The New Order of Trading: How CEX and DEX Reshape the Derivatives Market
- 核心观点:衍生品成为加密市场定价核心。
- 关键要素:
- 衍生品交易量占市场71%。
- 清算潮推动风险透明度需求。
- CEX与DEX呈现多极格局。
- 市场影响:推动交易所向性能与信任并重转型。
- 时效性标注:中期影响

Market rebalancing: derivatives return to the core of the industry
The crypto market in 2025 is undergoing a profound restructuring. Since the October 11th wave of liquidations that swept across the entire network, over $40 billion in leveraged positions have been forcibly liquidated, prompting the market to reassess the balance between risk, transparency, and efficiency. Derivatives have moved from being a fringe speculative tool back to the core of market pricing, becoming the foundation of the entire trading system.
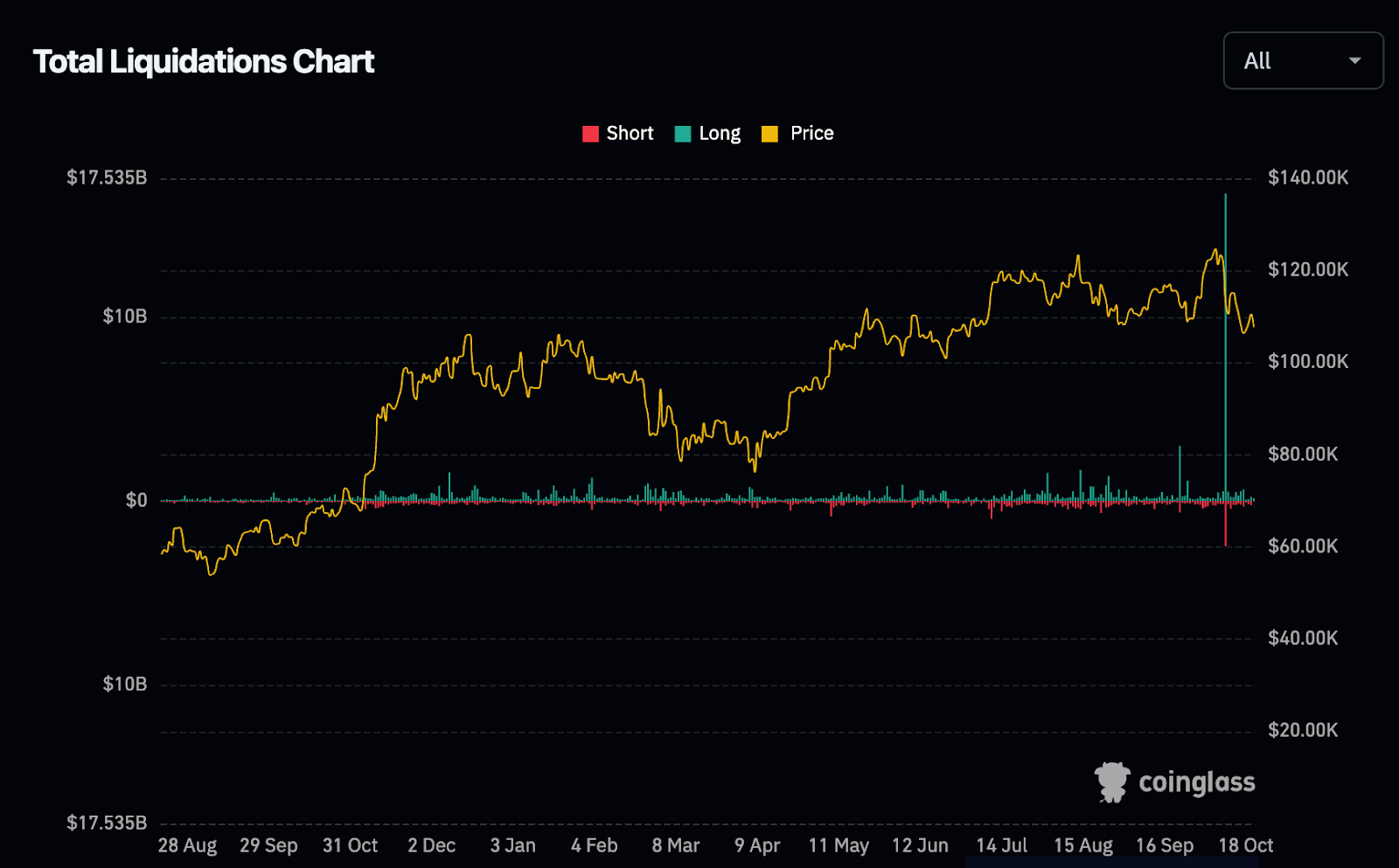
According to data from CoinGlass and Kaiko, derivatives trading volume already accounts for 71% of the total crypto market, exceeding $10 trillion on an annualized basis, an increase of nearly 20 percentage points from 2023. Binance, OKX, and Bybit still control approximately 60% of the market, but their focus is shifting downward.
