How to build a safe and efficient DEX on Layer 3
Original author: Fox Tech CEO Kang Shuiyue, Fox Tech CTO Lin Yanxi
The concept of Layer 3 is currently gaining traction in the blockchain community and is considered by many to be a revolutionary advancement as developers can create a wide variety of smart contracts and decentralized applications (dApps) on top of the blockchain platform . Layer 3 is a great engineering innovation for the Ethereum scaling ecosystem. If the emergence of Layer 2 solves the problem of general-purpose expansion, then the emergence of Layer 3 solves the problem of higher speed, lower cost, and customized expansion.
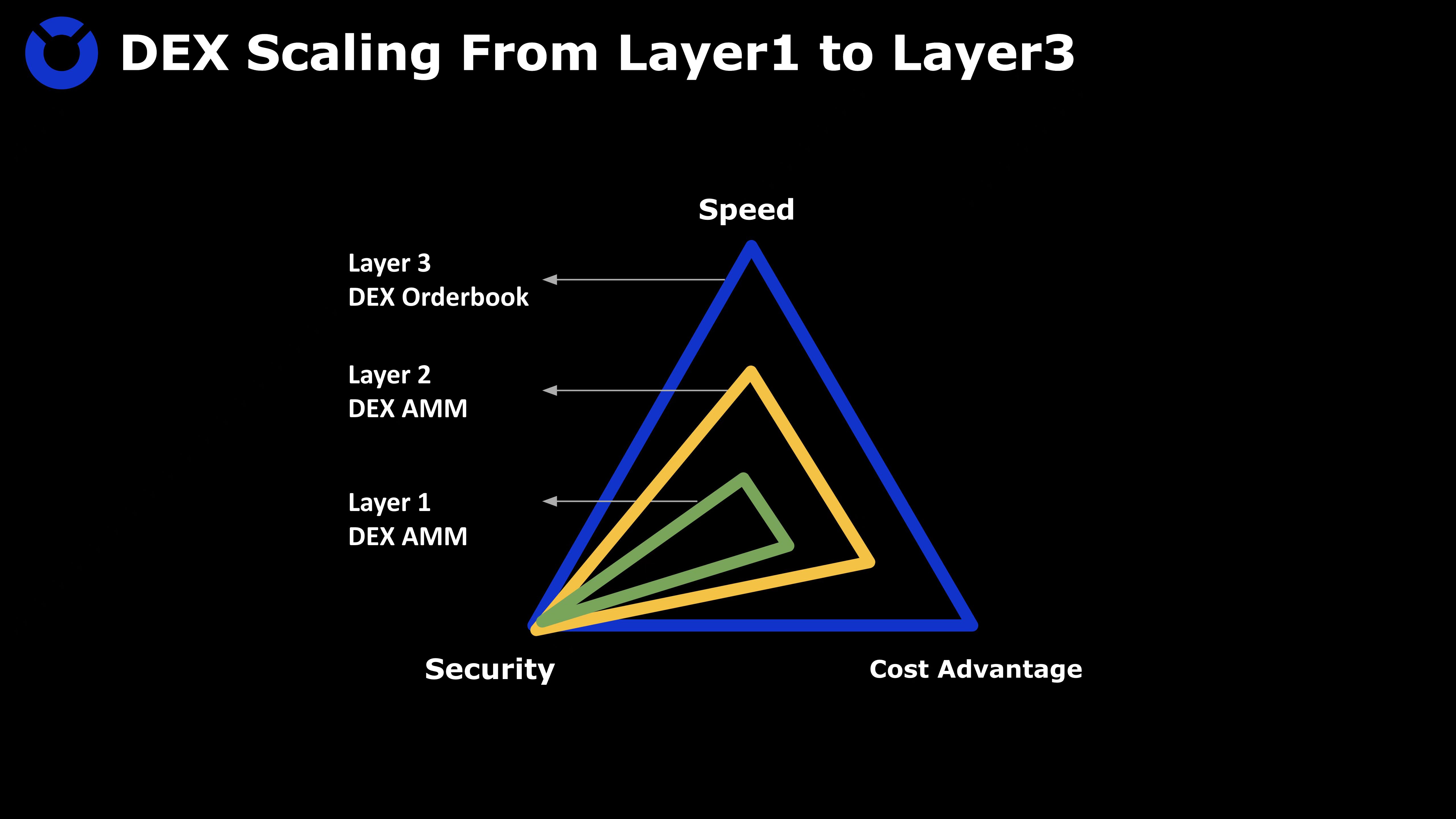
There are already many decentralized exchanges DEX built on Layer 2, so why do we need to build DEX on Layer 3? Most DEXs built on Layer 2 adopt the AMM model, and a few Layer 2 DEXs using the order book model, such as ZigZag, have transaction costs that are somewhat higher than CEX. Whether it is the AMM model or the order book model, the transaction speed and cost of DEX on Layer 3 will have a better user experience.
