LD Capital: Crypto asset management from the perspective of US stock index return enhancement strategy
introduction
introduction
In the traditional financial market, index products represented by ETFs have developed rapidly in recent years, showing the characteristics of Smart Beta ETF-active management ETF market capital inflow growth rate is higher than that of ordinary index ETF products. The attention of the asset management industry has gradually shifted from ordinary index products to more innovative index product series, such as ESG ETFs, actively managed ETFs, and theme ETFs. Among them, active ETFs in the equity market have made new breakthroughs, attracting active transformation of over-the-counter products, and becoming a hot spot in the development of active products in recent years. Global index providers are constantly innovating and improving the index system to meet new market demands, promote the industry's in-depth development of refinement and diversification, and promote continuous innovation of indexed products. Crypto index-enhanced products are still at a very early stage compared with traditional financial markets. With the growth of the overall encryption market value, the market growth space for index-enhanced structured products should also increase rapidly. We believe that the market size and status quo of index funds and index-enhanced funds/ETFs in the US stock market have reference value for the development path of index-enhanced funds in the encryption market, and believe that encryption index-enhanced funds can enhance their returns through these methods, no matter how much they are Factor quantitative stock selection model, subjective timing model, sector rotation model or stock index futures derivatives income enhancement model, to obtain excess returns that meet the needs of investors with different wind biases.
Scale and development trend of Hong Kong stocks and U.S. stock general index ETFs and index-enhanced funds/ETFs
From 2015 to 2023, whether it is the index funds of US stocks or Hong Kong stocks, or the scale of index-enhanced funds/ETFs, they all show steady growth, while the scale of index-enhanced funds/ETFs, that is, the growth trend of actively managed ETFs is faster , an increase of 10 times in 8 years, and the scale in 2023 has reached nearly ⅓ of that of ordinary index funds.
Table 1 From 2015 to 2023, the comparison of the total size of ordinary index funds and index-enhanced funds/ETFs in US stocks and Hong Kong stocks
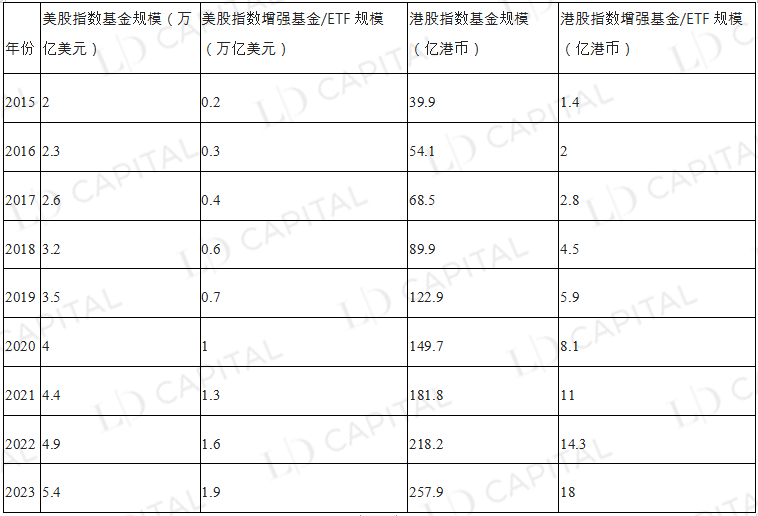
Source: VettaFi, Statista
In the traditional financial market, the scale of index funds in US stocks and Hong Kong stocks even tends to exceed their corresponding market value, while the scale of index funds/ETFs in the encryption market is far below their market value. Interest is growing, and there is a bright future for cryptocurrency index funds and exchange-traded funds (ETFs).
