Xiao Sa's team: China's NFT industry legal risk research report · 2022
Original source:first level title

foreword
foreword
Undoubtedly, 2022 is still the golden age for the development of China's NFT digital collection industry, but compared with 2021, when the entire industry is growing wildly, a series of new changes are about to appear, and these new changes will be mainly reflected in two aspects: (1) Further expansion of NFT applications; (2) Further improvement of legal norms.
In terms of the application of NFT, although various uses including digital collections, social avatars, identification, equity certificates, brand IP, GameFi props, etc. have been developed overseas, the casting and distribution of traditional digital collections are still used in the Chinese market. , Transaction-based. NFT products in China's mainstream market are mostly issued on the alliance chain, and Token cannot be mentioned in one's own wallet. This is the biggest difference between China's NFT market and overseas markets. Although the centralization and data security of the alliance chain have been criticized for a long time, in fact, we should also see that the open market of overseas NFT has brought various hidden dangers such as improper speculation, knock-on transactions, financial risks, and money laundering. Let go blindly, hard to say good or bad. There is no doubt that diversified NFT applications are bound to be the general trend in the future, but how to safely and comprehensively utilize the intrinsic value of NFT to promote economic development still needs to be done step by step. We believe that with the development of blockchain technology, NFT has great potential in current product traceability, certificate storage and identification.
China's NFT digital collection industry is facing unprecedented challenges, and whether it is well compliant is related to the life and death of a platform.
01 Overview of NFTs
secondary title
1.1 What is NFT
The full name of NFT is non-fungible Token, and the literal translation of the Chinese name is "non-fungible token". NFTs are special tokens minted from the blockchain as representations of digital or non-digital assets. We can use NFT to confirm and record the ownership of a specific item, including but not limited to: music, video, text, images, games, artwork, tickets, real estate, etc.
According to FATF's "Updated Guidance for a Risk-Based Approach to Virtual Assets and Virtual Asset Service Providers" (Updated Guidance for a Risk-Based Approach to Virtual Assets and Virtual Asset Service Providers), for NFT, FATF has given a definition: digital assets are unique (unique), Rather than being interchangeable, and actually used as collectibles rather than payment or investment tools, they can be called "non-homogeneous assets" (NFT) or "crypto-collectibles" (crypto-collectibles) ).
secondary title
1.2 History of NFT development
1. 1993 - Crypto Trading Cards
Andrew Steinwold pointed out in the article "the history of non-fungible tokens nfts" that in 1993, Hal Finney (the first senior cryptography expert to receive Bitcoin from Satoshi Nakamoto, a Bitcoin pioneer) shared an interesting concept , The method of displaying the digital cash you own can be done through "encrypted trading cards". This encrypted trading card shall be a mixture of one-way functions and digital signatures and random blinding. This is the earliest explanation and idea about NFT that can be found in public channels. Although its logic is similar to that of the collectible card game, its expression is based on the presentation of cryptography and mathematics, and then randomly arranged to form a series. set of cards, which Hal defines as "encrypted cards".

(Memorable Hal Finney 1956 - 2014)
text
2.2014 - Colored Coin (Colored Coin) was born as a pioneer of NFT
Andrew Steinwold pointed out in the article "the history of non-fungible tokens nfts" that Colored Coin is the pioneer and prototype of NFT. Because they expand the practicality of the Bitcoin blockchain, they directly promote the huge development of the Bitcoin blockchain. Leap forward, prompting Bitcoin to enter the 2.0 era. Colored Coin is a record of real-world assets on the blockchain. We can use Colored Coin to prove ownership of any physical asset, from precious metals to cars to real estate, stocks and bonds, and Colored Coin is very easy to mint and issue.
The earliest mention of Colored Coin was in "bitcoin 2.X (aka Colored Bitcoin)" by Yoni Assia.
— initial specs" article. In this article he discusses what Colored Coins are, emphasizing that "Since Colored Coins are part of the "Bitcoin Blockchain Genesis Transaction", these tokens are unique and can be obtained from regular Bitcoin transactions." Identify. On December 4, 2012, Meni Rosenfeld published a paper titled "Overview of Colored Coins", when the potential of Colored Coins to determine the ownership of objects seemed to be realized.
In 2013, Yoni Assia, Vitalik Buterin, Lior Hakim, and Meni Rosenfeld jointly published a paper titled "Colored Coins—BitcoinX", which further explored the feasibility of using Colored Coins to confirm the ownership of real assets.
Sadly, ColoredCoin didn't really catch on, nor was it widely used. The main reason is the creation of the Ethereum blockchain and the mass use of ERC-20 tokens. Coinprism, a platform providing Colored Coin wallets and services, announced its closure in early April 2018. Nevertheless, Colored Coin has laid a good foundation for the development of NFT. The design concept of NFT is almost the same. After a more scalable blockchain is born, NFT can become a reality.
3. 2017 - The Birth of Ethereum and the Ethereum Token Standard (ERC)
On the Ethereum blockchain, different types of tokens have different technical standards, so that the interaction of different tokens can be completed normally. According to the "Network of Ethereum Non-Fungible Tokens: Agraph-based analysis of the ERC-721 ecosystem" published by S. Casale-Brunet et al., the Ethereum ERC technical standard research paper, the full name of "ERC" is "Ethereum Request for Comment". . The most common ERC standard on Ethereum is ERC20, which has rules that allow tokens to interact in the intended way. This standard framework is useful for developers when creating tokens that need to interact with other tokens or applications on Ethereum. But ERC20 tokens are technically not the best choice for creating "unique tokens". For this reason, the ERC721 standard came into being. ERC721 Although similar to ERC20 in many ways, ERC721 was purpose-built as a technical standard for non-fungible tokens on Ethereum. The main difference between the two standards is that ERC721 can track the ownership of a single token in a block and its transfer path, which allows NFT to be distinguished from other homogeneous tokens (such as Bitcoin, etc.) with unique attributes . The first NFT project created using ERC721 technology is the famous CryptoKitties.
Andrew Steinwold pointed out in the article "the history of non-fungible tokens nfts" that in June 2017, two "creative technologists" John Watkinson and Matt Hall decided to use Ethereum to create their own NFT project. The duo realized they could create a unique digital artwork native to the Ethereum blockchain. The total number of these digital art flats is capped at 10,000 and varies. The project is called CryptoPunks, a tribute to the pioneers who influenced Bitcoin in the 90s by the two artists. The 10,000 digital artworks created in the CryptoPunks project are freely available to anyone with an Ethereum wallet. 10,000 Cryptopunks digital artworks were quickly claimed, creating a thriving Cryptopunk secondary market. Interestingly, Cryptopunks did not follow the current ERC721 standard for NFT, because the standard had not yet been invented at the time, but Cryptopunks digital artworks were not entirely ERC20, to be precise, they were a mixture of ERC721 and ERC20.
4. October 2017 - the birth of CryptoKitties NFT
It can be seen that CryptoKitties is a virtual game developed based on blockchain technology, which was launched in October 2017 by a company called Axiom Zen in Vancouver. The game allows players to adopt, feed and trade virtual digital cats that they breed (in fact, born on the blockchain). CryptoKitties became popular in Ethereum in just a few days, causing the entire network to become congested. A secondary market for trading CryptoKitties was quickly established, and the price of a rare cat was even fired into the hundreds of thousands of dollars. The rise of CryptoKitties coincided with the stock bull market in 2017. People frantically bought, bred, and traded virtual cats. The huge profits visible to the naked eye made many people see the potential of NFT. Axiom Zen then spun out a company called Dapper Labs, which raised about $15 million in funding from top investors including a16z and Google Ventures.

