Developers must read: Starting from the technology of Zcash and Aleo, understand the design principles of private transactions
introductionfirst level titlezerocashintroductionzerocashFrom the perspective of the paper, the privacy design adopted by Aleo's programmable privacy design and the early Zcash white paper ( In addition to the technical details described above, there are still some other technical details that have not been covered yet, such as the delegate prover scheme, zero-knowledge proof algorithm, recursion/aggregation scheme, etc. Interested students can continue to study. |
Zcash
first level title
1. About Zcash?
https://zcash.readthedocs.io/en/latest/rtd_pages/basics.html
Features:
A short video about Zcash, about 2 minutes long.
• Anonymous version of BTC, UTXO-like model
• Can only be used for payment scenarios, not programmable
first level title2. Main concepts, we only focus on the latest version. Mainly introduce the core concepts in Zcash.
2.1 Key components
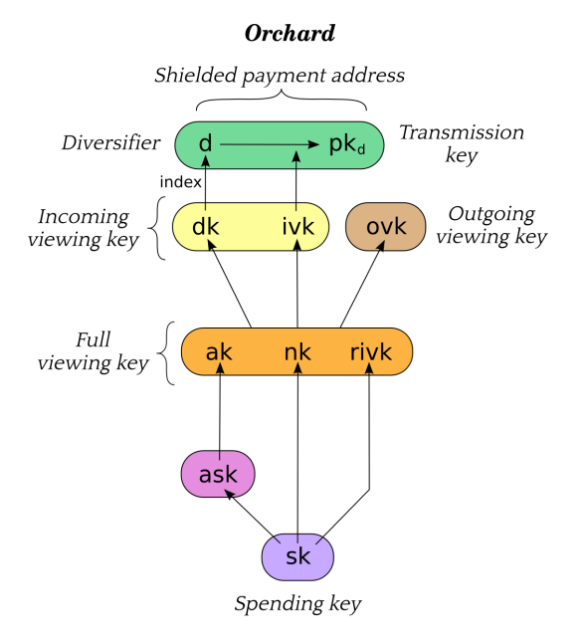
secondary title
(Zcash protocol specification: section 3.1, page 12)

image descriptionZcash protocol specification: section 4.2.3, page 36you can at
2.2 Note
Learn how these keys are calculated.
note is the basic unit in the Zcash protocol, similar to UTXO in BTC; in Zcash, the input and output of all transactions are notes. Of course, Zcash also supports non-anonymous transactions, which is the same as the transaction mode of BTC.

Therefore, if you want to understand Zcash more deeply, you must first understand the data structure of the note:
(Zcash protocol specification: section 3.2, page 14)

Image Source

image description
(Zcash protocol specification: section 3.2, page 15)
2.3 Action transfer
secondary title

image description
(Zcash protocol specification: section 4.6, page 41)

2.4 Action statement
Image Source

secondary title
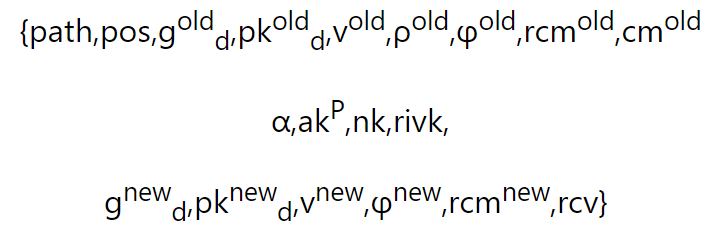
![]() The privacy input is:
The privacy input is:

The proof statement is:
(Zcash protocol specification: section 4.17.1, page 40)
image description
Image Source
• The integrity of the spent note is uniquely bound to the noteplaint
• The validity of the spent note, the existence proof of the cm tree
• The integrity of the Value promise, uniquely bound to rcv, old value, new value
• Integrity of Nullifier, preventing double spend, maintaining a spent note set
• Legality of spent notes
• Integrity of new notes
• The legality of the flag
2.5 Transaction structure and examples
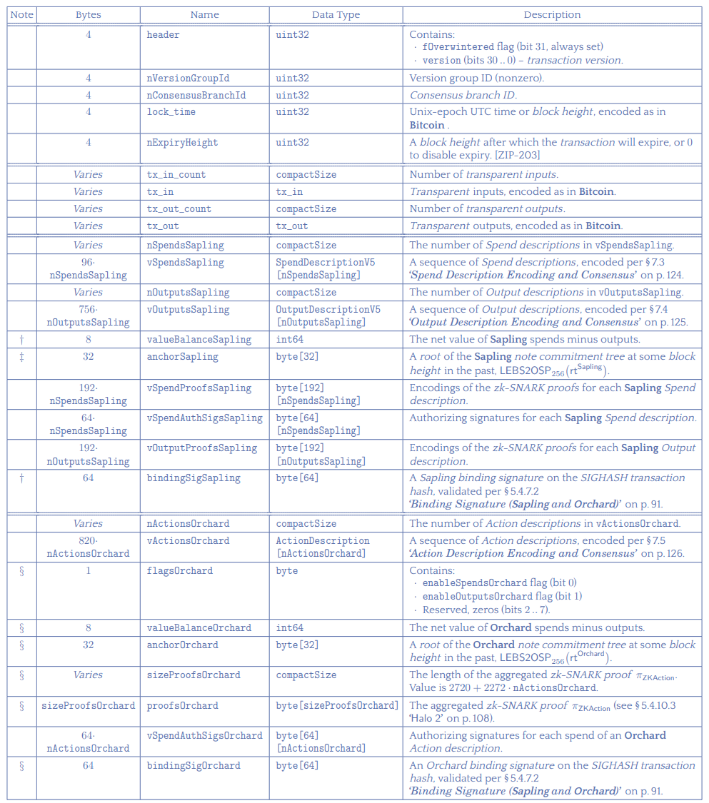
2.5.1 Transaction Structure
(Zcash protocol specification: section 7.1, page 119)
image description
• Public info (1 - 5)
• Transparent transactions info (6 - 9)
• Sapling transactions info (10 - 16)
• Orchard transaction info (17 - 25)
Image Source
The entire transaction structure consists of four parts:
• Public info (1 - 5)
• Transparent transactions info (6 - 9)
2.5.2 From transparent to shield
The Orchard protocol contains two types of addresses, transparent address (TA) and shield address (SA). Generally, in order to execute a private transaction, it is necessary to transfer money from TA to SA first. At this time, the corresponding transaction structure should be:
• Sapling transactions info (10 - 16)
ⅰ. tx_in_*: actual value
• Orchard transaction info (17 - 25)
ⅱ. tx_out_*: default value
ⅰ. All: Default value
ⅰ. All: actual value
• Public info (1 - 5)
• Transparent transactions info (6 - 9)
2.5.3 From shield to shield
• Sapling transactions info (10 - 16)
The Orchard protocol contains two types of addresses, transparent address (TA) and shield address (SA). Generally, in order to execute a private transaction, it is necessary to transfer money from TA to SA first. At this time, the corresponding transaction structure should be:
• Orchard transaction info (17 - 25)
ⅰ. All: Default value
ⅰ. All: Default value
ⅰ. All: actual value
• Public info (1 - 5)
• Transparent transactions info (6 - 9)
2.5.4 From shield to transparent
The Orchard protocol contains two types of addresses, transparent address (TA) and shield address (SA). Generally, in order to execute a private transaction, it is necessary to transfer money from TA to SA first. At this time, the corresponding transaction structure should be:
• Sapling transactions info (10 - 16)
ⅰ. tx_in_*: default value
• Orchard transaction info (17 - 25)
ⅰ. All: Default value
secondary title
• Unlinkable
2.6 How to achieve privacy?
• Private
ⅰ. Sender address:
text
ⅱ. Receiver address:
The generated note is represented by cm, and the spent note is represented by nf. There is no connection between nf and cm. Therefore, no one can use this information to judge in which transaction any generated note was spent .
ⅲ. Value:
The Note is hidden in the form of pedersen commitment, and the balance property of the transaction is guaranteed through bindsig.
Aleo
first level title
Zcash can only perform privacy transactions based on the OUTX model, and does not have programmability; therefore, the main difference between Aleo and Zcash is privacy programmability; the same point is that both support privacy attributes (transaction privacy, not only including asset classes).
2. Aleo VS Zcash
2.1 Unit
secondary title