Table 2 Comparison of U.S. stocks, Hong Kong stocks, encrypted market capitalization and the corresponding index fund/ETF scale
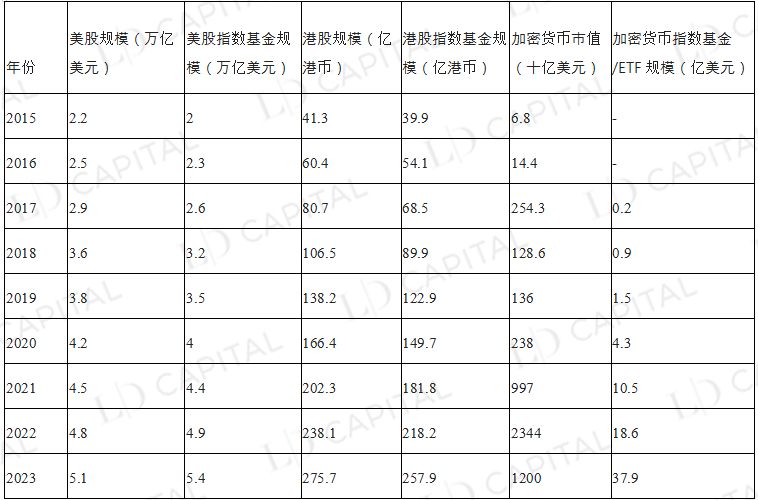
Source: VettaFi, Statista
Active Management Characteristics of Index Enhanced Funds
Index funds can obtain the income (β income) brought by following the benchmark market by tracking the characteristics of the index, such as tracking error, market value style, valuation style, industry weight ratio and individual stock weight ratio.
The enhanced index fund strives to obtain additional income (α income) beyond the market through the active management of the fund manager, so that when the market falls, the decline is less than the underlying index, and when the market rises, it can obtain more income than the tracking index. , and strive to obtain relatively stable compound interest performance in the long-term dimension.
As far as tracking indexes are concerned, index enhancement funds can track a wide range of indexes, which can be broad-based indexes, single industry indexes or other theme indexes. Judging from the current market environment of U.S. stocks and Hong Kong stocks, broad-based indexes such as S&P 500, Nasdaq-100, Russell l2 000, DJIA, HSI, and HSCEI are the mainstream choices for index-enhanced funds to benchmark at the beta end.
Ways to Enhance Index Fund Returns
With the continuous innovation of the financial market, index enhancement funds can obtain excess returns in various ways, so as to achieve the effect of "enhancement" of returns. The income of the "enhanced" part of the index enhanced fund can be realized through, for example, multi-factor quantitative stock selection model, subjective timing model, sector rotation model, stock index futures derivatives income enhancement model, etc. These are the more common index enhanced products at present. Revenue Enhancement Pathway.
Quantify Multifactor Augmentation Strategy Products
The goal of a quantitative multifactor augmentation strategy is to pick stocks by using multiple factors simultaneously for better returns. These factors are divided into many dimensions, such as technical factors (market dynamics and technical indicators), macro factors, statistical data mining (machine learning, deep learning), fundamental factors, etc. From the perspective of fundamental factors, it includes company financial stability Sex, dividend yield, valuation, etc.
Table 3 Common multi-factor stock selection enhanced index funds in US stocks
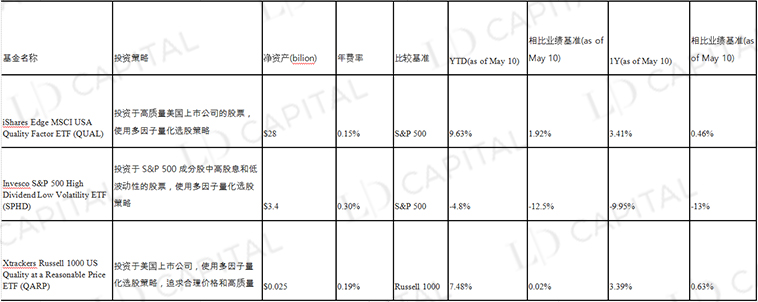
Take the Invesco S&P 500 High Dividend Low Volatility ETF (SPHD), for example. SPHD tracks the S&P 500 High Dividend Low Volatility Index, employing a multi-factor stock selection strategy that focuses on high dividend yield and low volatility stocks. It selects 50 securities in the S&P 500 Index with the highest dividend yields and low volatility. Constituents are weighted by dividend yield, with individual stock weights capped at 3% to ensure diversification. To maintain its low-volatility objective, the fund rebalances semi-annually, reevaluating stock picks based on updated dividend yield and volatility metrics. Because of its low volatility, the ETF typically outperforms the broader S&P 500 in bear markets, but can lag in strong bull markets.
