to deposit ETH in the market contract to make offers on MoonCats. Owners can accept offers or sell their cats through the "Request" feature. Genesis MoonCats (black and white) are showcased on a bonding curve, starting at 0.3 ETH and incrementally increasing by 0.3 ETH with each Genesis purchase, making it the first market bonding curve. Acclimated MoonCats can be purchased on OpenSea.
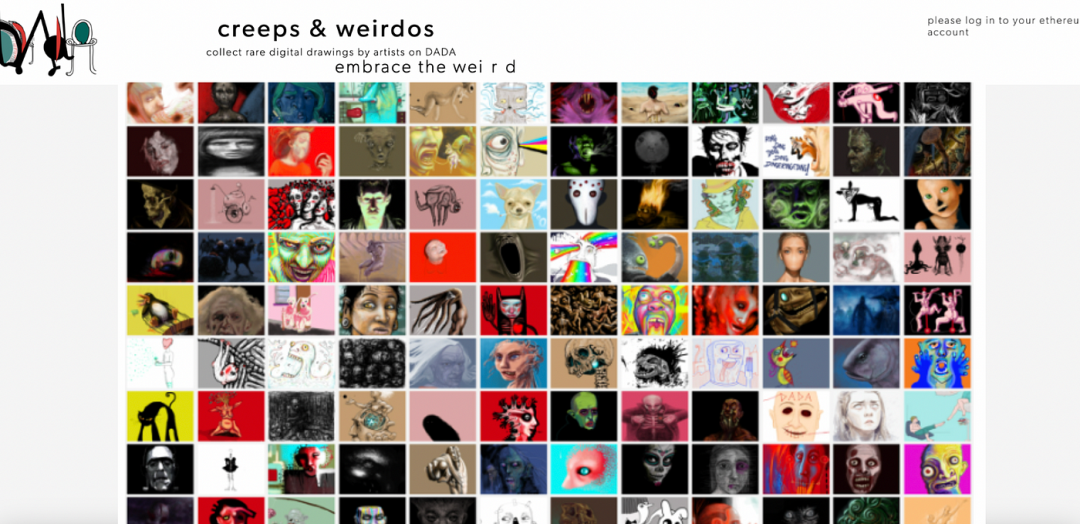
November 2017
Dada launched their first non-fungible token (NFT) project, Creeps & Weirdos (CW), along with a native trading marketplace in 2017. This marketplace stood out as the first known market to offer creator royalties. Prior to CW, markets like CryptoPunks and MoonCatRescue did not provide royalties to creators, and when OpenSea launched several months later, it became a leader in protecting creator royalties. Dada's introduction of creator royalties on the CW market had a significant impact on the NFT industry. Wrapped Creeps & Weirdos can be purchased on OpenSea.
June 2017
Monaparty was launched at the end of 2017 as a branch of the Counterparty platform for creating tokens on the Bitcoin blockchain. It operates as a sidechain of the Monacoin blockchain, which was influenced by Japan in 2013. On January 8, 2018, the most popular NFT series of MonaCard was launched on Monaparty. Similar to Rare Pepes, MonaCard was planned by the community and received over 6,000 donations in the past four years. MonaCards can be purchased on Monapallete and Emblem Vault.
December 2017
CryptoKitties is an NFT project launched by Dapper Labs on November 23, 2017. It is widely considered as a pioneer in the NFT industry and gained immense popularity in 2017, nearly clogging the Ethereum network with the breeding and trading of kitties. Despite facing competition from other series, CryptoKitties remained popular for a long time and is still well-known today. In addition to innovation, the CryptoKitties marketplace is known for its user-friendly interface and appearance, featuring functions such as sorting, categorization, and colorful storefronts, which have been imitated by many other NFT marketplaces. CryptoKitties can be purchased on the native CryptoKitties marketplace and OpenSea.
