BTC NFT Explained: What is Ordinal?

Ordinal NFT inJanuary 20, 2023by developerCasey RodarmorandCounterpartyandStacks) already supports BTC-based NFTs, but Ordinal NFTs have a fundamentally different architecture than NFTs on other BTCs.
image description
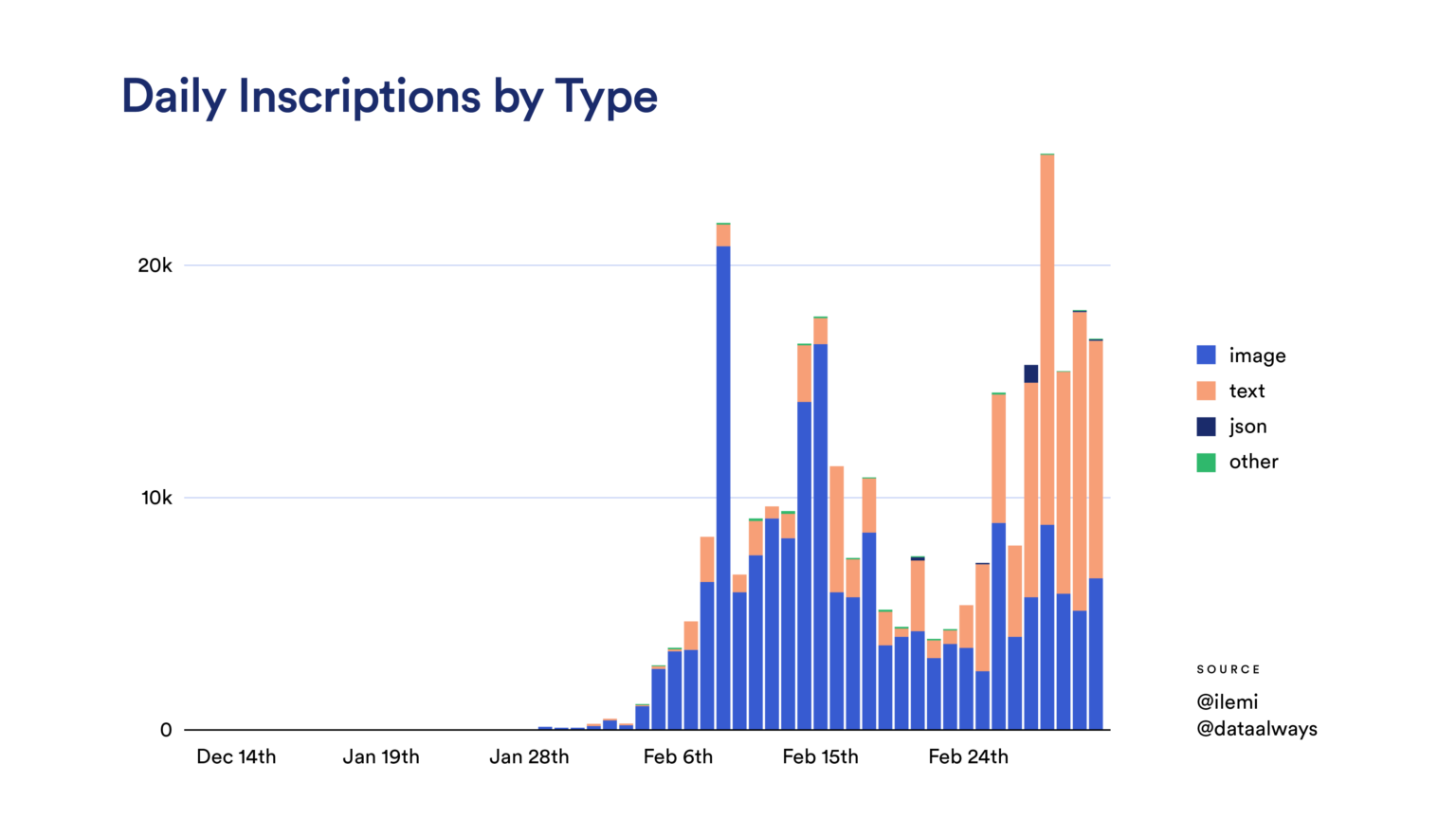
first level title
What are Ordinal inscriptions?
