Learn about the safety track rookie Forta Network led by A16z in this article
first level title
Investment Summary
Investment Summary
From 2009 to 2022, during the 13 years of rapid development of the blockchain, numerous financial loss incidents have occurred in the blockchain industry due to hacker attacks, protocol loopholes, private key leaks, and internal crimes. The loss in 2020 will exceed 510 million US dollars, and the loss in the first four months of 2022 alone will exceed the sum of 2021 and 2020. With the development of the industry, various attack methods emerge in an endless stream. If the Web3 project wants to develop from the current billions of dollars to the future trillions of dollars, security issues cannot be neglected. Security standards In addition to the current routine audits and bug bounties, the entire industry needs to establish a complete set of solutions from perception to practice.
While smart contract development and security practices have changed significantly since the launch of the Ethereum mainnet in 2015, smart contract auditing and reusable codebases have become standard practice. Yet while auditing, code repositories, and other techniques are helpful in identifying or preventing bugs and vulnerabilities in code, their effectiveness is limited. Once a smart contract is deployed on the blockchain, the risk profile changes. How contracts are managed, how they interact with other contracts, and how they respond to unexpected market events all add additional uncertainties. In other words: code can work, but smart contracts can still encounter problems, and smart contract security requires continuous effort.
Under normal circumstances, developers usually discover certain logical loopholes when they passively receive user feedback when the program is running, which means that a considerable number of loopholes can only be found after deployment, and exploiting loopholes often requires multiple abnormal transactions to complete. The monitoring system can send out an alert when the first or second transaction in a series of abnormal transactions has just been completed, which will save huge losses for the project and help the team fix the loophole. So monitoring systems are essential in the Web3 world.At present, most monitoring solutions are based on centralized systems. The disadvantage of centralized monitoring systems is that they cannot cover newly deployed smart contracts at a fast enough speed. Once a decentralized open source project reaches a certain scale, its development momentum will be too rapid, and the centralized monitoring solution can only cover a small part in a short time. To solve this problem, Forta chooses to useDecentralized incentive monitoring system
To ensure the efficient deployment of smart contract monitoring, to ensure that smart contracts can be fully monitored at the first time.
At present, Forta has passed the testnet stage and officially launched. The overall condition is good. During the testnet stage, InverseFinance’s price manipulation oracle attack was monitored and a warning was issued in time. But the project still needs to pay attention to the following:
Currently, there are few monitoring robot templates. Even if an early warning is issued for the attack of InverseFinance, the warning template is not a warning of currency price changes but a warning of large eth transfers, which is easy for developers to ignore the warning.
Although the current total weekly rewards of $FORT tokens are fixed, the monitoring reward shares of different chains are still distributed by the team.
secondary title
1. Basic overview
1.1 Project Introduction
1.1 Project Introduction