Part of SPHD's yield enhancement comes from an overweight to high-dividend and low-volatility stocks. However, SPHD has significantly underperformed the benchmark S&P 500 in the interest rate hike environment of the past year. The main reason may be that industries with high dividends, such as finance, energy, aviation and tourism, have been negatively affected during the epidemic. Among these industries Many high-dividend stocks may perform poorly during the epidemic. In particular, the financials sector, which accounts for 26% of SPHD's portfolio, has been hit hard by the recent banking crisis. The below-benchmark performance resulted in a larger decline in AUM.
Strictly speaking, SPHD and QUAL are considered passively managed funds that partially use enhancements. These enhancements are designed to optimize specific elements of the portfolio, but the Fund's overall investment strategy remains focused on tracking specific indices. In addition to using passive management methods to track the index, QARP also uses some enhancement methods and active management strategies to select the constituent stocks of the portfolio, so it is a typical active management fund.
When implementing quantitative multi-factor enhancement strategies, the weights of different factors and the number of holdings in the portfolio need to be considered. According to the actual situation, use different factor weights and holdings to achieve different investment goals. For example, use more financial stability and earnings stability factors to invest in solid stocks, or use more market momentum and technical indicators factors to invest in growth stocks.
subjective timing enhancement strategy
As an investment strategy, subjective timing can be subdivided into multiple methods, including technical timing, fundamental timing, macro timing, emotional timing, and event-driven timing. These methods are based on different analytical and decision-making factors and aim to identify market trends, values and opportunities for better decisions to buy, sell or adjust portfolios.
1. Technical Analysis Timing: Technical analysis is the method of identifying underlying market trends by studying historical price and volume data. Investors can use technical analysis tools (such as trend lines, moving averages, relative strength index, etc.) to determine the direction, strength and turning points of the market, so as to determine when to buy or sell.
2. Timing of fundamental analysis: Fundamental analysis focuses on factors such as the company's financial status, competitive advantage, and industry status. Investors can evaluate the company's value and growth potential through in-depth research on the company's fundamentals. When the market price underestimates the true value of the company, investors can buy; when the market price overestimates the true value of the company, investors can sell.
3. Macroeconomic analysis and timing: The macro timing enhancement strategy is based on the impact of macroeconomic data on market trends to make timing judgments for more accurate asset allocation. These strategies typically involve the analysis of factors such as interest rates, inflation, monetary policy and geopolitics. For example, during an economic expansion, investors may increase their exposure to stocks; during a recession, investors may reduce their exposure to stocks or move to safer assets. Fund managers make strategic decisions to adjust their portfolios based on their outlook and expectations for global macroeconomic conditions. Compared with passive index funds that only track benchmarks, it can bring excess returns from macro timing.
4. Timing of market sentiment analysis: market sentiment analysis focuses on the impact of investor sentiment and psychological factors on market prices. Investors can use market sentiment indicators (such as panic/greed index, investor confidence index, etc.) to judge whether the market is overly pessimistic or overly optimistic, and make timing accordingly. Buying when the market is overly pessimistic and selling when the market is overly optimistic may help investors obtain excess returns. Sentiment strategies are becoming increasingly popular, and other sentiment strategy indicators include the AAII Sentiment Index, VIX, Market Sentiment, Put/Call Ratio, and more.
5. Timing of event-driven strategies: Event-driven strategies focus on specific events (such as mergers and acquisitions, spin-offs, reorganizations, etc.) that affect the value of the company. The timing of buying or selling can be determined based on the anticipation and analysis of these events.
Take the Pacer Trendpilot US Large Cap ETF (PTLC) as an example. The Pacer Trendpilot US Large Cap ETF (PTLC) is an exchange-traded fund (ETF) based on the US stock market that uses an active timing strategy. Its goal is to adjust its exposure to U.S. large-cap stocks according to market trends in order to achieve relatively stable investment returns.
