One article to understand cross-chain liquidity staking tokens

Cross-chain liquidity staking allows users to deposit assets into a liquidity staking agreement on a certain blockchain, and then use the mortgage assets of equal value to seek income on another blockchain.
Liquidity staking has become one of the most popular ways to generate revenue in the crypto market. As of September 2023, more than 25 million ETH have been pledged, accounting for approximately 21% of the circulating supply, with approximately half of the pledged ETH being deposited into the liquidity staking protocol.
Liquidity staking, as an extension of the Proof of Stake mechanism (PoS), allows the pledged tokens to regain liquidity. However, these tokens are typically only usable on the blockchain they are issued on.
Cross-chain LSTs (Liquidity Staking Tokens) allow liquidity staking to be cross-chain, opening up new development space for the DeFi ecosystem.
In this article, we will briefly explore what liquidity staking is, the opportunities and risks of cross-chain liquidity staking, and how Chainlink can become the key infrastructure for cross-chain LST in the Web3 space.
What is Liquidity Staking?
Traditional staking in PoS requires locking cryptographic tokens on smart contracts to ensure network operation and obtain additional tokens as rewards. While this ensures the security of the underlying network, it can be a less flexible option because the staked assets lack liquidity and cannot be used on DeFi.
Liquid Staking Tokens (LSTs) can solve this problem. It unlocks liquidity for staked tokens while allowing users to continue to earn rewards. The user deposits the token to a liquidity staking provider, which pledges the token on behalf of the user and issues the user a new token as a receipt, which can be exchanged for the pledged token and a certain percentage of accrued rewards or fines .
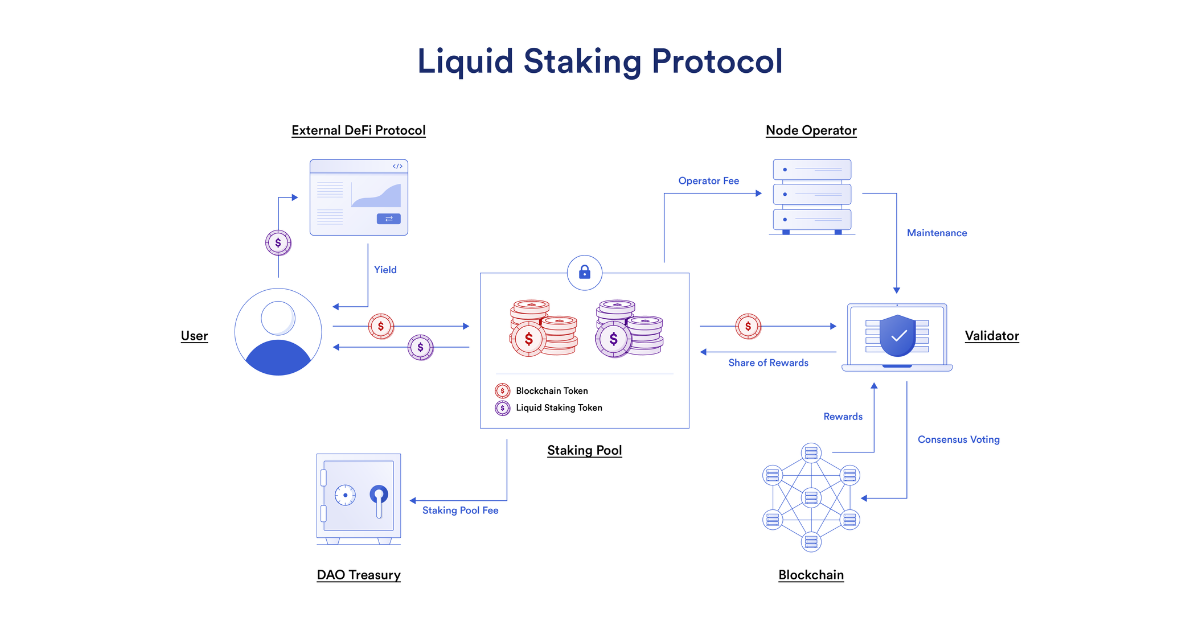
Liquid staking tokens can be used in external Defi protocols
For example, users can deposit ETH into the Lido staking pool and receive stETH (staking ETH). These stETH can be used as collateral or to earn income in other DeFi protocols, while not preventing users from receiving Lido’s staking rewards. However, LST can usually only be used on the blockchain that issues them, which is where cross-chain LST comes into play.
What is a cross-chain liquid staking token?
Liquidity Staking Token (cross-chain LST) combines liquidity staking and cross-chain interoperability. Cross-chain LST enables users to deposit their assets into a liquidity staking protocol on one blockchain, and then use these pledged assets to obtain income on another blockchain. Cross-chain LST can be used across multiple chains without affecting the original pledged assets to obtain rewards.
As mentioned before, many large PoS ecosystems have a strong interest in liquidity staking. However, LST is usually limited to use on one chain, which not only cuts off liquidity, but also limits the flow of capital between various blockchain ecosystems. Cross-chain LST allows these tokens to be used on multiple chains, releasing more utility.
How does cross-chain LST work?
Cross-chain LST works similarly to single-chain LST, but has the added advantage of supporting cross-chains.
The liquidity staking provider obtains tokens from users on chain A and pledges on behalf of users, and then provides users with receipts using another token on chain B, which can be redeemed for assets pledged on chain A ( plus bonus/minus penalty).
Benefits and risks of cross-chain liquidity staking
The benefits of cross-chain LST are the same as other cross-chain tokens, providing more liquidity, enhanced composability, and improved opportunities to earn rewards. Tokens that operate across multiple blockchains can often expand their utility, resulting in better liquidity and revenue opportunities.
