Abstract Research Report on Ethereum Accounts: Dismantling 10 related EIP proposals and the bottleneck problem affecting tens of millions of daily active users
In Splurge, the sixth phase of the latest Ethereum roadmap recently released by Ethereum founder Vitalik, the newly included ERC-4337 has become the main implementation of the current Account Abstraction (Account Abstraction).
Why is the account important? Because when any web2 user enters web3, the first layer of resistance encountered is to save the private key or mnemonic, and also face the possible loss of the private key without knowing it, and cannot judge in the face of stolen signatures from phishing websites, or even go online The theft of the chain bridge of 100 million US dollars also occurred due to the private key problem, so the realization of a better Ethereum account system has always been the bottleneck of the Ethereum network for impacting tens of millions of users
And if you want to have a deep understanding of the iterative process of Ethereum and the underlying infrastructure of the blockchain, you must also have an absolutely deep understanding of the complete concept and principle of account abstraction, and the evolution history of the account abstraction scheme in the past seven years The road of iteration, this research report will present you a panoramic view with nearly 10,000 words. It is strongly recommended to prepare coffee and read it carefully.
This article will tryStarting with the first AA proposal from 2015, to systematically sort out the main content of all EIP proposals so far and comprehensively evaluate the advantages and disadvantages of each plan. Looking back on the process, many proposals have already been at the stage of stagnation or even just drafts.
This article divides the 10 EIP proposals into three major paths based on their optimized template links: transforming the type of transactions on the chain, transforming the subject objects on the chain, transforming the packaging process of transactions on the chain
first level title
1. Background
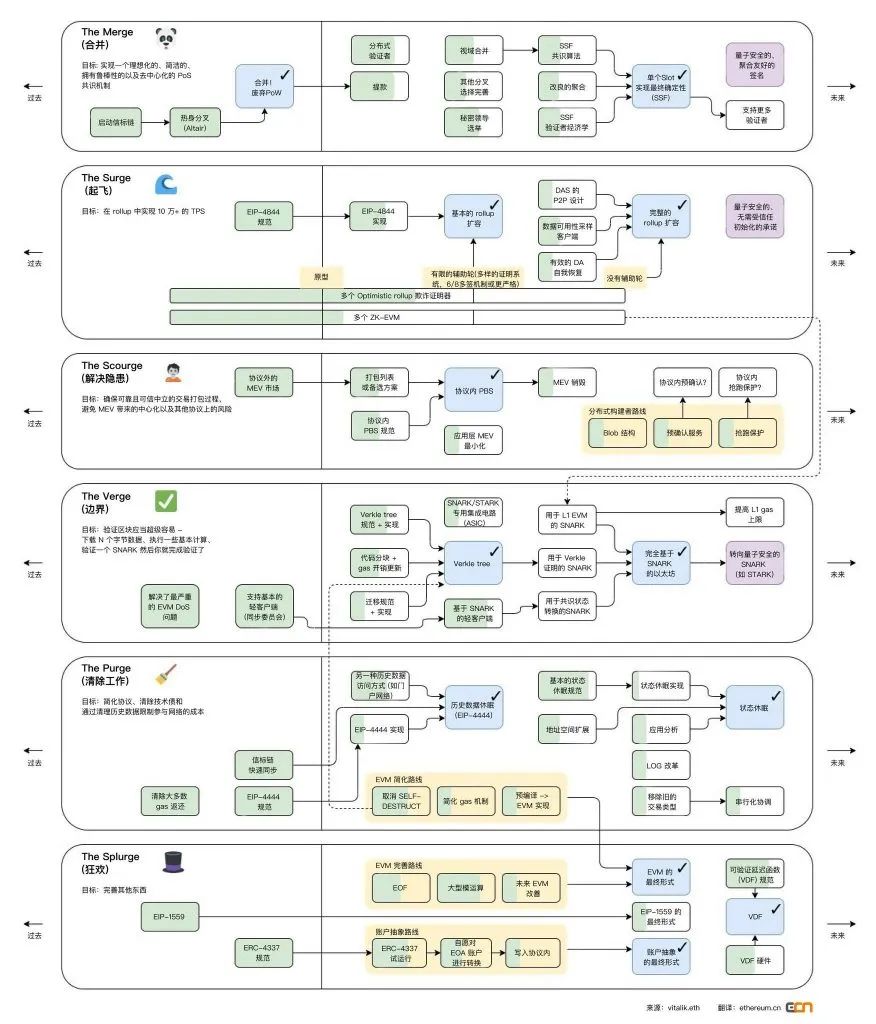
V God, the founder of Ethereum, recently updated the ETH development roadmap, in which the goal of the sixth phase of Splurge is: fix everything else.