The fund primarily tracks the S&P 500 Index and employs a timing strategy based on moving averages. When the S&P 500 is above the 200-day moving average and the closing price of the last five trading days is higher than the five-day moving average, the fund invests in the S&P 500 index; when the S&P 500 is below the 200-day moving average, the fund Allocate 50% of its assets in the S&P 500 index and the other 50% in short-term U.S. Treasury bonds; when the S&P 500 five-day moving average is below the 200-day moving average for five consecutive trading days, the fund will invest all in short-term U.S. national debt.
Observe the performance of Pacer Trendpilot US Large Cap ETF (PTLC) in some specific market environments, such as the bull market in 2017, the volatile market in 2018, and the market turmoil caused by the epidemic in 2020 to discover the characteristics of timing enhanced funds. In 2017, The S&P 500 index delivered a strong annual return, gaining about 21.8%. For the year, the PTLC fund returned about 20.4%, slightly underperforming the benchmark index. While PTLC captures some gains in rising markets, it has slightly underperformed the S&P 500 in this market environment due to management fees and transaction costs.
In 2018, the market environment fluctuated violently. The S&P 500 index had a large increase at the beginning of the year, but then there was a significant decline at the end of the year, and finally fell by about 4.4% for the whole year. In contrast, PTLC fared better in 2018, returning around -3.7% for the year, achieving some level of impairment relative to the benchmark index.
At the beginning of 2020, the COVID-19 epidemic triggered a sharp shock in global stock markets. The S&P 500 index fell about 34% in a short period of time, but then rebounded strongly to reach a gain of about 16% for the year. PTLC was a relatively weak performer for the year, returning around 11.5% for the year. Although the fund achieved a certain degree of loss reduction through timing strategies during the market decline, its performance was relatively poor during the subsequent rebound process, resulting in a lower return than the benchmark index for the whole year.
Thus, in an up market, PTLCs perform similarly to the benchmark index; while in a down market, the fund's timing strategy may help mitigate losses, but will not beat the benchmark in all market situations due to tracking error .
Plate rotation enhancement strategy
The plate rotation enhancement strategy judges who is about to take the lead according to the business cycle rotation of different sectors before the market starts, and increases the allocation of upward trending industries or reduces the allocation of sluggish industries (that is, the industry is "overweight" or "underweight"). By deviating from the industry configuration of the tracking index to achieve excess returns higher than the rise and fall of the tracking index.
Table 4 Common industry rotation stock selection enhanced index funds in US stocks
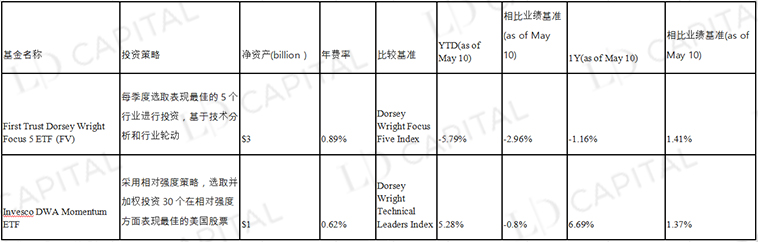 Taking PDP (Invesco DWA Momentum ETF) as an example, PDP aims to track the performance of the Dorsey Wright Technical Leaders Index, adopts a relative strength strategy, selects and weights investments in 30 US stocks with the best performance in terms of relative strength. Assuming that in the market, stocks in the technology sector are the best performers with high relative strength, the PDP will select the stocks with the best performance in the technology sector.
Taking PDP (Invesco DWA Momentum ETF) as an example, PDP aims to track the performance of the Dorsey Wright Technical Leaders Index, adopts a relative strength strategy, selects and weights investments in 30 US stocks with the best performance in terms of relative strength. Assuming that in the market, stocks in the technology sector are the best performers with high relative strength, the PDP will select the stocks with the best performance in the technology sector.
To execute the strategy, PDP regularly rebalances its holdings to ensure continued exposure to technology stocks with the highest relative strength. If the market environment changes, the relative strength of other industries starts to rise, such as the consumer goods industry. In such cases, PDPs may adjust positions and weight investments in new best-performing sectors based on new relative strength data and market trends.
Overall, PDP's approach to strategy execution is based on relative strength stock selection, adjusted for market performance and trends. Stocks are selected based on relative strength, that is, performance relative to other stocks or sectors. By periodically rebalancing positions. The two funds in the table outperformed benchmark performance returns in the one-year time dimension, but performed relatively poorly in YTD.