June 2017
XChain was launched at the end of 2017 by CoinDaddy, a long-time supporter of Counterparty. The release of the Counterparty blockchain explorer added numerous features to the platform, including a functional DEX and distributor, allowing the community to buy and sell tokens directly through the website. The platform also provided the ability to track asset value, issuance, burning, and trading, enabling communities like Rare Pepes and Spells of Genesis to achieve price discovery. In 2021, after the establishment and revival of the Dogeparty Foundation, XChain added support for Dogepary.
February 2018
OpenSea is an NFT marketplace launched in December 2017, known as the first marketplace to sell multiple series of NFTs. It offered over 30 different projects within months of its launch. At that time, most NFT projects were hybrid projects of ERC-20 tokens, as the ERC-721 standard wasn't fully standardized until March 2018 with Su Squares. It was only later that OpenSea became a marketplace compatible with ERC-721 as it is today. Over the past five years since its launch, OpenSea has become a leading marketplace for Ethereum and has expanded to NFT markets on other blockchains such as Solana, Polygon, Binance Smart Chain, Avalanche, and Layer 2.
August 2018
EtherRock was launched on December 26, 2017, as a native exchange for ERC-20 Pet Rocks. The project had virtually no scale before it was rediscovered in 2021. There was almost no trading volume for the project before it was rediscovered in 2021. During that time, NFT archaeologists and historical NFT enthusiasts flocked to the project and minted it, and it has been listed on the Joint Curve. Several months later, an EtherRock was sold for $1.3 million and featured on a CNBC segment. The 2017 market remains the only directory for anyone interested in spending over $100,000 on digital pet rocks.
January 2022
CryptoBots was created on December 29, 2017, becoming the first "play-to-earn" game on the Ethereum blockchain where players fight against robots and earn tokens based on the results. Since the project was deployed a few months before the release of the ERC-721 standard and during the initial release on OpenSea, the CryptoBots team established a native marketplace to purchase these modified ERC-20 tokens. The contract provides an auction and bidding system to participate in the game and win your favorite CryptoBot.
The Rise of Ethereum-based Marketplaces (2018)
April 2018
This San Francisco-based startup, Rare Bits, was founded in February 2018 and raised $6 million in funding, led by Spark Capital and Craft Ventures. Founder Amitt Mahajan announced that the marketplace would be a fee-free live auction marketplace system. Despite listing over 20 projects and 500,000 assets on the market, the project was shut down at the end of 2019 due to the inability to find suitable products for the market.
April 2018
The Wyvern Protocol migrated to the Ethereum mainnet in February 2018 with the aim of becoming a "marketplace for all digital assets." It aimed to enable the trading of anything from MyEthermon Monsters to smart contracts. Later that year, OpenSea integrated the Wyvern auction and bidding system, which they used until 2022. The protocol is still active, but the Wyvern exchange was taken offline in 2019 after failing to find suitable products for the market.
April 2020
Super Rare is an NFT marketplace designed specifically for artists, launched in April 2018. It is one of the first platforms to implement a whitelist application process for artists. To become a Super Rare artist, individuals must apply and obtain approval from the platform before they can publish their works in their online stores. The standard artist royalty fee for Super Rare is 10%, and it has introduced ERC20 tokens called $RARE (2021) and RarePass (2022).
August 2018
KnownOrigin is an NFT marketplace launched in April 2018, serving as a platform for artists to verify, showcase, and sell their artworks and collectibles. This artist-centric marketplace is similar to Super Rare and competes for artists' attention. KnownOrigin was acquired by eBay in June 2022 and continues to operate moderately.
May 2019
Markersplace was launched in June 2018 as a marketplace for digital creators to verify, collect, and sell their artworks. The platform aims to address the ownership issues that digital artists have faced for decades. In 2023, many renowned artists continue to create on the platform, maintaining a strong community with professional supporters. Despite growing competition over the past five years since its inception, Markersplace continues to collect a significant amount of historical artworks and remains active.