Many things in the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) need to be optimized. For example, VDF will generate real random numbers on the chain. The most important thing in this roadmap is that the core proposal EIP-4337 of account abstraction AA has become a reality. path.
secondary title
1.1. Why is the existing account system the bottleneck of tens of millions of users?
Currently, there are two types of accounts in Ethereum, namely external account (EOA) and contract account (Contract Account).The ownership and signature rights of external accounts are theoretically held by the same individual unit.
Simply put, holdprivate keyThe person not only has the "ownership" of this account, but also has the right to "sign and transfer all assets".
Currently, ownership and signing rights are integrated in Ethereum, and such an external account design may lead to some issues worth discussing:
Difficult to protect the private key: The user loses the private key (lost, hacker attack) means losing all assets.
Few signature algorithms: native protocols can only use ECDSA signature and verification algorithms for transaction verification.
High signature authority: no native multi-signature (multi-signature can only achieve collaboration through smart contracts), single-signature can perform any operation.
Transaction fees can only be paid by ETH, and batch transactions are not supported.
Transaction privacy disclosure: One-to-one transactions can easily analyze the private information of account holders.
Secondly, the simple contract wallet also has certain problems:
The operation on the contract wallet must be initiated by EOA (essentially calling the contract), and each transaction will consume an additional 21,000 Gas. (The verification method of the current Ethereum transaction is fixed, and a transaction is only valid if it holds a valid ECDSA signature, Nonce value and sufficient account balance).
EOA needs to have enough ETH to pay Gas (manage two accounts), or rely on Relayer to pay Gas (leading to centralization).
Appeal constraints make it difficult for ordinary users to use Ethereum:
First, to use any application on Ethereum, users must hold ether (and bear the risk of ether price fluctuations).
Secondly, users need to deal with complex fee logic. The concepts of Gas price, Gas limit, and transaction blocking are too complicated for users.
Finally, although many blockchain wallets or applications try to improve user experience through product optimization, they have little actual effect.
secondary title
1.2. The fundamental purpose of the abstract account
It is difficult for people who are moving from Web2 to Web3 to accept high-risk private key management methods, so they take it for granted that the Ethereum account abstraction experiment for many years is to cancel the private key, but now there is no free one in the decentralized field trust, authentication must be based on cryptographic proofs,So no matter which proposal is required to manage some kind of private key. Although everyone has their own constraints and responsibilities for managing private keys after all, there is also a way to achieve a compromise in experience through smart contracts.
secondary title
1.3. The historical path of the abstract account
The overall transformation method can be divided into three general directions according to the targeted objects or links
Transform transaction types on the chain (EIP-101, EIP-86, EIP-859, EIP-2718)
Transformation of main objects on the chain (EIP-2938, EIP-3074, EIP-3607, EIP-5003)
Transform the packaging process of on-chain transactions (EIP-4337, EIP-5189)
Retrace the journey to achieve such a goal
At the beginning, Ethereum distinguished external accounts and contract accounts by adding new transaction types such as EIP-86, EIP-101, and EIP-859, but they found that such changes were too large, and their complexity was no less than that of mergers. The transfer of the consensus algorithm. Once Ethereum changes the transaction type, the underlying signature verification algorithm must be modified accordingly. This must consider whether the miners accept the new type to help them go on the chain, and the income cannot be lower than ordinary transactions (otherwise the miners have no incentive to do verification). Also consider account address management, conflicts, forward and backward compatibility, and so on.
