Can encryption really rebuild social trust?
 In the blockchain industry, different people define the word "trust" differently. For software engineers, trust often refers to "zero-trust interactive systems", "trustless transactions", and other trust-minimizing techniques. Still, trust has been key to helping us truly understand cryptography.
In the blockchain industry, different people define the word "trust" differently. For software engineers, trust often refers to "zero-trust interactive systems", "trustless transactions", and other trust-minimizing techniques. Still, trust has been key to helping us truly understand cryptography.
Trust comes from the Old Norse word "traust", which means confidence and protection. The word has always meant what it means: to trust that people and processes will deliver as promised. Trust is the cornerstone of a functioning society — societies that trust each other often also develop more prosperous economies and harmonious societies, where counterparty risks are reduced and dispute resolution processes are fairer.
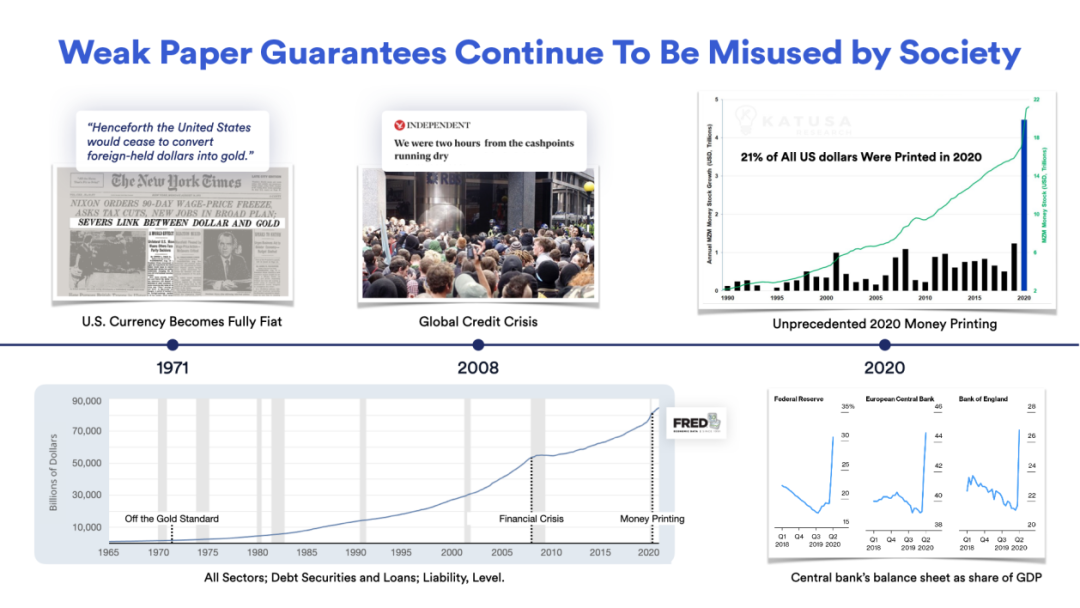
Unfortunately, the public has begun to lose trust in the core institutions responsible for keeping society's economy functioning. According to Gallup polls, the American public's confidence in the country's major institutions has been declining for the past 45 years. While the extent of the collapse of trust varies across industries and countries, judging by the negative sentiment towards the existing system, it is clear that everyone is seeking a fairer solution.
New technologies such as blockchain, cryptocurrency, smart contracts, and oracles are emerging to coordinate social and economic affairs in a more secure, transparent, and accessible manner. More importantly, these technologies prove that encryption guarantees can effectively rebuild people's trust in daily social and economic activities, and encryption guarantees are often referred to as "cryptographic truth".
first level title
Pain point: collapse of social trust
secondary title
Centralized ownership of data and processes
The initial design architecture of the Internet determines that applications are largely centralized. Typically, a centralized entity owns the intellectual property of an application, controls its backend algorithms, determines its future development direction, and profits from the data and revenue generated by the application. This centralized model leads to an unequal relationship between users and applications. Apps can easily extract value from users, and this has also led to users losing trust in the app.
image description

“A June 2020 Pew Research Center survey found that about three-quarters of adult Americans believe it is very likely (37 percent) or somewhat likely (36 percent) that social media platforms intentionally delete inappropriate platforms. A political view of values."
