First-class warehouse research report: sorting out the development of the cross-chain bridge track
foreword
foreword
If you look at the development of DeFi, you can see a clearer path. Starting from DeFi Summer last year, the Ethereum ecology began to explode, but on the other hand, the rapid development of the ecology also exposed the insufficient performance of the underlying Ethereum, which hindered the further expansion of the ecology. At the same time, some people "save themselves" and focus on Layer 2, and some people "want to go out and see" and devote themselves to other public chains besides Ethereum.
In 2021, the "JPG" market of NFT and the popularity of GameFi will further exacerbate this phenomenon. On the one hand, the ecological construction is thriving, on the other hand, the original expansion problem has reached the point of no delay. So this year, we have seen the comeback of old public chains, the strong rise of emerging public chains, and the successive launch of Layer 2 projects.
The superposition of various factors has promoted the arrival of the DeFi multi-chain era. However, under the multi-chain structure, the DeFi ecology of each chain is still relatively independent, and multi-chain interoperability has become an inevitable demand for adapting to development. Under such a background, the cross-chain bridge has become a new outlet to follow the DeFi trend and has attracted market attention.
A cross-chain bridge is a chain-to-chain bridge tool that allows tokens and assets to be transferred from one chain to another. Two chains can have different protocols, rules, and governance models, and the bridge provides a mutual-communicating and compatible way to securely interoperate on both sides.
Cross-chain bridges are an important topic in the current multi-chain era. At the time of writing, the public chains and the DeFi ecology on Layer 2 of Ethereum have already locked cryptocurrencies worth more than 258.3 billion U.S. dollars. In the future, with the gradual improvement of the cross-chain bridge, we will see it bring more composable gameplay to the entire DeFi ecosystem.
Track analysis
secondary title
backgroundWith the development of blockchain, it has entered aMultiple chains coexistmarket structure, and gradually formedEthereum as the core, and other public chains with stars and moons
situation.
In the past two years, we have taken the lead in seeing application scenarios with practical needs on Ethereum: DeFi, NFT, GameFi and the future Web 3, and the ecological construction is thriving. But on the other hand, with the rapid development of the ecology, it has also exposed the problem of insufficient performance of the underlying layer of Ethereum. Network congestion and high Gas fees have hindered the further expansion of the ecology. At the same time, some people "save themselves" and focus on Layer 2, and some people "want to go out and see" and devote themselves to other public chains besides Ethereum.
Especially after the DeFi Summer in 2020 and the "JPG" market in 2021, you can clearly feel the rapid development of the ecology of the public chain track outside of Ethereum. Many emerging public chains (such as: BSC, Solana, Near, Avalanche, Terra, Fantom, etc.) have made corresponding trade-offs in the impossible triangle, supplemented and expanded in terms of scalability, and because most of these chains are related to EVM Compatible, can more easily integrate DeFi and NFT type projects, so as to complete the simple replication of the applications that have been successfully implemented on Ethereum.Although these emerging public chains offer significantly lower fees, shorter transaction confirmation times, and some additional features, Ethereum is still the first choice for most DeFi projects, mainly due to the high liquidity and transaction volume on this network . In the current DeFi era where "liquidity is king", in order to attract more users in the early stage, the major public chains have attracted users through high APY, so the liquidity competition caused by involution has started. According to statistics from DeFi Llama, as of October 22, 2021,The locked-up volume of DeFi on Ethereum has exceeded US$161.5 billion, and other public chains such as BSC, Solana, and Avalanche have also attracted US$78 billion in funds
, and its development has formed a scale that cannot be underestimated.
The coexistence of multiple chains is the current market pattern, and with the increase in the number of public chains and Layer 2 projects and the gradual improvement of their respective ecologies, the demand for cross-chain user assets on the chain will also grow rapidly, and cross-chain bridges are bound to become rigid needs.
secondary title
development context
expansion
The classification of capacity expansion technologies is roughly as follows in Table 1-1:
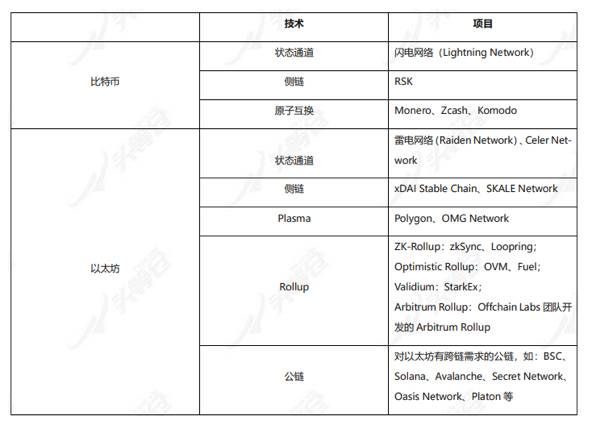
Table 1-1 General classification of capacity expansion technologies
From the perspective of expansion technology, Bitcoin’s expansion technologies include: state channels, side chains, and atomic swaps.
text
Ethereum’s expansion technology has roughly gone through: a process from state channel→side chain→Plasma→Rollup. In fact, this is also a Layer 2 development process. Ethereum Layer 2 has experienced several years of development, and now it has developed a variety of Different Layer 2, the details are as follows:
Note: Ethereum sharding (Sharding) is a performance solution for scaling inside Ethereum, while Layer 2 is a solution for scaling outside the Ethereum blockchain.