Second-tier trading platforms such as Gate, Bitget, and LBank all recorded significant growth in the third quarter of 2025. Among them, LBank's contract trading volume increased by 92% month-on-month, making it one of the fastest-growing exchanges in the mid-tier camp.
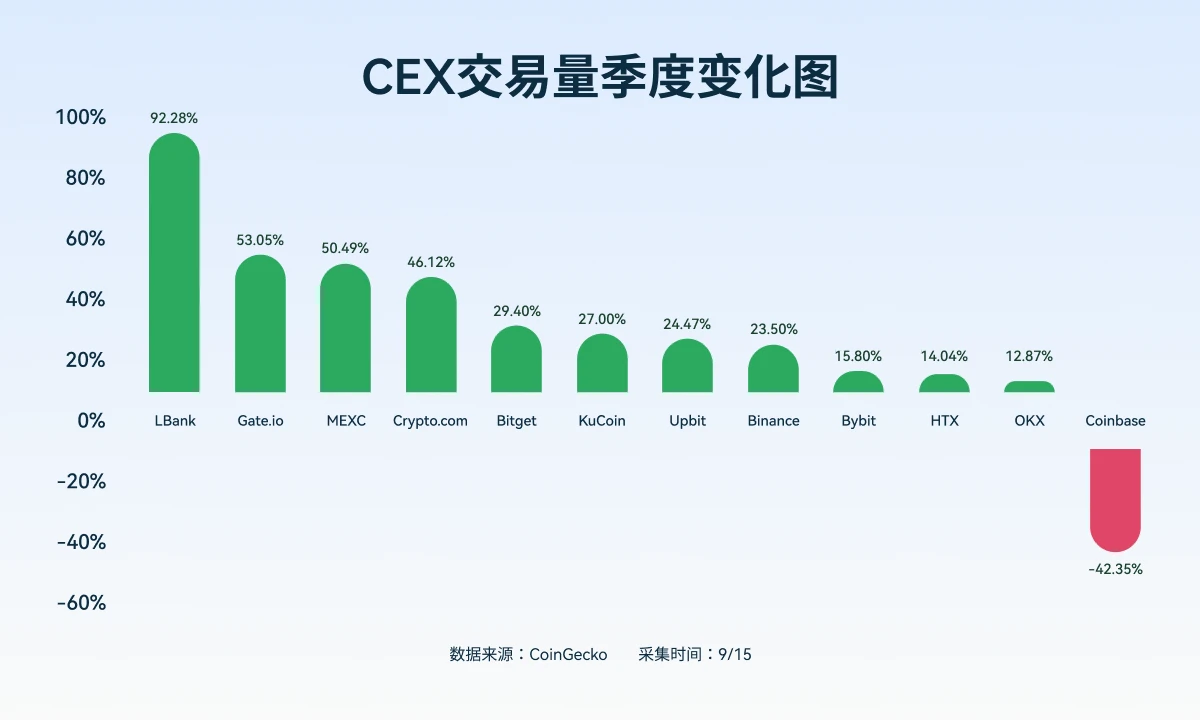
This trend indicates a structural shift in the logic of market competition. Traders are no longer solely focused on liquidity and leverage; instead, they are seeking platforms that offer both high performance and robustness. Platforms like LBank, with their stable architecture and clear risk management systems, are embodying this realistic approach.
