Under the background of Real yield, a preliminary study on the sustainability of DeFi business model
Author: David
In the DeFi summer of 2020, many projects have provided short-term TVL surges through the provision of liquidity mining and token rewards, but as other projects provide more APY through the bottomless issuance of tokens, funds have frantically flocked to other project, resulting in a short-term TVL plunge. The sharp ups and downs brought about by such price wars have become a major hot spot for DeFi to attract market attention in the short term, but the actual result is that the funds are too speculative and cannot continue to be deposited in the project for long-term ecological construction and improvement.
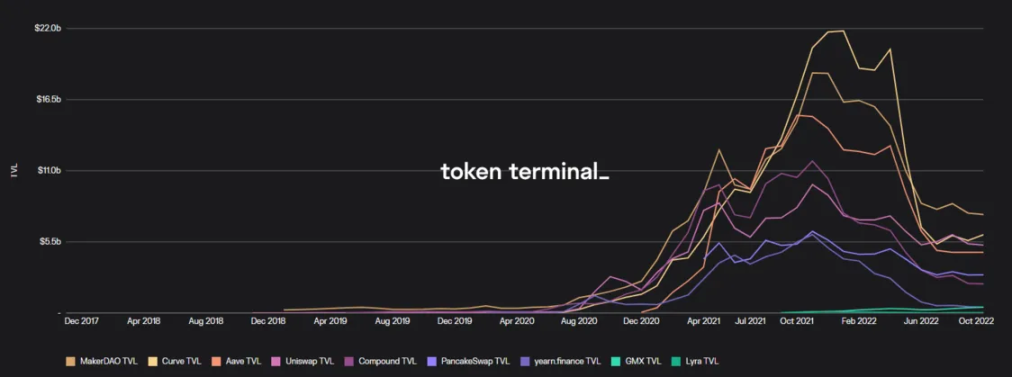
The last round of DeFi boom came to an abrupt end in the middle of this year with the collapse of projects such as Terra and Celsuis. With the advent of the bear market and the mud and sand in the currency circle, the market began to question the actual role of DeFi. Many people even think that apart from short-term hype such as Pond's funds, nesting dolls, and legends of getting rich, DeFi does not have much practical value.
The arrival of the bear market has led to the ebb of speculative funds, and the market has also turned its attention to DeFi projects that can truly create long-term profits. Thus was born the core narrative logic of this round of bear market DEFI: Real yield. Real yield is no longer based on the excessive issuance of protocol native tokens, but encourages the sharing of protocol profits to motivate token holding and liquidity provision.
capital utilization efficiency
The previous DeFi growth strategy focused too much on the growth of TVL. After attracting TVL through unlimited issuance of tokens, the TVL was then used to generate related income (money for money, the core business logic of the financial industry). Although the acquisition of TVL is a prerequisite for the development of the industry, the scale and growth rate of TVL are not the best indicators for evaluating the business model of the agreement.
TVL is not a fund owned by the agreement itself, but a third-party fund. From the perspective of the balance sheet of a traditional financial institution, it is more like a liability. Only when TVL is combined with better token economics and focuses on how to use TVL to increase profit income and the assets owned by the agreement (similar to net assets), can it be used as an indicator to evaluate the pros and cons of the agreement's business model.
In this article, we mainly introduce the total revenue/TVL (fee/TVL) indicator to evaluate the unit capital utilization efficiency of the agreement. This indicator is similar to ROA under the traditional financial framework and is the core indicator for evaluating the efficiency of business models. The combination of TVL and total revenue is always a reminder not to focus on TVL unilaterally. After all, if the assets are too large but not very profitable, it means that some core aspects of the business model are inefficient.
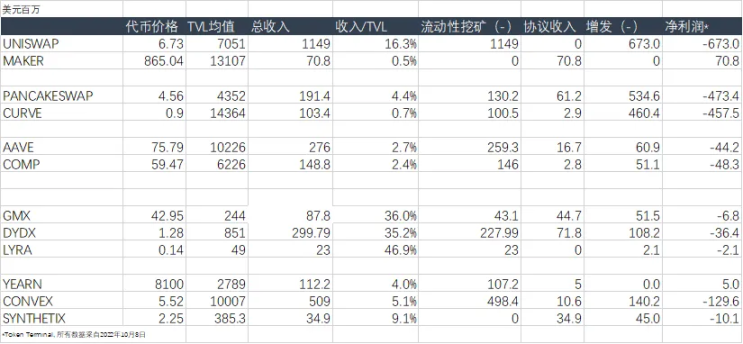
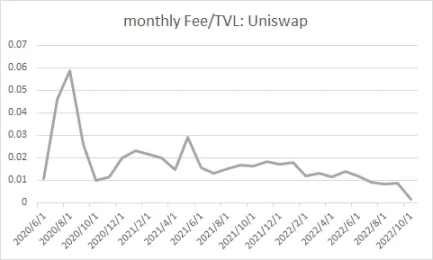
We are concerned that the previous round of DeFi projects are often inferior to new projects in terms of capital efficiency due to the historical legacy of focusing too much on TVL. At the same time, the performance of leading projects such as UNISWAP is much higher than that of peers in terms of capital efficiency, mainly due to the USDC/ETH pool on V3, which has created a huge transaction volume with a very small TVL.