Centralization can also lead to the phenomenon of power concentration. A small group of people has the right to control the distribution of platform income and the direction of platform development, while users have little right to speak. Granted, the founders are the founders who drive the success of the app to a certain extent, since the app is initially created and managed. But at the same time, users have also created rich content and great value for the app. For example, users bring value to social media platforms through content creation. App developers can monetize these contents directly through advertisements. And users can't help but wonder if they're being paid and given their say.
image description
secondary title
no accepted source of truth
Another reason for the collapse of trust is that actors in social and economic affairs cannot refer to a single source of truth. For example, in many business collaborations, participants each maintain their own set of records. Inadvertent mistakes by either party can lead to inconsistencies in the process, and it takes a lot of time for all parties to coordinate and unify. It is even possible for one party to deliberately falsify records to delay the progress of reaching an agreement, evade responsibility or falsify the results to the counterparty.
image description
Wirecard's bankruptcy filing has left many UK customers unable to access cash in their accounts, as several major fintech apps use Wirecard to process payments.
image description

Although Robinhood's banner is "to provide financial services for everyone", after the platform suspended the GameStop transaction, many retail investors can't help wondering: Is Robinhood serving everyone or only Wall Street hedge funds?
secondary title
Lack of enforcement and accountability
In some cases, disputes are unavoidable. Therefore, when a dispute arises, it must be resolved in the fairest way. However, large institutions usually have a greater say in the dispute resolution process. This problem is especially acute when signing agreements between large institutions and individual users. These agencies know they have more leeway to break their promises because users don't have the time, money, or clout to win even a lawsuit. In fact, in some developing countries, the rule of law is vulnerable to power and bribery, so that some economic relationships are entirely castles in the air.
image description
secondary title
Process inefficiencies at multiple stages
image description
first level title
Solution: Trust Network Based on Blockchain and Oracle
Imagine if we can develop an infrastructure so that counterparties do not need to trust each other, nor do they need to use a third party to monitor the fulfillment of their commitments, so that fair results can be guaranteed? And this infrastructure doesn't have any centralized administrators yet!
In order to achieve the above goals, this infrastructure must follow two key design principles, namely: minimal rent-seeking behavior and trust-minimized execution.
Minimal Rent Seeking BehaviorIt means that the infrastructure should try to eliminate rent-seeking behavior when assisting user interaction. This infrastructure is different from general for-profit enterprises, its only function is to connect users together, and it does not pursue any economic returns other than that. For example, a financial market with very low transaction fees, where users can trade financial assets.
trust-minimized executionRefers to the very high probability that the process will run correctly, statistically almost 100%. In other words, users do not have to trust the infrastructure because it is highly deterministic and all potential variables that could affect the process have been eliminated or reduced. Therefore, the probability that the process does not execute according to the code is almost zero. While complete trustlessness is an ultimate ideal, some refer to this type of infrastructure as "trustless infrastructure."
Blockchain combines the above two qualities, providing users with minimal coordination and executing code in a trust-minimized manner. This is because the blockchain does not have a centralized administrator. Instead, it is a decentralized computer network that maintains ledgers based on economic incentives, which record the ownership of data and assets in the network. Every time a user creates a new asset, transfers an existing asset to another user, or stores data on the blockchain, the decentralized network of nodes must reach a consensus on the validity of each interaction before publishing it on-chain . For example, if a user wants to transfer funds from one account to another, the blockchain needs to verify that there are enough funds in the account to complete the transaction before the transaction can be executed.
Combining decentralized consensus and cryptography, the blockchain lays the foundation for cryptographic facts, i.e., the verification of new transactions based on historical data already stored in the blockchain ledger and considered factual. Blockchains are deterministic in the sense that no additional or external data is required to approve new transactions.