image description
(Crypto Kitties Schrödinger's cat)
image description

Beeple:《Everydays: The First 5000 Days》
secondary title
1.3 The value and legal attributes of NFT
1.3.1 Talking about the dual structure of NFT
The so-called surface structure refers to the pictures, music, video, etc. that we can directly see, hear, and feel through the platform. These pictures, audio and video located on the surface structure of NFT are electronic data that are easy to be copied, downloaded and collected. Some friends who are interested in well-made but expensive NFT, the most common simple method is to "take a screenshot and own it". Even the OpenSea official does not prohibit this kind of behavior. TokenID can be found in the Details of each digital collection. As shown in the figure below, we can easily obtain the original image of an on-chain NFT.
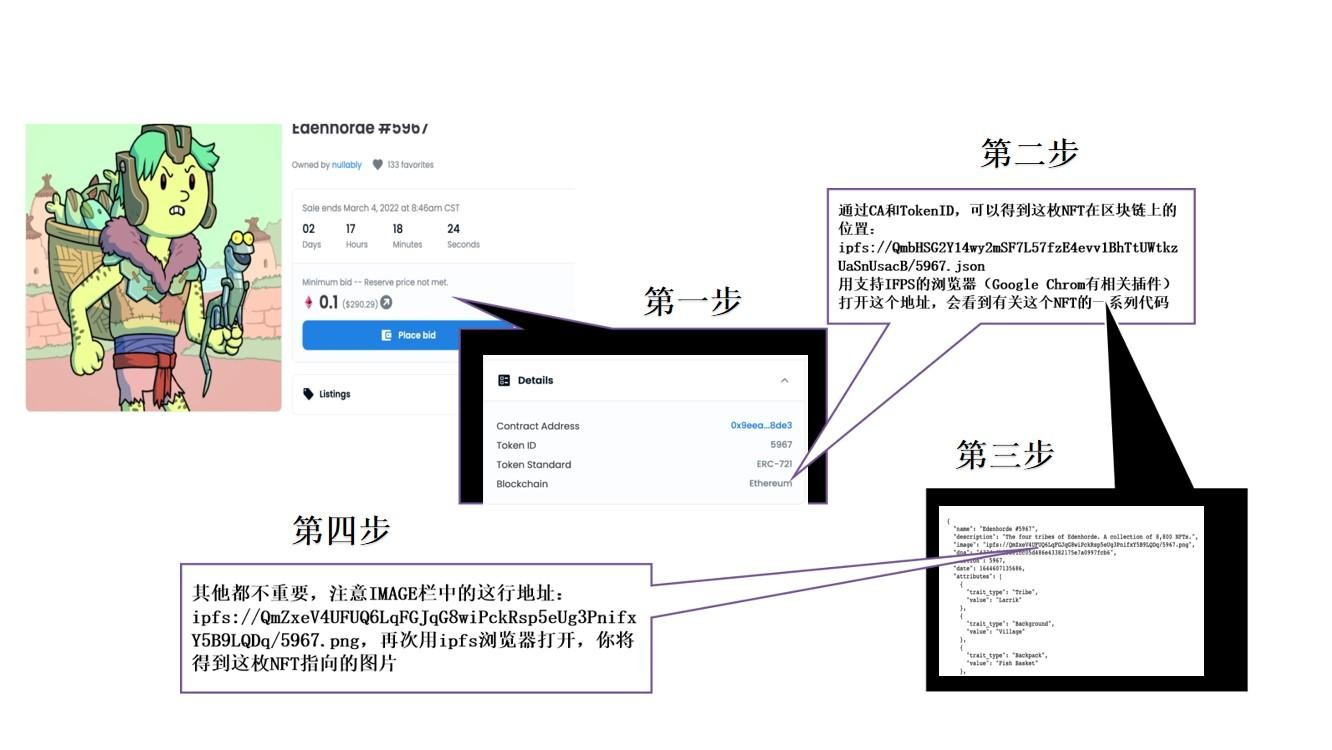
image description
The NFT comes from the official website of OpenSea, it is only for learning, and the copyright belongs to the author
The core structure refers to the private key we use to possess, use, transfer, and dispose of NFT. The private key is essentially a string of data, and only the person who has mastered this string of data is generally considered to be the owner of the NFT.
The current key point is that due to the easy duplication of pictures, audio and video, no matter whether we buy NFT or not, anyone can download the surface resources of NFT at will, and there is no scarcity. And as long as you want, you can use these pictures as your desktop wallpaper or mobile phone ringtone without paying, and even the NFT owner has no way of knowing. According to this, the negotiability and scarcity of NFT seem to be brought about by the private key of the kernel structure, which is very similar to virtual currency.
1.3.2 Looking at the legal nature of NFT from the dual structural value system
Obtaining an NFT does not necessarily mean that it has obtained the copyright of the image, audio and video pointed to by the NFT. For example, NBA Top Shot clearly states that NFT holders do not have copyright to the NFT itself. But there are also NFT projects such as BAYC (Boring Ape Yacht Club), which allow holders to enjoy complete copyright property rights and use their NFT for any commercial purposes. From this point of view, the value of NFT largely depends on how the project party operates and what kind of marketing ideas it adopts. Of course, a thousand project parties have a thousand Hamlets in their hearts, which also makes the legal nature of NFT more complicated.
The pictures, audio and video as the surface structure give NFT transaction (use, viewing) value to a certain extent, but to a large extent, what really gives NFT scarcity is the key as the core structure. In this sense, NFT It is not much different from Bitcoin, Tether, etc.
Therefore, we can draw the following conclusions from the dual attributes of NFT:
(2) Although the private key in the NFT core structure has data appearance, it is completely different from traditional information network data. The acquisition and use of data is not exclusive. However, the code of NFT is unique and exclusive, and it is more of a property right nature, which also determines that from a legal perspective, the "uniqueness" and "non-homogeneity" of NFT are realized by a specific combination of data Yes, the person's possession of this specific set of data forms a specific set of "quasi-property" legal relationships.
secondary title
1.4 Sinicization of NFT: digital collections, harmony but difference
1.4.1 How did NFT become a digital collection?
In 2021, the "Notice on Rectifying Virtual Currency "Mining" Activities" jointly issued by ten Chinese ministries and commissions
The most fundamental difference between Chinese digital collections and NFT lies in the fundamental difference in value orientation and positioning. Since NFT itself has multiple value attributes, it is mainly developed and utilized at present as: (1) The value of ordinary virtual goods and digital artworks. NFT, which exists as an ordinary virtual commodity, is bound to real or virtual artworks, videos, pictures, etc., thus becoming a virtual commodity or digital asset that can be actually controlled by people and has a certain value; (2) a certain The value of a new type of financial instrument and financial product. Scarcity created by artificial means such as limited issuance, NFT, which undertakes the functions of investment and financing tools, equity certificates, etc., is endowed with a special financial value similar to stocks, futures, and securities, making it in a sense a The carrier of speculative profit and financial intermediation.

image description
Taking the digital collection of a large factory as an example, the holder cannot mention it to his wallet, but can only watch it
Based on these two value attributes, NFT has been developed including but not limited to: digital collectibles, social media avatars, brand ip, GamFi (chain game) props, various community and DAO organization rights certificates, metaverse identity certificates, Practical applications such as currency certificates.