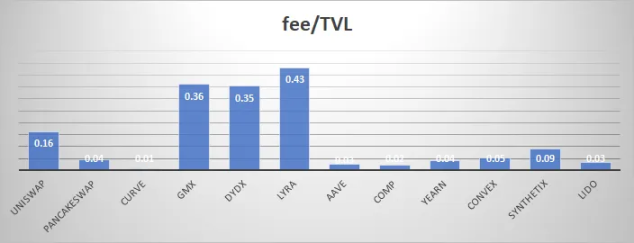
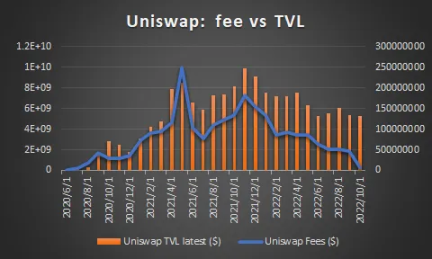
Agreement Retention Ratio
At the same time, in the last round of DeFi, general DeFi protocols generally obtained TVL by introducing liquidity mining, resulting in the inability to retain most of the income in the protocol. Among them, UNISWAP and MAKERDAO are two extremes: the former basically distributes all transaction fee income to LPs participating in liquidity mining, while the latter does not use liquidity mining, and all interest income is stored in the agreement.
Although Maker is a lending agreement, its essence is the issuance of stable coins. Considering that it does not actually need to increase liquidity mining, Maker may actually keep all income in the agreement, leading to the real net assets of the agreement. The concept of adding a layer of risk control safety cushion to future agreements is similar to the concept of protocol-controlled assets (PCA) proposed by TOKEMAK.
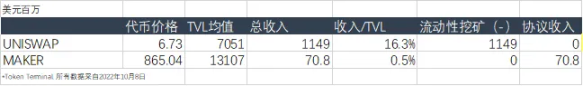
Most projects, in order to attract liquidity, send part of their income to LPs in the form of rewards, and many mainstream projects even basically send more than 90% of their income to LPs. Considering that many projects need to retain part of the profit after paying to LP to meet other expenses such as team expenses, marketing expenses, etc., but in fact most agreements do not seem to reserve enough budget for this part.
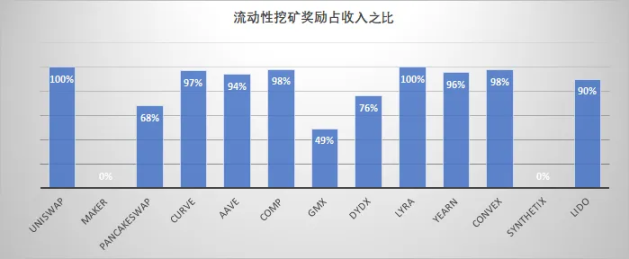
As a recent star project, GMX clearly stated in the white paper that LPs (GLP token holders) not only get GMX token rewards, but also get 70% of the platform fee income denominated in ETH (the actual LP fee share is only 49% ). This arrangement has laid a good foundation for the subsequent agreement construction costs and the accumulation of PCA of the agreement itself.
In addition, GMX is also very conservative in its own token release. A sign of a good project is whether the proceeds are distributed in USDC, USDT or any stablecoin, or in the native token of the blockchain such as ETH or AVAX.
Token empowerment
Token empowerment is an old-fashioned topic. Under the background of the bull market, the demand for token empowerment is put on the shelf, and the market is more likely to be moved by fresh stories and fashionable terms. As for whether the agreement captures value and whether token holders can share growth stories, speculators are often not concerned topic of. Neglecting token empowerment could expose us to a similar problem with TCP/IP — yes, TCP/IP is an integral piece of infrastructure, but it doesn’t deliver any value to stakeholders; similar to the many current The DeFi protocol is also the "primitive language" of the future decentralized financial system. Ignoring token empowerment will also make it face a similar fate to TCP/IP?