1) From Layer 1 to Layer 2
Ethereum is Layer 1. As a full-node public chain, the efficiency of multi-node cooperation is inevitable. At this time, scientists thought of the Layer 2 solution, which is to move some transactions on Ethereum to Layer 2 for processing. After the processing is completed Then return the result to Layer 1, so as to achieve the purpose of expansion.
Raiden Network (Raiden Network) is the early Layer 2 on Ethereum, but it has always been in a tepid state.
2) Side chain
3)Plasma
On Ethereum, because the early state channel failed to obtain large-scale application, it can be said that the original Layer 2 is a side chain. The advantage is that it implements Layer 2 and reduces the burden on Ethereum. However, the sidechain operates independently. If there is a problem on the sidechain, such as a sidechain node doing evil or being attacked, it will cause the sidechain to execute transactions incorrectly, and the result returned to Layer 1 will also be wrong, which is not safe enough.
Due to the worrying security of the early side chains, a more secure Plasma appeared. Plasma is not completely managed. It uses a fraudulent proof exit mechanism. On-chain exit, so plasma has higher security.
4)Rollup
However, it was also due to the defect that Plasma allowed the wrong results to be published on the chain, and then went through the complaint procedure, so it failed to become popular in the end.Rollup is based on PlasmaImproved the way data is validated
, to pack a large amount of transaction data in the second layer block into a compressed transaction and publish it to the chain. In order to ensure the validity of each transaction, various Rollup schemes have designed different mechanisms to ensure that the security of the entire process is consistent with Layer 1.
On the whole, several expansion technology prototypes were mainly proposed in the early stage, focusing on problems such as the capacity limitation of the BTC blockchain and high transaction fees, and developed projects or technologies such as Lightning Network, Pegged Sidechains, and sharding; Gradual development and improvement, focusing on more application scenarios, such as: realizing on-chain asset swaps, on-chain anonymous transfers, enhancing block interoperability, etc., and constantly exploring more scalable general cross-chain technologies .
Cross-chain bridge
Cross-chain bridgeNote thatCross-chain ≠ cross-chain bridge. First of all, we need to clarify a concept. Cross-chain technology means that data and assets can flow freely on different blockchains, which contains two dimensions:。
assets and data
Just as many people confuse the relationship between Polkadot, Cosmos and cross-chain bridges, Polkadot and Cosmos are essentially chains that use a unified framework, with high interoperability, and do not have any cross-chain for chains outside the framework Advantage.
A simple understanding is that the cross-chain of Polkadot and Cosmos is more like Layer 0, and users need to realize cross-chain based on their own standards; for cross-chain bridges, the two chains can have different protocols to solve the problem of different assets. Asset migration issues between different networks.
Note: At present, some places also classify the two ways of asset cross-chain as cross-chain bridges. The classification method is not absolute, and it is only for the convenience of understanding.