In order to achieve the purpose of compliant survival, domestic digital collections to the greatest extent: (1) reduce the financial attributes of NFT; (2) draw a clear boundary with virtual currency. Try to limit the value, use and form of expression of NFT to the scope of ordinary virtual goods. To this end, many digital collection platforms have implemented a series of measures including using private chains or alliance chains to sell digital collections, not supporting the transfer of digital collections to private wallets, prohibiting secondary transactions, setting time limits for transfers, and sealing accounts to prevent hype.
1.4.2 What do we really buy when we buy digital collections?
The rights enjoyed by buyers of digital collections are significantly different from those of NFTs issued on overseas public chains. Under normal circumstances, what a complete NFT holder enjoys should be an exclusive, similar property right, with the right to possess, use, dispose of, benefit from, etc., but the holders of digital collections are different from this .
As a result, the digital collection platform has completed the transformation from NFT to digital collections, creating a first-line compliance development vitality for it in the narrow gap.
02 Development status of China's NFT market
secondary title
2.1 Overview of Industry Development

To explain the development trend of China's NFT industry is inseparable from the analysis of the world's NFT industry landscape. Since the concept of NFT was first proposed in 1993, the development of the world's NFT industry can be roughly divided into four periods, namely the seed period (1993-2017) , the budding period (2017), the construction period (2018-2020) and the rapid expansion period (2021-present). The symbolic time of each period is shown in the figure:
It should be said that the outbreak of the epidemic has become an opportunity for the development of NFT. Western countries have adopted loose monetary policies to stimulate the economy, making some investment plans unattractive. In terms of venture capital, more investors are more radical, which caused the cryptocurrency market at that time. Prosperity. In the NFT market, digital artist Beeple began to draw one picture a day in 2007, and finally stitched 5,000 photos together to form a JPG file, which was sold as an NFT and named "Everydays: The First 5000 Days" ( See section 1.2 above), and was successfully auctioned at Christie's auction at a price of US$69.34 million. After that, each artist released various NFTs through the NFT platform, which eventually became a symbolic event of the rapid expansion of NFTs.
Against the background of the hot global NFT market, leading domestic companies have also entered the NFT market one after another, such as Ali Auction and other NFT trading platforms. NetEase also launched NFT blind box products that year, and companies such as Vision China have also followed suit.
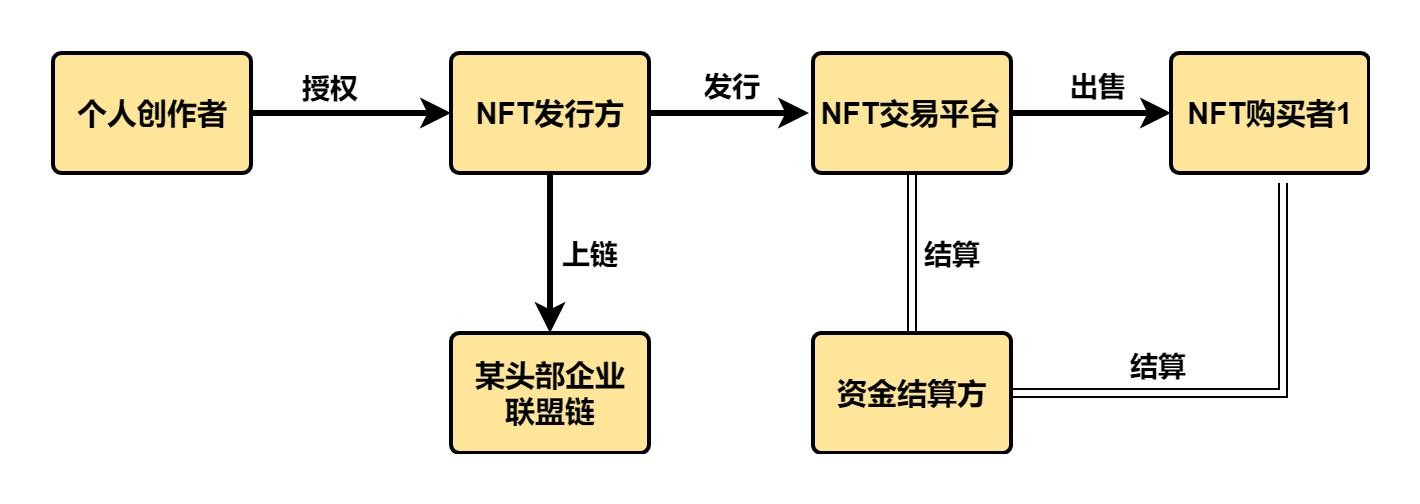
2.1.1 Industry chain map of China's NFT market
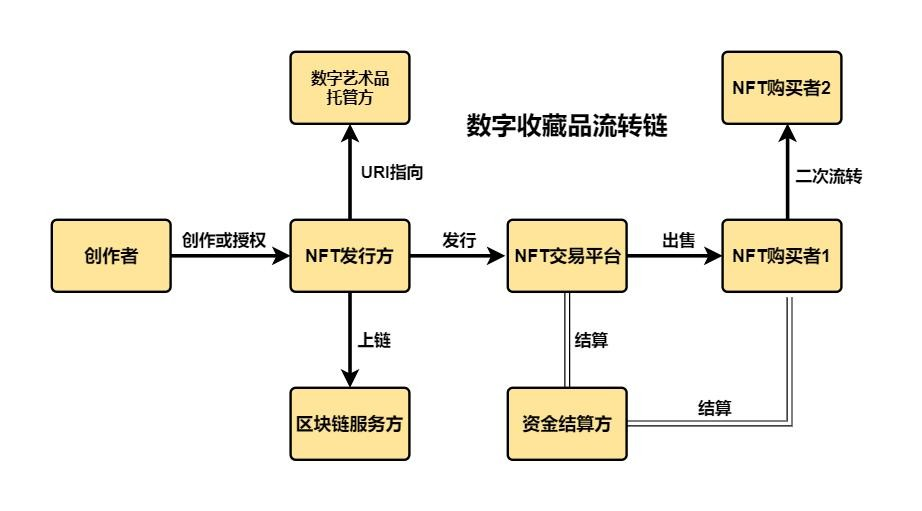 Before clarifying the industrial chain map of my country's NFT market, it is necessary to make a comprehensive picture of the NFT industrial chain. The following figure is a rough picture of the NFT industrial chain:
Before clarifying the industrial chain map of my country's NFT market, it is necessary to make a comprehensive picture of the NFT industrial chain. The following figure is a rough picture of the NFT industrial chain:
This picture roughly depicts the ecology of the entire NFT industry chain, in which creators and NFT issuers are at the core of the upstream of the industry chain; the core of the middle reaches of the industry chain is the NFT trading platform, surrounding NFT issuers and peripheral service parties outside the NFT trading platform. It is an integral part of the middle reaches of the industrial chain, which mainly includes industries such as fund settlement parties and blockchain service providers; the downstream of the industrial chain is mainly NFT buyers. ,
Analyzing my country's NFT market from the perspective of this industrial chain division, the following conclusions can be roughly drawn:
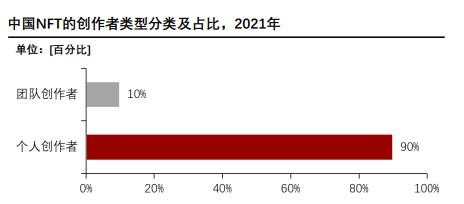
①The creators in the upper reaches of my country's NFT market are currently dominated by individuals. In 2021, the proportion of NFT creators dominated by individuals will exceed 90%, and team creators will only account for 10%
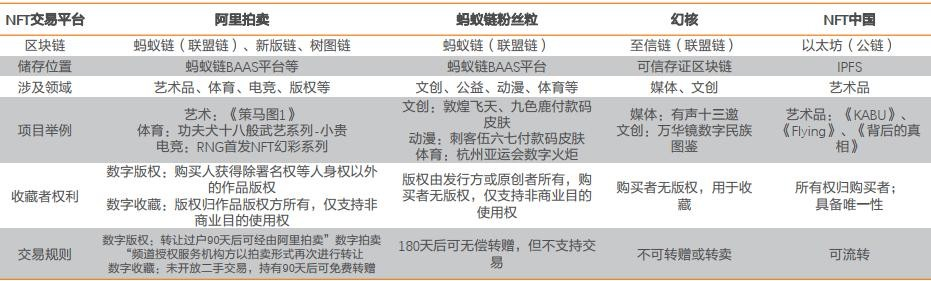
②The trading platforms in the middle reaches of my country's NFT market are currently showing a situation where multiple strengths stand side by side. The mainstream platforms include Ali Auction, AntChain Vermicelli and Magic Core. From the perspective of blockchain and other underlying services, my country's NFT market and foreign countries also show significant growth. Different, the Chinese market is mainly dominated by alliance chains such as Ant Chain and Chang'an Chain.