To learn more about blockchain, read"Understanding the similarities and differences between blockchain and oracle machines and their synergistic effects in one article"and"Understanding the similarities and differences between blockchain and oracle machines and their synergistic effects in one article"image description
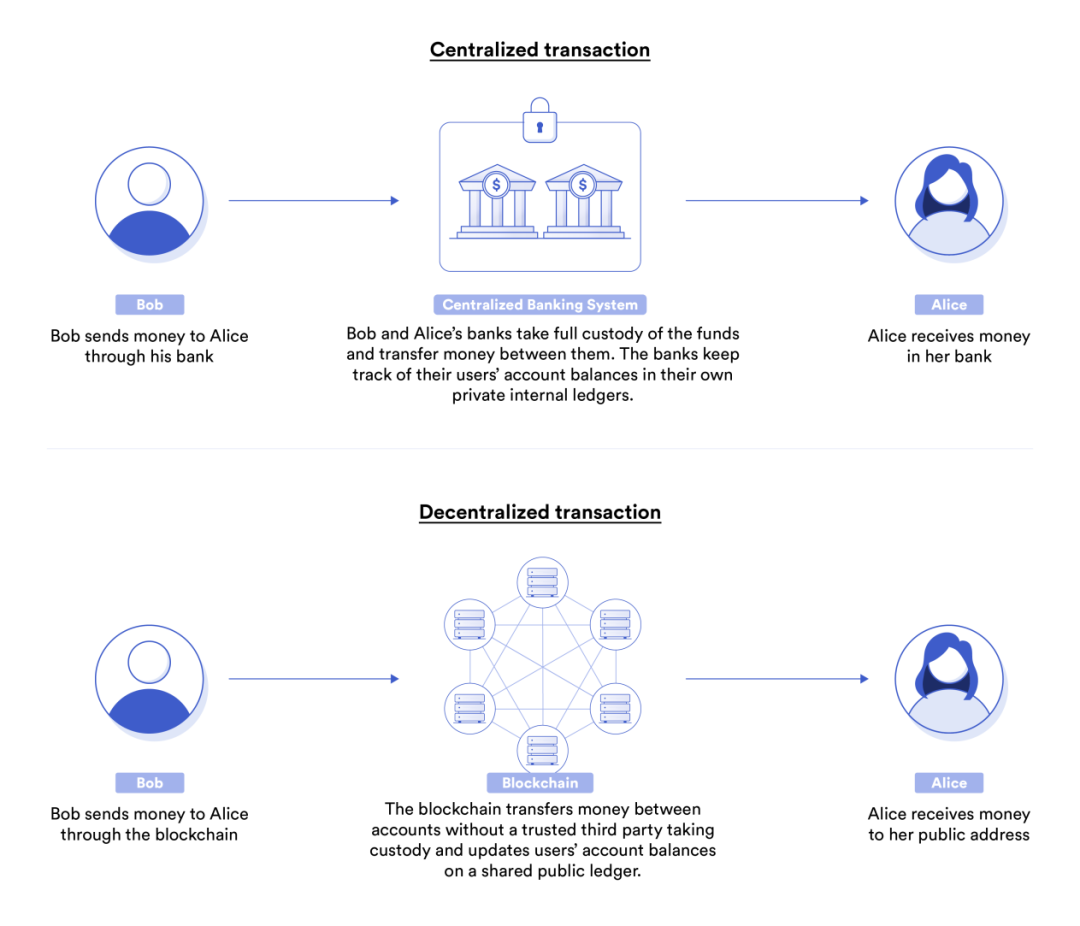
In the traditional bank payment system, the bank is a trusted custodian between users; while in the blockchain payment system, the blockchain is a trust-minimized non-custodial intermediary.
"Understanding Smart Contracts in One Article""Understanding Smart Contracts in One Article"。
Hybrid Smart ContractHybrid Smart Contract, an application contains two modules, on-chain and off-chain.