December 2017
Rare Art Labs (RAL) solidified its position as a promotion group and organized the legendary Rare Digital Art Fest in January 2018, inviting artists such as Joe Looney, Matt Hall, Shaban Shaame, and Bea Ramos. After a very successful launch, Rare Art Labs introduced the R.A.R.E. NFT trading market, showcasing a piece of Lost XCOPY artwork. The team received strong support from the small NFT community and seemingly the mainstream media as well. However, after 3 years of establishment and 2 years in the market, RAL closed the market in late summer of 2020, locking all NFTs in its contracts and permanently losing most of them.
June 2018
Digital Objects (DO) is a carefully curated art market and a small but historically significant community center. The platform was founded in the summer of 2018 and closed in the summer of 2020. The first tokenized AI artwork created by the OBVIOUS group in 2018 was sold at Christie's auction house for $450,000, marking a significant success for the platform. The DO smart contract also showcased three Lost XCOPY artworks, which can still be viewed on OpenSea today. Artists on the platform had the option to integrate Digital Objects' unique "Back of the Canvas" technology, while collectors could purchase tokens using Bitcoin, Bitcoin Cash, Litecoin, and Ethereum. Despite its innovative features, the platform failed to generate sufficient demand and was ultimately forced to close.
February 2019
The Cock Foster twins launched Nifty Gateway in 2018, bringing a new feature to the NFT market: the ability to purchase NFTs with US dollars. This was a significant advancement as there were no major NFT markets offering this option at the time. In 2019, Nifty Gateway differentiated itself from competing markets by using an auction system and caught the attention of the Winklevoss twins, who later acquired the platform and integrated it into the Gemini ecosystem. Nifty Gateway also added Beeple to the platform, contributing to a breakthrough moment in the NFT industry. Despite competition from other markets, Nifty Gateway remains the preferred platform for auctions and open edition NFTs.
The Lone 2019 Project
April 4, 2020
Rarible is an NFT marketplace launched in the winter of 2019. Just six months later, it introduced the first-ever native NFT marketplace token, $RARI. The governance token aims to reward collectors and creators and envision a future for the platform as a decentralized autonomous organization (DAO). However, the token is primarily used for wash trading, where users can trade and then repurchase their tokens to inflate their value. Since then, Rarible has transitioned to zero fees for users staking their $RARI tokens and has added support for other blockchain platforms, including Tezos, Solana, and Immutable X.
Gaining Some Momentum in 2020
September 2020
Foundation is an NFT platform that announced its launch in May 2020 and launched its first collection in October of the same year. In February 2021, it opened the NFT marketplace to the public and provided a unique invitation system for NFT creators. To mint NFTs on the platform, creators must have an invitation code, which can only be sent by a member who has already sold at least one NFT on the platform. Collectors can participate in auctions without any restrictions. Foundation is an "artist-centered" platform that focuses on protecting creators' royalties and provides a range of tools and utilities for creators, including an auction system and minting portal.
October 2020
NBA Top Shot is an NFT series launched on the Flow blockchain in 2020 by Dapper Labs, the creators of CryptoKitties. The marketplace features categories such as players, teams, collections, challenges, and more. NBA Top Shot is similar to traditional basketball cards, but with dynamic videos instead of static images. The series gained popularity in early 2021, with some NFTs selling for over $100,000 and helping thousands of people enter the world of NFTs. Many believe that NBA Top Shot played a significant role in the recent bull market of the NFT market.
2021 NFT Market Boom
December 2022
NFTX is an NFT protocol launched by developer Alex Gausman in January 2021. It is the first protocol for NFT-supported index funds, bringing traditional financial attributes into the NFT world and creating truly DeFi x NFT products. NFTX allows users to create NFT pools supported by ERC 20 tokens representing the instant liquidity amount in the pool. This is a unique approach in the NFT market as it allows users to purchase "fractional shares" of NFTs using ERC 20 tokens. NFTX is the first NFT market to host multiple ERC 20 tokens on its platform.