Forta Network is a decentralized real-time security and monitoring system, suitable for monitoring threats and anomalies on DeFi, NFT, governance, cross-chain bridges and other Web3 systems on the chain, by providing users with information about their system security and stability Timely and useful information allows contract owners to make timely defensive and remedial measures to minimize losses.Forta Network adoptsPermissionless decentralized incentive model
. It uses $FORT token incentives to attract node suppliers and monitoring robot developers to join the network, and build a timely, complete, easy-to-use and wide-coverage monitoring system on this basis. Through the existing monitoring robot template, contract developers can easily monitor contract exceptions in a code-free manner, or use forta-sdk to write monitoring robots to perform a series of custom monitoring. Forta Network also supports the webhook notification method, which contract developers can use for automated anomaly defense.The most outstanding feature of Forta Network is theContract monitoring modularization, standardization, codeless
2. Project details
1.2 Basic information
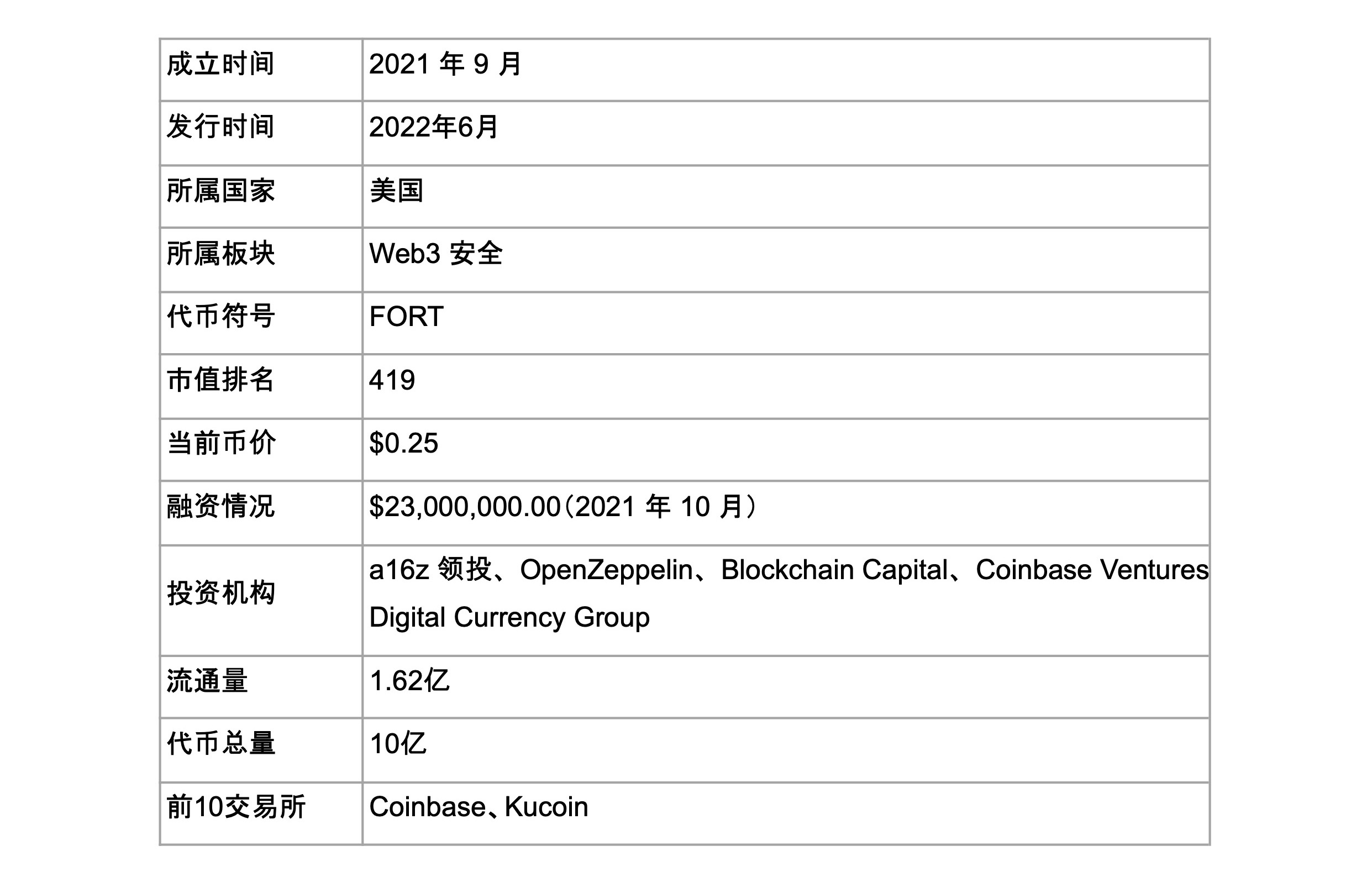
2. Project details
secondary title
2.1 TeamForta Network was developed and introduced to the community by an innovative and interdisciplinary team of individuals within the OpenZeppelin team. The Forta project has not disclosed much about the team composition at present, but judging from the submissions of Forta's core projects forta-core-go and forta-node on GitHub, most of the code submitters belong to the OpenZeppelin organization or have submitted OpenZeppelin-related code .It can be understood that Forta is a subordinate team in the OpenZeppelin company, and all personnel actually work for OpenZeppelin
. The public information that can be found is: Jonathan Alexander, CTO of OpenZeppelin, is the co-founder of Forta.
OpenZeppelin has established the most widely used contract code library in Ethereum evm. Most of the existing erc-20, erc-721, erc-1155 tokens use OpenZeppelin's products for no-code or low-code creation. OpenZeppelin also has in-depth cooperation with well-known projects or companies such as AAVE, Ethereum Foundation, Coinbase and The Graph.
Jonathan Alexander, CTO of OpenZeppelin and co-founder of Forta Network. Graduated from UCLA in 1984, served as CTO of Vonage (the largest broadband telephone service provider in the United States) from April 2010 to March 2016, responsible for the architecture of Vonage's cloud communication platform. From March 2016 to March 2020, he served as CTO of QASymphony / Tricentis (the two companies merged in 2018, both of which are software testing companies), and joined OpenZeppelin as CTO in April 2020.From the resume of Jonathan Alexander, it can be seen that the founder has rich experience in software management and technology platform construction.Vocational skills are relatively in line with Forta's technical product positioning
Forta is backed by the well-known company OpenZeppelin, coupled with its good performance in seed round financing, it has already gained popularity in the Web3 world. As a standard code base creator and auditing company on Ethereum, OpenZeppelin's development level is beyond doubt. I believe that Forta will bring users a better experience in the future.
2.2 Financing situation
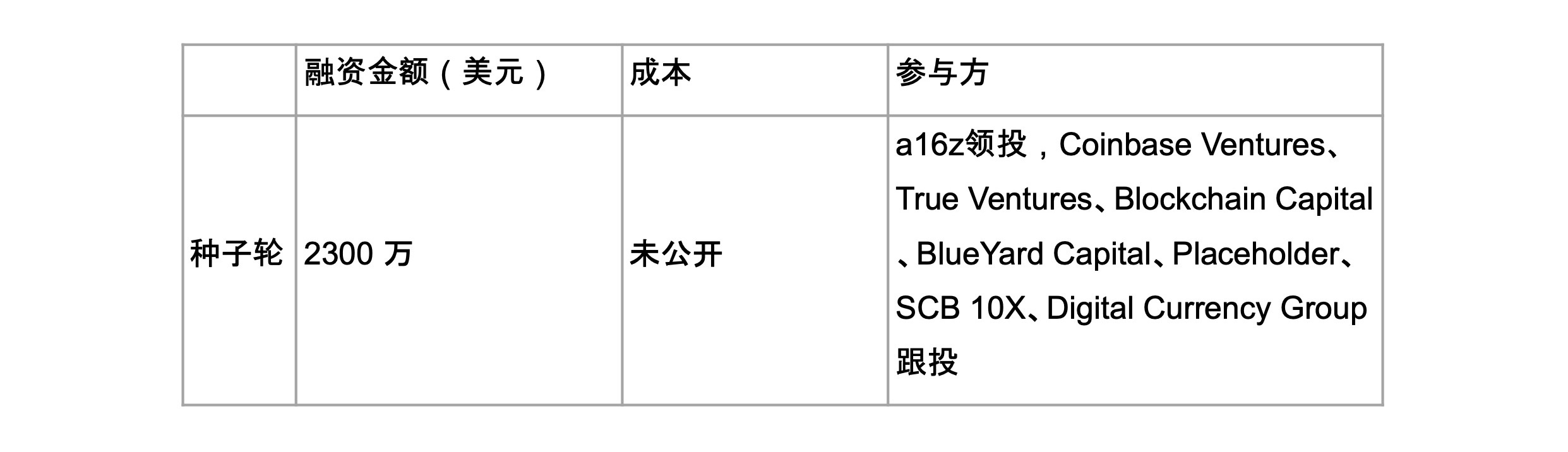
secondary title
2.3 Code and development tools
Most of Forta's code contributors on GitHub are members of the OpenZeppelin team. Judging from the quality of OpenZeppelin's open source projects, the team's screening of developers is quite strict.