③The buyers in the downstream of my country's NFT market industry chain are mainly first-level buyers, which is related to my country's financial risk supervision of the NFT industry. From the perspective of age composition, the downstream buyers are mainly post-80s and post-90s.
As of April 2022, the trend of traditional consumer companies entering the domestic NFT market has become very obvious. At the same time, blockchain games and metaverses will drive the expansion of the NFT industry in the future. With the release of the three associations' initiative, my country will gradually establish and improve NFT Relevant trading rules, under the premise of ensuring that financial risks are controllable, should also be optimistic about the gradual opening of the NFT secondary market.
secondary title
2.2 General form of domestic NFT digital collections
2.2.1 NFT in the direction of digital cultural creation

A typical representative of this kind of NFT digital collection is Tencent's "Magic Core" APP. The "Magic Core" APP has focused on digital cultural and creative products from the very beginning. Due to the "non-reproducibility" of the works, the digital collection platform can also allow fans to truly obtain and permanently The ritual sense of collecting a collection coincides with the cultural attributes of digital cultural and creative products. The road to cultural and creative products can be said to be the mainstream choice in my country's NFT market at present. In addition to the "Magic Core" APP, the NFT series of "Guochao Forbidden City Ice Fun Picture" also achieved great success during the Winter Olympics.
2.2.2 NFT+ blind box
A typical representative of this is the NFT blind box launched by Netease. On July 12, 2021, the "NARAKA HERO" series of NFT blind boxes authorized by NetEase's game "Eternal Tribulation" IP will be launched. Each blind box will randomly generate a card with three card qualities. Players can purchase Multiple NFT blind boxes to collect cards. This type of business model will also be imitated by many NFT companies in 2021 and 2022, and the form of NFT + blind box has also become one of the main business models in my country's NFT market.
A typical representative of this model is Visual China. NFT often uses a piece of encrypted code as a proof of ownership of digital art assets. NFT works of art will use smart contracts to form a flexible and effective partnership with creators. Creators can still create and sell NFT works through the blockchain. Encryption technology is used to realize the confirmation and traceability of ownership, which will greatly stimulate the creative motivation of creators. The 500px community under Visual China will empower creators to create NFT works of art in various aspects such as technology and operation, assist them in synchronously packaging images and video works into NFT assets on the chain, and store, promote and sell their works for creators. The work provides one-stop service and becomes a typical representative of the NFT+ copyright trading model.
secondary title
2.3 Case studies
Now use a domestic NFT trading platform as a template to show the NFT transaction process in the form of a case. In order to protect business privacy, the platform name is omitted here.
2.3.1 Trading features of the platform
The development model of the NFT trading platform is a spot listing model, which has the following characteristics:
①Adopt full goods and full payment, listing and delisting, one-to-one real-name transaction, T+5 transfer mechanism, and abandon centralized trading activities such as electronic matching;
② With physical goods + digital copyright as the transaction object, the mode of ensuring physical goods and digital copyrights can maximize the protection of digital collection collectors with the six determination processes of confirmation of rights, confirmation of authenticity, confirmation of price, confirmation, confirmation of continuation, and confirmation of order Benefit;
③ There are no behaviors such as using standardized contracts as transaction objects and centralized transactions;
2.3.2 NFT transaction flow chart of the platform
03 China's NFT Industry Supervision Status
secondary title
3.1 Overview of the status quo of NFT industry supervision
So far, China has not formulated corresponding norms for digital collections. It has not clearly identified digital collections, nor has it regulated and supervised relevant trading platforms. It is still blank at the level of laws and regulations. At present, the official regulations related to NFT and digital collections Documents only include risk warnings, initiatives, and self-regulatory conventions.
On the policy side, there are mainly the following regulatory constraints: the risk of virtual currency speculation, the Chinese government has always supervised the virtual currency; in terms of secondary transactions, according to the guidelines of Guofa [2012] No. 37 and Guobanfa [2011] No. 38, the country There are strict restrictions on the trading platform; in addition, issues such as the confirmation of NFT rights and copyright protection outside the financial attributes of NFT are still unclear.
3.1.1 Prevent the risk of hype
There is no relevant law in China to clarify whether NFT is a security. Compared with FT, NFT cannot interact and divide each other, but there are still platforms that use NFT to speculate on virtual currency, which may face problems such as illegal fundraising, so it cannot be completely denied that NFT has the nature of tokens . my country's crackdown on virtual currency is very severe, and the development path of NFT in China is more inclined to explore a kind of currencyless, emphasizing the certificate attribute of NFT as a digital asset, and paying more attention to issues such as copyright protection.
In December 2013, the People's Bank of China, the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, and the China Banking Regulatory Commission issued the "Notice on Preventing Bitcoin Risks", clarifying that Bitcoin is a specific virtual commodity and has no legal equivalent to currency. status, cannot and should not be used as a currency in circulation in the market. However, bitcoin trading is a kind of commodity buying and selling behavior on the Internet, and ordinary people have the freedom to participate at their own risk; it is stipulated that various financial institutions and payment institutions shall not use bitcoin as a product or service price, and shall not buy or sell or serve as a central Counterparties shall not directly or indirectly provide customers with other bitcoin-related services when buying or selling bitcoins. In September 2017, the People's Bank of China, the Central Cyberspace Affairs Commission, the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, the State Administration for Industry and Commerce, the China Banking Regulatory Commission, the China Securities Regulatory Commission, and the China Insurance Regulatory Commission issued the "Announcement on Preventing the Risks of Token Issuance and Financing", clarifying that token issuance and financing are essentially An act of illegal public financing without approval is suspected of illegal sale
Illegal and criminal activities such as token coupons, illegal issuance of securities, illegal fundraising, financial fraud, and pyramid schemes; it is stipulated that no organization or individual shall illegally engage in token issuance financing activities. In September 2021, the National Development and Reform Commission, the Central Propaganda Department, the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology of the Central Cyberspace Administration, and the State Administration of Taxation issued the "Notice on Rectifying Virtual Currency "Mining" Activities", announcing that virtual currency "mining" activities It will be officially listed as an eliminated industry. In September 2021, the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, the Ministry of Public Security, and the Ministry of Market Supervision of the Supreme People's Procuratorate issued the "Notice on Further Preventing and Dealing with the Risk of Hype in Virtual Currency Transactions", clarifying that virtual currencies such as Bitcoin and Ethereum do not have the same value as legal tender. Equivalent legal status: related business activities are illegal financial activities; overseas virtual currency exchanges providing services to residents in my country through the Internet are also classified as illegal financial activities. In March 2022, the Supreme People's Court revised the "Interpretation on Several Issues Concerning the Specific Application of Law in the Trial of Criminal Cases of Illegal Fund-raising", and added virtual currency transactions as an objective manifestation of crimes related to illegal fund-raising.
