RaaS’s ZK/OP route debate: Why is ZK-RaaS better?

TL; DR
Compared with Optimistic Rollups, ZK-Rollups have the following advantages:
Compressed transaction data saves L1 gas costs
Safer and trustless
Faster transaction confirmations and shorter withdrawal times
In addition to these benefits, ZK-RaaS also has advantages in the following aspects through network effects:
ZK-RaaS passedZK-PoWProvide large-scale computing power for massive ZK-Rollups, thereby reducing the cost of ZKP calculations
Thanks to ZK-Rollup’s faster transaction confirmation speed (minutes level), ZK-Rollups can achieveNative Cross-Rollup Communication (NCRC)protocol, thus solving the problem of liquidity fragmentation
What is RaaS?
Rollups-as-a-Service (RaaS)Provides an abstraction layer on top of the Rollup framework and SDK to easily deploy, maintain, and build on top of custom, production-grade application-specific Rollups (AppRollups). RaaS is similar to a software-as-a-service offering, allowing developers to focus on building the application layer, turning a process that used to take dozens of hours with multiple engineers into a 10-minute code-free deployment process.
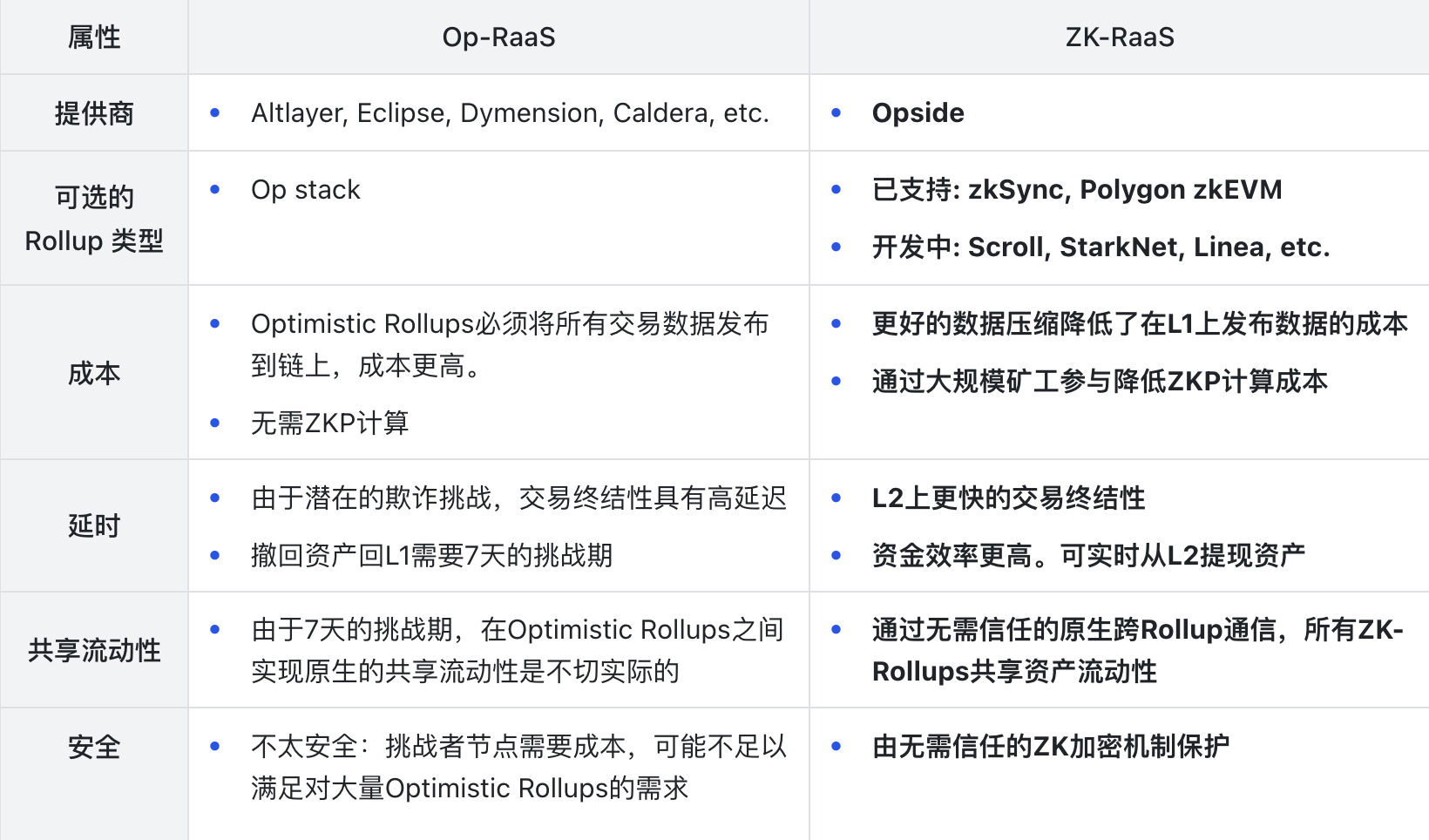
The two main types of Rollups areOptimistic rollupsandZK-Rollups. They differ in transaction verification and dispute handling, and have different advantages and disadvantages. According to the type of Rollup provided, this article divides RaaS into Op-RaaS and ZK-RaaS.
