Messari Report: Detailed explanation of cross-chain infrastructure Axelar
Original text: Understanding Axelar: A Comprehensive Overview
Author: Red Sheehan
Compiled by: Odaily How about
Messari recently wrote a long article analyzing Axelar. The article starts from the multi-chain environment and conducts a comprehensive analysis of Axelar from the perspectives of technology, AXL token economics, ecological status, future planning and competitors.
The following is the original text of the report, compiled by Odaily.
Key insights
Axelar has the ability to program cross-chain logic and transfer arbitrary data;
The upcoming Axelar VM will allow permissionless connections to new chains;
Axelar’s cross-chain token service is under testing and supports cross-chain transfers of local tokens rather than encapsulated tokens;
Updated AXL token economic model. This model enables the network to sustainably support more chains by reducing the token inflation rate for each additional chain;
Currently, 10 of Axelar’s top 15 chains by activity are based on EVM. Axelar focuses on connecting more compatible EVM and Ethereum-based chains.
background
The number and diversity of blockchains continues to expand with the growth of modular blockchains, Layer 2, and application-specific chains. But the market lacks solutions for developers to cost-effectively span multiple multi-chain ecosystems. Axelar provides developers with a secure cross-chain development platform through API and SDK accessibility. These developer resources focus on easy-to-use plug-and-play integration solutions. Therefore, Axelar is a good choice for DApps that want to quickly build cross-chain capabilities.
Founded in 2020, Axelar leverages various Cosmos technologies to enable interoperability with Ethereum and other networks. Axelar’s technology is designed to allow for more complex cross-chain functionality beyond simply transferring encapsulated assets to different blockchains. Axelar solves this problem by focusing on full-stack interoperability - full-stack means that Axelar not only supports the bridging of any information/asset, but also supports permissionless overlay programming to enable smart contracts and DApps across the network.
The Axelar community is working hard to expand the number of connected networks (55 at time of publication) through a three-pronged approach:
Adjust the economic structure of the network;
Release of Axelar VM to support permissionless connections for projects;
And explore more efficient solutions such as lightweight clients.
These initiatives aim to connect Axelar to hundreds of chains.
technology
Axelar has three main components:
Distributed network: mainly built on open source Cosmos technology.
Gateway smart contract: Provides the connection between the Axelar network and its interconnected external chains.
Software development kit (SDK) for developer tools and APIs, including Axelarscan, a block explorer for tracking cross-chain transactions.
Network Architecture
The Axelar network is built using the Cosmos SDK, CometBFT and CosmWasm VM. The Cosmos SDK is an open source software development kit (SDK) for building sovereign, multi-asset, public PoS blockchains. It is used to build a custom application layer or state machine, while CometBFT is used to safely replicate that state machine across all nodes in the network. CometBFT is an application-agnostic engine that handles the network and consensus layers through two main components:
Consensus algorithm, namely Tendermint;
Socket protocol, Application Blockchain Interface (ABCI).
Tendermint is used to validate requests on the source chain and confirm changes on the target chain. Tendermint consensus provides instant finality and Byzantine fault tolerance. While this particular consensus method only verifies cross-chain communication, Axelar can connect various forms of consensus. For example, Axelar is one of the few cross-chain protocols capable of connecting the EVM and Cosmos chains.
Consensus Security Solution
The Axelar network adopts the Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) consensus mechanism. Validators generate new blocks, participate in multi-party signatures, and vote on external chain status. Token holders stake AXL by delegating their tokens to a staking pool of validators. With only the first 75 validators in the active set, this parameter can be adjusted through on-chain governance. There is no permission to delegate to the validator and run the validator.
Every PoS consensus mechanism runs the risk of concentrating voting power in the hands of a few dominant players. Axelar mitigates this risk by employing a quadratic voting mechanism where voting rights do not increase linearly with staking. In order to increase their voting power, Axelar validators must exponentially increase the stake of their delegation.
Additionally, Axelar applies network capabilities that allow it to pause traffic from malicious interconnected chains and employs contract limits to limit the maximum amount that can be transferred over a period of time. Axelars hub-and-spoke network topology increases the efficiency of these functions. During a multi-chain crash, cross-chain exchange services built with Axelar are able to remain secure and liquid by isolating compromised connections.
Axelar VM
The introduction of Axelar VM (AVM) extends Axelar’s functionality from bridging and messaging to a fully programmable cross-chain layer. It enables developers to deploy smart contracts and build cross-chain development tools on Axelar. Smart contracts can help reduce developer overhead and simplify user experience by abstracting cross-chain tasks such as token conversions. Developers can deploy contracts on AVM using any language compiled to WebAssembly (Wasm). Additionally, AVM is expected to play a key role in the token economic model of Axelar’s native token, AXL.