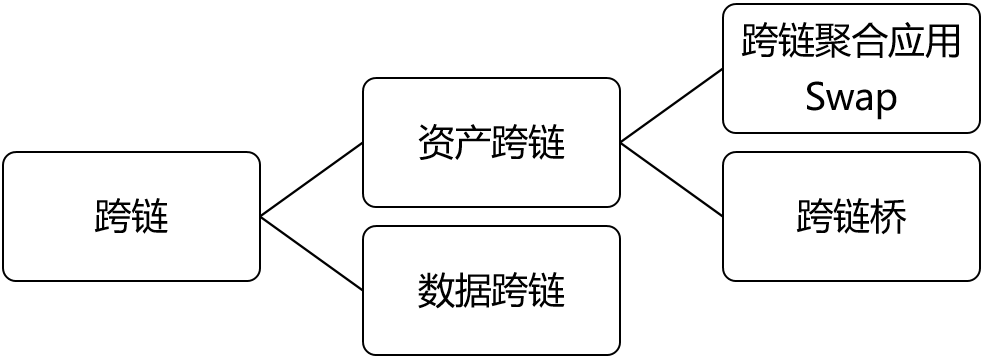
image description
Figure 1-1 Cross-chain subdivisions
From the perspective of the development of cross-chain bridges, please refer to Figure 1-2 below for details:
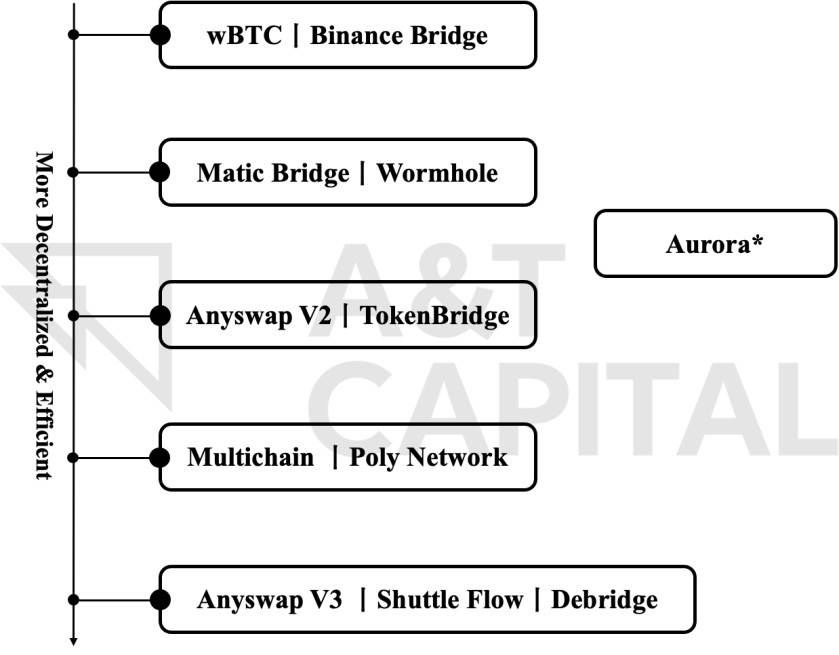
image description
Figure 1-2 Cross-chain bridge optimization process
Note: As part of the bridge, Aurora has a certain prototype of cross-chain information.The concept of cross-chain has always existed along with the development of blockchain, and the cross-chain bridge is a sector that has only become popular in the past two years. From the perspective of cross-chain development, it is generally a process from centralization to decentralization (to a certain extent, people will roughly equal the degree of decentralization to the degree of security of cross-chain, but the degree of decentralization is not security. The only influencing factor, the example here is only for the convenience of understanding). becauseDue to the different needs of users, a variety of bridges with different focuses may also emerge later.
For example, users with a large amount of funds often hope to use a more secure bridge to cross-chain assets, while ordinary users are more interested in the efficiency of the bridge.early,Centralized Exchange (CEX)
is the bridge each of us uses the most. In addition, centralized wBTC and HBTC account for nearly 90% of the current market share of BTC-anchored coins. Such single-point verification bridges, relying on their own reputation in the early days, can naturally attract a large part of the traffic.
With the development of the industry, people are gradually dissatisfied with the absolutely centralized management method, so a multi-point verification method has evolved. After all, the possibility of collective evil is smaller than the centralized method, which seems more reliable. PoS+Plasma adopted by Polygon Bridge, Solana's cross-chain bridge Wormhole is verified by 19 independent verifiers on the network, etc., all adopt multi-point verification cross-chain bridge methods.A more decentralized approach based on multi-point verification has further evolved intoRely on miners on both chainsTo maintain, this is also the way that can be seen on many chains now—that is,Mint/Destroy
, by locking the corresponding aToken on the A chain, and the oracle machine informs the smart contract on the B chain, after the miners verify it, a new bToken is minted on the B chain; when the user returns to the A chain from the B chain, destroy the bToken on the B chain bToken, release the aToken originally locked by the user. At present, many projects on the single-chain bridge also adopt this native verification method. However, the premise is that the minted token (bToken) can be used directly on the target chain. For example: the user transfers the USDC on Ethereum to BSC through AnySwap. At this time, the user obtains anyUSDC, which is a form of token. It is not possible to exchange directly on BSC. It is necessary to perform one more step of swap through its built-in AMM to convert anyUSDC 1:1 into USDC, and this method will be limited by the size of the fund pool. Therefore, this mode cannot well support many projects of multi-chain bridges.
However, atomic swap also has its limitations. For example, the development cost is high, and it needs to be developed on two chains 1-to-1 instead of 1-to-N. It does not have good versatility, and it cannot be realized between any two chains. Atomic swap, atomic swap is easier to implement between two of the same algorithm, which is why the seemingly perfect scheme of atomic swap has not been realized on a large scale.
secondary title
definition
definition
Previously, 1kx research partner Dmitriy Berenzon gave a more authoritative definition of the cross-chain bridge:On an abstract level,One can define a "bridge" as a system for transferring information between two or more blockchains. In this case, information can refer to assets, contract calls, proofs of identity, or state.
The design of most cross-chain bridges consists of several components:
Monitoring: There is usually a participating role, or Oracle, or Validator or Relayer, responsible for monitoring the status on the source chain.