The forta-node project is the software run by the Forta Network node operator. It requires the team to precompile and generate a docker image to run directly on the operator's server. The code does not directly face the user. The unit test of this project is relatively complete, and a performance test is also carried out to prevent insufficient server resources or excessive memory usage. However, there are still several issues marked as bugs under this project that have not been closed so far. This includes the problem that the automatic update of the v0.5.1 version on July 20 did not take effect. There are also several issues marked as obsolete on the to-do board but not closed in the issue, reflecting the problem that the small team is not rigorous enough in project management.
Generally speaking, OpenZeppelin, as the largest provider of open source code libraries on evm, can be said to have excellent overall development quality, and sufficient guarantees for development progress and project availability can be obtained. The fly in the ointment is that the internal project management is not so rigorous, but it does not affect the overall project quality.
secondary title
There are two modules and three roles in Forta Network to maintain network operation. To understand how the entire network works, we need to understand these two modules and three roles
text
2.4.1 Two modules
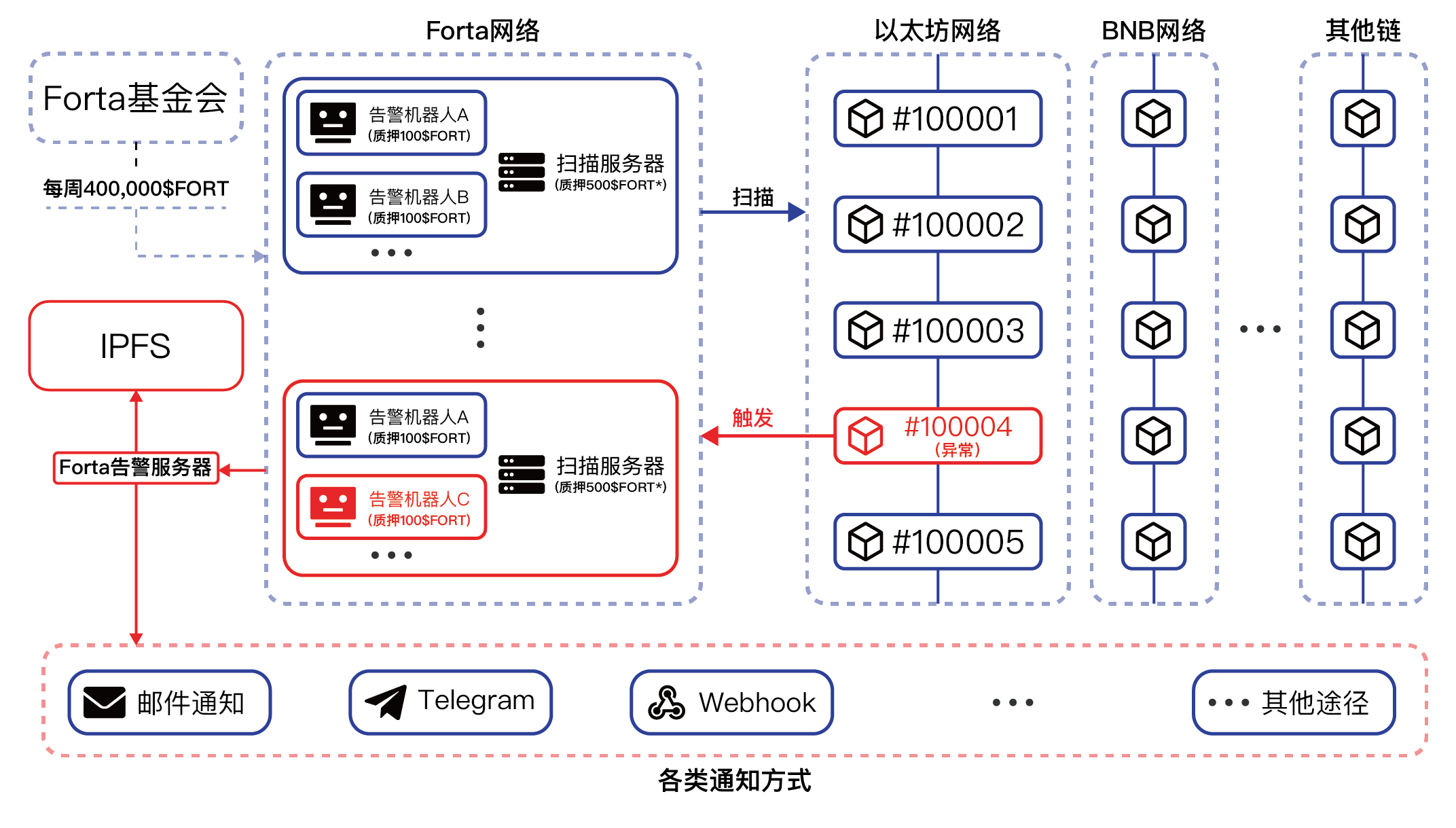
Forta Network has two modules: alarm robot and scanning nodeAlert robot: Alert robot is a piece of logic (script) used to find certain transaction characteristics or state changes of smart contracts (such as anomaly detection) on any supported chain, which can also be understood as aSecurity cameras monitoring the blockchain
, as a developer can program it and specify content that meets the conditions for monitoring. For example, the behavior of changing governance of a contract, changing a key setting of the contract, calling a method of the contract interface has abnormal operation behavior, etc. It is also possible to monitor a certain state on the chain, such as monitoring the price change of a certain token in the price oracle, monitoring the abnormal transaction volume of a certain token, and monitoring the large decrease/increase of all account balances in the entire network. Bot developers can even use machine learning models in alert bots, using machine learning to predict attacker behavior and stop attackers before they start. With the efforts of Forta developers, no code has been implemented to write alarm robots. You don’t need any programming background to set monitoring conditions for most contracts, so that ordinary people can easily complete the monitoring purpose.Scanning node: Responsible for scanning all transaction data in each block of the specified chain, which can be considered ascharacter of. When the alarm robot in the scanning node matches a specific condition or event in the data, an alarm will be sent to the network, which will be stored on IPFS, and anyone can subscribe to relevant alarms through Forta Explorer or API.