Since AVM is permissionless, any developer can take advantage of it. The Axelar Foundation supports development teams working on expanding the ecosystem, improving security, and designing interchain orchestration templates on AVM. The first product is the Interchain Token Service (ITS), which is currently available on the testnet. Other services enabled by AVM include Cross-Chain Amplifier and Cross-Chain Master.
Cross-chain token service
Interchain Token Service (ITS) is a service designed to preserve native token versatility and custom functionality across multiple blockchains. These reserved tokens are called cross-chain tokens. This will be a familiar feature to those familiar with LayerZero’s Omnichain Fungible Tokens and IBC Connect network using Interchain Accounts (ICA) and Interchain Query (ICQ).
Unlike these alternatives, Axelar ITS supports canonical packaging and standardized tokens; these features enable one-click deployment to multiple chains. ITS also natively supports arbitrary data and fast finality devices.
With ITS, developers can deploy cross-chain tokens on multiple chains simultaneously and automate tasks such as supply management. Cross-chain tokens are supported by the Axelar Network’s security protocols and can run on any EVM-compatible chain connected to the Axelar Network.
Interchain Amplifier
Interchain Amplifier will allow developers to connect new blockchains to the Axelar network permissionlessly. This will benefit new ecosystems, such as those building modular blockchains on Ethereum, as well as DApps looking to customize cross-chain processes.
Interchain Maestro
Interchain Maestro is a set of orchestration contracts and templates that help design, deploy, and manage DApps on multiple chains. Interchain Token Service (ITS) is a component within the broader scope of Interchain Maestro.
Axelar is an overlay network
The Internet, like the crypto space, is made up of diverse networks. The protocols BGP and HTTP enable these diverse networks to communicate only on this basis, without guarantees, improvements or added functionality. Overlay networks are networks built on top of existing networks to provide richer and more seamless service levels. Examples of overlay networks include Akamai and Cloudflare.
Axelar can be thought of as an overlay network for the blockchain. Axelar employs various cross-chain communication protocols and smart contract logic to facilitate its connectivity and interoperability.
universal messaging
Since launching on mainnet in May 2022, General Messaging (GMP) has allowed applications connected to Axelar to transfer any payload between different chains, including function calls and other logic. GMP leverages Axelar’s validator set for security and decentralized protocols for routing and transformation. Unlike other cross-chain bridges, GMP supports the secure transmission of arbitrary data, including function calls, enabling composable liquidity and computation between different blockchains. For example, an application can bridge tokens and instructions across chains, depositing them into contracts or exchanging them on decentralized exchanges, enabling a one-click user experience regardless of blockchain boundaries.
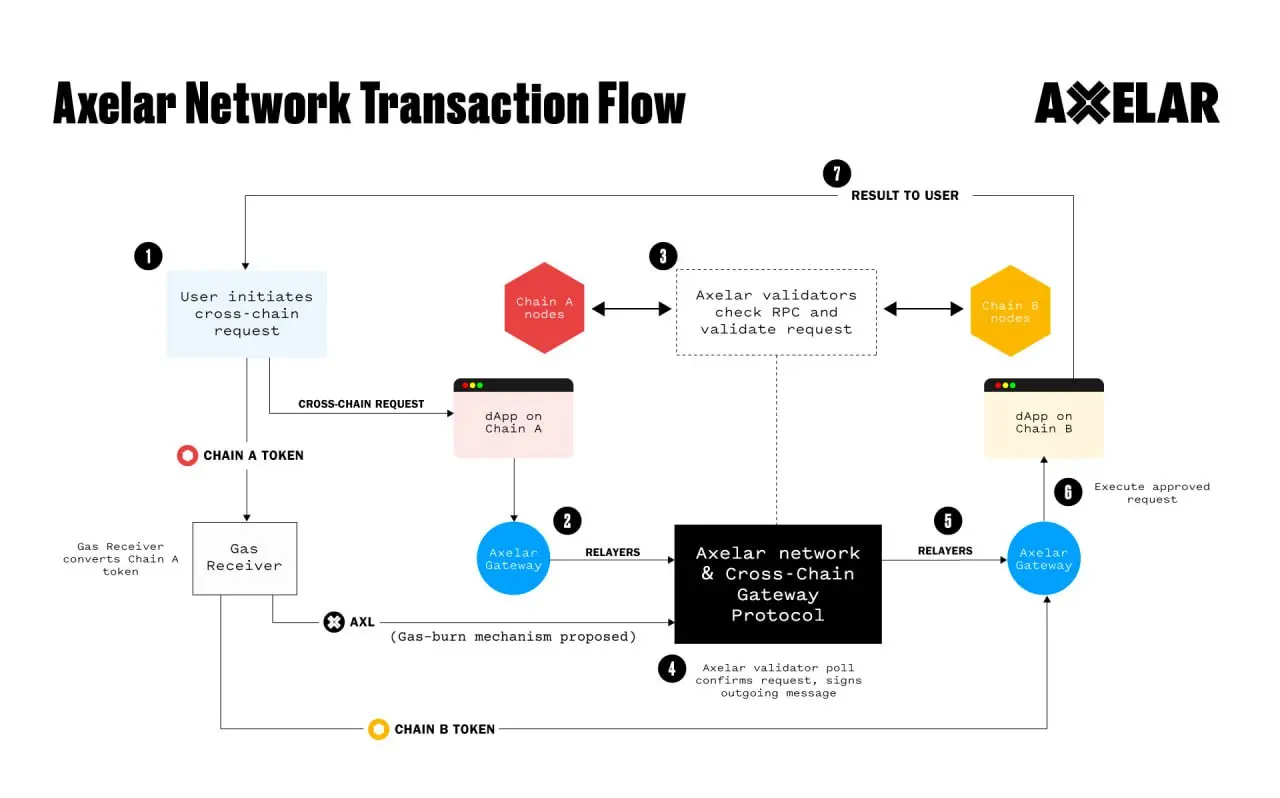
Cross-chain gateway protocol