Messaging/relaying: After a monitoring actor receives an event, it needs to transfer the information from the source chain to the target chain.
Consensus: In some models, consensus needs to be reached among participants monitoring the source chain before this information is relayed to the target chain.
track status
track status
secondary title
Previously, on September 8, 2021, when Dmitriy Berenzon systematically summarized the cross-chain bridge track, there were more than 40 different cross-chain bridge projects, as shown in Figure 1-3 below for details. As of October 28, 2021, it is conservatively estimated that there are at least nearly a hundred cross-chain bridge projects on the market. Although some projects have not been entered by Dmitriy Berenzon before, overall, the newly added cross-chain bridge projects There are also many.
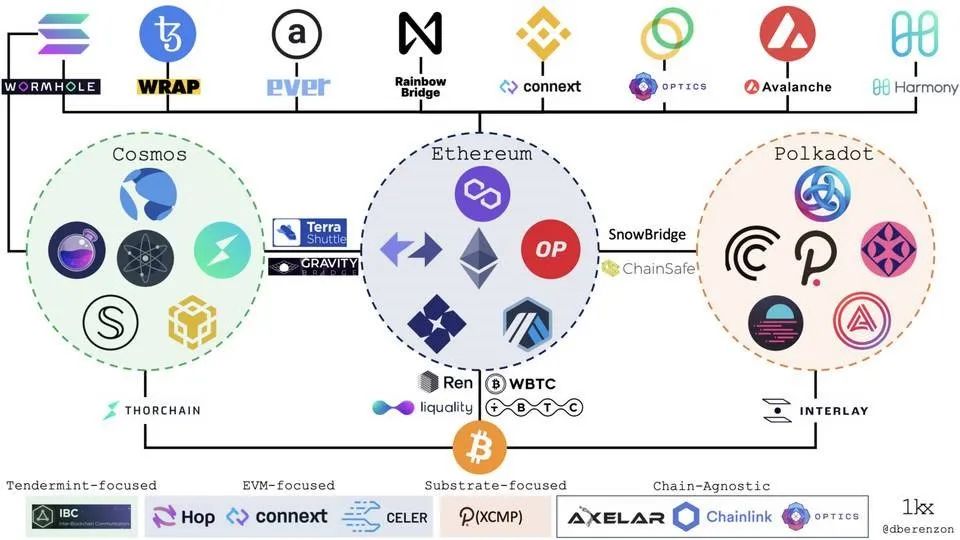
image description
Figure 1-3 Incomplete demonstration of the cross-chain bridge project
The three ecology from left to right in the picture above are Cosmos, Ethereum and Polkadot ecology, and the ones listed in the picture are basically representative projects of cross-chain bridges in their respective ecology.Combined with the current cross-chain bridge projects,Most of the main cross-chain bridges on the market are layer-2 extended cross-chain bridges, and they are mainly built on Ethereum.
, such as Arbitrum Bridges, Optimism Bridges, Polygon Bridges, etc.
And with the rapid development of EVM-compatible chains and Layer 2 this year, the network based on the Ethereum virtual machine is becoming more and more diverse. At this time, people are gradually realizing that asset cross-chain is the current rigid need.
The overall scale of the cross-chain bridge
1)TVL
According to data monitoring from Dune Analytics, as of November 1, 2021, the total locked positions of the 16 major cross-chain bridges currently included by @eliasimos have reached about 22.032 billion US dollars, accounting for about 9.10% of the total locked positions of DeFi. The TVL has increased by 37.40% in the past 30 days, and the TVL has increased by 135.36% in the past 60 days. An obvious upward curve can also be seen from Figure 1-4 below.