The reasons why Layer 3 can build a safe and efficient DEX are as follows:
Layer 3 DEX can use a language that is more powerful than Layer 1 Solidity to write a matching engine such as Rust;
Layer 3 can be highly customized and simplifies the user's transaction steps, without having to call the wallet authorization every time an order is placed;
The TPS of Layer 3 is 100 times higher than that of Layer 2, and the cost is reduced by 1/100 again, supporting the Orderbook mode;
Layer 3 is the same as Layer 2, the consensus layer of both is assumed by Layer 1, and the security level is high enough;
Layer 3 has an independent data availability layer, and the visibility of off-chain transactions and asset status can be easily known and obtained;
image description
first level title
Layered Structure of Blockchain Infrastructure
At present, the blockchain infrastructure is mainly divided into four layers: Layer 0, Layer 1, Layer 2, and Layer 3. What exactly do these "Layers" refer to? Layer 1, which we are most familiar with, usually refers to the main network of the blockchain, which can be connected and traded through each node P2P without going through a centralized client server, among which Ethereum is the most typical. Every transaction is registered as a block and stored in a distributed database. Layer 1 is the earliest of these 4 layers. In order to realize cross-chain assets, the Omnichain interoperability protocol, which is Layer 0, has emerged, and its main application is various cross-chain bridges.
The classic blockchain Trilemma "trilemma" refers to different solutions in the same layer, and it is difficult to satisfy the three aspects of decentralization, scalability, and security at the same time. A typical case is that ETH chose decentralization and security at the expense of scalability, while many later public chains rely on a framework with a lower degree of decentralization to achieve higher TPS. Because of the existence of the "trilemma", with the increase in the number of transactions, transaction delays and fee surges inevitably occurred. In order to solve network congestion, developers have proposed a Layer 2 expansion solution based on OP or ZK.
In this multi-layer structure design, Layer 1 provides consensus for Layer 2 and ensures transaction security, while Layer 2 separates calculations from the main blockchain as a relatively independent execution layer, minimizing delays and reducing transaction costs. cost. Layer 3 provides an abstraction layer between users and the underlying blockchain technology, making it easier for users to interact with dApps and smart contracts while keeping them secure through the underlying blockchain. Layer 3 can further compress data on the basis of Layer 2, and then pack the proof back to Layer 1 for on-chain verification through Layer 2, thereby achieving faster and lower-cost transactions than Layer 2.