ChainlinkSmart Contract Use CasesSmart Contract Use Casesdecentralized financedecentralized finance(DeFi)、Non-homogeneous token(NFT)、Play-to-Earn Gameswait.decentralized insurancewait.
and"Understanding Blockchain Oracles in One Article"and"Understanding Chainlink in One Article"image description
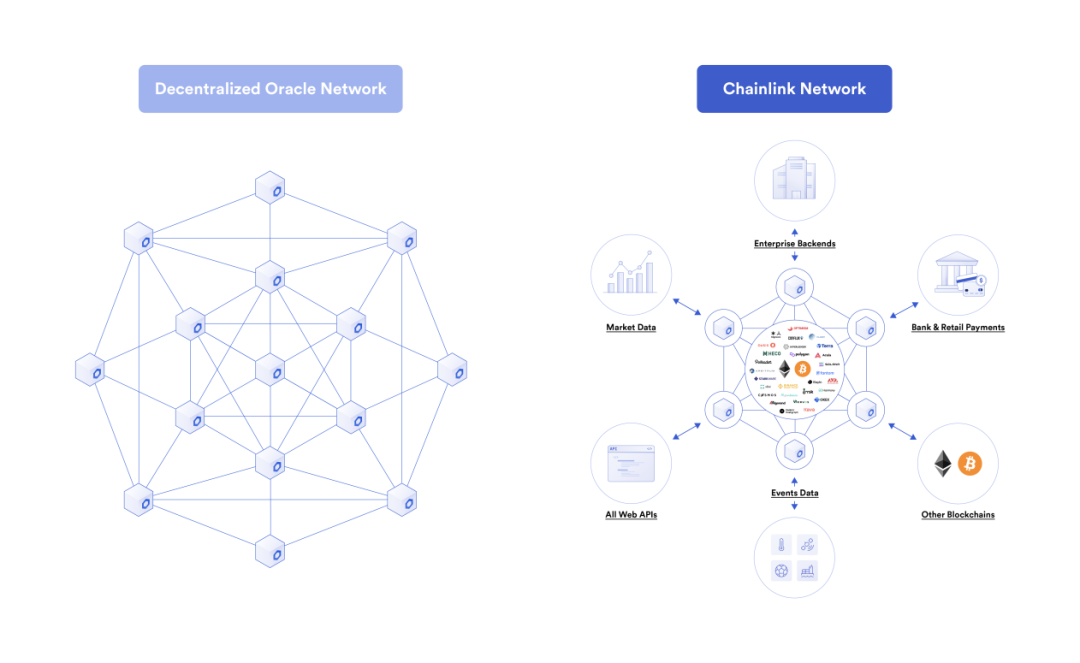
Chainlink's decentralized oracle network allows smart contracts on any blockchain to achieve two-way interaction with any external system or resource, and guarantees security, reliability and accuracy in the process.
first level title
Future Prospects: Rebuilding Social Trust with Encrypted Facts
secondary title
Data is owned by individuals, process ownership is decentralized
One of the biggest advantages of blockchain technology is that it can decentralize the applications or institutions responsible for running social and economic activities. Blockchain technology can create a completely neutral platform, and the platform cannot arbitrarily censor user content due to any economic, political or social pressure. Once the terms are written into the smart contract and stored on the blockchain, anyone can view the relationship between the user and the dApp, and neither party, not even the administrator, can tamper with it.
A decentralized system also eliminates intermediate custodians. The blockchain is more like a non-custodial facilitator, all data generated by the dApp can be viewed publicly and cannot be tampered with by anyone. Users can directly control their own data and assets through the private key, and only the user can own the private key. For example, anyone can view the complete transaction history of the Bitcoin ledger, and can host and send the Bitcoins in their account to other users in the network without the participation of the bank.