text
2.4.2 Three roles
There are three roles in Forta Network: Alert Subscriber, Alert Bot Developer, and Scan Node Operator
Alert Subscribers: Anyone can use Forta to monitor transaction activity and receive alerts for security, financial, operational, and governance-related events on a given chain. The public alert bots that are usually published on Forta Network are open source, and everyone can freely subscribe to these bots to get alerts. The alarm push method supports Email, Slack message push, Discord webhook push, Telegram robot push, and custom webhook push. Subscribers can use the custom webhook method to automatically take defensive measures on the contract when the alarm is triggered to prevent losses. Assuming that subscribers need to hide the alarm robot policy to prevent attackers from disturbing the normal operation of the project by maliciously triggering automatic defense measures after reading the alarm robot code, then a private network can be built and the robot can be deployed on the private network. The network is completely independent from the Forta main network and does not participate in the distribution of public warning robots.
Alert Bot Developer: Any developer can write and stake a portion of $FORT on the Forta Network to release an alert robot. Since there are not many types of basic state detection on the chain, the early public basic detection robots were issued by the Forta Foundation to reward developers who write basic robots for the Forta Network. As time goes by, the basic robot templates on the network are gradually improved. After that, the alarm robots on the network will basically be protocols, DAOs or organizations with specific detection requirements. In order to prevent developers from writing malicious robots to send spam through mail subscriptions or abuse Forta Network node resources, developers need to pledge at least 100$FORT when starting the robot.
Since Forta went live in September 2021, the community has deployed more than 650 detection robots, and 2,000 scanning nodes have participated in the network, continuously scanning Dapps in 7 chains (including Layer1 and Layer2). As of August 2022, the community has deployed more than 1,200 detection robots, and more than 9,000 scanning nodes have participated in the network, showing a strong growth momentum.