1. Cost
The L1 Gas cost of ZK-Rollups is lower than that of Optimistic Rollups
One of the main goals of the Rollup solution is to increase the throughput of transactions on Ethereum and reduce gas fees for users. Optimistic Rollups and ZK-Rollups achieve this by batching transactions and submitting them to the mainnet at regular intervals. Therefore, they all need to bear the gas fee for data submitted to L1.
Due to the use of fraud proof, Optimistic Rollups must publish all transaction data to the chain. Therefore they require more Gas to submit batches of data to the main chain.
Since ZK-Rollups have efficient data compression techniques (such as using indexes to represent user accounts instead of addresses, this saves 28 bytes of data). This helps reduce the cost of publishing transaction data on the underlying chain.
Therefore, ZK-Rollups can save more L1 Gas than Optimistic Rollups.
ZK-RaaS reduces ZKP computing costs through large-scale miner participation
However, ZK-Rollups require the additional computational cost of generating zero-knowledge proofs. This is exactly what ZK-RaaS aims to solve.
With the large-scale implementation of ZK-Rollup, the generation of ZKP requires a large amount of CPU, GPU, FPGA and other hardware and mining machines to provide computing power. Opside(https://opsi.de) also proposedZK-PoWThe concept of miners is introduced to participate in the maintenance of zkEVM nodes and the calculation of ZKP. The Opside ZK-PoW protocol will be deployed on multiple chains, including but not limited to Ethereum, BNB Chain, Polygon PoS, and Opside Chain itself.
In order to encourage more miners to participate in ZKP computing tasks at the same time, Opside proposesZKP's Two-Step Submission Algorithm. The PoW reward share corresponding to a ZKP will be distributed to the submitter of a valid ZKP, that is, the miner according to certain rules.

Submit proofhash: Within a time window, for a certain sequence, multiple miners are allowed to participate in the calculation of zero-knowledge proof. After each miner calculates the proof, they do not directly submit the original proof, but calculate the (proof/address) proofhash and submit the proofhash to the contract.
Submit ZKP: After the time window, the miner submits the original proof and verifies it against the previously submitted proofhash. Miners who pass the verification can receive PoW rewards, and the reward amount is distributed in proportion to the miners pledge amount.
In Opside, the two-step submission algorithm of ZKP realizes the parallel calculation and serial submission of ZKP, allowing mining machines to perform multiple ZKP generation tasks at the same time, thus greatly accelerating the generation efficiency of ZKP.
2. Transaction finality and capital efficiency
Optimistic Rollups: There is a challenge period of up to 7 days, and the transaction will not be finalized on the main chain until the end of the challenge period. Therefore, Optimistic Rollups have a high latency for transaction finality.
ZK-Rollups: The advantage of ZK-Rollups is that the delay of transaction finality is low, usually tens of minutes or even minutes. Once the proof of validity is verified by the node operator, this results in a state update.
Since Optimistic Rollups have a challenge period, users cannot withdraw funds before expiration, causing inconvenience. However, ZK-Rollups has no challenge period, and users have better capital/liquidity efficiency and can withdraw funds at any time.
3. Shared liquidity
It is worth mentioning that,Since the transactions of ZK-Rollups can be confirmed quickly, it is possible to realize trustless communication between ZK-Rollups, so that all Rollups can share asset liquidity.And because of fraud proofs and the 7-day challenge period, native trustless communication between Optimistic Rollups is unrealistic.