Derivatives Enhancement Strategy
Derivatives enhancement strategies are the use of derivatives such as options, futures, and swaps to enhance the performance of a portfolio. These strategies often involve considerations of factors such as leverage, hedging risk and speculation.
Some of the US stock-based derivatives enhancement strategies include:
1. If the stock index futures contract has a discount space relative to the spot index, then you can simulate some index positions by investing in stock index futures, and at the same time obtain the enhanced income of negative premium convergence. If the point of the futures contract is lower than the real point of the spot index, buy the futures contract. Theoretically speaking, when the contract expires, the two points must be extremely close, so the longs who hold the futures contract during this period must earn a little more than the spot index. This method tracks the underlying index by allocating part of the funds in stock index futures, while the remaining idle funds are invested in fixed income or arbitrage strategies to obtain relatively stable returns.
2. Calendar Spread: Use the price difference between futures contracts of the same index with different expiration months to carry out arbitrage. When the forward contract has a higher premium than the near-term contract, you can establish a long position in the near-term contract and a short position in the forward contract at the same time. Over time, the spread between the two contracts may converge, leading to excess returns
3. Inter-market arbitrage (Inter-market Arbitrage): When there is a pricing difference between two highly correlated markets (such as commodities, interest rates, exchange rates, etc.), it is possible to establish a long position in one market and simultaneously trade in another The market establishes a short position, and over time, the pricing differential between the two markets may converge, leading to enhanced returns.
4. Option strategy: Option is another common derivative, for example, by selling call options (Covered Call) to increase the return on existing stock investments. In this strategy, the fund owns a certain number of shares and sells a corresponding number of call options. This allows for the option premium to be collected, increasing the overall return on investment. But the risk with this strategy is that if the stock rises more than the option strike price, you may miss out on some of the potential gains.
5. Pairs Trading: This strategy involves two stocks in the same industry or highly correlated. When the price difference between two stocks exceeds the historical normal level, a long position can be established in a relatively undervalued stock, and a short position can be established in a relatively overvalued stock at the same time. Over time, the spread between the two stocks could converge, leading to excess returns.
Take ProShares UltraPro Short QQQ ETF (SQQQ), an index enhancement fund based on US stocks using derivatives enhancement strategies, as an example.
The ProShares UltraPro Short QQQ ETF (SQQQ) uses a market timing and derivatives augmentation strategy to deliver -3 times the daily performance of the Nasdaq-100 Index. This inverse leveraged ETF is designed for experienced investors. If it believes that technology stocks and large-cap stocks in the Nasdaq-100 will fall in the short term, to achieve investment goals, SQQQ uses financial assets such as swaps, futures contracts, and options. Tool to gain short exposure to the Nasdaq-100 Index. Therefore, SQQQ can magnify gains when the underlying index falls, but also magnify losses when the index rises.
Specifically, in the swap strategy, SQQQ obtains short exposure by signing swap contracts with other financial institutions. In a swap contract, SQQQ agrees to exchange the proceeds of an underlying asset (such as the Nasdaq-100 index) at a fixed price for a specified period of time. This allows SQQQ to gain short exposure to the Nasdaq-100 without actually owning the stock.
In the futures contract strategy, SQQQ obtains short exposure by selling Nasdaq-100 index futures contracts. With this method, SQQQ agrees to sell the underlying asset (Nasdaq-100 index) at a certain price on a certain date in the future. This strategy allows SQQQ to take a short trade in the Nasdaq-100 without actually owning the stock.
In the option strategy, SQQQ uses the purchase of put options to achieve short exposure. A put option gives SQQQ the right to sell the underlying asset (Nasdaq-100 index) at a specific price on a specific date in the future. Purchasing a put option allows SQQQ to earn a gain when the underlying asset falls, thereby achieving short exposure to the Nasdaq-100 index. SQQQ executes these trades across multiple trading platforms and venues to ensure liquidity and the best prices. However, this ETF is generally considered a high-risk short-term investment and is not recommended for long-term holding.
