Hairdressing tools cause safety accidents, alternative infrastructure must be guarded against
Original |
Author | Loopy Lu

Last weekend, a product that seemed to have little connection with the encryption world entered the field of vision of the encryption community. Bitbrowser, which is often used for multi-opening and group control, has caused large-scale wallet theft, and the amount of damage has reached hundreds of thousands of dollars.
Before that, random number generators, smart contract programming languages, iOS/Android system risks, etc., have all caused large-scale security incidents. With the maturity and complexity of the encryption world, the security situation is becoming more and more dangerous, and risks are quietly appearing in many places that are difficult for people to detect...
What is Bit Browser?
For most encryption users, the name of the product Bit Browser may be unfamiliar.
Its full name is Bit Fingerprint Browser. According to information on its official website,The main function of this product is environment simulation, similar to the sandbox function, which can simulate different user tracking information in each window, including IP, device information, browser information, etc.
This series of functions mainly serves one goal: to simulate multiple users so that each user can have independent information. The browser even provides a group control function.
The market audience of Bit Browser is mostly foreign trade e-commerce (such as Amazon, Shopee, etc.) and social media operations (Facebook, Tiktok, etc.). The advertising slogan on its official website states - A bit browser can easily manage your cross-border business.
Although this product is not specially designed for users in the encrypted world, its series of functions just fit the demands of the wool party. Therefore, a large number of fluffing people have used this product.
There are different opinions on the reasons for the theft.
Recently, a group of members of the Luomao community discovered that their Lumao wallets had been stolen. After self-examination, the victims all believed that the theft was caused by the use of a bit fingerprint browser, and the direct cause was the leakage of the private key.
Bitfingerprint Browser officially responded in the community as soon as possible: Some versions of WPS For Windows have a remote code execution vulnerability. An attacker can use this vulnerability to execute arbitrary code on the victims target host, control the host, etc. (What does WPS have to do with Bit Browser users? Bit Browser’s explanation is that because this vulnerability is easier to trigger, you may be hacked after clicking on an unknown link.)
And because the software is far away from the encrypted world, it gave a ridiculous response for a while.

The initial response was widely circulated as a meme by the crypto community
Bit Browsers explanation undoubtedly failed to convince users. On August 26, Bit Browser followed up on this incident and issued an announcement saying, The server cache data has been hacked. User wallets that have turned on the Extended Data Synchronization function are at risk of being stolen. It is recommended to transfer wallets assets.
Safety accident, whose fault is it?
At the beginning of the incident, there were different opinions on the reasons for the theft.
In the MetaMask plugin we often use, the private key is not saved in plain text. Therefore, hackers only rely on the users local cache data and cannot gain control over the users assets.
In wallet transfer, besides the most common export function, the backup function is a function that is less used by people.
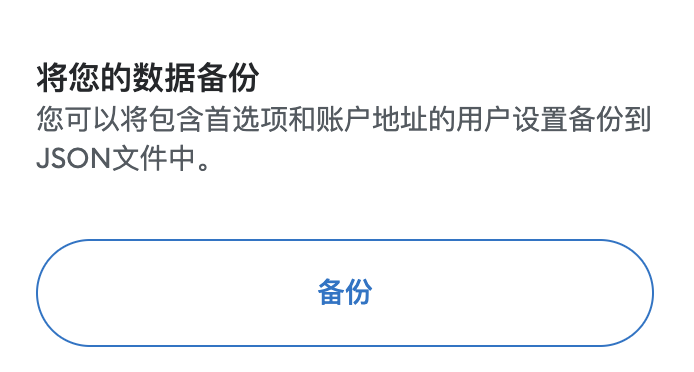
MetaMask’s “Backup” feature
It should be noted that the backup function provided by MetaMask is completely different from the function of exporting private keys/mnemonic words. After backup, users can get a json file, which is also called keystore.(Odaily Note: A simpler explanation is: private key = mnemonic = wallet control = keystore + password)
The same is true for locally cached data, so how was the users wallet stolen?