According to the operating mode of the existing overseas NFT trading platform, the Ethereum it relies on is a platform for paid use, and corresponding fees need to be paid for uploading NFT works to the chain, and buyers usually need cryptocurrency to pay for the purchase of NFT works. Therefore, if NFT transactions are carried out according to the existing model, whether it can be priced in cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin and Ethereum, and how domestic creators and buyers obtain and legally use cryptocurrencies are also legal concerns. Since my country has always adopted a strict regulatory attitude towards cryptocurrencies and virtual currencies, almost without exception, domestic NFT platforms draw a clear line from virtual currencies. In terms of future regulation, preventing the risk of virtual currency speculation is still the top priority in the work. In order to maintain the stability of the economic order and financial order, it is the key to maintain the healthy development of the digital collection industry to prevent NFT from being "broken" with virtual currency, so as to derive some new gameplay and new tricks.
3.1.2 Restrictions on exchanges
From 2011 to 2012, the state cleaned up and rectified the irregular trading market. If secondary transactions are involved, the trading market needs to follow Guofa [2011] No. 38 "Decision of the State Council on Cleaning up and Rectifying Various Exchanges to Effectively Prevent Financial Risks" and Guobanfa [2012] No. 37 "State Council General Office on Cleaning Up Implementation Opinions on Political Rectification of Various Stock Exchanges. The core points of these two documents are as follows: first, the establishment of the exchange must be approved by the relevant departments of the State Council in accordance with the law; The number of holders shall not exceed 200; three, centralized trading methods such as centralized bidding, electronic matching, anonymous transactions, and market makers are not allowed to conduct standardized contract transactions; four, continuous trading is not allowed, and the trading cycle is T+5. To sum up: If NFT is recognized as a financial product, it must have a corresponding exchange transaction and must hold a relevant financial license. On this basis, the number of holders of NFT products cannot exceed 200, and standardized contract transactions are not allowed. Relatively speaking, it is more difficult to establish a new exchange on the NFT platform, which needs to be approved by the State Council or the financial management department of the State Council. The issuance of new financial licenses is even more difficult for traditional financial institutions.
NFT issuance and trading must avoid splitting, centralized trading and other behaviors that encourage speculation, otherwise related products will be removed from the shelves under supervision. In terms of domestic specific cases: the NFT skins of Dunhuang Flying Apsaras and Nine-colored Deer jointly released by a head platform and a certain academy of fine arts, each priced at 10 points plus 9.9 yuan, with a global limit of 8,000 copies each. After the NFT was released, it was even hyped to millions of yuan on the second-hand trading platform, and then the platform quickly took the NFT product off the shelves, and declared again that NFT is not a virtual currency. Since then, the platform has restricted the secondary transfer period of NFT products on the platform, and the NFT buyer who has been transferred must hold the NFT for a certain period of time before transferring it again. This case also proves once again that the opening of the NFT secondary market actually greatly increases the risk of its speculation, which may affect financial security and stability, and even disrupt financial order. Mainstream Internet platforms adopt the form of prohibiting secondary transactions, mainly to prevent the risk of speculation and weaken the financial attributes of digital collections.
3.1.3 Existing problems in NFT confirmation and copyright protection
By purchasing NFT digital artwork, NFT buyers may only obtain the ownership of the digital asset, but the NFT casting process has no restrictions on the artwork itself or the copyright itself: 1) NFT issuers may infringe the reproduction rights of other people's works , distribution rights and information dissemination rights; 2) The blockchain can trace information on works that have been uploaded to the chain, but the artwork or copyright before casting cannot be confirmed. At present, most of the NFT creators in China are individual creators, and native digital artworks account for 90%. At present, the relevant rights confirmation of NFT digital collections in China has not yet been in place. If NFT is combined with the traditional art collection industry, the evaluation process of artworks and other related collections still lacks the supervision of a tripartite neutral agency.
To give a typical case related to NFT copyright confirmation, Caixin Weekly published a special report
Since NFT projects are basically created by creators, for most NFT platforms, there are users uploading infringing, illegal offensive or other destructive content. Therefore, although the platform can restrict this uploading behavior through user agreements, it will be more effective to take technical measures to detect and delete prohibited content. Otherwise, the sheer volume of banned content can deter users and draw regulatory scrutiny.
secondary title
3.2 Multi-dimensional analysis of NFT industry regulation
3.2.1 NFT platform
In the NFT industry, NFT platforms often play multiple roles. From the perspective of platform operation, the operator of the NFT platform provides users with blockchain information services involved in digital collection transactions, and provides a platform for NFT artwork casting and operation for original artwork rights holders; from the perspective of blockchain technology , platform operators need to cooperate with platform technology developers to provide users with the technologies involved in accessing, sharing, and purchasing digital collection platforms. Generally speaking, the technology developer will also provide technical support services such as operation and maintenance for the platform operator; from the perspective of digital collection transactions, according to the transaction mode, there may be two situations in practice: the platform operator does not participate in digital collection transactions The model: that is, the platform operator only provides the service of putting artworks on the chain and then casting NFT, and the platform itself does not participate in the transaction of digital collections. The model in which the platform operator directly participates in the transaction of digital collections: the platform may directly participate in the transaction of digital collections as an issuer after obtaining the authorization of the artwork owner, and the casting and selling of NFT artworks are all directly controlled by the platform operator. In this mode, the platform itself also participates in the transaction of NFT artworks as a party.
To sum up, NFT platforms play such an important role and are naturally subject to strict supervision. At present, there are no laws and regulations specifically regulating NFT platforms in my country, but after analyzing the multiple roles it undertakes above, NFT platforms are subject to my country's existing administrative management system, filing procedures, qualification review and other methods.
1. The NFT platform needs to conduct blockchain security assessment and filing
The existence of NFT is inseparable from the blockchain. According to Article 2 of the "Regulations on the Administration of Blockchain Information Services", the term "blockchain information services" in these regulations refers to the provision of information services to the public based on blockchain technology or systems through Internet sites, applications, etc. . The blockchain information service provider referred to in these regulations refers to the subject or node that provides blockchain information services to the public, and the institution or organization that provides technical support for the subject of blockchain information services; the blockchain information service provider referred to in this regulation Blockchain information service users refer to organizations or individuals who use blockchain information services.
The NFT platform may be identified as a blockchain information service provider. Therefore, according to Article 9, blockchain information service providers who develop and launch new products, new applications, and new functions shall report to the Internet Information Office of the country, provinces, autonomous regions, and municipalities directly under the Central Government for security assessment in accordance with relevant regulations. If you want to set up an NFT platform in the country, you need to conduct a security assessment in accordance with relevant laws and regulations, and according to Article 11, the blockchain information service provider should pass the National Internet Information Office within ten working days from the date of providing the service. The blockchain information service filing management system fills in the service provider's name, service category, service form, application field, server address and other information to perform the filing procedures. The platform can conduct the assessment by itself or entrust an assessment institution with corresponding qualifications, and submit a security self-assessment report through the national Internet security management service platform.