In addition, there are some oracle solutions with privacy protection functions, such asChainlink DECOimage description
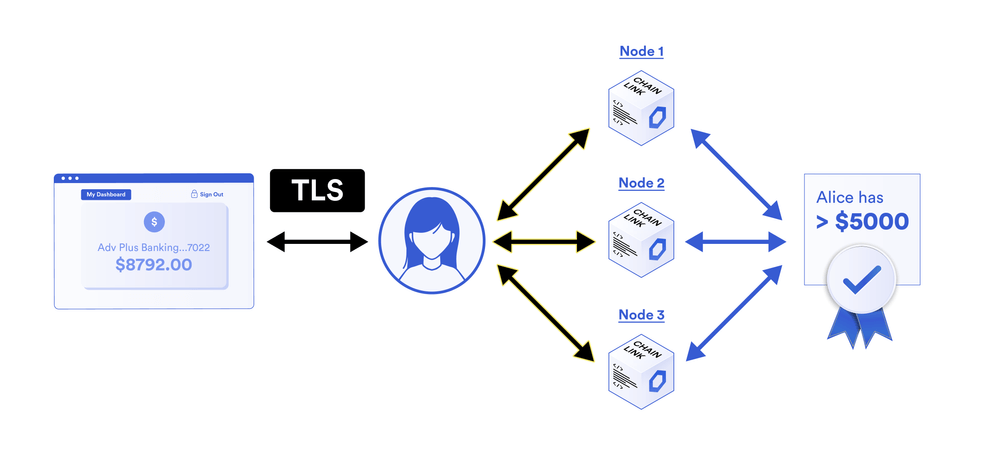
Chainlink DECO uses zero-knowledge proof to protect data privacy in smart contracts and does not disclose data content to the blockchain.
Blockchain and dApps on the chain are also gradually lowering the barriers to entry. For example, Ethereum is currently transitioning to a PoS consensus mechanism, which aims to allow anyone in the world to pledge Ethereum in a smart contract and become a verification node in the network (note: pledge refers to locking the pass in a non-custodial manner). After the user becomes a verification node, he can share part of the value generated by the Ethereum block by verifying the transaction.
Curvesecondary title
Recognized facts (Shared Truth)
Blockchains and dApps are usually open-source technologies, and all users can view the underlying code of the dApp and the data it produces. Blockchains are public, unified databases that are fairly open to all participants, so there are no disagreements and any systemic risks are readily apparent. Transactions are verified through a decentralized consensus mechanism, rather than based on the subjective judgment of a certain user or administrator. In other words, the relationship between users and dApps will be carried out in accordance with clear contractual terms.
If external data needs to be verified, the oracle usually uses a decentralized network of nodes and multiple data sources to avoid the risk of a single point of failure in the verification and execution process. for example,Chainlink Price FeedsDecentralized Finance (DeFi)Decentralized Finance (DeFi)borrow moneyborrow money, derivatives, andstablecoinimage description
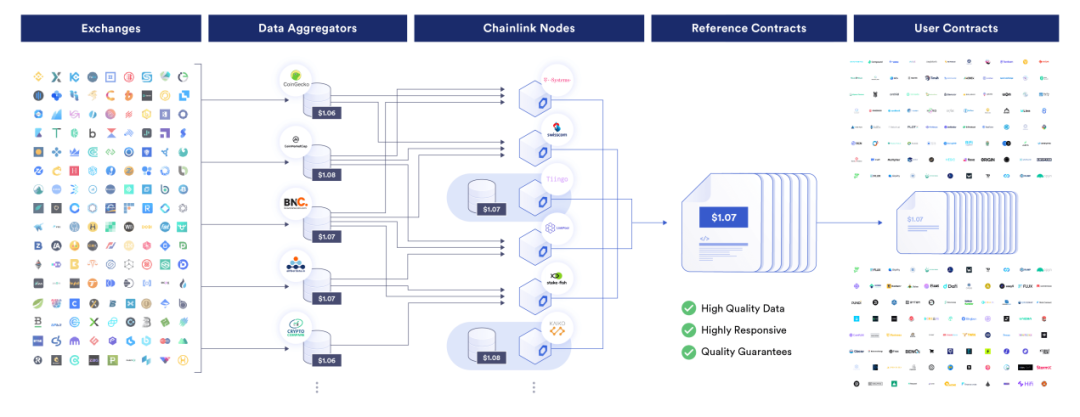
Chainlink Price Feeds currently guarantees tens of billions of dollars in value for various DeFi applications. It has achieved decentralization at the three levels of data sources, nodes, and oracle networks, and can provide real-time asset price feeds for dApps.