August 2022
Crypto.com quickly recognized the potential of the emerging NFT market and launched its own marketplace in March 2021. To differentiate itself, the marketplace adopted a strategic approach by partnering with well-known traditional brands such as the Philadelphia 76ers, Coca-Cola, and UFC to help them launch their token collections. Considering Crypto.com had previously spent $700 million to acquire naming rights to the Los Angeles Lakers' stadium, it's not surprising that they entered the NFT market. However, despite these efforts, the platform still faces many challenges in gaining attention in the highly competitive NFT market over the past two years.
November 2021
Royal is an NFT marketplace dedicated to music NFTs. It was founded by renowned music artist and early NFT pioneer DJ 3LAU and launched in early 2021. In just a few months, Royal has raised over $16 million in funding from Founders Fund and Paradigm. It is the second NFT marketplace of its kind (after art NFT marketplaces like Super Rare, KnownOrigin, and Foundation) and focuses on music NFTs. Royal aims to revolutionize the music industry by utilizing NFTs.
December 2022
OBJKT is an NFT marketplace launched on the Tezos blockchain in July 2021. It is currently the largest art-focused NFT marketplace on Tezos. OBJKT initially started as a platform that provided tools for another Tezos NFT marketplace, Hicetnunc (HEN). After HEN faced challenges, OBJKT took over and became the leading NFT marketplace on the Tezos blockchain. Art NFTs have found a fitting market on Tezos, helping establish the platform as a hub for pure NFTs.
December 2022
Magic Eden (ME), a competitor of the NFT market, was launched in September 2021 with the aim of becoming a top platform for buying and selling NFTs on the Solana blockchain. At that time, the Solana ecosystem was thriving, and the timing for the NFT space was ripe. Magic Eden's first NFT series, Kreechures, was launched in February 2021, and the platform quickly gained popularity due to its user-friendly interface. In June 2022, Magic Eden raised $130 million in funding and integrated Polygon into its platform. The company plans to become a leading multi-chain marketplace.
December 2022
Scarce.City, launched at the end of 2020, has a unique history as initially a marketplace for physical BTC art and assets. In the summer of 2021, it expanded to include a digital marketplace for buying and selling Counterparty assets. The platform utilizes the Bitcoin Lightning Network for low-cost and fast payments, making it the preferred destination for all types of Bitcoin-related art.
December 2022
Binance NFT was launched in June 2021 as a way to support NFTs in the Binance ecosystem, and it has gained popularity worldwide. The platform has been successful due to its low fees on the Binance Smart Chain and user-friendly interface. However, it has also received criticism for the prevalence of scams on the platform and its centralization around BNB. Despite these challenges, Binance NFT remains a popular marketplace in the BNB NFT ecosystem.
December 2021
Quantum was launched in October 2021 by renowned NFT photographer Justin Aversano and is a vertical marketplace focused on photography NFTs. It aims to make it easier for artists and collectors to access NFT photography works by curating and releasing NFT collections. Justin gained the trust of the art world with his $1 million auction "Twin Flames" at Sotheby's in 2021. Since its launch, Quantum has expanded to open physical stores in Los Angeles and has also added digital art on the platform.
November 2021
Sudoswap was launched in October 2021 as a full-chain AMM protocol for NFT trading. It gained popularity in mid-2022 for offering 0% creator royalties and low market fees of 0.5%. During a challenging period in the cryptocurrency market, many traders were looking for ways to preserve their funds, and Sudoswap's product attracted a lot of attention. As Sudoswap gained market share, it caused some disruption in the industry, with some markets imitating its 0% royalty offer, while those that didn't provide fair compensation to creators were boycotted. Today, Sudoswap remains a popular choice for many NFT traders.
The Hot 2022 NFT Market
January 2022
Looks Rare suddenly emerged in January 2022, conducting a vampire attack on OpenSea and rewarding users with $LOOKS airdrops based on their OpenSea trading history. This decentralized marketplace provides 100% of the transaction fees to buyers, sellers, and other stakeholders on the platform. In the first 30 days of its launch, the release of $LOOKS was very high, with daily APY consistently exceeding 500% growth. Users generated income, and wash trading became rampant. The anonymous team of 40 members recently announced the deployment of Looks Rare V2 in Q1 2023, which includes a mobile application, NFT aggregator, and more.