And over the course of these seven years of research, a wealth of information and ideasNot abandoned, but inherited and carried forward。
Through EIP-86/208: the contract address needs to be distinguished from the external account, so the contract address must be customizable and anti-collision, so EIP-1014 and EIP-2470 have been implemented.
Through EIP-859: For the first time, the contract initialization code attached to the transaction appeared. If there is no contract address, one will be deployed on site, which becomes the basic function of EIP-4337.
Pass EIP-2718: Make future Ethereum compatible with any newly proposed transaction types without taking too much care of the historical baggage of forward compatibility.
Through EIP-2938: a clear summary of the various advantages of contract accounts, such as social recovery, key rotation, custom authentication algorithms, meta-transactions, etc., let contract accounts gradually become popular.
The final consensus focuses on two paths:
Let the current external account have the function of smart contract (EIP-3074 series).
Let the current smart contract have the function of external account (EIP-4337 series).
Now EIP-4337 is included in the roadmapfirst level title
2. What is the best form of the next-generation account?
How big is the space? Can speak with numbers:
Number of external accounts: The number of from addresses that appear in the total transactions of Ethereum is about 150 million after deduplication.
Number of SCW/A accounts: The total number of accounts using the top two products, Gnosis Safe and Argent, is 150,000.
The author believes that the account form that subsequent users will contact is two-stage, distinguishing off-chain key management and on-chain account entities.
On the off-chain key management side, the MPC (Multi-Party Secure Computing) + TSS (Threshold Signature Scheme) with the best experience is adopted, especially 2/2, 2/3 will be parameter schemes that are compatible with regulatory requirements and convenient use requirements .
In the 2/2 mode, the project party holds 1 and the user holds 1. If any party disagrees, at least the funds will not be lost. It is suitable for scenarios that require supervision in the future (team vault private key management, etc.).
In the 2/3 mode, the project party holds 1 and the user holds 2. The user can manage the shard key on the two terminals separately, and the daily local + the shards held by the project party combine signatures, even if the project party runs away , the user can restore it by himself.
On the main side of the account on the chain, an upgradeable smart contract model will be adopted, and at this time there will be a variety of functional points to expand:
Custom signature algorithms: such as Multisig Verification, Schnorr sigs, BLS sigs, Quantum-resistant sigs (eg Lamport, Winternitz), in effect, they naturally support multi-signatures and thresholds from cryptography.
Packing of multiple transactions: Miners can sign and aggregate the data of multiple transactions, as long as they can be executed successfully. The effect of this is that the average Gas consumption can be lowered when the transaction volume is large enough.
Social recovery and replacement of private key: If one day a person’s WeChat account is hacked, even if all the money is transferred, the friend list and chat history in it can be restored, and the original account can still be used because the SBT soul token will not be lost.
Upgradable and decentralized: The contract itself can be designed and upgraded, and ownership can be changed. The main account on the chain is naturally uncustodial and completely decentralized.
Yuan transaction and multi-coin payment: users can use other Token transfers to pay miners Gas in the contract wallet, so that there is no need to recharge native tokens for handling fees.
Anti-DoS and quantum attack: Anti-malicious miners blocking the system and key blasting.
Advantages for arbitrageurs: After account abstraction is realized, arbitrageurs do not need to pay for failed arbitrage behaviors, and the chain will not include failed arbitrage transactions, which can effectively improve the reliability of the chain Scalability
However, AA is implemented through EIP-4337, and there are many risk problems:
The verification process of the node will be more complicated, which will add a lot of useless computing burden to the node, thus increasing the risk of resisting DoS attacks.