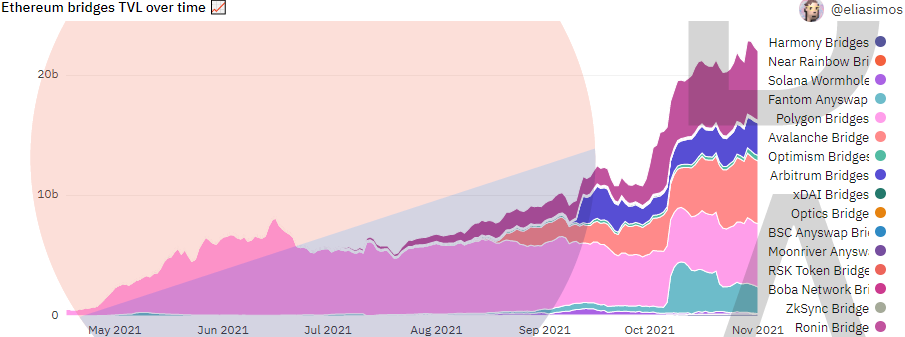
image description
Figure 1-4 TVL scale of cross-chain bridges (incomplete statistics)
2) Distribution of locked assets
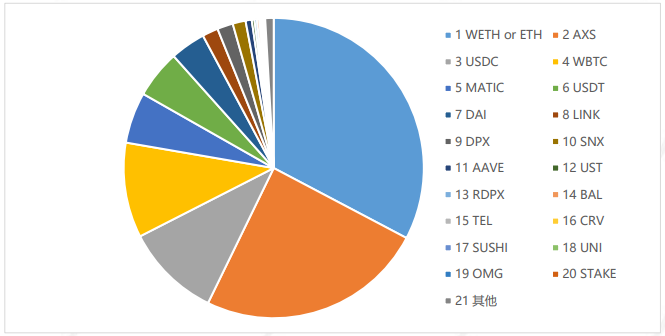
image description
Figure 1-5 Distribution of cross-chain bridge locked assets (sorted by asset size from high to low)
At present, the main trading assets on the cross-chain bridge can be divided into the following categories:
1) WETH and ETH;
2) Various stable currency assets, such as: USDC, USDT, DAI, UST, etc.;
3) Governance tokens of various DeFi applications, such as: SNX, AAVE, CRV, DPX and rDPX, etc.;
4) The original tokens of the side chain ecology, such as: AXS, MATIC, etc.;
5) Cross-chain oracle, such as: LINK.
Among them, WETH and ETH are currently the most locked-up assets in cross-chain bridges; AXS has attracted a large number of users by virtue of the Play to Earn model, and currently ranks second; stable coins and governance tokens for DeFi applications also occupy a considerable part In addition, affected by the vigorous development of the DeFi ecosystem on Polygon and the extensive demand for cross-chain oracles, the total amount of locked positions of MATIC and LINK on the cross-chain bridge is also relatively high.Overall, from the perspective of the lock-up scale of cross-chain assets, we can clearly see that,
3) Overview of the number of independent addresses of the cross-chain bridge
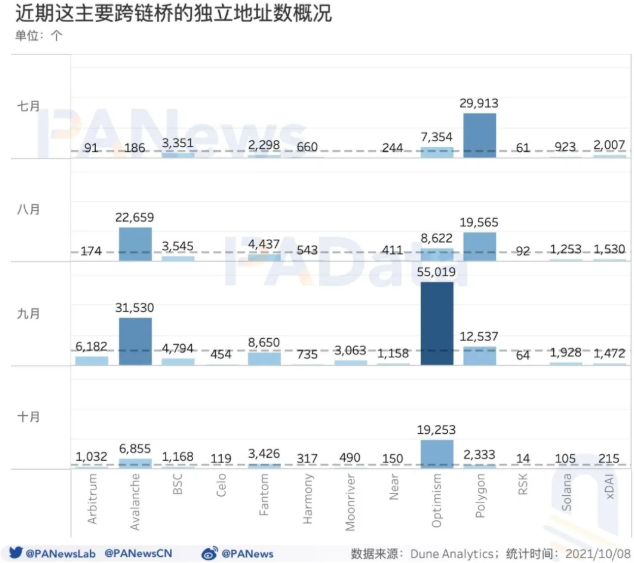
image description
Figure 1-6 Overview of the number of independent addresses of major recent cross-chain bridge projects (unit: number)
In addition, the information collected by @eliasimos in Dune Analytics shows that as of November 1, 2021, the number of independent addresses on Ethereum that have interacted with cross-chain bridge projects has reached 203,426.
first level title
Core points of the track
The core of the development of the cross-chain bridge mainly includes the following points:1) Security (Security):
Trust and liveness assumptions, tolerance to malicious actors, security and reflexivity of user funds;2) Speed (Speed):
The delay in completing the transaction, and the guarantee of finality. Often there is a trade-off between speed and security;3) Scalability (Connectivity):Select target chains for users and developers, and integrate additional target chains
different levels of difficulty;4) Capital efficiency:
Economic concepts, including the transaction costs of capital and asset transfers required to secure the system;5) Statefulness:
Different projects have different trade-offs in terms of safety, efficiency, and connectivity. In order to better understand the core points of the development of cross-chain bridge projects, we can first roughly classify the track, and then specific to each The different trade-offs of the two solutions, as well as the corresponding advantages and disadvantages.
Classification (Solutions for cross-chain bridges)
text
At present, cross-chain bridge designs can be roughly divided into four types, which can be classified according to the mechanism for verifying cross-chain transactions (different validator types):
1) Centralized Exchange (CEX)
Before the rise of cross-chain bridges, if users needed to cross-chain assets between different chains, the most primitive method often used centralized exchanges such as Binance and Huobi. The cross-chain process of CEX only involves changes in the balance of various assets on the cross-chain bridge. Involves the minting and burning of assets.
Strictly speaking, this is not a bridge at all, but it is indeed a simple and effective solution. However, although we can choose to trust Binance’s reputation in the short term, no one can guarantee that it will never make mistakes and generate potential risks. So there are several other plans in the future.