The Cross-Chain Gateway Protocol (CGP) operates similarly to the Internet’s Border Gateway Protocol (BGP). BGP is essentially a relay hub designed to securely pass data between Internet networks. Axelars CGP has two key functions: state synchronization and asset transfer.
Cross-chain transfer protocol
Cross-chain Transfer Protocol (CTP) is similar to Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) on the Internet. It is an application-level file transfer mechanism that sits on top of CGP. CTP allows DApps to interact with various blockchains, enabling the transmission of cross-chain assets and arbitrary messages.
AXL Token Economics
The AXL token provides the following functionality to the Axelar network:
Pay transaction fees on Axelar. This includes the cost of building services on top of Axelar’s programmable interoperability layer, such as developer automation, cross-chain gas conversion, and fast deterministic gadgets;
Pay transaction fees on connected networks. AXL tokens can be automatically converted into Gas tokens required to connect to the chain;
Participate in the consensus through staking or delegation and reward consensus participants;
Vote on governance proposals.
Launched in 2022, the AXL token aims to make Axelar’s network permissionless. The initial supply of AXL is 1 billion and will be fully released in 2026. The issuance of team, company, backer and community projects is scheduled to begin three months after the token launch; the issuance of community sale tokens begins earlier.
There is some inflation in the AXL token due to the issuance of staking rewards. But as new token economic models are proposed, this situation may change.
New Token Economic Model
The updated AXL token economic model introduces a series of changes designed to increase the utility and value capture of the AXL token as the Axelar network scales. In the long term, these changes could make AXL deflationary overall, with increased activity on new chains. The changes include adding a step in the process to burn gas between the gas receiver and the network.
lower inflation rate
Until recently, Axelar validators were incentivized to support more chain connections by linearly increasing the reward by 0.75% for each additional externally supported chain (such as the EVM chain). This means a total inflation rate of 11.5% (1% base inflation + 14 external support chains of 0.75% each).
In October, a new AXL token economic model was proposed that aims to gradually reduce the rewards per chain from 0.75% to 0.3%. The proposal passed on-chain voting and gradually came into effect, finally locked on December 8, 2023. This would reduce annual inflation from 11.5% to 5.2%, based on the equivalent number of chains. Since the proposal was released, Axelar has added two new chains (Scroll and Centrifuge), bringing Axelar’s current inflation rate to 5.8%.
Gas combustion mechanism
Currently, gas fees paid in AXL are distributed between validators and stakers. The Axelar Foundation’s proposal would burn these fees, putting deflationary pressure on total supply. This variable supply pressure can deflate the network with enough activity.
Increased demand for new chain connections
Currently, connecting new chains to the Axelar network is a complex process. This requires support from Axelar developers and votes from Axelar validators. Axelar is developing a more permissionless path that is non-inflationary and could generate purchase demand for AXL tokens.