Other main obligations that need to be performed by the platform under the "Regulations on the Management of Blockchain Information Services" include that the platform needs to implement information security management responsibilities, have technical conditions suitable for its services, have technical solutions that comply with national standards, and have public Management rules and platform contracts, user real identity authentication, information recording and backup, etc.
2. The NFT platform needs to apply for the "Internet Information Service Value-Added Telecommunications Business License"
Article 7 of the Measures for the Administration of Internet Information Services stipulates that to engage in commercial Internet information services, an application shall be made to the telecommunications management agency of the province, autonomous region, or municipality directly under the Central Government or the information industry department of the State Council for an Internet information service value-added telecommunications business license.
As a telecommunications service provider, the NFT platform may be regulated by relevant telecommunications laws at that time. If the NFT platform is used as a platform for operating Internet information services, it may be necessary to obtain a value-added telecommunications business license for information service business, that is, an ICP certificate; For data processing and transaction processing services, it is necessary to apply for a value-added telecommunications business license for online data processing and transaction processing services, that is, an EDI certificate.
Both the EDI certificate and the ICP certificate belong to the value-added telecommunication business license, which respectively belong to the B21 category (online data processing and transaction processing business) and category B25 (information service business). According to the "Category of Telecommunications Business Classification (2015 Edition)", category B21 of value-added telecommunications business refers to "online data processing and transaction processing business, which refers to the use of various data and transaction/transaction processing services connected to public communication networks or the Internet. The application platform provides users with online data processing and transaction/transaction processing services through the public communication network or the Internet. Online data processing and transaction processing services include transaction processing services, electronic data exchange services, and network/electronic device data processing services." The business classification that the NFT platform may involve is mainly transaction processing business. Value-added telecommunications business B25 Information service business refers to the business of providing information services to users through public communication networks or the Internet through information collection, development, processing, and information platform construction. According to technical service methods such as information organization and transmission, ICP certificate It mainly includes "information publishing platform and delivery service, information search and query service, information community platform service, information instant interaction service, information protection and processing service, etc." For the NFT platform, some typical business scenarios that may involve ICP certificates are as follows: NFT artwork information release, paid advertising and other services may involve information release platforms and delivery services; NFT artwork retrieval, that is, to provide users with information on NFT artwork etc., which may involve information search and query services; NFT artwork evaluation, providing users with commodity evaluation functions, etc., which often involve information community platform services.
3. The NFT platform needs to obtain the "Online Publishing Service License", "Information Network Dissemination of Audio-Visual Program License" or "Internet Culture Operation License"
Article 2 of the "Regulations on the Administration of Online Publishing Services" stipulates that the term "online publications" in these regulations refers to digital works that are provided to the public through information networks and have publishing characteristics such as editing, production, and processing. The scope mainly includes: (1) Informative and ideological texts, pictures, maps, games, cartoons, audio and video readings and other original digital works in the fields of literature, art, science, etc.; (3) Digital works such as online literature databases formed by selecting, arranging, and assembling the above works; (4) Other types of digital works recognized by the State Administration of Press, Publication, Radio, Film and Television. Article 7 stipulates that to engage in online publishing services, one must obtain the "Online Publishing Service License" after being approved by the publishing administrative department in accordance with the law. Obviously, NFT works should be online publications, and what the platform provides is online publishing services. Therefore, according to the provisions of Article 7, engaging in online publishing services must be approved by the publishing administrative department in accordance with the law and obtain the "Online Publishing Service License".
Article 2 of the Provisions on the Administration of Internet Audio-Visual Program Services (Revised in 2015) stipulates that Internet audio-visual program services referred to in these regulations refer to the production, editing, integration, and provision of audio-visual programs to the public through the Internet, as well as the provision of audio-visual programs for others to upload and disseminate. Program service activities. Article 7 stipulates that to engage in Internet audio-visual program services, one shall obtain the "Information Network Broadcast Audio-Visual Program Permit" issued by the competent department of radio, film and television in accordance with these regulations or perform filing procedures. NFT works are produced and edited by the producer and the audio is provided to the public through the Internet, that is, it belongs to the Internet audio-visual program, so the service provided by the platform belongs to the Internet audio-visual program service. Therefore, according to this regulation, it is necessary to obtain the corresponding license or go through the filing procedures.
According to Article 8 of the "Interim Regulations on the Administration of Internet Culture" issued by the Ministry of Culture of the People's Republic of my country, to apply for commercial Internet cultural activities, an application shall be submitted to the cultural administrative department of the people's government of the province, autonomous region, or municipality directly under the Central Government where the application is located, and the people's government of the province, autonomous region, or municipality directly under the Central Government shall apply. Approved by the cultural administration department. The regulation defines "Internet cultural products" as "cultural products produced, disseminated and circulated through the Internet", mainly including: (2) Making and duplicating cultural products such as music entertainment, games, dramas (programs), performances, works of art, and animation on the Internet with certain technical means Internet cultural products disseminated on the Internet; "activities of providing Internet cultural products and services" are also clearly defined, which refers to "activities of providing Internet cultural products and services", mainly including: (1) Production and reproduction of Internet cultural products (2) Publishing cultural products on the Internet, or sending cultural products to clients such as computers, fixed telephones, mobile phones, televisions, and game consoles through information networks such as the Internet and mobile communication networks And Internet access service business places such as Internet cafes, online dissemination behaviors for users to browse, appreciate, use or download; (3) Exhibitions, competitions and other activities of Internet cultural products. Therefore, although the casting, distribution and sale of music works NFT itself is not the creation of Internet cultural products, it is a cryptographic expression generated through blockchain technology, which provides NFT buyers with the ability to browse and use original works or replicas. , downloading, which fall under the "provision of Internet cultural products and services" in this provision, shall obtain the "Internet Culture Business Permit".
4. The NFT platform must comply with the relevant business compliance requirements for artworks
Article 2 of the "Measures for the Administration of Art Works" stipulates that the term "art works" in these measures refers to paintings, calligraphy and seal cutting works, sculpture sculptures, art photography works, installation art works, arts and crafts works, etc., and limited reproductions of the above works Taste. Artworks mentioned in these Measures do not include cultural relics. Artwork business activities regulated by these measures include: (1) acquisition, sale, and lease; (2) brokerage; (3) import and export operations; (4) appraisal, evaluation, commercial exhibition and other services; Investment and business activities and services for the subject matter. These Measures apply to the use of information networks to engage in art business activities. Article 5 stipulates that the establishment of a business unit engaged in art business activities shall apply for a business license from the administrative department for industry and commerce of the people's government at or above the county level in the place of residence, and within 15 days from the date of obtaining the business license, go to the county of the place of residence. The cultural administrative department of the people's government at or above the level shall file for the record. Other business units that add art business shall go through the filing procedures in accordance with the preceding paragraph. If the objects targeted by the platform are paintings, photography, arts and crafts works and other works of art, then it may be necessary to abide by the provisions of the "Artwork Management Measures" and go through the filing procedures with the corresponding cultural administrative department. In addition, according to Article 11 of the Auction Law of the People's Republic of China, an enterprise obtaining a license to engage in auction business must be reviewed and approved by the department in charge of the auction industry of the people's government of the province, autonomous region, or municipality directly under the Central Government where it is located. If the NFT platform is sold in the form of bidding auction, it should obtain an auction license or cooperate with an auction company that has obtained an auction license to conduct auction activities.