2) Single-point/multi-point external authentication
Single-point/multi-point external verification, there is usually one or a group of validators monitoring a specific address on the source chain. In the process of asset cross-chain, the user first sends the asset to the specific address of the source chain, and then locks it. A third-party validator will verify this information and a consensus needs to be reached. Once a consensus is reached, an equal amount of assets will be minted on the target chain. These validators generally use different tokens as collateral to ensure security. The usual forms of external verification technology are: secure multi-party computing (MPC) system, oracle machine network, threshold signature, etc.
A typical representative of single-point external verification is wBTC. Representatives of multi-point external verification include Anyswap, Synapse, PolyNetwork, etc., which are similar to single-point external verification on the whole, except that under the conditions of asset pledge + game, they are less likely to make mistakes collectively, which is theoretically more likely than single-point external verification. Point verification is more reliable, and the actual effect depends on the design of the mechanism and the participants.
3) Native authentication
Native verification literally means that verifiers (miners/nodes) on the source chain are witnessing and guaranteeing, without relying on third-party verifiers or pledged assets. This is usually done by running a light client of one chain inside the other chain's Ethereum Virtual Machine (VM).
The biggest advantage of this model is that it does not require trust, and it completes the verification by running the light client of the source chain in the virtual machine of the target chain. The participants of the cross-chain bridge monitor the messages on the source chain, and then forward the monitoring records and block headers including encrypted proofs to the contracts on the target chain. Actions are performed on the target chain after validation of recorded events. Overall, because it is a trustless model, the security performance is better.
In addition, under the witness of miners on both sides of the target chain and the source chain, users can not only realize asset transfer, but also realize generalized information transfer.
However, the shortcomings are also obvious. To deploy such a native verification bridge between any two chains, developers need to develop and deploy new light client smart contracts on the source chain and the target chain to verify the information of the source chain. At the same time, this verification itself will be relatively expensive. Therefore, its shortcomings mainly lie in high cost, slow speed, and it is not easy to expand to more chains, and there will be certain restrictions in the early stage.
Projects like Cosmos' IBC, Near's Rainbow Bridge, Polkadot SnowBridge, LayerZero, Movr, Optics, Gravity Bridge and other projects all adopt native verification solutions.
4) Local verification (liquidity network)
Local verification is a local verification mode, which is also a point-to-point liquidity network. Each node itself is a "router", and the router provides the original assets of the target chain, not derivative assets. Additionally, routers cannot take user funds away through lock-in and dispute resolution mechanisms.
Like many newly launched cross-chain bridge projects, this model is adopted, such as: Hop, Connext, Celer, Liquality, and some simple atomic swap systems. It can be seen that this peer-to-peer model performs well in terms of security. At the same time, its fee, speed, and multi-chain connection expansion are not bad. However, its main disadvantage is that it is limited in the transmission of information and cannot be generalized.The cross-chain bridge form of this liquidity network may give birth to one or more cross-chain underlying protocols: for protocols or Dapps that want to provide cross-chain functions, they only need to access these cross-chain protocols to support cross-chain.
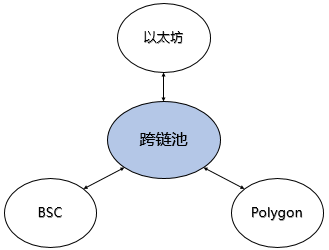
Figure 1-7 Simple demonstration of cross-chain pool
If the cross-chain bridges on the market are distinguished according to the above ideas, the results in the following table can be obtained:
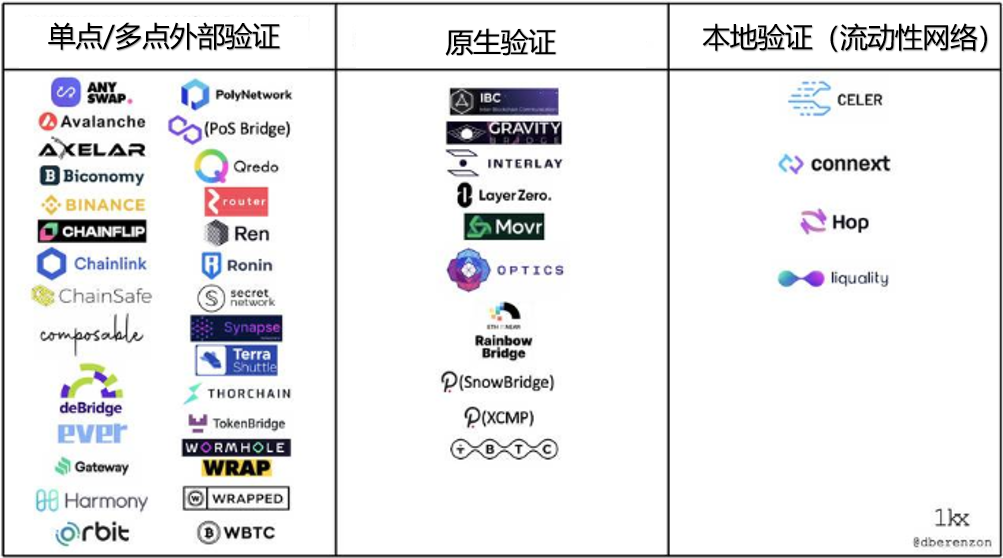
Table 1-2 Classification of cross-chain bridge projects
image description
Note that any particular bridge is a two-way communication channel, and there may be separate models in each channel, and the above classification does not accurately represent hybrid models, such as Gravity, Interlay, and tBTC, because they all have Light client, with validators in the other direction.