secondary title
 2.5 Operating Mechanism and Token Economics
2.5 Operating Mechanism and Token Economics
We will elaborate on the entire workflow and token economics from the perspective of the alarm robot:
Before the warning robot is released, there will be a series of scanning nodes on the Forta network, and these nodes will carry the operation tasks of the warning robot. The creation of these nodes requires a stake of at least 500$FORT (which will become at least 2500$FORT after September 30, 2022).
The robot developer will pledge 100$FORT to release the alarm robot. After the alarm robot is released, the network will package the robot into a Docker image and send it to one or more high-quality nodes in the network. The high-quality nodes will be judged according to the node SLA score. Generally, when the SLA score is higher than 0.9, it can be judged as high-quality node. (SLA score is the minimum between the weighted average of resource score, data quality score, and uptime score)
The alarm robot checks the data of each block on the chain registered by the scanning node. When the alarm robot strategy matches the data in the previous block, it will use Graphql to send the alarm content to the Forta Network server.
After the Forta Network server receives the alarm, it will first store the content in IPFS, and then send an alarm notification to the preset alarm channel of the subscriber (E-mail, Telegram robot, webhook, etc.).
Forta Network will allocate 400,000$FORT tokens every week to reward qualified scanning nodes in the network, which is also the main way of token output at present.
The current distribution of tokens is as follows:
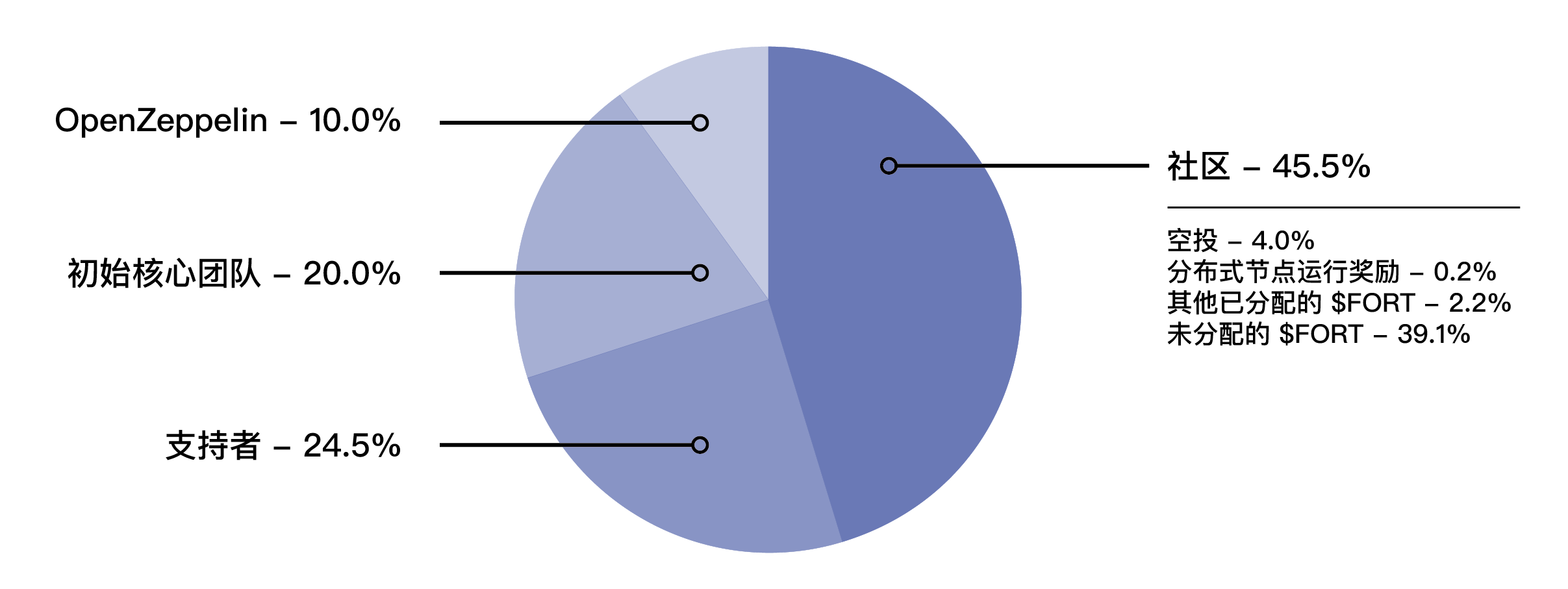
image descriptioncommunity allocationandand
Early Contributor AllocationCommunity distribution:Community distribution includes rewards in the early network test phase, early test airdrops and a series of reward distributions in the future, currently held by the foundation