Orinal creates Bitcoin NFTs by attaching data such as images, videos, etc. to a single satoshi (Satoshi) on the underlying BTC blockchain. Unlike BTC's NFT that has appeared before, Ordinal NFT does not exist on the second-tier network that is different from Bitcoin. Instead, they use a method calledordinal theoryAn arbitrary but logical ordering system to assign a unique number to each bitcoin satoshi. In this regard, ordinal NFTs are completely native to BTC. They work without changing the Bitcoin protocol, do not require any additional layer 2 network, and are backward compatible with the BTC network.
secondary title
History of Ordinal NFTs
Although Ordinal NFT is based on the Ordinal theory, the realization of the current Ordinal NFT also depends on the technical updates of Segregated Witness (SegWit) and Taproot for the Bitcoin protocol in 2017 and 2021.
It is worth noting that these updates were not developed with the purpose of enabling these new types of NFTs. But since both updates increased the data size of a block — meaning there is now room for images, videos, and even games — the deployment of Ordinal NFTs was inadvertently made possible.
Segregated Witness (SegWit)
image description
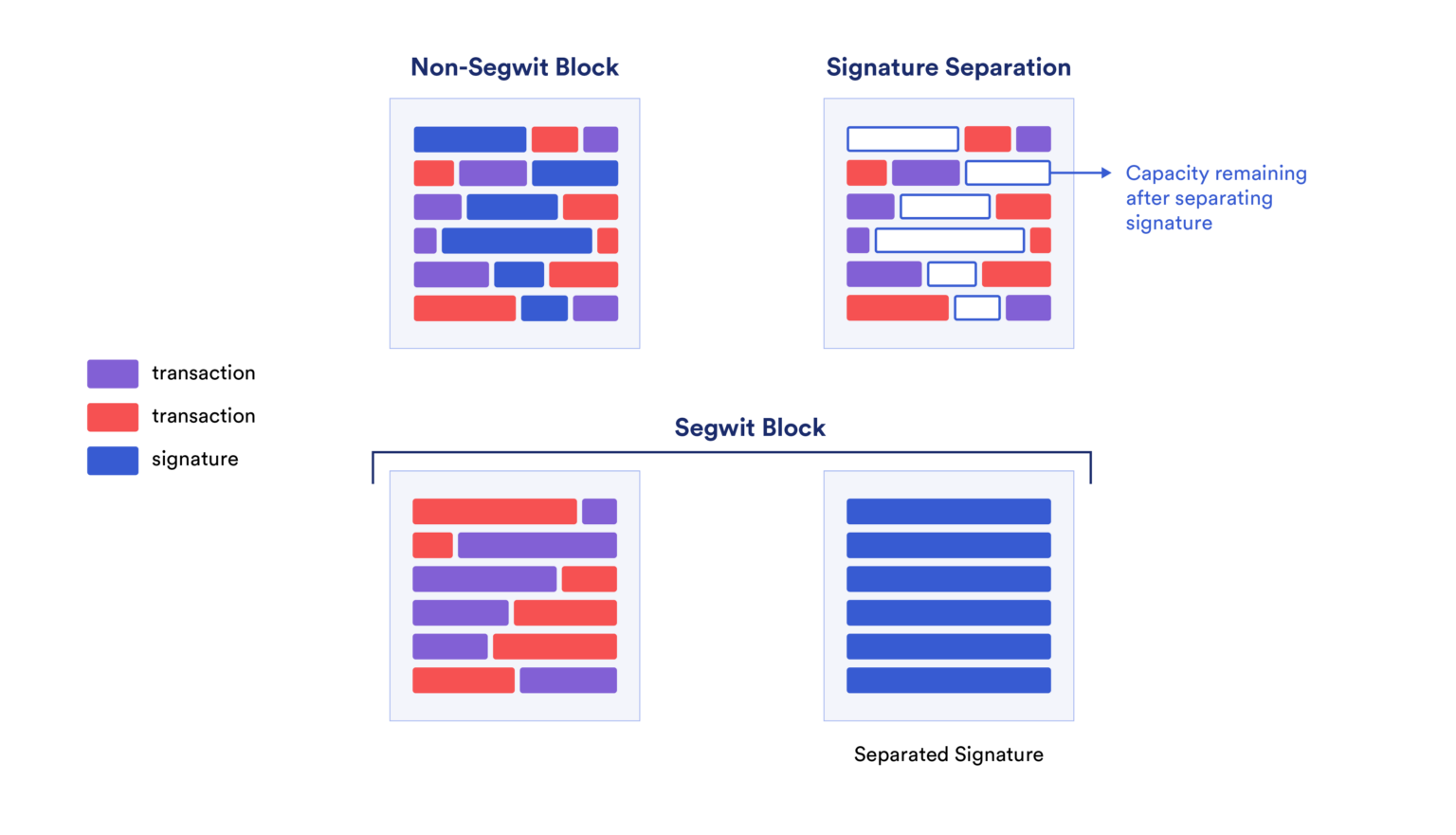
SegWit separates transaction and witness (signature) data into different parts and allows arbitrary data to be stored in the witness part.