April 2022
X2Y2 was released shortly after Looks Rare in February 2022 in a similar way. They held an Initial Liquidity Offering (ILO) for 1,000 investors in February and then airdropped $X2Y2 tokens to users based on NFT transaction records, which had some complexity. The difference here is their 0% market fee. The platform went through some turbulence when announcing the cancellation of creator royalties, but later reversed that decision a few months later. Now, the platform has ventured into NFT lending business and gained some market share in that field.
December 2022
Coinbase NFT could be considered one of the most disappointing NFT marketplace releases ever. The platform was announced in October 2021 but was only publicly launched in April 2022. In the first three months of its launch, Coinbase NFT's sales failed to surpass $1 million and only had 1,200 registrations. Its "Social NFT Marketplace" allows users to connect with other clients and comment on NFTs, similar to social media platforms. Nonetheless, by the end of 2022, Coinbase NFT was not mentioned in any NFT conversations.
April 2022
ENS Vision was launched in March 2022 as a tool to help ENS enthusiasts search for their Web3 identities. Over the following months, fueled by the hype around three-digit and four-digit domain names known as the "10k Club," ENS domains experienced a frenzy of demand. The quantity and demand became overwhelming for OpenSea's general NFT marketplace, and ENS Vision saw an opportunity to capitalize on it. ENS Vision has become the preferred choice for any market related to Ethereum Name Service, offering lower market fees and additional tools that other markets can't provide.
January 2023
In July 2022, Gamestop, the beloved video game retailer that holds a special place in the hearts of many millennials, decided to enter the rapidly growing NFT industry with a particular focus on the gaming sector. Rumors started swirling after the Gamestop saga in 2021, and due to the actions of retail investors against Robinhood, the iconic retail brand was poised to enter the world of cryptocurrency following the crypto resurgence. To achieve this, the company integrated multiple Layer 2 scaling solutions, including ImmutableX and Loopring, to provide a smooth and efficient user experience on its platform. Despite a strong initial launch, the platform's activity and interest have declined since its release.
December 2022
Uniswap, the top decentralized exchange for ERC-20 tokens, acquired NFT Aggregator and Floor Sweeper Genie in June 2022, signaling its intention to enter the NFT market. With its billions of dollars in funding and experience with fungible tokens, Uniswap is expected to become a top-tier NFT marketplace over time. There are indications that Uniswap will allow the purchase of NFTs using multiple ERC-20 options, potentially giving it a significant advantage in the market.
December 2022
Blur raised $11 million in seed funding in early 2022 under the leadership of Paradigm. It wasn't until October 2022 that Blur launched the "NFT Bloomberg Terminal," a data-driven user interface built for traders. It is the first platform that offers both an NFT aggregator and market under one product. With 0% market fees, optional creator tips, and three phases of token incentives for the $BLUR airdrop in January 2023, Blur quickly became a top market. However, the sustainability of the platform's volume and community remains to be seen beyond the initial token incentives.
This is a brief history of the NFT market! It has been over a decade since the first non-fungible token was registered on the Namecoin blockchain on April 21, 2011, creating "bitcoin.bit." Stay tuned for the updated version 2 of our "NFT Market Roadmap" in the future !
January 2014 - December 2022
Here are some NFT dating markets that are mentioned but not accompanied by images, but you should still keep an eye on them!
Etherlambos' native market (January 2018)
EtherWaifu's native market (March 2018)
Kaleidoscope's Counterparty market (March 2018)
DIGIRARE's Counterparty Market (April 2018)
Mintable Ethereum NFT Market (November 2020)
Hic et nunc Tezos NFT Market [XTZ Launch] (February 2021)
FXHash Tezos NFT Market (October 2021)
Stargaze Cosmos NFT Market (October 2021) Etheria V1.1/1.2 (2021) Note: Previous versions of Etheria, 0.9 and 1.0, reportedly had built-in markets but were never used. Versions 1.1 and 1.2 were created prior to their rediscovery in 2021.