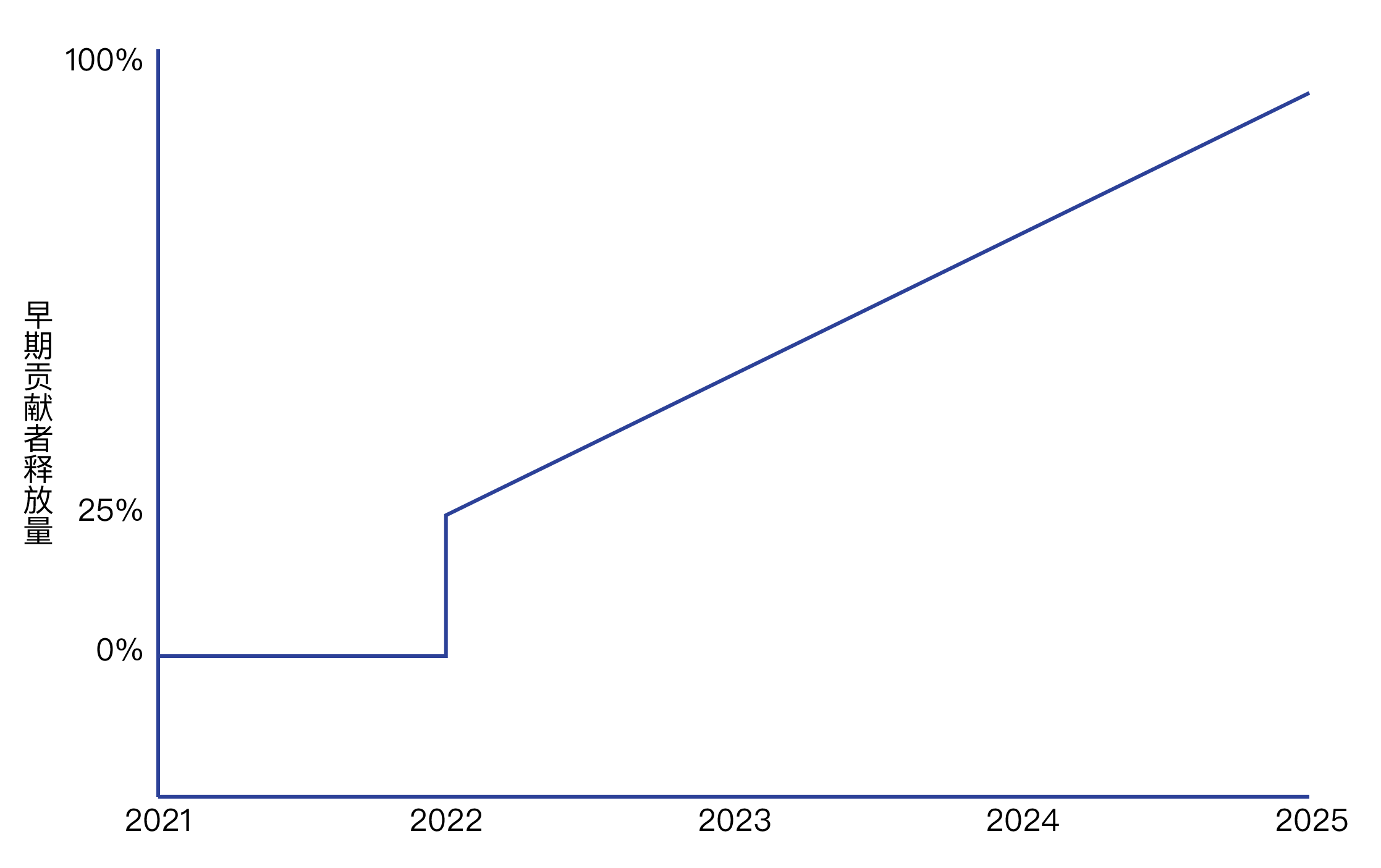 . In principle, there will be no mandatory lock-up or transfer restrictions for the part allocated by the community, but in order to ensure the long-term alignment of interests of the community, some recipients of community allocation need to agree to some restrictive terms. For example out of the 2.2% allocated, about 1.2% of the tokens will have a 2 to 4 year limit. For the principle of fairness, the community distribution part will not have any intersection with early contributors. That is, those who get early contributors will not have community allocations.Early Contributors: Early Contributors mainly include Supporters, Initial Core Contributors and OpenZeppelin. Supporters refer to community members who provide Forta with, but not limited to, funding, network, and node support in the early stages of the project. Core contributors refer to the developers who first worked on OpenZeppelin and participated in Forta Network. They have obtained 20% of the total tokens. OpenZeppelin, as the parent company incubating Forta Network, will receive 10% of the total tokens. All early contributors will accept3. Development
. In principle, there will be no mandatory lock-up or transfer restrictions for the part allocated by the community, but in order to ensure the long-term alignment of interests of the community, some recipients of community allocation need to agree to some restrictive terms. For example out of the 2.2% allocated, about 1.2% of the tokens will have a 2 to 4 year limit. For the principle of fairness, the community distribution part will not have any intersection with early contributors. That is, those who get early contributors will not have community allocations.Early Contributors: Early Contributors mainly include Supporters, Initial Core Contributors and OpenZeppelin. Supporters refer to community members who provide Forta with, but not limited to, funding, network, and node support in the early stages of the project. Core contributors refer to the developers who first worked on OpenZeppelin and participated in Forta Network. They have obtained 20% of the total tokens. OpenZeppelin, as the parent company incubating Forta Network, will receive 10% of the total tokens. All early contributors will accept3. Development
3. Development
3.2 Status

3.2 Status
text
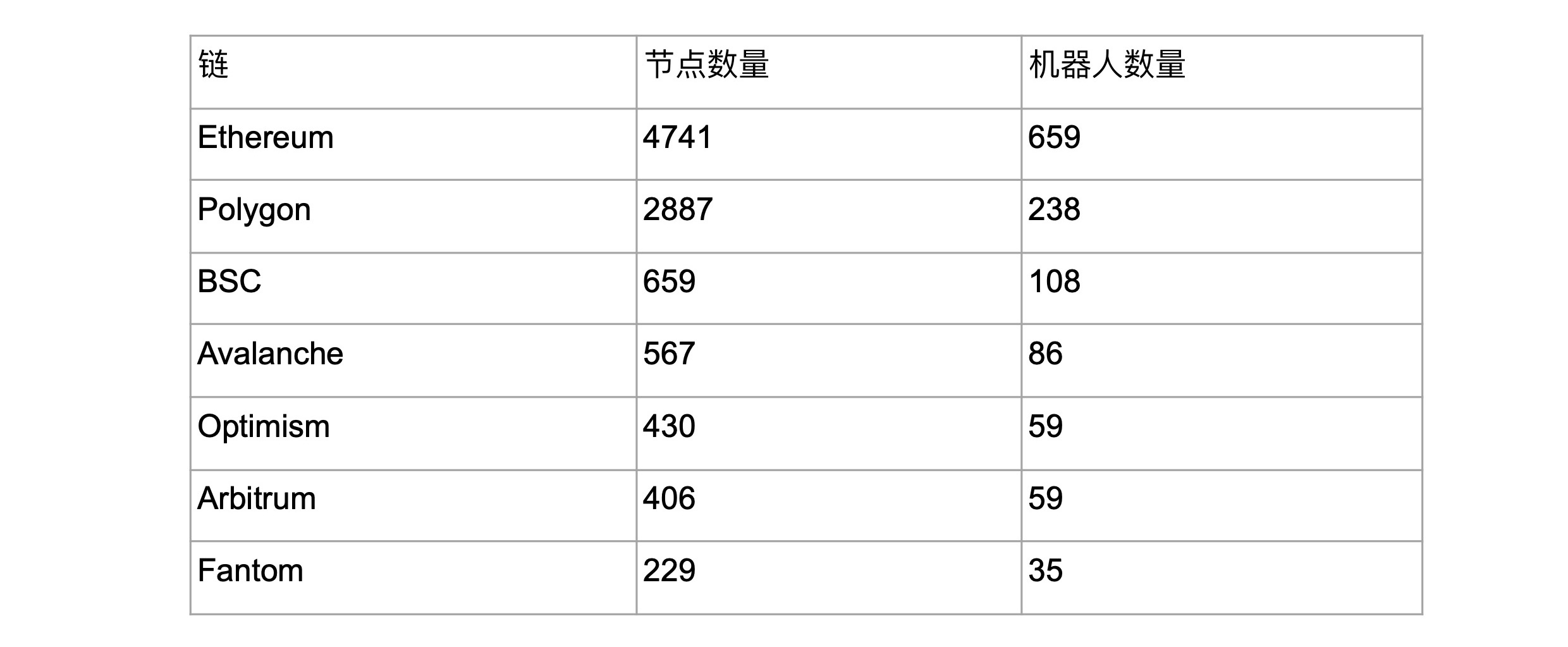 As of September 9, 2022, Forta Network has a total of 9,949 complete nodes and 1,243 robots, monitoring 7 chains including Ethereum, Polygon, and BSC.