first level title
How to use zero-knowledge proof to connect DEX to Layer 3
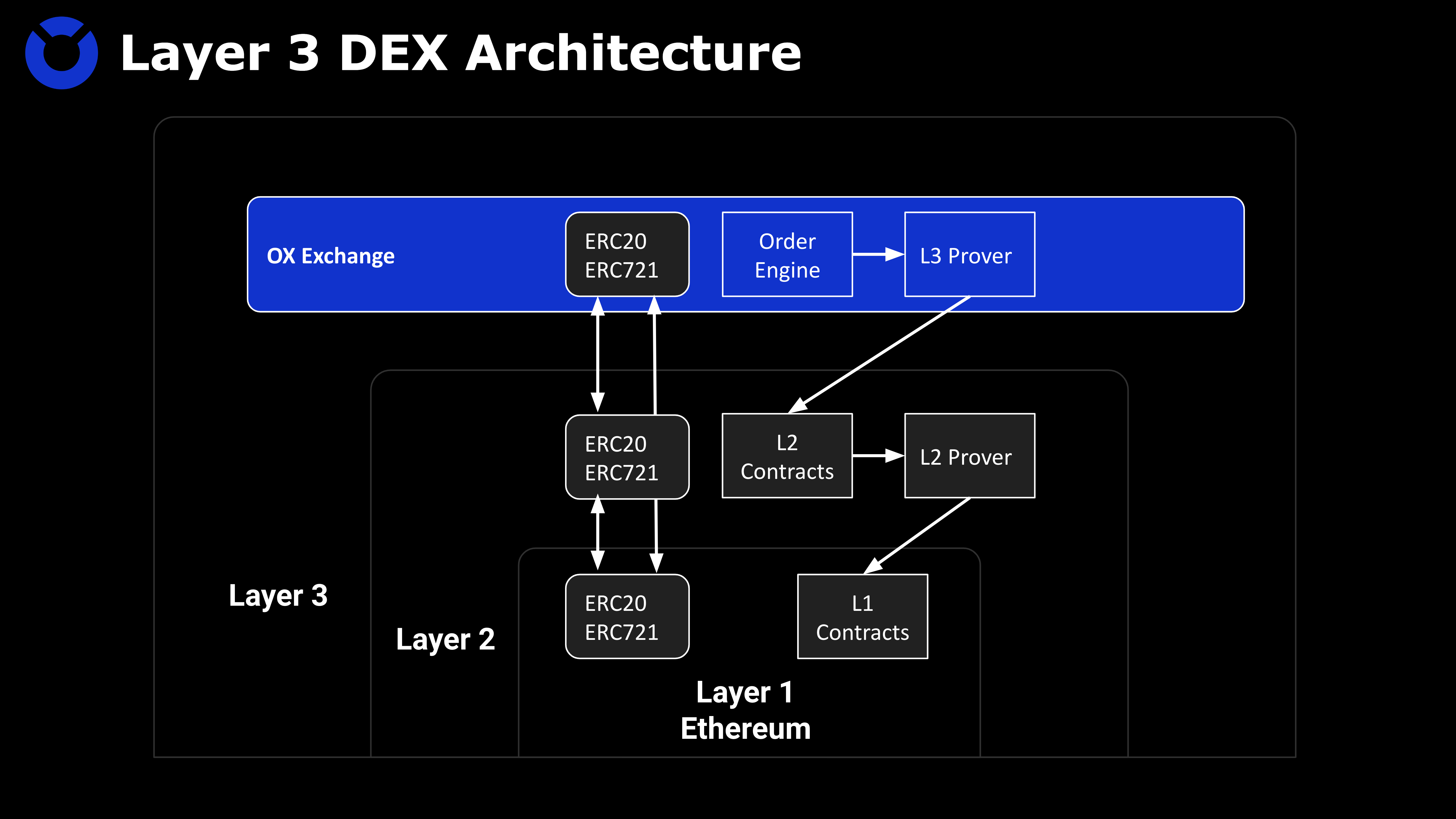
DEX is a very important type of Layer 3 application. If you want to build a DEX called OX Exchange on Layer 3, what is the most critical technology to achieve this purpose? To deploy such a decentralized exchange at Layer 3, the use of zero-knowledge proof is the most critical.
From the perspective of interaction logic, the user's operation in OX Exchange will be implemented in the form of calling a smart contract, that is to say, every buy and sell order will be converted into a call transaction (transaction) to the contract function, and such Every transaction will be submitted to Layer 2 nodes and executed through zkEVM.
In terms of specific implementation, smart contracts deployed in Layer 2 will interact with Layer 3 applications. After receiving the batch transactions from Layer 3, the nodes of Layer 2 will perform zkrollup proof generation, including splitting the opcode and generating a circuit, and then prove the correctness of execution based on the zero-knowledge proof algorithm. Finally, submit the generated execution correctness proof to the Layer 1 chain, pass the verification of the contract on the chain, and accept the status update.
The services provided by Layer 2's zkrollup can achieve lower latency and better user experience. Specifically, OX needs to interact with zkRollup at Layer 2, so as to take advantage of Layer 2 "packaging" to achieve greater throughput. OX can provide a rich front-end operation interface, and the underlying complex interaction logic is completely transparent to users. Users can connect to Web3 wallets and directly use various services of DEX as in all DEXs.
image description
first level title
How to protect user assets through data availability DA
Data Available plays a vital role in all Web 3.0 projects. All traditional applications, including the centralized exchange CEX, usually do not use DA, so the transparency of user data is extremely low, and the asset security level of CEX users depends entirely on whether the exchange is doing evil or not. Layer 3 DEX adopts proprietary data availability (DA), so while greatly reducing user fees, it also guarantees the security of user transaction data and assets.