first level title
Trade-offs of different cross-chain bridgesAccording to the above description, in summary, in addition to CEX, in addition
According to the above-mentioned dimensions: security, speed, scalability, capital efficiency, and status, the following figure can be obtained:
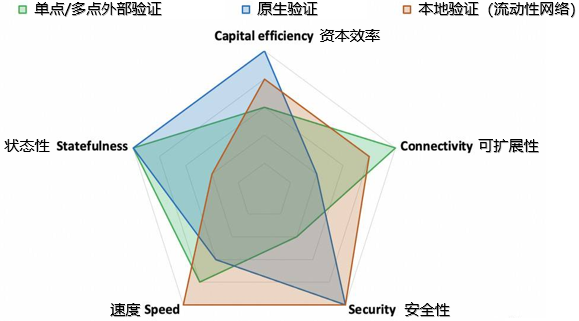
image description
Figure 1-8 Comparison of advantages and disadvantages of different solutions for cross-chain bridges
Figure 1-8 above, the data compiled by Dmitriy Berenzon, can clearly reflect the advantages and disadvantages of different cross-chain bridge solutions. Specifically, to see:
1) External verification, the advantage is that it is faster, cheaper, can pass common data, and allows interaction with the data on any number of target chains, making it easier to connect to more chains. However, the disadvantage is that this method is at the expense of security, requiring users/LP to fully trust the funds/data of the external validator, relying on the security of the bridge, not the source chain or the target chain.In some cases, external verification often adopts additionalStaking or bonding mechanism
, to try and add security to the user. This requires the verifier to over-collateralize to ensure that the collateral assets > the verification amount, and as the throughput increases, the demand for collateral will also be proportionally expanded, so it is economically capital inefficient.
2) Native verification, for the data transmitted between chains, it is completely verified by the verifier of the underlying chain itself, and the verifier of the underlying layer is directly responsible for the security of the bridge, which is currently the most trustless form of cross-chain bridge. If there is a security problem, it is also a problem with the chain itself. At the same time, there is no need to pledge assets (higher capital efficiency).
However, these advantages come at the cost of scalability. For each chain connected, the developer must deploy a new light client smart contract on the source chain and the target chain. In addition, native verification also has the disadvantages of slow speed and high cost. For example, when encountering an Optimistic model (such as Optimism) that relies on fraud proofs, the transaction delay may reach more than 4 hours.
3) Local verification is a model of the liquidity network. It uses local verification and does not require global verification, so it is faster and cheaper. And it is also trustless, their security is supported by the underlying chain, because Rollups share some reasonable guarantees, it also has the advantage of security. At the same time, the throughput of the point-to-point liquidity network is also relatively large. The disadvantage is that it has limitations in information transmission and cannot achieve generalized information transmission (but it is enough for the current DeFi).
Different modes of cross-chain bridges have different trade-offs. Users with different capital scales have different considerations for capital efficiency and security systems. Each bridge focuses on areas that have corresponding user needs. Therefore, there is a high probability that the cross-chain bridge will not be dominated by one company in the future, and it is more likely to be a situation where multiple bridges develop together.
first level title
track project
As we mentioned above, there are currently at least 70+ cross-chain bridge projects on the market. Faced with such a large number of projects, in this chapter, First Class Warehouse will take stock of some representative cross-chain bridge projects on the market to show the current status of this track. service capabilities and assist users in making investment choices.
The classification of cross-chain bridges in this chapter mainly refers to the division of the track by Mr. Pan Zhixiong, who was previously heard by Lianwen:1) Official bridges, including Solana's Wormhole, NEAR's Rainbow Bridge,
The safety of this type of bridge is the most guaranteed.
2) Professional, asset-based bridges, including Ren Protocol, Keep Network, DeCus, pNetwork, etc., focus on crossing Bitcoin to other networks, the solutions are different, and the capital efficiency needs to be improved, but in the past DeFi Nice growth in Summer.3) More general third-party bridges, such as Poly Network, Celer, Anyswap, Hop Protocol, Synapse Protocol, etc.