Witness data was originally created as a way to:
Bypass the strict restrictions of the block size limit
Allow optional, arbitrary data transfers
Preventing unintentional transaction malleability
In a technical sense, the implementation of SegWit means that transactions no longer need to include witness data (usually the sender's digital signature). Instead, an extra space is created at the end of the block for the witness data as a separate structure. It supports arbitrary data transmission, and makes the "block weight" smaller (because the witness data in segwit is stored in an independent data structure, so the transaction signature data is no longer counted in the block weight), cleverly integrates a large amount of data Stay within Bitcoin's block size limit to avoid hard forks.
secondary title
Taproot
Implemented in November 2021, Taproot is a multifaceted upgrade designed to improve Bitcoin's privacy, scalability, and security. With this upgrade, Taproot created a simpler system for storing arbitrary witness data, and relaxed restrictions on how much arbitrary data can be placed in a Bitcoin transaction. The original goal of this upgrade was to further enhance Bitcoin-based smart contracts, such as the time-locked contracts often used in witness data.
first level title
What is the principle of Bitcoin NFTs?
To understand how Ordinal NFTs work, it is necessary to distinguish between the terms "Ordinal" and "inscription", both of which are used to refer to this new type of BTC-based NFT.
The ordinal number is a system for sorting sats (Satoshi), thus creating the "sats" necessary for NFTIrreplaceable” property. Inscriptions are the content of the Ordinal NFT itself — images, text, video, or any other arbitrary data that the user deems usable in the NFT.
secondary title
TokenID
Fungible Tokens are interchangeable. For example, two different ETHs cannot be distinguished, just like one dollar cannot be distinguished from another dollar. TokenID injects "non-fungible" attributes into NFTs - they provide each NFT with a unique barcode, enabling users to distinguish Tokens from each other. TokenID is what makes NFT unique.
*NFT can have the same TokenID if created by different smart contracts. In this case, smart contracts are the means of distinguishing one NFT from another.
Ordinal Theory as TokenID
Bitcoin is fungible, which means that one BTC is indistinguishable from another. This is where ordinal number theory comes into play.
The key innovation of Ordinal NFTs is that they provide a system for numbering each individual satoshi. The result: each individual satoshi on the Bitcoin blockchain has a unique ID. Each Ordinal, in its most basic form, is just a satoshi assigned a unique number. Here's how it works.
image description

Ordinals are numbered in the order they were mined. Based on a first-in, first-out process, orders will be held in trade.
secondary title
metadata
In non-Bitcoin blockchains, metadata is an optional attachment to NFTs that can store arbitrary data. It is used to represent and display art, a wide range of in-game assets, profile pictures, financial assets, and more, which have become synonymous with the term "NFT."