3.2.2 NFT service
1. Secondary transaction and consignment service
At present, based on whether the transaction mode between users is open or not, the current domestic NFT platforms can be divided into three categories: the closed type that cannot transfer collections, the restricted type that only supports the transfer of collections, and the open type that opens the collection trading platform between users. There is no major legal problem in opening a secondary market. The key is that this business is a licensed business, and it cannot be done by consignment platforms, distribution platforms or SPV companies. As mentioned above, [2011] No. 38 "Decision of the State Council on Cleaning up and Rectifying Various Exchanges to Effectively Prevent Financial Risks" and Guobanfa [2012] No. 37 "State Council General Office on Cleaning up and Rectifying Various Exchanges" "Implementation Opinions" is still the legal bottom line of the secondary market.
2. NFT Blind Box
For digital collections and blind boxes, there are currently no clear and targeted laws and administrative regulations. The Shanghai Market Supervision and Administration Bureau formulated the first domestic normative document for blind boxes on January 10 this year-"Shanghai Blind Box "Guidelines for Compliance with Business Activities" has certain guiding significance and reference value. According to Article 16 of the "Shanghai Blind Box Operating Activities Compliance Guidelines", blind box operators shall not illegally use blind boxes to carry out financial business activities and quasi-financial business activities; shall not illegally carry out second-hand blind box business activities to induce non-player users to join Speculation and hype intentionally cause violent fluctuations in second-hand market prices and disrupt the normal order of transactions. Blind box operators are not allowed to spread false market information to hype sky-high prices; excessive marketing should not encourage consumers to show off their psychology of comparison; hunger marketing should not be carried out to deliberately lower the probability of picking specific products. It can be seen that for platforms that issue NFT in the form of blind boxes, their business methods will be regulated by blind box normative documents. It is foreseeable that as NFTs gradually receive more and more attention from the minority, it is possible to introduce legal norms with higher effectiveness and wider scope of application for blind box NFTs in the future.
3. The platform brings a single teacher
First of all, the behavior of operators to arbitrarily drive up and hype NFT and digital collections belongs to the first paragraph of Article 14 of the "Price Law of the People's Republic of China" (hereinafter referred to as the "Price Law") as stipulated in the first paragraph of Article 14, manipulating market prices, and harming other operators. Or consumers' legitimate rights and interests; at the same time, Article 14 of my country's "Price Law" also prohibits making huge profits by fabricating and disseminating information about price increases, driving up prices, pushing commodity prices to rise too high, and other violations of laws and regulations. unfair price behavior. Violations of the relevant provisions of the "Price Law" not only face administrative penalties, but may even constitute the crime of illegal business operations if the circumstances are serious.
Secondly, if the platform or team to which Mr. Dai Dan belongs uses virtual currency to trade NFT and digital collections, it is a violation of Article 16 of the "Notice on Rectifying Virtual Currency "Mining" Activities" issued by ten ministries and commissions in 2021. For illegal financial activities, the domestic platform will face administrative penalties and may have criminal risks. For a teacher who is a platform employee and provides assistance to the platform, if the platform constitutes a crime, the operation of pulling down the line and rebate depends on the specific situation. If it plays a greater role in the crime committed by the platform, then It will also be regarded as an accomplice to the conviction and punishment of the platform.
4. Airdrop, limited sale, lottery
In August 2019, the State Administration for Market Regulation issued the "Interim Provisions on Regulating Promotional Behaviors such as Prize-winning Sales (Draft for Comment)", which put forward compliance requirements for prize-winning sales. If the platform violates the corresponding regulations, it may be involved in unfair competition Or infringe on consumer rights. Under this marketing model, whether the prize sales information is clear, whether the lottery method is fair and reasonable, whether the total amount of prizes and the distribution of each region are publicized in accordance with legal regulations, and whether the probability of winning is clear need to be confirmed.
There are many types of NFT platform issuance marketing activities, and here we only discuss the more common methods in each platform. In short, no matter how "variety" the gameplay is, once some illegal operations are involved and have a negative impact on the economic and financial order, the regulatory authorities will never turn a blind eye.
3.2.3 Summary and analysis of official regulatory documents for the NFT industry
So far, the country has not formulated corresponding norms for the NFT industry, neither has it clearly identified digital collections, nor has it regulated and supervised related trading platforms, and it is still blank at the level of laws and regulations. However, in the reality of the explosive growth of NFT, supervision and compliance are an inevitable issue that cannot be bypassed. In the past period of time, various institutions and enterprises have begun to establish NFT-related standards and issued some formal documents.
In September 2021, the Standardization Working Committee of the China Technology Market Association under the Ministry of Science and Technology and several organizations set up a special working group to jointly carry out the development and drafting of the "NFT Platform and Product Evaluation" group standard. It aims to establish a set of relevant group standards that are suitable for China's national conditions and meet the long-term and healthy development needs of the domestic NFT industry.
In October 2021, the first self-regulatory convention in the NFT industry was released. The National Copyright Trading Center Alliance, the China Academy of Art, the Hangzhou Internet Notary Office of Zhejiang Province, and domestic leading Internet companies jointly issued the "Digital Cultural and Creative Industry Self-Discipline Convention".
On February 18, 2022, the Office of the China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Commission's inter-ministerial joint conference on dealing with illegal fund-raising issued the "Risk Reminder on Preventing Illegal Fund-raising in the Name of "Yuan Universe"", reminding investors to pay attention to the following four types of " The relevant methods of illegal fund-raising in the name of “Metaverse”: first, fabricate false Yuanverse investment projects; second, defraud under the banner of Yuanverse blockchain games; third, maliciously hype Yuanverse real estate to mislead money; currency for illegal profit.
On February 21, 2022, the Metaverse Industry Committee of the China Mobile Communications Federation issued the "Metaverse Industry Self-Discipline Convention", proposing to resolutely resist the use of metaverse hotspot concepts for capital speculation, resist fabricating false metaverse investment projects, and issue metaverse virtual currency and other illegal financial activities.
At the end of March 2022, WeChat banned a number of public accounts of digital collections. Later, Tencent responded that, in accordance with relevant national laws and regulations, in order to prevent the risk of hype in virtual currency transactions, the WeChat public account platform has standardized and rectified the public accounts and small programs that hype and re-sell digital collections. For official accounts that only provide digital collection display and primary transactions, they are required to provide a certificate of cooperation with a blockchain company that has been filed and approved by the Cyberspace Administration of China as a qualification certificate, and secondary transactions are not supported.
On April 14, 2022, the Metaverse Industry Committee of the China Mobile Communications Federation and the Blockchain Professional Committee of the China Communications Industry Association jointly issued the "Self-Discipline Requirements for Regulating the Healthy Development of the Digital Collection Industry", calling for resisting disorderly hype and guiding reasonable expectations , Resolutely resist the tendency of financialization of digital collections. These industry standards and voluntary actions will provide a certain reference value for the formulation of NFT-related regulatory measures in the near future.
secondary title
3.3 Future trends of NFT industry regulation
Compared with the traditional financial field, due to its own informatization and technology, NFT activities have different regulatory methods. We should not only consider regulatory measures from the perspective of activity links and participants, but also set up regulatory mechanisms based on technology itself and market development. The future trend of NFT industry regulation can start from the following aspects:
Effectively supervise the issuance of digital collections. Due to the similarities between digital collections and traditional publications, limited edition souvenirs and other products, it is recommended that relevant departments formulate management measures for the issuance of digital collections, supervise the release of illegal and bad digital collections, and further cultivate and strengthen mainstream awareness in the digital environment Form a digital collection creation group, promote the positive growth of digital collection creation, and disseminate excellent Chinese cultural content.
