Holiday Security Reminder: Cover your wallet, hackers have to go home for the New Year

Recently, CertiK published "2022 Web3.0 Industry Security Report", in the report we can see that 2022 will be a difficult year for the entire digital asset industry.
Malicious actors stole over $3.7 billion worth of assets from Web 3.0 protocols in 2022, a 189% increase from the $1.3 billion lost in 2021.
Most of these assets were stolen due to private key leaks in phishing attacks or vulnerabilities in smart contracts, but a considerable amount of funds were also stolen from digital currency wallets.
These wallet incidents not only affected individual users, such as Bo Shen of Fenbushi Capital: $42 million in digital currency assets were stolen; they also affected a large number of user groups, such as the Slope and Bitkeep wallet incidents, which affected more than 9,000 user accounts.
However, some of these incidents could have been avoided - because these vulnerabilities can be found in the wallet security assessment.
CertiK has secured hundreds of wallet applications over the past few years.
In this article, we will revisit the major security incidents related to digital currency wallets in 2022 and explore their technical details.
first level title
secondary title
Slope wallet
The most famous and influential cryptocurrency wallet security incident in 2022 originated fromSlope walletImproper handling of private keys.
Slope Wallet is a non-custodial digital currency wallet for iOS and Android, Chrome browser extension.
It supports multiple blockchains, but is primarily active on the Solana blockchain.
On the night of August 2, 2022, approximately $4.1 million worth of assets were stolen from the wallet addresses of 9,231 users over a period of approximately four hours.
In the first hours of the incident, when the root cause was unknown, users panicked and rumors of a Solana blockchain hack began to spread like wildfire.
Hours after the attack, a Twitter user posted a screenshot showing HTTP traffic from Slope's mobile wallet (which included the user's seed phrase). CertiK discovered that when importing a wallet account, the user's seed phrase would be sent to Slope's Sentry log server, and anyone with access to the log could take over the account and transfer all assets from that address.
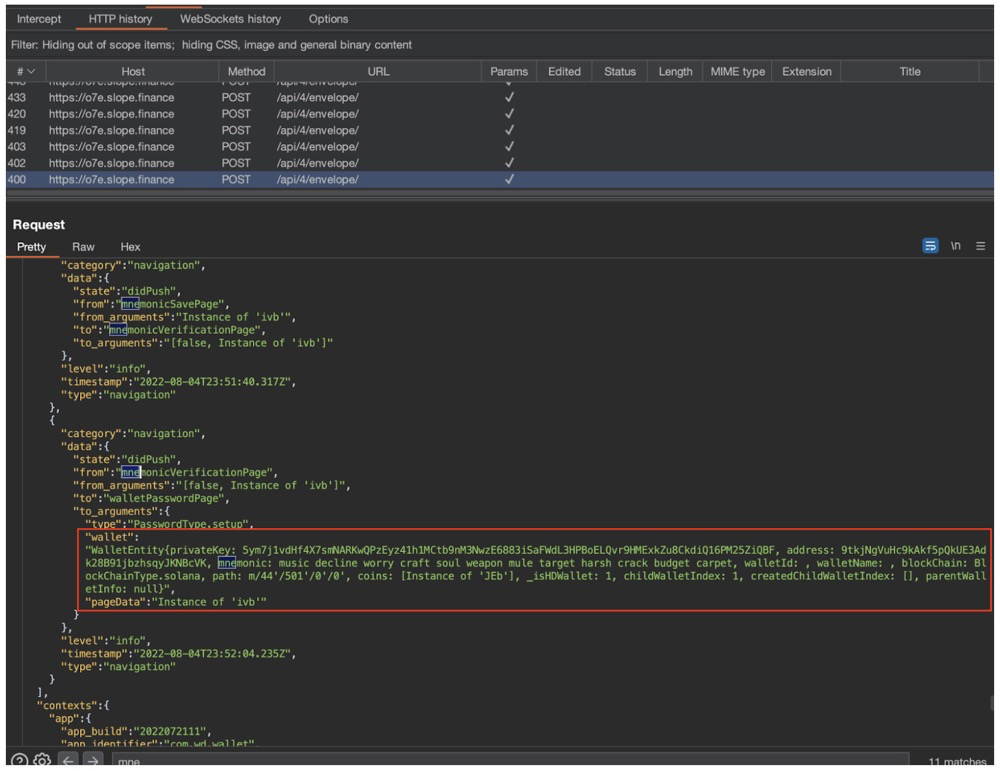
Two weeks after the attack, Slope Wallet published a “Forensics and Incident Response Report.”