Inscriptions as Metadata
image description
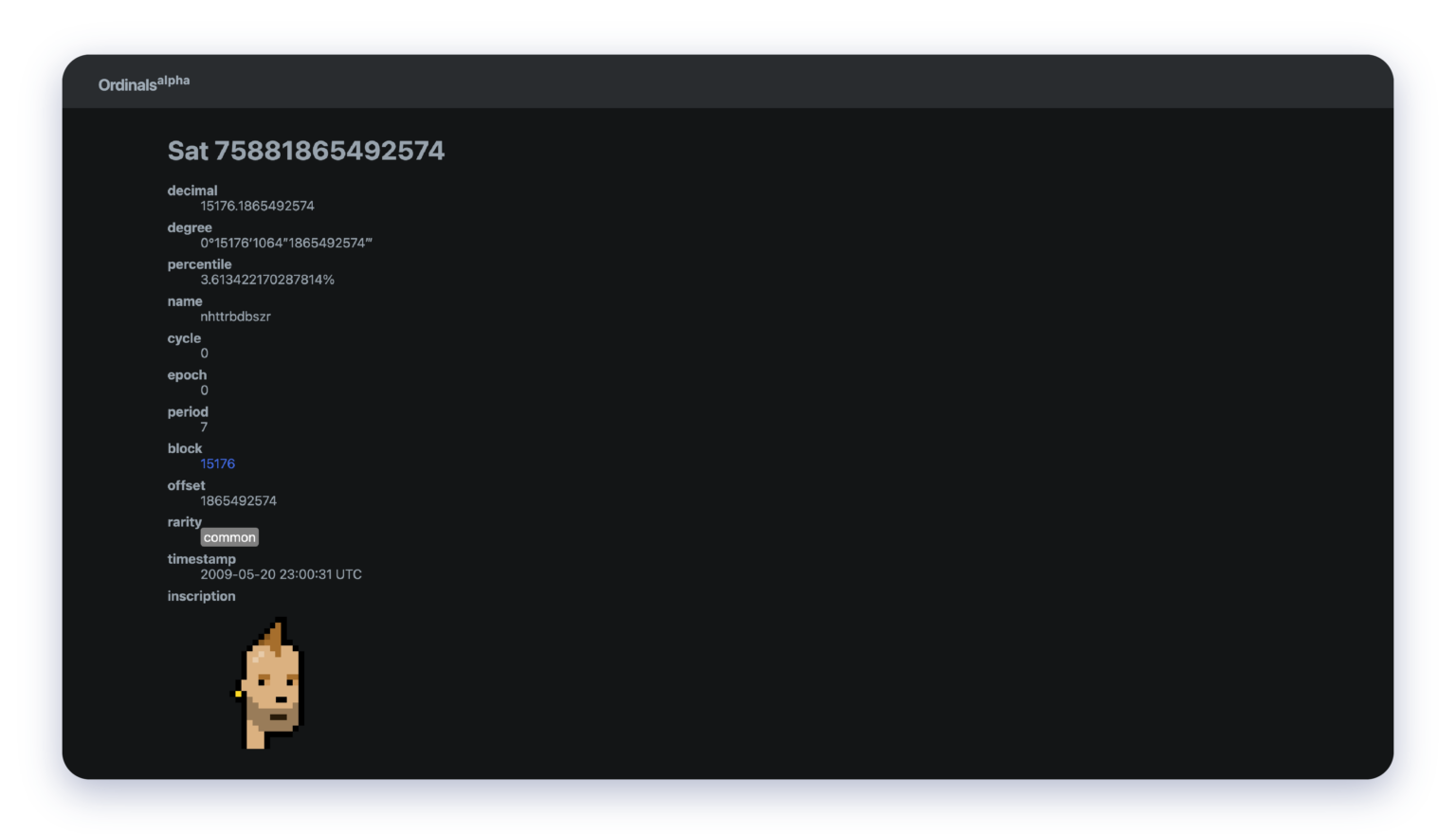
Example of a Bitcoin inscription - a CryptoPunk image that was repurposed by its owner.
first level title
How are Bitcoin ordinals different from NFTs?
The main difference between Bitcoin Ordinals and more standard NFT types is their liquidity. Because the Bitcoin protocol does not formally recognize the theory of ordinals, ordinals can be fungible or non-fungible. It all depends on who owns the ordinal and whether they wish to keep this single satoshi.
first level title
The debate surrounding Ordinal NFTs
The rise of Ordinal NFTs has sparked discussions within the Bitcoin community about the fundamental role and spirit of BTC.
Some argue that BTC should be used for secure financial transactions, and the meme-fueled rise of ordinal inscriptions unnecessarily fills up Bitcoin's block space and drives up transaction fees. Others are excited about the meme/cultural value that ordered NFTs can bring to the Bitcoin blockchain and the idea of Bitcoin extending its immutable, decentralized database beyond financial transactions.
Because ordinal numbers are perfectly valid in today's Bitcoin software, removing the ability to create Ordinal inscriptions would require an update to the Bitcoin protocol. Therefore, it is ultimately up to the Bitcoin community to collectively decide whether to keep Ordinal.