04 Legal risks in China's NFT industry
secondary title
4.1 Technical Security Risks
Compared with traditional physical currency, NFT, which was born based on blockchain technology, has higher security and anti-counterfeiting. Compared with general virtual currency, it also has non-homogeneous characteristics, but this does not mean that NFT It is absolutely safe and foolproof.
Although my country's NFT is quite different from the popular NFT in foreign markets, its essence is still the application of blockchain technology, and it is still a network technology. It is not uncommon for users' virtual currency or NFT to be stolen or lost due to technical security flaws and loopholes on major overseas virtual currency or NFT trading platforms.
Therefore, although NFT is technically different from traditional virtual currency, and its non-homogeneous characteristics also provide a certain guarantee for its applications such as certificate storage and traceability, we have to be alert to the possible damage to NFT caused by various network attacks. threaten.
secondary title
4.2 Data and Information Security Risks
The risk of data information security mainly comes from two aspects.
Second, from the enterprise. As a participant in the NFT industry, limited by China's regulatory laws, companies often collect more personal information and data when operating NFT-related businesses. Therefore, the preservation of these data is particularly important. If relevant personnel within the enterprise sell or provide the above-mentioned information privately, or if external personnel illegally obtain the information through technical means, it may constitute an illegal and criminal act in the field of personal information.
secondary title
4.3 Financialization risk
For most NFT operators, the financialization risk of NFT is their most concerned area.
4.3.1 The concept of financialization
Commodities can be further divided into ordinary commodities and financial products according to their specific uses and transaction characteristics. The latter refers to various non-physical assets that have economic value and can be traded or cashed in public, also called securities. Although there is no doubt about the nature of NFT as a common commodity, even so, it still has the possibility of financialization. And once NFT products are over-financialized and even regarded as a financial product, then it will no longer be subject to the adjustment of laws such as the "E-Commerce Law of the People's Republic of China", but will belong to the field of financial products, with greater legal risks .
The process of the gradual financialization of ordinary commodities and finally being regarded as financial products is called the financialization of ordinary commodities. According to Professor Zhang Chengsi, the financialization of ordinary commodities has two meanings: “First, the financial nature of the transaction mechanism of ordinary commodities gradually strengthens, causing the decision mechanism of commodity prices to deviate from the supply and demand factors at the output level, and to depend more on The scale of funds corresponding to the market; second, ordinary commodities in commodity transactions are no longer the transaction targets in the traditional sense, but the ownership of the corresponding commodities is regarded as a quasi-financial asset, and the purpose of purchasing commodities is no longer the commodities themselves, but It’s the resale of ownership for a profit.”
To put it simply, the financialization of an ordinary commodity means that on the one hand, the price of the commodity itself is no longer determined by the relationship between supply and demand or its own value, but depends more on the scale of funds in the market; On the one hand, it also means that the commodity itself is no longer valued, and the purchase of commodities is no longer for consumption, but for functions such as value preservation and appreciation, and ultimately to resell their ownership for profit.
4.3.2 Conditions for financialization
Through the study of most common commodity financialization cases in history, such as the "Luoyang Zhigui" incident in the Jin Dynasty, the tulip financialization incident in the Netherlands in the 17th century, and the stamp financialization incident in modern my country, it can be found that there is a logical existence of commodity financialization. Certain consistency, this consistency is reflected in the following three characteristics of the product:
First, the commodity generally has certain unique attributes or scarcity or can form a monopoly market. The reason for this is that the value of commodities with this characteristic is difficult to determine, and therefore the price is also difficult to determine, and thus has great volatility. This volatility also endows these commodities with the ability to resist inflation, maintain value and increase value, thus embodying more financial attributes. However, due to the difficulty in determining the value of its characteristics, the price of NFT can fluctuate violently, which belongs to this type of special commodity.
Second, in most cases, the financialization of commodities begins with speculation. In order to promote the financialization of commodities, speculators often take certain actions such as speculation, reducing supply, etc., which cause the commodity prices to fluctuate violently and start to rise, and then sell them after the price rises to near its expected value, thus obtaining high profits. amount of profit.
From the above three characteristics, we can know that due to its non-homogeneous characteristics, NFT certainly has the potential of financialization, so its financialization risk is a legal risk that the NFT industry needs to be especially vigilant about. At the same time, combining the second and third points, we can see that in order to restrain the financialization of NFT products, it is necessary to prevent the occurrence of speculation and the excessive influx of funds as much as possible, so as to restrain the excessive growth of commodity prices. This means that NFT operators It is necessary to control the intensity of hype, and at the same time strictly control the influx of funds from all parties, so as to resist the review of the financial regulatory system.
secondary title
4.4 Risk of cyber fraud
For operators, they need to ensure that there is no fraudulent behavior in their NFT business process and operate legally and compliantly, otherwise they may be found to constitute a crime of fraud. Under certain special conditions, such as illegality, openness, and temptation It may also constitute a very serious crime of fund-raising fraud. For NFT consumers, they need to carefully screen the authenticity of NFT or NFT-related items to ensure that they truly understand the conditions of the items they purchase or consume, and avoid falling into online fraud and suffering property losses. Since this risk is relatively routine, it will not be described in detail.
secondary title
4.5 Risk of infringement
For the current NFT industry, since most NFT business models are selling NFT digital collections, and NFT digital collections often rely on the bonus brought by some IP authorization to promote their sales, the most common infringement in the NFT industry is The risk is the risk of copyright infringement.
This risk typically emerges in three modes:
First, the IP party itself does not have corresponding intellectual property rights and is suspected of infringement. In order to ensure that minted NFT digital collections can be sold legally, the seller usually signs an IP authorization agreement with the IP party, requiring it to promise that it legally holds the IP and legally authorizes the IP to the seller. If the IP party does not have legal intellectual property rights in the above process, or the IP party is not legally authorized, it will cause the NFT digital collection sold by the seller to fall into the risk of infringement.
Second, there is no legally authorized source for the works uploaded by users themselves and used to make NFT. Similar to the first one, in this case, since the user does not own the legal intellectual property rights of the work, the seller may bear certain liability for infringement. The more famous Hangzhou Internet Court’s first NFT infringement case recently fell into this category. In the judgment, the court held that the seller should undertake a higher obligation of prior review and also need to perform the “notification-deletion” obligation.
The above three situations all indicate that there is a risk of infringement in the NFT industry.
secondary title
4.6 Money Laundering Risk
During the period when virtual currency was popular, virtual currency has been used as a tool for money laundering. Although NFT, which was born out of virtual currency, has not been used for money laundering in large quantities, it still has a greater risk of money laundering.
And if you want to understand how virtual assets such as virtual currency and NFT are used for money laundering, the most intuitive, effective, and easy-to-understand way is to observe what role they play in each link of money laundering. In the final analysis, the purpose of money laundering is to convert illegal proceeds, criminal proceeds or all other "black money" obtained through illegal means into "white money" recognized and protected by law. Therefore, money laundering is essentially to help black money holders convert black money The origin of the activity is explained clearly.
4.6.1 Can NFT be used for money laundering?
1. Why can virtual currency be used for money laundering?
As mentioned earlier, the reason why virtual currency can become a convenient and easy-to-use money laundering tool is to take advantage of its characteristics such as anonymous transactions, point-to-point transmission, cross-border circulation, irreversibility, and relatively objective market value. Among them, anonymity and cross-border circulation Convenience is at its core.