Multiple enhanced strategies tracking the same index provide investors with suitable exposure
Even if the same index is tracked, by providing different index tracking strategies and leveraged products, investors can choose an index fund investment representative with a suitable risk exposure according to their risk tolerance, investment goals and expected returns. The following is an introduction to some series of products tracking Nasdaq-100. Most of these products are passively managed, aiming to provide investors with different strategies for tracking the Nasdaq-100 index in order to obtain corresponding exposure and income.
QQQ (Invesco QQQ Trust): As a core product of Invesco, QQQ is the most popular and well-known ETF (AUM 175780 mln) tracking the Nasdaq-100 index. It seeks to replicate the performance of the index, which includes the 100 largest non-financial companies listed on the Nasdaq stock market, by investing in the same securities in the same proportion as the index. QQQ is a market-cap-weighted ETF, meaning holdings are weighted by their market capitalization.
QTR (Global X NASDAQ 100 Tail Risk ETF) is designed to track the performance of the Nasdaq-100 index while reducing tail risk. This ETF invests in the same securities as QQQ, but also holds put options on the Nasdaq-100 to hedge against sharp market declines.
QQQM (Invesco Nasdaq-100 ETF): QQQM is a low-cost alternative to QQQ. It also tracks the Nasdaq-100 index, but with a lower expense ratio. The investment strategy and holdings are similar to QQQ, but with lower fees, more cost-effective for long-term investors.
QQQN (Invesco NASDAQ-100 Triple Q Disruptive Innovators ETF) is an exchange-traded fund (ETF) launched by Invesco. The fund seeks to track the Nasdaq Q-50 Index, which includes non-financial companies ranked 101 to 150 by market capitalization on the Nasdaq Market. These companies are generally considered to be growth-stage businesses with innovative capabilities and breakthrough technologies. QQQN provides investors with exposure to a group of potential businesses in the growth stage.
The QQQA (ProShares Nasdaq-100 Dorsey Wright Momentum ETF) strategy is designed to track the performance of the Dorsey Wright NASDAQ OMX CTA Momentum Index, and its enhanced strategies include momentum strategies that select stocks based on relative strength signals. Relative strength refers to the performance of an individual stock relative to the market or industry. Select Nasdaq-100 index constituents that have performed well in the short term based on relative strength signals. Based on a momentum investing strategy, stocks are selected based on their relative strength and weights are adjusted accordingly. Stronger performing stocks will receive higher weights, while weaker performing stocks will receive lower weights or be excluded from the portfolio.
TQQQ (ProShares UltraPro QQQ): Designed to track the Nasdaq-100 High Beta Index, TQQQ is a leveraged ETF designed to provide three times the performance of the Nasdaq-100 Index. It is designed to track the performance of the entire Nasdaq 100 Index. Due to its leverage amplification effect, TQQQ will generally exhibit higher volatility and risk than the index.
QQQX (Nuveen NASDAQ 100 Dynamic Overwrite Fund): QQQX is an actively managed fund based on the Nasdaq-100 index. Adopt the override strategy, that is, the strategy of simultaneously holding the constituent stocks of the Nasdaq-100 index and selling call options. The overwrite strategy is designed to increase the income of the portfolio, in which the fund holds stocks in the Nasdaq-100 index and simultaneously sells the corresponding call option contracts. If the price of the Nasdaq-100 index is lower than the strike price of the call option on the expiration date, the call option will expire without exercise and the fund can retain the premium received. In this way, the fund can obtain additional income by selling call options when the market trend is stable or falling.
Summarize
Summarize
Compared with the U.S. stock-based equity ETF/Index Fund market, the encrypted index-enhanced product market is still in a very early stage. With the growth of the overall encrypted market value, the growth space of the index-enhanced structured product market should also increase rapidly. We believe that the various enhancement strategies of US stock index funds and index enhancement funds/ETFs can correspond to the strategy construction of index enhancement funds in the encryption market. Encryption index enhancement funds can help investors with different wind biases to obtain corresponding risk exposures through these income enhancement methods, including multi-factor quantitative stock selection models, subjective timing models, sector rotation models or stock index futures derivatives income enhancement models, etc. and excess returns.