As of September 9, 2022, Forta Network has a total of 9,949 complete nodes and 1,243 robots, monitoring 7 chains including Ethereum, Polygon, and BSC.
text
3.2.2 Revenue status of network nodesNode income in Forta Network is a major source of $FORT circulation release.400,000$FORT tokens allocated to each chain is different, but each node will be allocated differently according to network conditions to achieve enough nodes available on each chain to prevent the number of nodes in some chains from being too low or resource overflow. As of September 5, 2022, a single node with an SLA score of 1 can earn about 57 $FORT per week. The monthly cost of renting a server on Contabo according to the official minimum requirements for nodes is $12, plus the current currency price is $0.23, and it can be roughly calculated that the current Apr of a single node is about 242.9%. After September 30, 2022, the minimum pledge amount of a single node will be increased to 2500$FORT. According to statistics, the current total network pledge plus $FORT for the withdrawal freeze period is 7 million. After 30 days, it is still a valid pledge, so the maximum number of nodes in the entire network is 2800. Assuming that the proportion of the number of nodes on each chain is consistent with the proportion of reward distribution, a single node with an SLA score of 1 can obtain about 142$FORT per week, and Apr is roughly estimated to be about 218%.
text
3.2.3 Usage
Inspired by the Forta Foundation, the Forta Network has a series of bots that have been built and released on the network. These robots can be directly subscribed by users, and quite a few projects have adopted Forta Network to ensure their own security, such as dYdX, Lido, Maker DAO, Polygon, Gnosis and Balancer. At the same time, Forta Network can also monitor many well-known Dapps. Some projects that can be directly subscribed to monitor are listed below (data source: Forta official website)
Decentralized exchanges: Uniswap, Curve, Dodo, dYdX, PancakeSwap, Balancer, Perpetual Finance, ApeSwap
Lending category: AAVE, Alpaca Finance, Benqi Finance, Compound, Maker DAO, Umee
Others: Ethereum Merger, Poly Network
4. Competition
4.1 Industry Overview
text
A monitoring system generally refers to a computerized control system with the ability to monitor programs and collect data. Mostly used in industrial processes, infrastructure or equipment. In software engineering, some centralized monitoring systems are often used to monitor and error alarm their own programs. Standardized monitoring systems like Prometheus have been widely used in the Internet industry, and some cutting-edge projects in the Web3 industry often use standard monitoring systems like Prometheus to monitor nodes.
text
The biggest difference between Web3 monitoring and Web2 monitoring is that Web3 needs monitoring to cover applications in a timely manner. The reason why Web3 needs to be covered in time lies in the fact that the data on the blockchain cannot be tampered with. Assuming that a vulnerability in the service in Web2 is exploited, but the database and business logic codes are hosted on the server under the control of the project owner, generally speaking, there will be no irreversible loss of assets, because the project owner will Data can be changed on its own, preventing asset loss. However, Web3 applications are generally built on a decentralized network, and it is very difficult for nodes in the network to reach a consensus on rolling back data. It is almost impossible for something similar to the 2016 DAO event to directly roll back data stolen from Ethereum, which means that theoretically, the loss of assets on a decentralized network will be permanent. Therefore, Web3 applications have much higher requirements on the timeliness of monitoring than Web2 applications.
text
4.1.3 How monitoring can prevent asset loss
Generally speaking, after the monitoring detects an event that the user pays attention to, it will trigger the behavior specified by the user. Generally, the behavior that users may specify is email notification, but in fact this behavior can be customized. Assuming an external monitoring is used, the user can use webhook as the specified behavior, and when the alarm detects an event, the user can trigger the pre-set defensive measures through the webhook. Here is a simple example of monitoring to prevent asset loss:
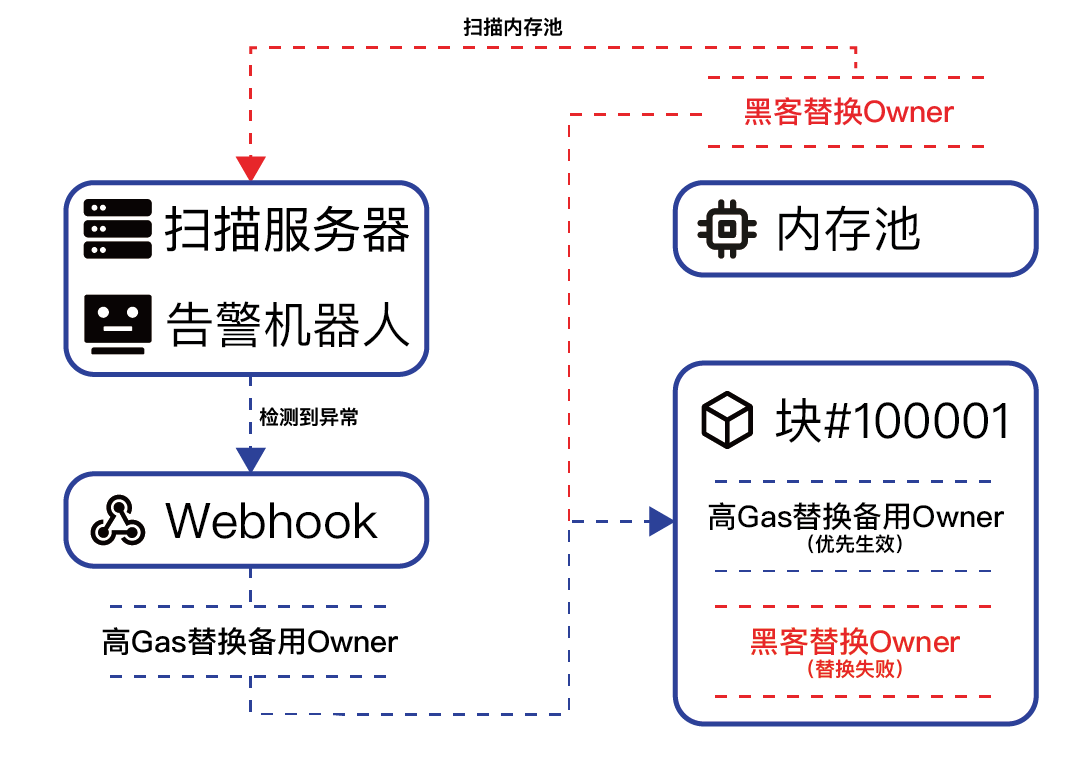 Although the above example generally illustrates how the monitoring system works and takes defensive measures, although the actual situation will be much more complicated than the example, this basic framework cannot be avoided.