ZK-RaaS Platform Opside’sNCRC (Native Cross Rollup Communication) protocolProvides a trustless Rollup interoperability solution. The NCRC protocol does not add an additional third-party bridge to each Rollup, but transforms the ZK-Rollups own bridge (native bridge) at the system level, thereby directly using the native bridge of each ZK-Rollup to achieve cross-Rollup communication. This approach is more concise and thorough. It not only inherits the absolute security of the native bridge, but also avoids the system complexity and trust costs brought by the third-party bridge.
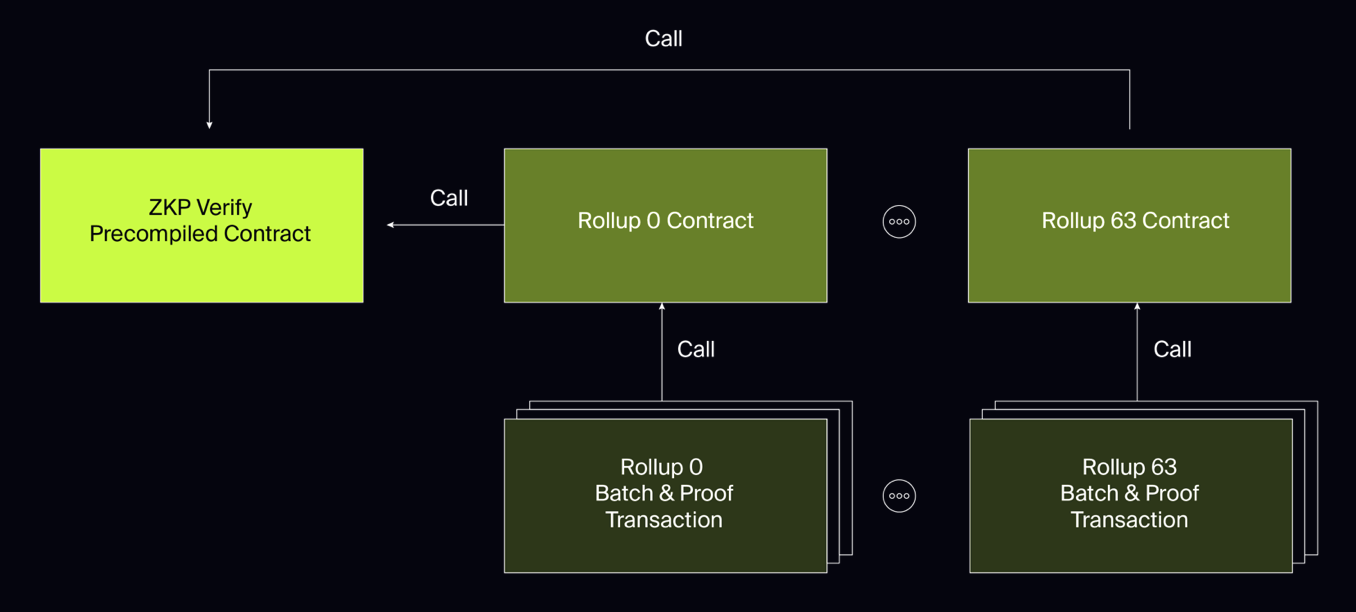
NCRC has been launched on the test network, and users can experience it directly https://pre-alpha-assetshub.opside.network/.
4. Security
Optimistic Rollups: Fraud proofs ensure the validity of transactions by having honest validators secure the blockchain network. Without honest nodes to challenge invalid transactions, malicious actors can steal funds and these optimistic rollups would be unsafe.
ZK-Rollups: Instead of relying on honest validators, ZK-Rollups use zero-knowledge proofs to verify transactions. The advantage is that ZKPs provide security guarantees through mathematical proofs rather than human actors. Therefore, ZK-Rollups are trustless.
Although fraud proofs of Optimistic Rollups are theoretically possible, there are already a handful of Rollups in operation. However, as time goes by and the number of Optimistic Rollups increases, the risks of this security model will gradually be exposed, becoming a gray rhino or even a black swan. Because running an honest validator costs money and most of the time there is no gain. When Op-RaaS creates a large number of Optimistic Rollups,Except for a few head rollups, it is difficult to guarantee that every rollup has honest nodes, especially those rollups that are not concerned.
The security of ZK-Rollups is trustless, because they do not rely on users or verifiers to challenge fraudulent transactions, but provide security guarantees through mathematical proofs.
Summarize
Whether it is ZK-RaaS or Op-RaaS, developers can have their own Rollup application chain without having to manage complex software and hardware.
The ZK-RaaS platform represented by Opside (https://opsi.de), launched the ZK-PoW and NCRC protocols, making the advantages of ZK-Rollups more obvious.