Meanwhile, decentralized derivatives protocols have become a second growth driver. Hyperliquid achieves highly transparent matching through a fully on-chain order book (CLOB), while Aster employs a hybrid architecture combining an independent consensus chain with off-chain matching, balancing performance and verifiability. The rise of these two models has led to a multi-polar landscape in the derivatives market, where centralized efficiency and on-chain transparency coexist.
Mechanism Comparison: The Tradeoff Between Centralized Performance and On-Chain Transparency
The liquidation wave on October 10–11, 2025, became a true test of the resilience of the derivatives system. According to CoinGlass data, global markets liquidated approximately $19 billion in leveraged positions within 24 hours that day, the largest single-day liquidation in nearly three years.
In extreme market conditions, derivatives platforms with different architectures exhibit vastly different stress responses:
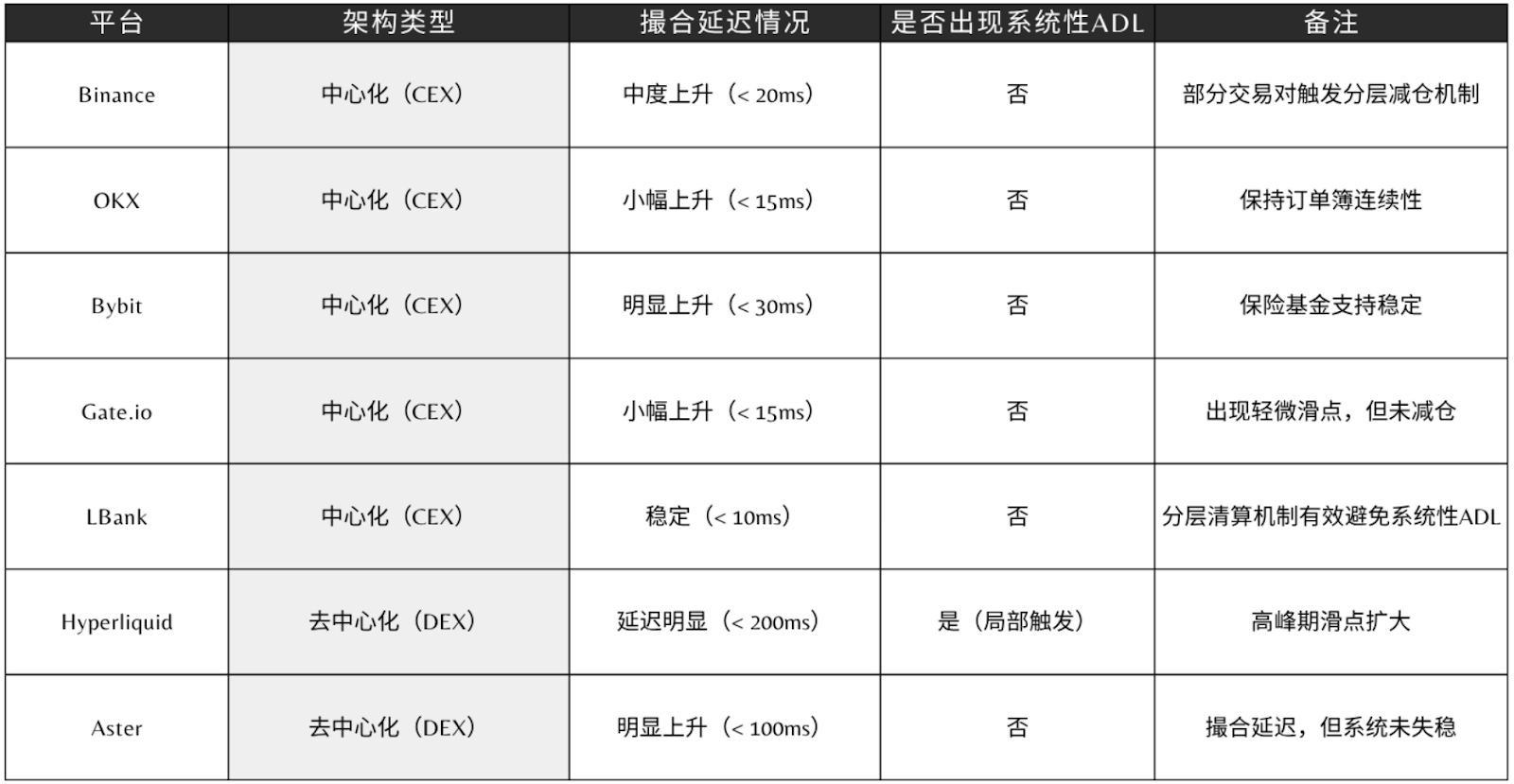
Centralized platforms rely on sophisticated matching systems and layered risk control mechanisms to maintain high execution efficiency and liquidity during periods of extreme volatility. Liquidation is typically completed within seconds, preventing widespread cascading liquidations. However, this type of architecture suffers from a lack of transparency, making it difficult for users to directly verify the system's specific processing logic under extreme conditions.
Decentralized platforms are characterized by openness and transparency. All transaction and settlement records are traceable, providing greater credibility for risk control. However, their performance is limited by block throughput and gas costs, making them prone to delays, increased slippage, and even delayed oracle updates in extreme market conditions. While transparency fosters trust, it also creates technical constraints.
Between these two models, more and more platforms are choosing a compromise of "flexible centralization": core matching and clearing remain centralized to ensure performance, while key risk nodes are auditable and on-chain to enhance verifiability. This structure isn't perfect, but it offers a more balanced approach in real-world market conditions and is gradually becoming a consensus within the industry.