After the LP incentives are paid and the income finally settles to the protocol level, the protocol still needs to face various expenses such as liquidity token issuance incentives, team and marketing expenses, and the actual retained final profit is even less. For the convenience of analysis, we only assume that the issuance of tokens is the largest cost item here. The scale of additional issuance every year can reflect the attitude of the protocol itself towards token empowerment to a certain extent.
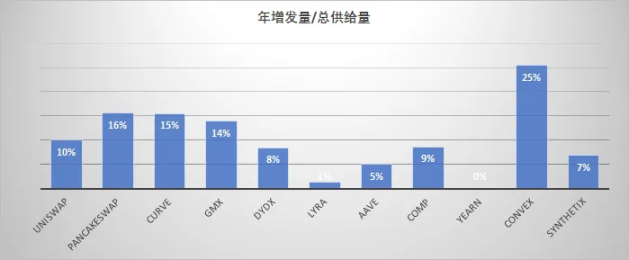
Protocol Profit Estimation
Here we introduce the concept of protocol profit, that is, the retained income of the protocol—token issuance fee. The cost item is the amount of newly added tokens multiplied by the current currency price. This calculation does not necessarily reflect the actual situation, but it can show us to a certain extent which DeFi protocols are in terms of capital efficiency, protocol retention, and token empowerment. Demonstrated real profitability prospects.
Business continuity of different DeFi tracks
Dex:
It is mainly an agreement to obtain transaction fee income by providing transaction services. Transaction fee income is allocated to LP and token holders, and LP income can be regarded as the main cost.
Due to the fee rate, the income of futures (perpetual) trading is generally far better than that of spot trading. This is mainly reflected in the efficiency of capital utilization, because derivatives transactions are charged according to the nominal transaction amount (after leverage). The income generated by unit TVL, UNISWAP (the most efficient spot exchange) is only one-third of that of GMX.
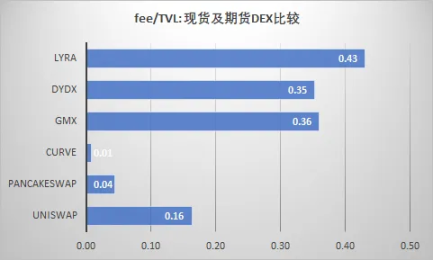
Secondly, spot exchange fees tend to decline in the long run. For example, in order to expand the trading audience, UNISWAP is deployed to the cheaper POLYGON. At the same time, in order to compete with CURVE, the 0.01% fee TIER for stablecoin pairs is introduced, which leads to its overall capital Utilization efficiency is reduced.
Borrowing:
The agreement that provides lending services mainly earns income through the commission of interest charges or the origination fee of undercollateralized loans.
The cost item is mainly the interest charges and GRANTS paid by the depositor.
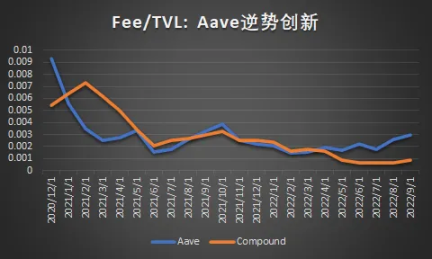
Lending platforms earn interest income from their lending business. To maximize loan revenue and profitability, it can adjust three key levers beyond simply raising fees: capital efficiency, new customers, and improving margins. For example, Aave has launched an enhanced version of its core product (Aave V3, improving capital utilization) and a number of complementary products (GHO stablecoin and Lens Protocol), all of which aim to align one or more of these three key strategic levers.
Although the market has entered a bear market this year, Aave's capital utilization efficiency has risen against the trend, which shows that its new strategy explains the success of its new product strategy to a certain extent.
Undercollateralized loan products, even those that do not require collateral such as flash loans, etc., have stronger pricing power because they focus on compliance and institutional clients (*hedge funds, venture capital and market makers*), thus Benefit from higher barriers to entry for competitors.
At the same time, the lending industry is still facing the pressure of price wars. For example, a platform that claims to provide interest-free loans recently obtained financing, which shows that the overall lending model will face price pressure in the future.
ASSET MANAGEMENT and Liquid Staking Platform:
Asset managers earn income from AUM-based management fees, performance fees, and/or minting and redemption fees for structured products. In the long run, this model has a stronger profit quality and is less susceptible to price wars.
Question: Which DeFi models are more promising?
Original link