From the report, we can know that from July 28, 2022, the user's private key will have been recorded in the database. However, this vulnerability risk is actually very easy to be discovered after a security audit or internal review.
secondary title
Profanity
Profanity is a GPU-based Vanity address (pretty name address) generation tool that allows users to generate their favorite Vanity custom external account (EOA) and smart contract addresses.
Profanity uses a random seed number to expand it into the initial private key, and calculates millions of accounts based on the initial private key through the GPU, so as to brute force create addresses that meet user requirements.
Profity isn't technically a wallet app, but it does have a feature common to almost all cryptocurrency wallets: generating wallet accounts.
This is a perfect example of risky accounts leading to bad results.
September 15, 2022The 1Inch team published an article "A Vulnerability Disclosed in the Ethereum vanity address tool Profanity", which tells about the use of insecure seeds by the Profanity tool, which generates account private keys that can be easily cracked. The vulnerability has since attracted attention for the first time.
Five days later, on September 20, one of the largest digital asset market makersWintermuteA wallet account in , which was hacked, was used by attackers to withdraw approximately $162.5 million from a smart contract.
On October 11, the deployer account of Qanx Bridge was hacked, and the attacker used the account to withdraw $Qanx from Bridge and sell it. Multiple attackers were also actively hunting for vulnerable accounts on the blockchain and stealing funds.
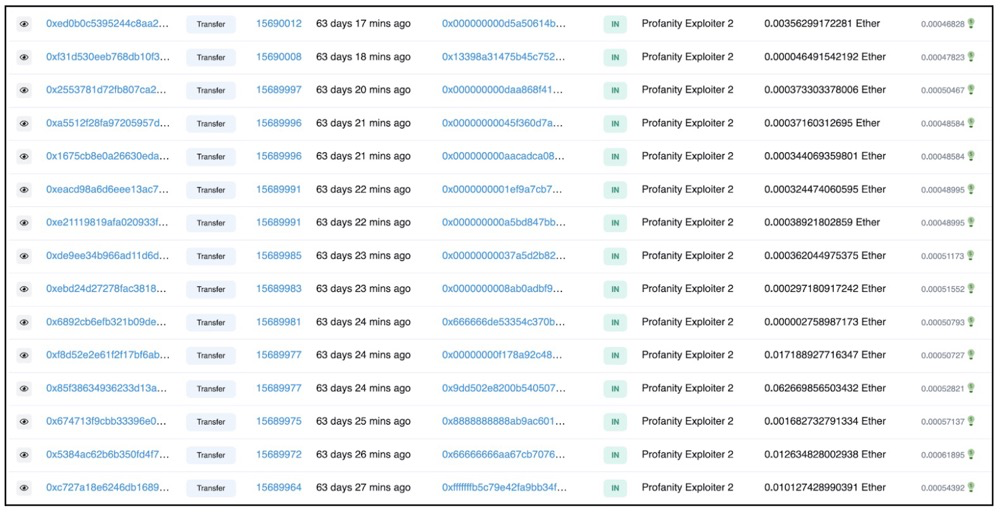
The root cause of this type of problem is that the total number of seeds may only be 2^32 (4 billion). Insecure seeds and a reversible brute force process make it possible to recover the private keys of accounts generated using the tool. CertiK successfully developed a proof-of-concept and was able to recover the private keys of Wintermute and Qanx deployer accounts.
Such incidents are not unique.
In 2013, a similar vulnerability was discovered in Android's random number generator, affecting the creation of Bitcoin wallets.
Cryptography is a complex field, so it's easy to make mistakes that compromise security. A golden rule is "don't roll your own crypto" (don't build an encryption function from scratch. Because the new function has not been tested long enough, it may have many loopholes).