LBank's risk management practices epitomize this trend. In March of this year, the platform established a $100 million contract risk protection fund to mitigate user losses caused by system anomalies or price manipulation. If abnormal fluctuations result in forced liquidation or stop-loss orders, the platform will compensate users at 120% of their losses and distribute additional airdrops proportionally to all holdings. The core of this mechanism is to establish a risk mitigation and trust-restoration path, introducing a quantifiable accountability mechanism to a centralized architecture and reflecting the exchange's institutionalized approach to risk governance.
Trading Experience: Balancing Leverage and Depth
The quality of derivatives trading experience depends on two dimensions: execution speed and market depth.
CEX Model: High Performance and Centralization Risk Coexist
In the centralized trading model, mainstream platforms such as Binance, OKX, Bybit, and LBank rely on centralized liquidity pools and professional market maker systems to build an ultra-low latency and high-throughput matching network.
Its order matching latency is typically less than 10 milliseconds, enabling it to support institutional-grade high-frequency trading and large-volume liquidations. Furthermore, the exchange utilizes a tiered risk engine, insurance fund, and automatic position reduction (ADL) mechanism to maintain market stability and continuity during extreme market conditions.
The hidden danger of this centralized architecture lies in single-point vulnerability: when the core matching node or clearing engine fails, the matching and clearing system may become unbalanced instantly, the market depth may drop sharply, and order execution may be hindered.
DEX Model: Redistribution of Efficiency and Trust
In contrast, the DEX model represented by Hyperliquid and Aster shifts trust from institutions to code. Hyperliquid's fully on-chain order book model ensures on-chain verification of every order and transaction. Aster achieves high-performance matching on the main chain, but some settlement still relies on off-chain nodes.