secondary title
Based on consensus, execution is guaranteed through encryption technology
Since the blockchain is based on a decentralized consensus mechanism to verify transactions in the network, neither party will receive special treatment when a disagreement occurs. There are no administrators in the blockchain, so dApps in crisis cannot be rescued, nor can they press the reset button at will. Blockchain replaces administrators with a decentralized network that is secure based on cryptography and economic incentives, making it nearly impossible to tamper with consensus or previously stored data.
Blockchains and dApps can also change, but changes usually require many independent users to reach a social consensus, rather than a single person making decisions like a centralized application. For this reason, many dApps adopt a decentralized autonomous organization (hereinafter referred to as DAO) for governance, and all users vote together to initiate changes. In fact, many dApps have their own native tokens and use these tokens in the DAO, using a token-weighted voting mechanism to decide whether the proposal is passed or not.
Executing digital contracts on a globally accessible and highly tamper-resistant blockchain platform can significantly reduce counterparty risk. Many blockchains and dApps also introduce automatic penalties to punish participants for misbehavior. For example, the PoS blockchain will confiscate some tokens pledged by malicious nodes as a punishment. dApps can also temporarily escrow users’ funds until certain conditions are verified before releasing the funds. This way, it becomes nearly impossible for the losing party to evade payment.
Decentralized oracle networks also achieve the same guarantees by creating authoritative facts. Each dApp can clearly define how they want to obtain facts from the outside world, and formulate clear boundary conditions. That is, oracles can more flexibly verify external events for smart contracts. Users can choose to trust different data sources, or they can choose to spend more money to improve the decentralization level of the oracle network. No matter how users design the oracle machine mechanism, they must first reach a consensus on the fact that the oracle machine transmits and recognize its authority. The agreement reached between the user and the oracle machine can be written into a service level agreement (hereinafter referred to as SLA) smart contract to prevent anyone from tampering with the content of the agreement, and automatically execute the reward and punishment mechanism when the task is completed.