Although the above example generally illustrates how the monitoring system works and takes defensive measures, although the actual situation will be much more complicated than the example, this basic framework cannot be avoided.
text
4.1.4 Classification of monitoring systems
At present, the Web3 industry monitoring system can be roughly divided into two modes: centralized and decentralized.
The advantage of a monitoring system built with a decentralized model is that it can motivate monitoring robot developers at the network level, prompting more developers to spontaneously build an ecosystem together, and achieve timely coverage of monitoring needs. But the disadvantage is that it is more difficult to formulate incentive methods at the network level.
secondary title
4.2 Competitive Product Analysis
For monitoring systems, there are usually several core points for product horizontal comparison:
Functional completeness: whether the monitoring type is comprehensive
Configurability: configurability of monitoring thresholds (specifically, out-of-the-box monitoring types)
Scalability: Whether it is possible to monitor a contract or function separately, and whether it is convenient to add the same type of monitoring
Availability: High availability of the monitoring system
text
Here are a few featured and widely used on-chain monitoring products for comparison
Epns、Hal、Tenderly

image description
The above figure can clearly reflect the focus of different products
Forta: The advantage is that the monitoring function is relatively complete, and it is relatively easy for 0-based users to customize monitoring based on existing templates. Benefiting from the incentive mechanism on the decentralized network, the development of monitoring types for different types of on-chain behavior is very timely. Also because the network model is a decentralized model, system availability is guaranteed to a certain extent. The disadvantage is that the alarm robot cannot be parameterized. The specific thresholds of words such as "large amount" and "abnormal" are completely defined by the alarm robot developer. Although the network model of Forta Network is decentralized, there are still some functions that need to be completed by centralized servers, which poses hidden dangers to the high availability of the system.
Epns: Epns pays more attention to the monitoring of personal wallets. The advantage is that when subscribing to major applications, you can directly send relevant reminders by viewing the attention content of personal wallets. For example, subscribing to Snapshot will directly remind new proposals based on the wallet’s attention list, eliminating The cost of individual configuration by the user. The disadvantage is that the monitoring content is less, and the function update is not timely.
Hal: The advantage is that the existing basic functions of DeFi and NFT monitoring have been developed, and there are ready-made monitoring for a series of indicators such as liquidity, loan/deposit rate, token price, large transaction volume, and on-chain loan mortgage rate . Hal can also configure some parameters for the above indicators, which is a bright spot compared to Forta Network subscribers who cannot modify the specific thresholds of "large amount" and "abnormal". The disadvantage is that Hal relies more on its own developers for the development of various monitoring, which is not time-sensitive.
From a product perspective, although Forta Network is difficult for subscribers to configure monitoring, the existing alarm robot threshold may not be suitable for some project owners to carry out custom monitoring. However, due to the existence of decentralized network incentives, there is bound to be a group of developers willing to customize parameters according to the needs of subscribers. Also with the development of Forta Network, the parameter configuration of the alarm robot will also be developed.
secondary title
Although Web3 security has been mentioned for many years, and a series of behaviors related to asset security such as contract auditing and code open source are increasingly valued by users, the current Web3 security track is still in a very early stage. Well-known projects such as dYdX and Lido have adopted Forta, which shows that the security defense of Web3 must be an unavoidable topic in the future blockchain compliance. At the same time, there are still a large number of projects that do not use monitoring methods to ensure contract security, which also shows that the incremental market for the security track is a very large number. OpenZeppelin launched Forta in 2021, which shows that it has already aimed at this blue ocean . Just as OpenZeppelin has led the contract development standard of Ethereum evm in the past four years, I believe that with Forta's forward-looking OpenZeppelin can also lead the standard of Web3 industry security solutions in the future.
first level title
5. Risk
1) Decentralized network does not have enough incentives for alarm robots
At present, there is no incentive for the development of alarm robots on the Internet. The current source of incentives is the robot development competition held by the Foundation and Gitcoin donations. From this point of view, Forta Network’s decentralized network has not played its strengths, but in recent months, the community has also discussed the incentives for robot development. Forta developers also attach great importance to this proposal, and I believe that it will be launched in the near future. incentive mechanism.
2) The industry has insufficient awareness of the importance of safety
Different from DeFi, public chain, Layer 2 and other tracks that directly or indirectly improve the upper limit of ordinary user experience, security is a track that improves the lower limit. When the entire industry is in a state of frenzy, everyone pays more attention to where the upper limit of the blockchain is, rather than paying attention to its lower limit. The importance of a safe track is likely to take a long time to wait for the industry to discover.
In the FP-3 voting that ended on September 17th, approximately 51.03% of $FORT was voted against, resulting in the rejection of the FP-3 proposal. This is uncommon in large communities where most votes end with one party having more than 70% of the votes. Although this to a certain extent reflects the community's concern for the project, it also shows that the two parties with different opinions in the community have a greater conflict of interest, which may hinder the progress and development of the project to a certain extent.
References
References
Forta Network official informationhttps://docs.forta.network/en/latest/
Official documentation:https://explorer.forta.network/network
Network statistics:https://github.com/forta-network
Team GitHub homepage:https://twitter.com/FortaNetwork/status/1567591457531527170?s=20&t=LbAJO2Tv7TWOqtBibinhKQ
Historical events:https://docs.forta.network/en/latest/governance/
《Forta》:https://blockchain.capital/forta/
Composition of the team management committee:https://a16z.com/2021/09/30/investing-in-forta/
Financing Information:https://dune.com/Sector920/forta
Forta network statistics:https://snapshot.org/#/forta.eth
Forta community proposal:
A unique and irreplaceable institution dedicated to the emerging frontier of crypto.