Once developed, Interchain Amplifier will allow developers to instantiate a series of smart contract templates to plug new chains into the Axelar network. This largely automated process will include a way to kick-start validator incentives by setting up an AXL-funded reward pool to reward early validators. These AXL-funded reward pools will be necessary for new chains, except those that already have significant transaction volume and where fees can be routed to validators instead of rewards.
With Ethereum-based infrastructure like the DAppchain ecosystem and tools like Rollups-as-a-Service, it will be easier to launch new L2 blockchains on Ethereum. Axelar is positioning itself as a component of permissionless connectivity in anticipation of growth. If the L2 category expands and the strategy is successful, it could become a significant driver of demand for the AXL token.
Current status of the Axelar ecosystem
Connected Ecosystem
Axelar is known for its interconnectivity within and between the Cosmos and Ethereum ecosystems. Axelar also has the ability to connect to unique VMs and consensus mechanisms. As of the time of the report, Axelar has connected 55 chains, including Arbitrum, Avalanche, Base, BNB Chain, Ethereum, Optimism, Polkadot, Polygon, Scroll, Sui, and various Cosmos-based chains. In addition, Axelar’s connection to one chain in the multi-chain ecosystem provides users with indirect access to the entire ecosystem. For example, connecting to Avalanche provides a secure path to the subnet, while connecting to Polkadot provides a secure path to the parachain, and so on.
According to data from Axelarscan, Polygon, Avalanche, and Osmosis were the most active source and target chains during the reporting period, while AXL, ETH, and USDC were the most popular assets. EVM users are particularly active on Axelar, with 10 of the top 15 chains based on activity being EVM-based.
Ethereum Ecosystem
Ethereum’s Rollup-centric roadmap is still in its early stages, with new Rollups and Rollup development tools being announced and released regularly. Ethereum’s modularity may see hundreds of L2 and L3 networks. In the absence of full-stack interoperability between L2s, user experience and developer capabilities will suffer due to fluidity and user fragmentation. Full stack interoperability includes bridging any message/asset and permissionless overlay messaging. Axelar Network meets both of these criteria through its existing communication protocols and the new AVM.
Cosmos Ecosystem
Axelar is the originator of most cross-chain activity on Osmosis, the largest Cosmos decentralized exchange by trading volume. Community members have even explored forms of secure sharing due to the symbiotic relationship between the two networks. One of them is Mesh Security, which is two-way security that leverages the validator sets of both networks. While this may just be a concept, other ecosystem collaborations are already happening. In early 2023, a portion of AXL tokens were airdropped to Osmosis users.
Axelar support apps
Axelar is already integrated into and leveraged by a variety of applications and services:
DeFi (decentralized finance): dYdX, Frax Finance, Lido, PancakeSwap, Uniswap;
Companies: Mastercard, Microsoft, Onyx owned by JPMorgan Chase;
Real asset loans (RWAs): Centrifuge, Circle, Ondo Finance, Provenance;
Wallets: Blockchain.com, Ledger, MetaMask, TrustWallet.
Cross-chain example
Axelar’s gateway smart contract allows for cross-chain token transfers, using encapsulated tokens for cross-chain bridging. By September 2023, GMP usage exceeded basic bridging for the first time in both number of transactions and notional volume. Since then, GMP has been ahead of the curve for basic bridging purposes.
To date, Axelar has executed over 1 million trades with a cumulative trading volume of nearly $7 billion.
Intent: Squid and MetaMask
Squid is an Axelar-based liquidity router that uses GMP to implement cross-chain exchange and bridging. Recently, Squid implemented a feature called GMP Boost to achieve fast finality. Normal cross-chain transactions typically take several minutes, as the bridge requires waiting for transaction finality on one chain before performing operations (such as minting encapsulated tokens) on the other chain. Essentially, GMP Boost allows dApps like Squid to deliver the required assets in seconds in exchange for a small fee that covers the risk of chain reorganization.
Utilizing offline paths to achieve on-chain results is an innovative application of intent. Unlike standard trading, which has clear instructions and clearly lists all steps, the intent is declarative and focuses instead on the results achieved.
Cross-chain governance: Filecoin and Uniswap
Uniswap was originally built on Ethereum and has since expanded to multiple chains. This makes it difficult to deploy updates outside of Ethereum. After selecting Axelar as one of two interoperability platforms that support cross-chain upgrades, Uniswap used Axelar for deployment on Filecoin’s smart contract blockchain, the Filecoin Virtual Machine (FVM).