The risks of cross-chain liquidity staking are also similar to the risks of single-chain LST. These include the risk of slashing, smart contract vulnerabilities or theft, and token price fluctuations.
It is worth noting that cross-chain may lead to an increase in risk factors because cross-chain LST requires additional cross-chain infrastructure to support it. This is why it is crucial to integrate a safe, reliable, decentralized cross-chain solution that provides the necessary infrastructure for cross-chain liquidity staking.
Chainlink’s role in cross-chain liquidity staking
High-quality Chainlink infrastructure can provide key Web3 services for cross-chain liquidity staking:Chainlink Data FeedsCan provide highly reliable and secure LST pricing data whileChainlink AutomationSmart contracts that can be used to trigger cross-chain liquidity pledged tokens.
As the most secure, reliable and easy-to-use interoperability protocol for building cross-chain applications and services, Chainlink CCIP allows developers to flexibly use Arbitrary Messaging (arbitrary messaging bridge) to build their own cross-chain solutions. It is worth noting that CCIP also provides simplified token transmission, ensuring that the protocol transmits tokens on the chain, and its security has been tested in practice. This saves a lot of time compared to developers building a solution themselves. CCIP provides audited token pool contracts that can handle complex cross-chain burning/minting, or locking/unlocking tokens.
In addition to offering fully audited token pool smart contracts, CCIP token transfers come with additional security features, such as allowing developers to limit rates for asset transfers within a certain period of time. Additionally, the Risk Management Network is an independent network of nodes that enhances CCIP’s security with secondary verification services.
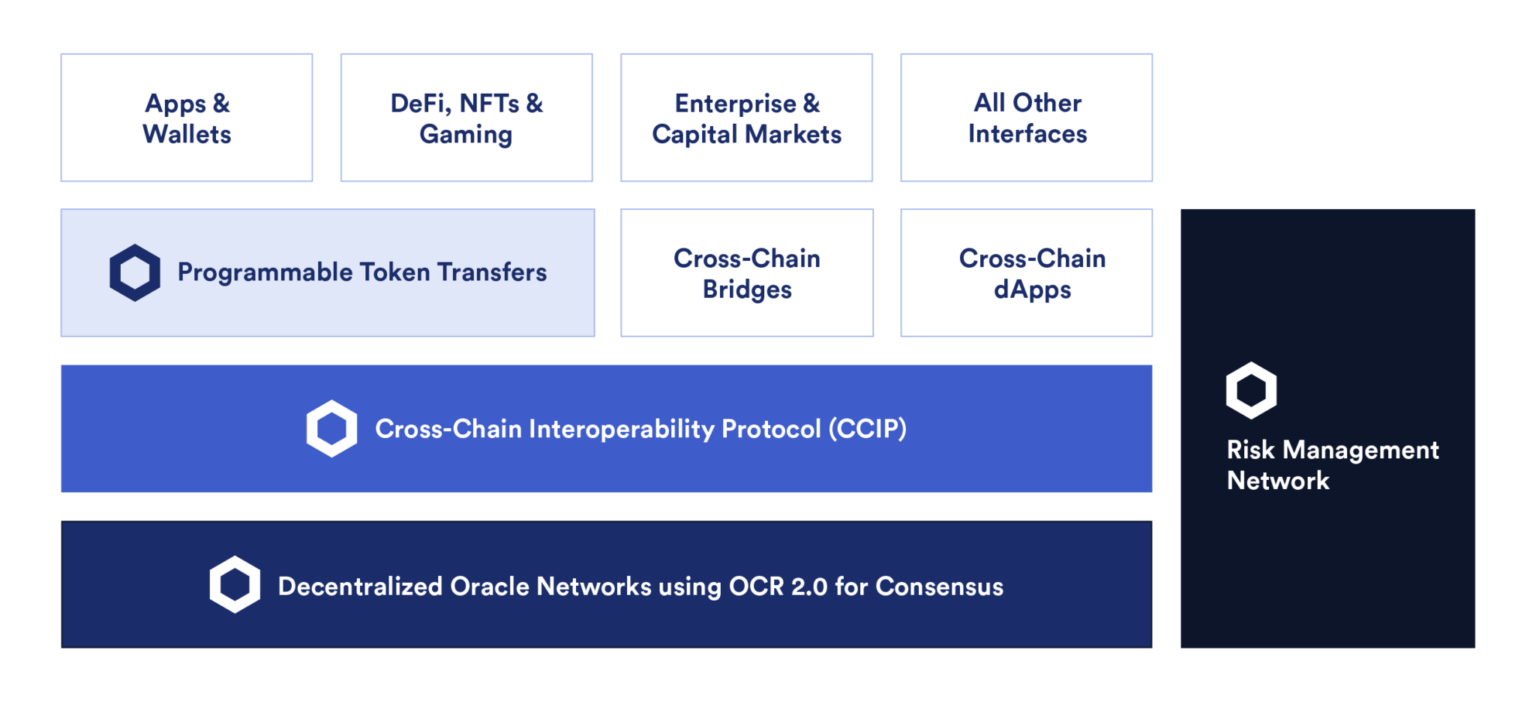
Chainlink CCIP is currently the most secure and reliable cross-chain interoperability protocol
Behind all of these features are Chainlink’s industry-standard decentralized infrastructure, which combine to enable the protocol to quickly and seamlessly create cross-chain LSTs.
Summarize
Achieving cross-chain liquidity for staking tokens can not only further increase its liquidity, but also help establish better connectivity on DeFi. Supported by Chainlinks powerful Web3 service platform, cross-chain LST can improve the capital efficiency of the cross-chain ecosystem and provide broader utility for staking on PoS.