Layer 3 DEX has high throughput, which means that there is a huge amount of data to process. These data adopt the hybrid storage mode of "DA layer + L2" to take into account the efficiency and security. Contracts deployed on L2 only need to record a few key data and a Merkel root, while all other data in the process will be recorded on the DA layer. When the user interacts with the L3 application, the original data during the interaction process will be stored in the DA layer, and the DA layer will calculate a new Merkel root for the updated data; at the same time, the L3 application will also send a Proof, the contract will thus check the correctness of the Merkel root update. Such a mechanism can ensure that the state of the L2 contract is consistent with the DA layer, that is, the recorded state is always correct.
image description
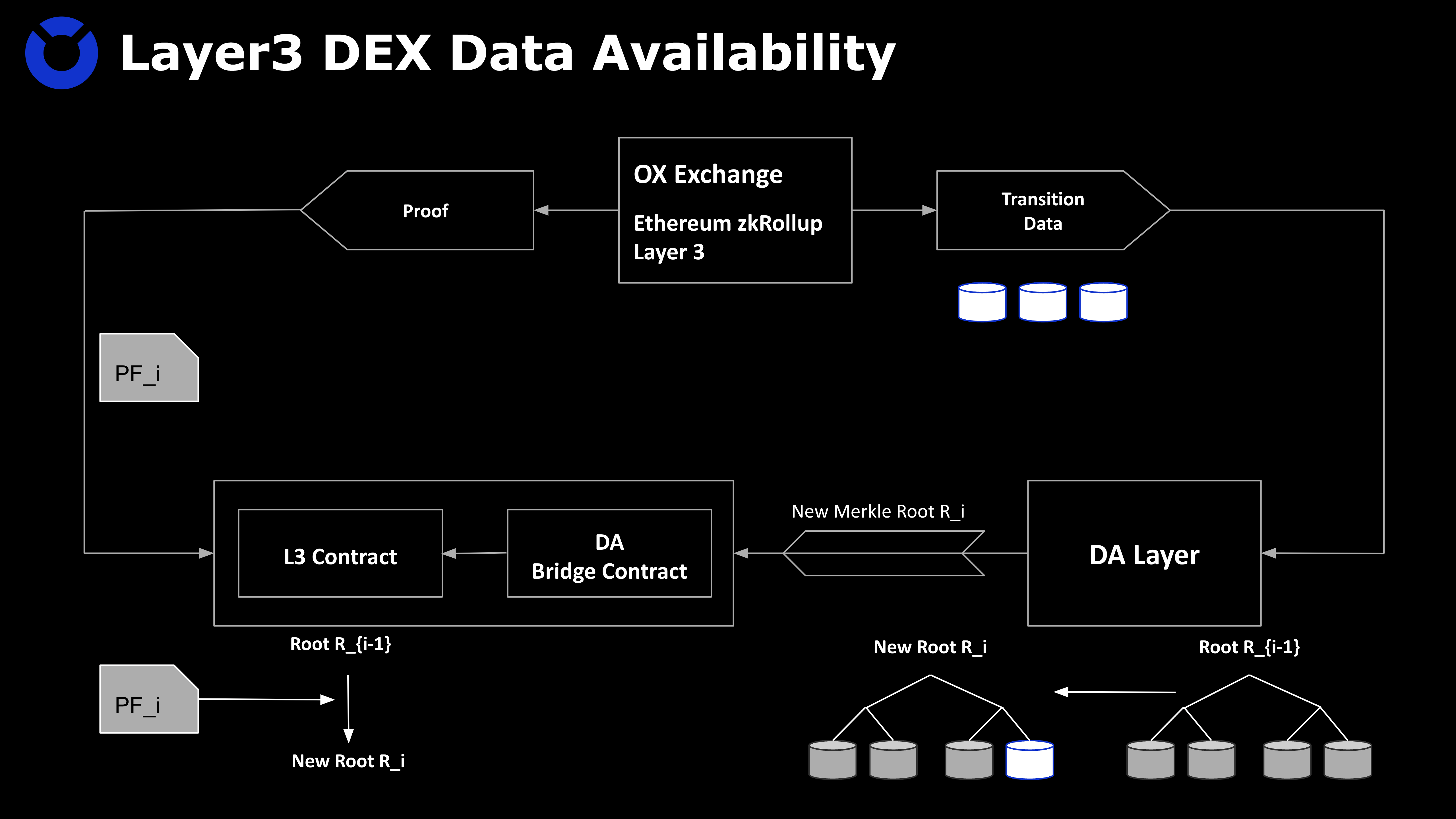
Figure 3: Data Availability DA of Layer 3 DEX