After two days of analysis by all parties, the cause of the case was finally ascertained. The hacker obtained the users extended cache by invading the server.(Odaily note: In this way, the hacker will have the local data of the wallet, but will not be able to log in.)Then, the hacker violently cracked the wallet password by trying common URL platform password collision, and then obtained the wallet permission.
Server records show that the server storing the extended cache has traces of being downloaded in early August (log records are as late as August 2), and has locked several IPs, all of which are overseas addresses except for one Jiangsu address. According to community members, the case has been accepted by the Changping Branch of the Beijing Public Security Bureau.
But when we reviewed this incident, we found that it was difficult to clarify the responsibilities of all parties in this incident.
The first is the first risk point: cache data leakage.
Some users questioned why the cached data was not encrypted? Bit Browser pointed out that when synchronizing extended data, the data transmission is encrypted. However, if the software but the main program EXE file is cracked by a hacker, the hacker may obtain the extended data.
However, relying solely on cached data cannot obtain user assets. Only the combination of cache data + password can control the wallet. In the daily use of users, it is normal for multiple accounts to share passwords. Passwords for our favorite Web2 sites are also frequently leaked. Hackers may obtain the passwords of other Web2 websites and try to credential library on the users Web3 wallet.
In addition, brute force cracking is also a possibility. Because the number of potential combinations of unlocking passwords is much smaller than the combination of private keys, it is entirely feasible to brute force the unlocking password.(Assuming the product doesnt introduce precautions such as maximum failed attempts lockout.)
From the users point of view, it is true that Bitbrowser has an inescapable responsibility for taking away the plug-ins cached data and eventually causing a leak. However, the protection failure of the wallet access password also comes from the long-term deterioration of the network security environment.
alternative infrastructure
For software developers, we don’t know where the “Bit” name of “Bit Fingerprint Browser” comes from, but one thing is clear. This product is not created for the encryption world, but just happens to meet Encryption user needs.
The more complex a system is, the more potential risk points there are, and any single point of failure may bring the risk of being hacked.
Recalling the era of encryption and wildness, people only used the most basic Bitcoin wallet. At that time, there were no interactive links such as DeFi and cross-chain. As long as you keep your own private key, it is safe enough.
But now, various off-chain auxiliary tools and on-chain capital pools have added additional risks. More and more products like Bitbrowser are becoming a new alternative infrastructure in the encryption world. Numerous non-encrypted security risks endanger the encrypted world:
On August 21, hackers stole 3.13 million USDT. Security personnel believe that the stolen Android system album was compromised this time, and hackers obtained screenshots of the users private key.
In early August, a huge theft occurred at Curve. The analysis at the time found that there is no problem with the security of the Curve contract, and the reason for the theft comes from a loophole in its programming language vyper. So the aleth, peth, mseth, crveth pools are utilized.
In May, Apple IDs synchronization function also caused the theft of more than ten million dollars. Many users will purchase or use other peoples US-area Apple IDs. The account owner can synchronize the local data of the wallet and gain control of the wallet by simply breaking the wallet access password. This is exactly the same as the theft of Bit Browser. Victim users have stolen more than $10 million in funds.
On the developer side, the security situation is more complicated. In the Solana wallet theft case last year, the risk point came from the random code related to the lower-level mnemonic generation.
As the encryption world becomes more complex, more and more tools, software, and services that are difficult for people to detect may be incorporated into the encryption world in the future, and risks will also expand.
Odaily hereby reminds you not to hand over the local data of the wallet to others or over-authorize. In addition, due to the hidden nature of the risk, please be careful to use electronic means to save the private key/mnemonic. Do not install too many unknown software on computers that often perform encryption operations.
Related Reading
Hacking incidents occur frequently, please accept this Crypto anti-theft guide