Kaiko data shows that the 1% liquidity depth for major trading pairs (BTC/USDT and ETH/USDT) on OKX, Binance, and LBank exceeds tens of millions of dollars, while the on-chain liquidity depth on Hyperliquid and Aster for similar pairs is only one-tenth of that. This means that CEXs can provide more stable transaction prices during periods of significant volatility. Binance, OKX, and LBank's major trading pairs all demonstrate robust liquidity depth, providing more reliable price support for the market.
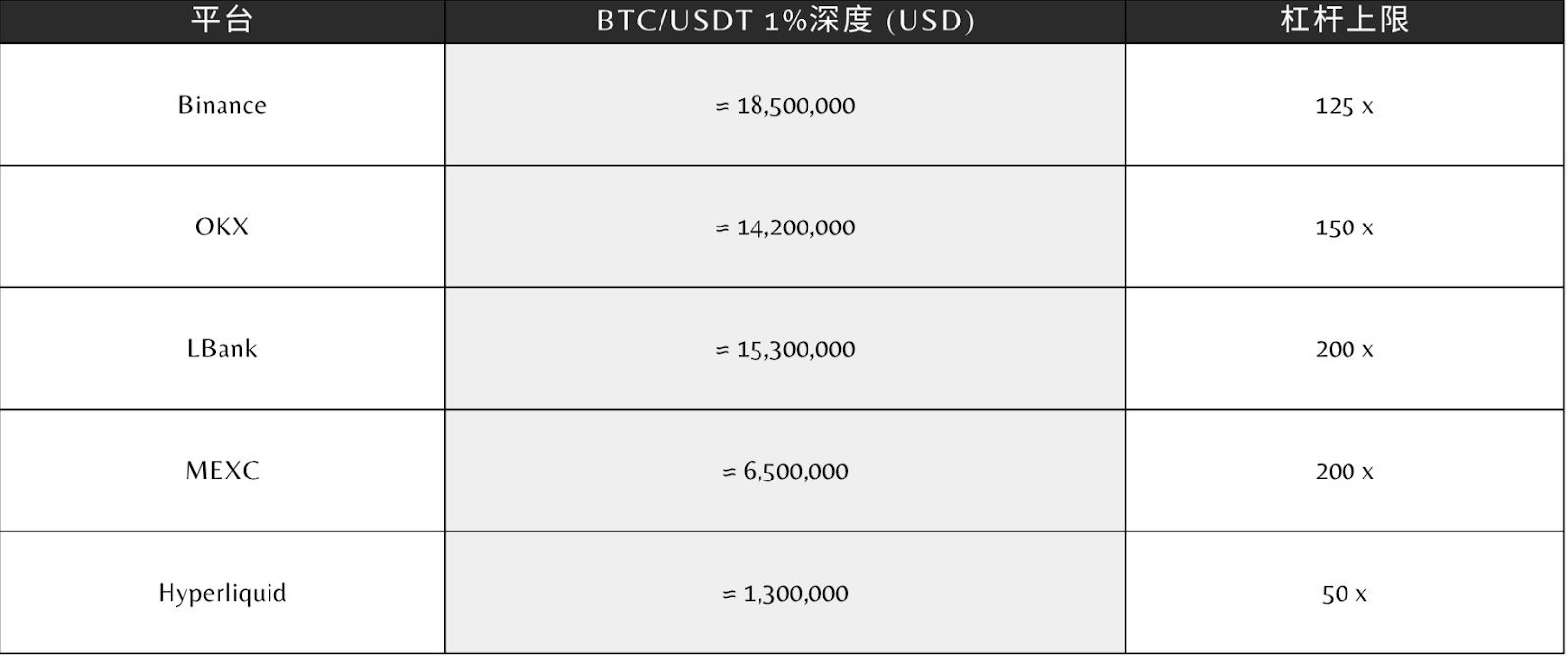
Leverage flexibility is another key differentiator. Platforms like LBank and MEXC offer up to 200x leverage, equipped with insurance funds and automatic position reduction mechanisms to manage risk. Hyperliquid's leverage cap is approximately 50x, limiting the contract risk associated with excessive leverage at a systemic level.