Real World Assets (RWAs): JP Morgan and Provenance
Onyx, owned by J.P. Morgan, recently announced a proof-of-concept project in which Axelar was used to connect Apollo funds tokenized on the Provenance blockchain to the Onyx digital asset blockchain, on which Onyx operates Logic for automated portfolio rebalancing.
DeFi entrance: dYdX and Squid
dYdX launches V4 version, which is built on a dedicated application chain. dYdX, the largest perpetual exchange decentralized exchange by trading volume, is using Axelar and Squid to facilitate streamlined deposits from any connected chain.
Connect traditional technology
Axelar and Microsoft announced a partnership in 2023 to integrate Axelar as an interoperability provider into Microsofts Azure marketplace. The partnership helps companies using Azure to seamlessly connect to crypto applications, protocols and blockchains.
route map
The new proposal aims to scale Axelar from dozens to hundreds or even thousands of chains. The strategy focuses on L2 and modular Ethereum networks. The proposal includes short-, medium- and long-term expansion strategies.
Short-term strategies have been discussed above in the AXL Token section. This strategy aims to reduce the inflation rate as new external links increase and increase deflationary pressure by burning transaction fees.
The mid-term strategy is based on the Axelar virtual machine. AVM will allow permissionless connections to new chains. AVM-enabled features, such as Interchain Amplifier, can automate much of the technical overhead required for new chain connections. Unlike the current system that incentivizes validators to support new chains through increased inflation, third-party sources can pool AXL tokens to directly fund supporting validators.
The long-term strategy focuses on lightweight clients. Given that lightweight clients are also connected to the Interchain Amplifier, the need for external validators will be eliminated. Only relayers need to be incentivized since packets still need to be relayed.
competitive landscape
Many protocols and teams are focused on interoperability, but they mostly view the problem in a more limited scope. Axelars full-stack interoperability bridges any information/asset, any data (GMP) and permissionless overlay messaging (programmability). Most interoperability solutions are bridges in nature and can only transfer encapsulated assets. There are other interoperability solutions that can transfer arbitrary data. But apart from Axelar, few solutions have overlay network capabilities and provide the ability to program cross-chain logic in a cross-chain environment.
LayerZero and Chainlink are two outstanding competing cross-chain networks. LayerZero’s Omnichain Fungible Tokens (OFT) and Chainlink’s Cross-Chain Interoperability Protocol (CCIP) are similar in many ways to Axelar’s various cross-chain protocols and ITS. Nonetheless, one of the main differences between Axelar and these two solutions is Axelar’s permissionless set of validators. Axelar uses this set to facilitate inter-chain messaging instead of using multi-signatures.
Among other interoperability solutions using a decentralized set of validators, Axelar’s validators can choose which chains to support. This allows for a more diverse set of validators to support Axelar’s security model, as different ideological factions can form to support a specific network. Forcing the entire validator set to validate is not inherently good or bad, but it may reduce the participation of opinionated operators with their own agendas, potentially limiting scalability. Axelar currently has more validators than any other cross-chain network (75 at the time of writing).
LayerZero
LayerZero allows for flexible and customizable configurations using oracles and relayers, but ultimately operates on a 2-of-2 multisig basis of these two off-chain entities (oracles and relayers). Axelar, on the other hand, has built an entire set of validators to work between chains and secure cross-chain messages. LayerZeros default configuration relies on oracles managed by Google and relayers operated by LayerZero Labs. Protocols can specify custom validation libraries, oracles, and relays, making decentralization dependent on the specific implementation. More trust is placed on these standard configuration oracles and relays than on individual Axelar validators, as a two-thirds majority vote is required to validate Axelar messages.
Chainlink
Chainlink is a well-known provider of DeFi price oracles, but Chainlink CCIP is a new product that is independent and not yet online. Similar to LayerZero, CCIP relies on multi-signatures to verify, order and deliver cross-chain messages. CCIP relies on Chainlink oracles, which are free to operate but require permission to include data in Chainlink’s price reference data. In contrast, Axelar’s permissionless validator set enables validators to assume all roles rather than separate node roles (such as oracle nodes, execution nodes, and risk management nodes).
Summarize
As Axelar adds new features for cross-chain programmability, it continues to add more differentiation than traditional bridging solutions. The upcoming Axelar VM will be at the core of many new features, such as cross-chain token services.
The development of the Axelar virtual machine and cross-chain services will complement Axelar’s existing universal messaging and transfer protocols. There are several proposed changes to the AXL token to make the network economically adaptable to dozens, hundreds, or even thousands of new networks. Modular roadmaps like Ethereum demonstrate the need for connectivity at this scale.



