A Brief Analysis of the Latest Roadmap of Ethereum: Six Key Routes
Original Author: GaryMa
secondary title
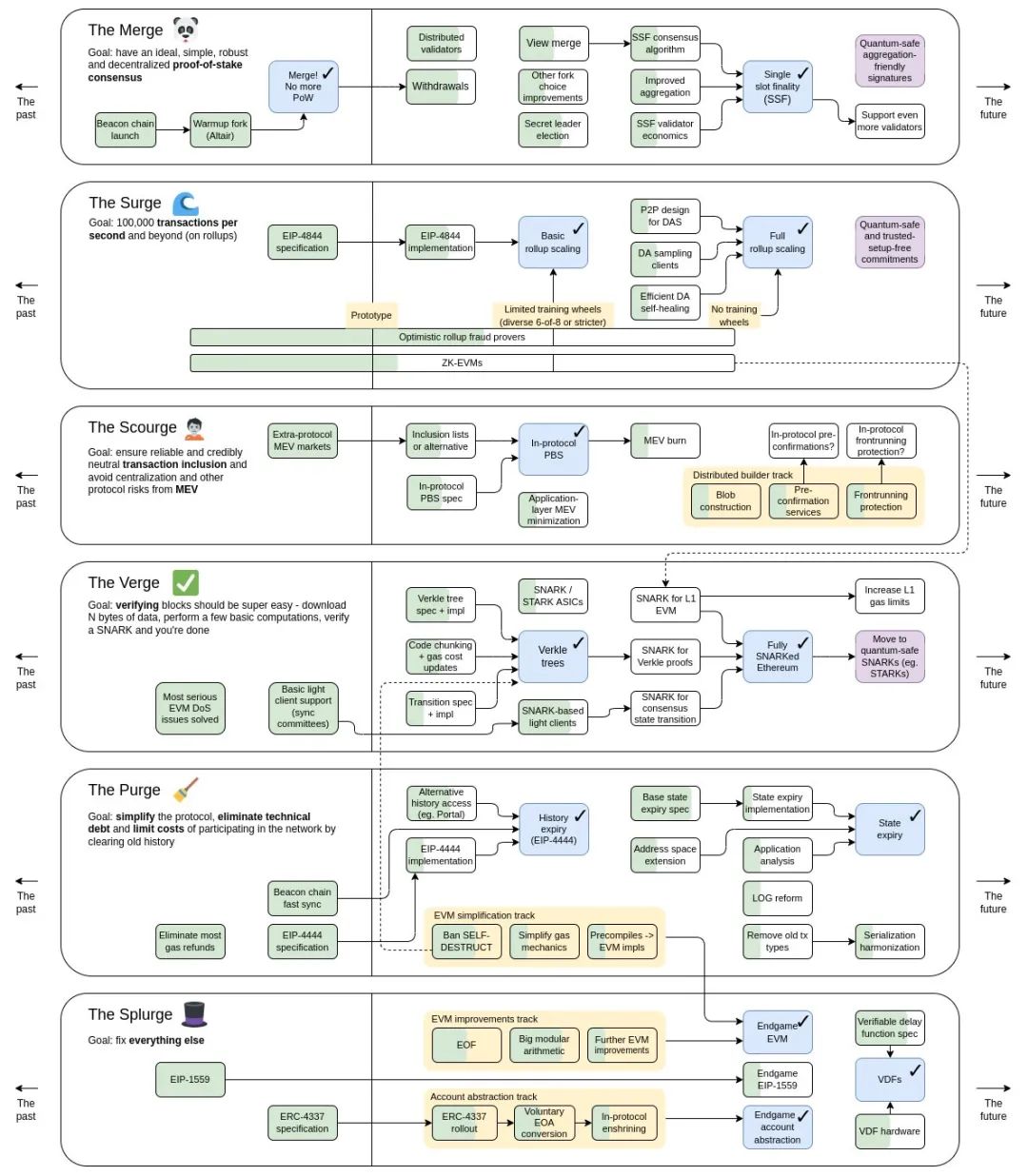
The Merge
The main goal of this route is to build a decentralized, robust and concise PoS consensus mechanism. Ethereum has successfully switched to PoS, and the next step is mainly for the security of network verifiers and patching of sporadic functions:
Activation of the withdrawal function of the beacon chain: it has been the main content of EIP-4895 and is ready to be deployed during the Shanghai upgrade. As for the specific implementation time, at the latest Ethereum core developer meeting, developers can only vaguely estimate a few months Inside.
Distributed Validators (DV): Distributed validator technology, which aims to distribute the work of Ethereum validators to a group of distributed nodes. Compared with the current traditional technology of running validator client orders on one machine, It can further improve security, online flexibility, etc., see DV technical specifications for details.
Single Secret Leader Election (SSLE): Single Secret Leader Election. Currently, the Beacon Chain uses Single Leader Election, that is, the proposers selected by each Slot will be disclosed in advance, making them vulnerable to DoS attacks. By encrypting and hiding this process, only the proposer knows his identity, which can effectively mitigate potential risks.
secondary title
The Surge
The main goal of this route is to promote Rollup-centered expansion to achieve 100,000 TPS per second, which is mainly divided into two stages:
Realize the initial expansion of Rollup: EIP4844 introduces a new transaction type to Ethereum, which carries short-lived blob data, which will reduce the overhead of rollup by 10-100 times, and combine the preliminary OP Rollup fraud proof and ZK -Assisted by EVMs to achieve initial expansion.
secondary title
The Scourge
The main goal of this route is to ensure that reliable, credible and neutral transactions are included in blocks, avoiding network centralization and MEV-related risks, etc., and the key milestone is to realize the separation of block proposers and builders at the protocol level, that is, Proposer -Builder Separation/PBS.
In the design of PBS, the block proposer is responsible for receiving transactions from the memory pool, and creates a list crList containing block transaction information and passes it to the block builders. The block builders reorder the transactions in the crList and build blocks with the purpose of maximizing MEV, and then submit their bids to the block proposer, and the block proposer will choose the highest bid as the valid one blocks.
secondary title
The Verge
The main goal of this route is to lower the threshold for validating blocks, and contains two key milestone checkpoints:
Verkle Trees: Optimize the Merkle tree around the Verkle tree design, making it possible for validators to participate in transaction verification without storing all states.
secondary title
The Purge
This route is mainly some piecemeal optimization fixes, such as account abstraction, EVM optimization, and random number scheme VDF, etc.
The Splurge
This route is mainly some piecemeal optimization fixes, such as account abstraction, EVM optimization, and random number scheme VDF, etc.
Related Links
DV | SSF | Smoothing MEV | Verkle Trees