Because of the scheduling of the contract, the Gas consumption will be higher than the direct signature transaction of the EOA account, which needs to use the same reduction principle as the NFT aggregator.
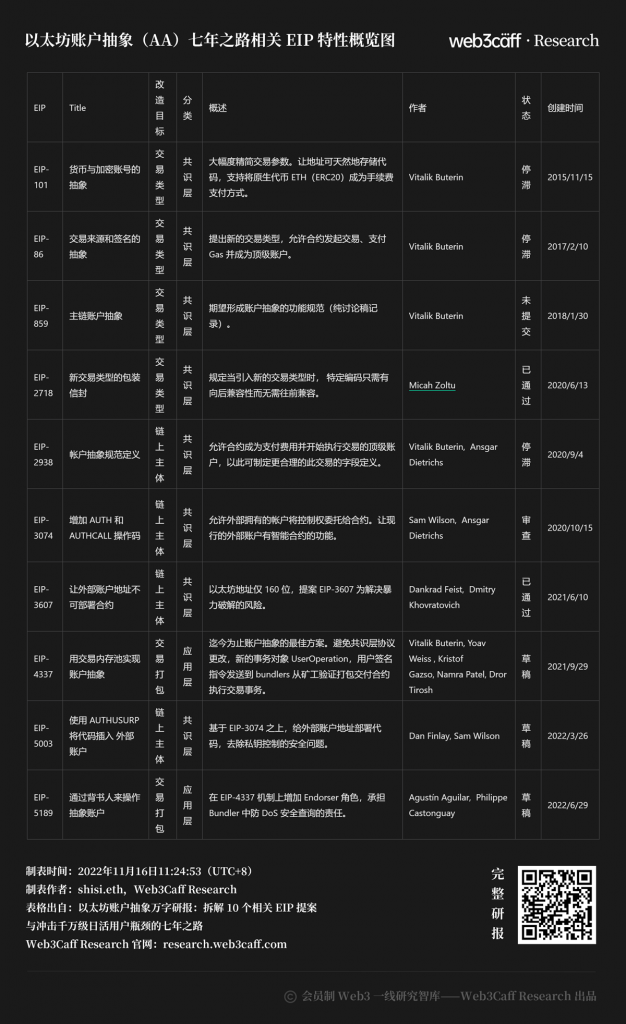
Overview of EIP features related to Ethereum Account Abstraction (AA) seven-year road
Unfinished content:
Interpretation of EIP Proposals Related to Account Abstraction (AA)
EIP-101: Money and Cryptographic Abstractions - 15/11/2015
EIP-86/208: Abstraction of Transaction Provenance and Signatures - 2017/02/10
EIP-859: Main Chain Account Abstraction (AA)——2018/01/30
EIP-2718: Wrapping envelopes for new transaction types - 2020/06/13
EIP-2938: Account Abstraction (AA) Standard - 2020-10-15
EIP-3074: Add AUTH and AUTHCALL opcodes - 15/10/2020
EIP-3607: Make external account addresses non-deployable contracts - 2021/06/10
EIP-4337: Account Abstraction Using Transaction Mempools - 2021/09/29
EIP-5003: Inserting codes into external accounts using AUTHUSURP - 2022/02/26
EIP-5189: Manipulating Account Abstraction Through Endorsements - 2022/06/29
Q&A:
1. Which wallets are currently implemented following EIP-4337?
2. Why did Ethereum choose EIP-4337 instead of EIP-3074?
3. What is abstract in account abstraction?
4. If there is a good enough MPC+TSS solution, no mnemonic words are needed, and the security is guaranteed, do we still need a contract wallet?
5. What are the benefits of custom signature algorithms?
6. EIP-4337 still relies on EOA account signature, can it really bring a qualitative leap to user experience?
7. What are the next improvement directions for EIP-4337?
Like and follow 14, bring you value from a technical perspective
Like and follow 14, bring you value from a technical perspective