Fortunately, most digital currency wallets will use such as"bip 39"secondary title
iCloud Backup for MetaMask
On April 17, MetaMask, a mainstream cryptocurrency wallet used by more than 30 million people to store and manage digital assets, warned its iOS users of the potential risks of storing wallet secrets in Apple iCloud.
Wallet-sensitive information such as seed phrases is encrypted when uploaded to iCloud, but if its owner's Apple account is compromised and a low-strength password is used, their digital assets are likely to be at risk.
The warning came in exchange for a costly phishing attack.
In this attack, Domenic Iacovone, a user whose Twitter account is @revive_dom, lost a large amount of digital currency and non-homogeneous tokens, with a total value of about 650,000 US dollars.
Pretending to be an Apple support agent, crooks gained access to Iacovone's iCloud account and used stored MetaMask credentials to drain his wallet, making him a victim of this social engineering attack.
secondary title
SeaFlower
A security research team has discovered that an organization, SeaFlower, is distributing malicious versions of legitimate digital currency wallets (including Coinbase Wallet, MetaMask, TokenPocket, and imToken) that will allow users' mnemonic phrases to be stolen through a backdoor. These modified wallets function as intended, but allow attackers to obtain users' digital currency by using stolen seed phrases.
SeaFlower spread Trojanized versions of digital currency wallet applications to as many users as possible through a variety of means including creating fake websites and attacks on search engine optimization (SEO), or promoting them through social media channels, forums, and through malvertising These applications, however, are primarily distributed through search services.
The researchers found that search results on the Baidu engine in particular were affected by SeaFlower, directing large amounts of traffic to malicious websites.
On iOS devices, attackers can bypass security protections to side-load malicious apps by abusing configuration files that link developers and devices to authorized development teams and allow devices to be used for testing apps code, so attackers can use them to add malicious applications to the device.
Common Security Issues of Digital Currency Wallet Apps
The wallet sensitive information is uploaded to the server, or the wallet is generated on the server side
One of the most critical risks is uploading wallet sensitive information to the server or generating the wallet on the server side. For non-custodial wallets, wallet-sensitive information should be stored on the user's device - even if it exists in encrypted form, this highly sensitive data may still be intercepted in transit or leaked to someone with access to the server database or log.
insecure storage
Security risks arise when sensitive information, such as wallet passwords and other secrets, is stored in plain text or in an unsecured location on the device.
This case includes external storage on Android or "UserDefaults" on iOS.
It can also occur when an insecure key derivation function is used to generate an encryption key, or when an insecure encryption algorithm is used to protect data.
Lack of security checks on the operating and operating environment
In addition to storing data securely, the wallet application should also ensure the security of its operation and the security of the underlying operating environment. Some common issues in this category include lack of root and jailbreak detection, inability to prevent users from taking screenshots of sensitive wallet information, failure to hide sensitive information while the app is running in the background, and allowing custom keyboards for sensitive input fields.
Lack of protection against malicious websites in the extension wallet
Most DApps are web applications, and using a browser extension wallet is the most common way to interact.
first level title
Advice for wallet users
It is important to take precautions to protect your digital assets and keep your wallet safe. The digital currency field is full of risks posed by hackers and fraudsters.
Below is a list of recommendations that users can refer to or follow to reduce the chances of being hacked.
① Select a wallet that meets security standards. Some wallets may be buggy and vulnerable to hacking or other security breaches. Please only use wallets that have been tested by security companies, thoroughly checked for potential vulnerabilities, and considered to meet security standards.
② Downloading apps from the official iOS store and Google Play store helps ensure that you are getting a legitimate version of the app.
③ It is important to keep devices updated, as software updates often include security fixes for discovered vulnerabilities.
④ Use a dedicated mobile phone or personal computer to install the wallet application, and do not use daily work equipment, which helps reduce the risk of being damaged by accidentally installed malicious applications.
write at the end
write at the end
New Layer 1 and Layer 2 blockchains are continuously being developed, and since many existing wallets are not compatible with these new blockchains, more digital currency wallets will be launched on the market.
Reducing the security risks of wallets as much as possible requires the joint efforts of users and wallet developers: users need to follow best practices and remain vigilant to prevent hacking; development teams need to write secure code and conduct security audits on their wallet applications .