image description
(Zcash protocol specification: section 3.2, page 14)
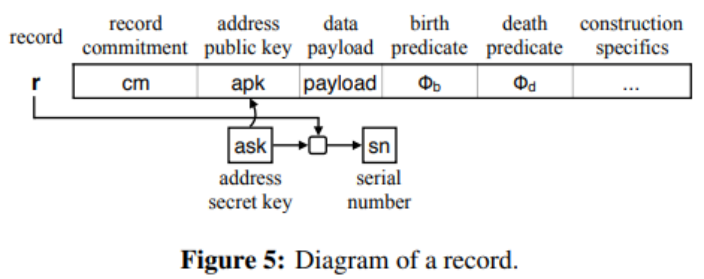
Image Source
(Zexe protocol specification: section 3.1, page 17)
image description
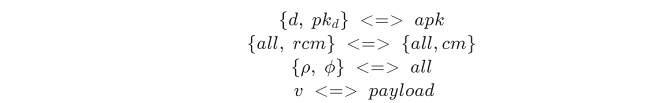
Image Source
Corresponding to the note owner's address information, promise-related information, nf/sn-related information, and value-related information.
secondary title

2.2 Transaction Structure
(Zexe protocol specification: section 3.1, page 17)
image description
Image Source
Compared with the main transaction structure of Zcash (2.5.1), it is still similar:
▪ The plaint of the newly generated record, including owner information, corresponding birth/death predicate, etc.
2.3 Prover statement
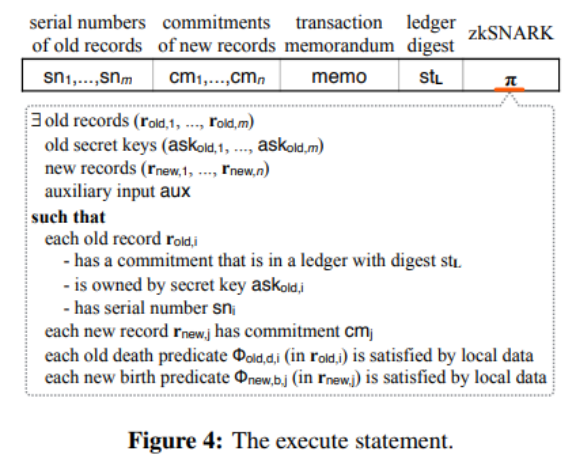
secondary title
(Zexe protocol specification: section 2.4, page 13)
image description
Image Source
Need to prove:
▪ Validity of Old record
▪ ▪ Validity of New record
first level title
3.1 Why are all utox-based, not account-based?
Remark2.3(Zexe protocol specification: section 2.3, page 11)
refer to
first level title
https://zips.z.cash/protocol/protocol.pdf
2. (Aleo)Zexe protocol specification(Figure4/5/6,Remark2.3):
https://eprint.iacr.org/2018/962.pdf
about Ushttps://z.cash/upgrade/
4. zerocash:https://eprint.iacr.org/2014/349.pdf
about Us
Sin7y was established in 2021 and is composed of top blockchain developers. We are both a project incubator and a blockchain technology research team, exploring the most important and cutting-edge technologies such as EVM, Layer2, cross-chain, privacy computing, and autonomous payment solutions.
WeChat public account: Sin7Y
GitHub | Twitter | Telegram | Medium| Mirror | HackMD | HackerNoon