Chainlink Verifiable Random Function (hereinafter referred to as VRF) is a service that creates authoritative facts through oracles.Chainlink VRFThe oracle machine technology is used to generate random numbers and encryption certificates off the chain, and then send the two to the chain. The blockchain will use encryption certificates to verify that the random numbers have not been tampered with by any oracle machine.NFTs and Game Appsimage description
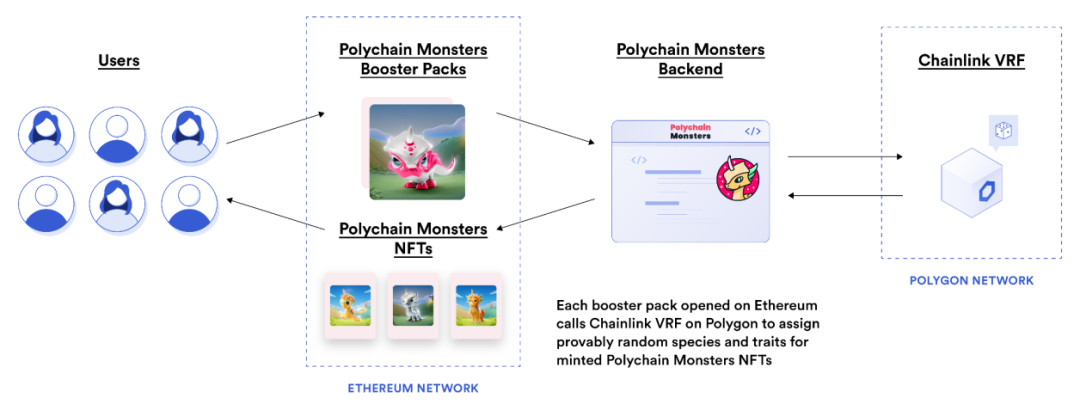
secondary title
Efficient point-to-point process
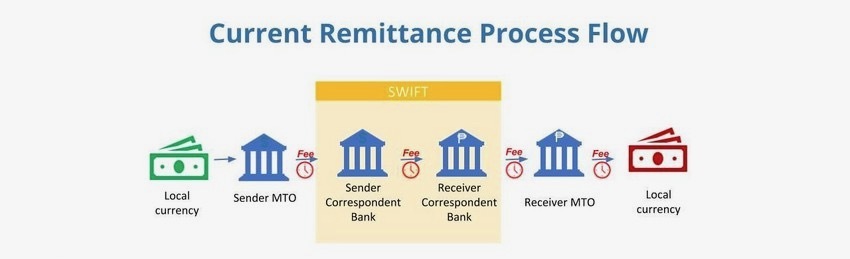
Blockchain computing is not only more secure, reliable and accurate, but also adopts a peer-to-peer model. Both rent-seeking behavior and settlement times are reduced as all intermediary parties are eliminated. This is especially prominent in the Ethereum Layer 2 expansion plan. Layer 2 is a network built on Ethereum, which has the advantages of lower cost and higher throughput, and at the same time is secured by the underlying Ethereum blockchain. With a variety of layer 2 options, users can send payments of any amount to anyone in the world in a matter of minutes and at a lower cost than standard international money transfer fees.
andArbolandEtheriscimage description
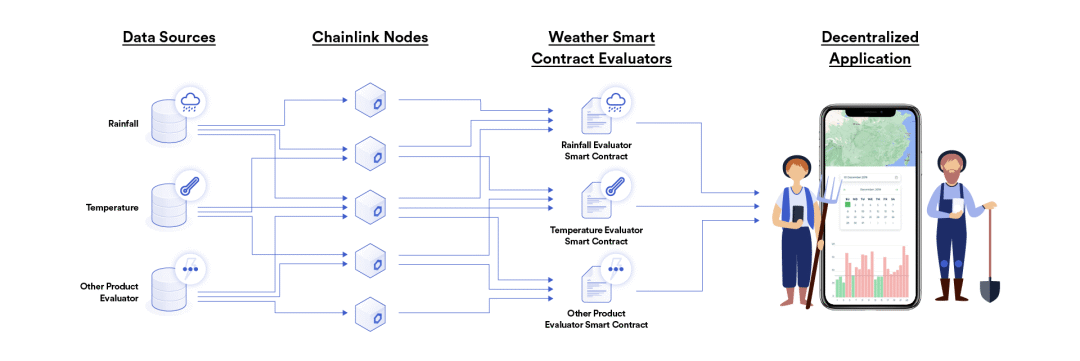
first level title
Join the blockchain industry now
Comparing the development history of the Internet, we judge thatBlockchain and Oracle TechnologyIt is still in the early stages of development. There will be infinite possibilities for innovation in the future, and blockchain and oracles have the potential to rebuild trust for the core processes of the social economy.
If you are interested in blockchain and want to join the industry, please read"How to Become a Smart Contract Developer"article to learn how to joinChainlink Labsfirst level title
text
If you want to learn more about blockchain and oracle technology, you can read popular science articles on the Chainlink blog. You can start with the following articles:
If you want more technical material, you can check outChainlink news、Chainlink 2.0 White Paperas well asdeveloper documentation。
To learn more, please visitchain.link,subscriptionChainlink newsFollow Chainlink on Twitter.Twitter、YouTubeandRedditFollow Chainlink on Twitter.