Product innovation: From leverage competition to ecological competition
The focus of derivatives competition is shifting from "single leverage efficiency" to "eco-friendly experience." Major platforms are attempting to establish more stable capital circulation and behavioral closed loops among different user groups.
Binance is building a strategic ecosystem through its Web3 wallet, Alpha. OKX is expanding its structured return potential. Bybit is improving capital utilization with a unified margin system. Mid-sized platforms are also exploring new directions in product mechanisms and user incentives. LBank combines its Meme section, BonusPro rewards program, and a points system to create an ecosystem where "trading is incentive," fostering a sense of engagement and sustained user retention.
After the sharp market fluctuations on October 10-11, several exchanges quickly launched compensation and incentive programs to stabilize user confidence and restore market activity.
- Binance was the first to announce a compensation plan totaling US$283 million to make up for losses caused by the depegging of collateral assets and settlement delays, and added a US$400 million "Peer Initiative" trust reconstruction plan, of which US$300 million was used to issue USDC vouchers and system compensation to users who suffered large forced liquidation losses, becoming a landmark event in crisis response.
- During the same period, Bitget continued to promote the multi-period contract elite list to maintain trading enthusiasm;
- Bybit launched the 0G Launchpool, the Autumn Trading War, and a $5 million welcome bonus program to expand user incentive coverage;
- OKX stabilizes traffic and retention through referral bonuses and USDG recharge activities.
- In mid-October, LBank launched the "Million Guardians" campaign with a total prize pool of US$1 million, and launched a special subsidy program for users who suffered losses in the market on October 11, providing additional support and compensation to affected users, helping them rebuild confidence and return to the market steadily after the extreme market conditions.
Innovation in decentralized derivatives focuses on underlying mechanisms. Hyperliquid is building an on-chain reputation points system, while Aster is exploring options and cross-margin structures, integrating traditional financial logic into smart contracts. These designs enhance the composability and autonomy of the protocols, but also increase operational barriers and fund management complexity.
Overall, DEXs emphasize transparency and algorithmic autonomy, while CEXs maintain their dominance through improved product experience, capital efficiency, and risk control. For institutional investors, the verifiability of on-chain protocols is attractive; for ordinary users, the advantages of centralized platforms in performance, security, and service systems remain more relevant.
Rebuilding trust and systematic competition
The evolution of the derivatives market is essentially a reconstruction of the trust system.
From the collapse of FTX to the rise of Hyperliquid, from Binance's institutional transformation to LBank's hybrid innovation, the market focus is shifting from scale expansion to competition for institutional credibility. Future exchanges will no longer simply be tools for matching orders, but will become complex financial systems that coordinate trust, risk, and returns. In this new system, CEX, DEX, and Hybrid represent three different trust logics:
CEX (Binance, OKX, Bybit, Bitget, LBank) relies on a centralized clearing network, emphasizing performance, stability, and compliance and security; DEX (Hyperliquid, Aster, Aevo, dYdX) focuses on transparency and autonomy; the hybrid model balances performance and verifiability between the two.
The boundaries between these three are gradually blurring: CEXs are introducing on-chain audits to pursue transparency, while DEXs are leveraging professional market makers to enhance liquidity. New platforms like LBank are finding a practical solution between the two through hybrid architectures, pushing the derivatives market into a new stage where both performance and trust are equally important.
The future of derivatives will no longer be dominated by a single model, but rather by a symbiotic relationship between efficiency, transparency, and mechanisms. Binance and OKX remain the cornerstones of global liquidity, while Hyperliquid and Aster push the boundaries of transparency. Emerging platforms like LBank are reshaping the market order with pragmatic and innovative approaches, defining a new trading order for the new cycle.