4) The cross-chain bridge aggregator is still relatively early. The main concept is to aggregate mainstream cross-chain bridges, and help users automatically match and recommend the best cross-chain bridge solution according to the actual needs of users.
secondary title
At present, the official bridge situation of the well-developed public chain is mainly as follows:
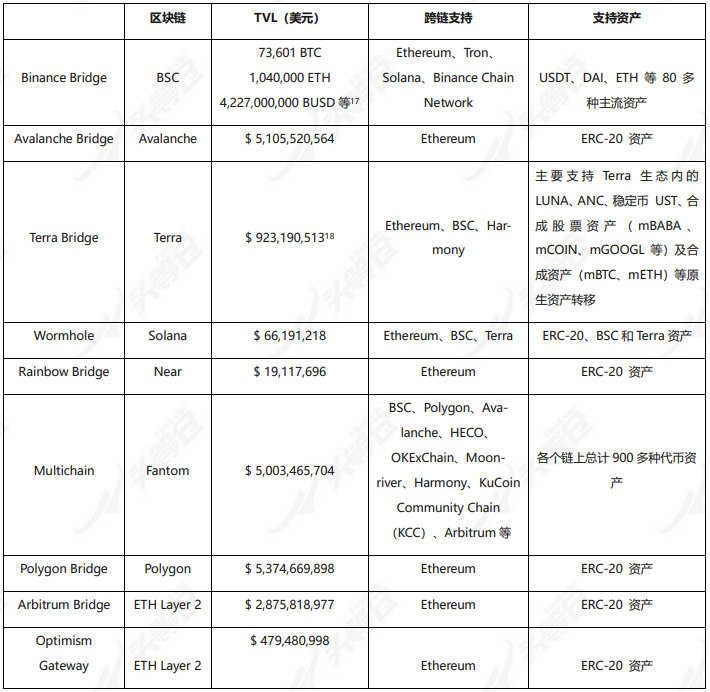
image description
Table 2-1 Introduction to the official bridge
The official bridge part is mainly to introduce the corresponding options when transferring assets on the chain. In addition, none of the official bridge projects introduced in this section have issued coins. Users who are familiar with cross-chain interaction can directly skip to the next part 2.2 chapter to read.
Binance Bridge
text
Official website: https://www.binance.org/en/bridge
The operating principle of Binance Bridge is to lock a certain amount of native assets first, and then encapsulate the native assets into cross-chain assets at a ratio of 1:1. Taking the cross-chain of ETH assets from Ethereum to BSC as an example, when the user wants to withdraw the assets (BETH, Binance-Peg Ethereum Token) cross-chained to BSC to Ethereum, the encapsulated assets (BETH) will be transferred according to the amount transferred Destroy and unlock the original asset (ETH) at 1:1. On the BSC chain, the cross-chain assets from Ethereum usually appear in the BSC ecosystem in the form of encapsulated assets, often marked with B, such as BETH and BDAI are encapsulated assets mapped 1:1.
Avalanche Bridge
text
Official website: https://bridge.avax.network/
Avalanche Bridge (AB Bridge) is the official cross-chain tool launched by Avalanche Protocol in early 2021. It is mainly used to solve the problem of users transferring assets under the ERC-20 standard on the Ethereum chain and Avalanche network assets.
It should be noted that Avalanche Bridge does not support native ETH and BTC assets, but it can transfer encapsulated assets such as WETH and WBTC through the bridge.
Terra Bridge
text
Official website: https://bridge.terra.money/
Terra Bridge is an asset cross-chain tool officially provided by Terra (LUNA). It currently supports the intercommunication of Terra native assets in BSC, Ethereum, and Harmony networks. It mainly supports LUNA, ANC, stable currency UST, and synthetic stock assets (mAAPL) in the Terra ecosystem. , mAMC, mGOOGL, etc.) and synthetic assets (mBTC, mETH) and other native asset transfers.
Wormhole
It should be noted that the minimum value of cross-chain assets supported by Binance Bridge is around $50 - $130 (the minimum limit for different assets is slightly different), and the minimum value limit of the Avalanche Bridge cross-chain of the Avalanche Protocol is not less than $75. Each cross-chain bridge has a minimum cross-chain amount limit, while Terra Bridge does not have any asset quantity and value restrictions.
Official website: https://wormholebridge.com/#/Wormhole is an asset cross-chain tool jointly developed by Solana and Certus.One. Launched on September 22, 2021, it is mainly used to realize cross-chain assets between Ethereum and Solana. At present, with the launch of the V2 version, Wormhole has added support for the asset transfer function on the BSC and Terra chains,NFT support will be further expanded in the future
, to realize the cross-chain transfer of ERC-1155 assets.
Before the emergence of Wormhole, when users on Solana want to exchange assets with other blockchain networks, the usual operation is to first sell the SPL assets on the Solana chain to the centralized exchange FTX, and then buy other chains When entering the Solana ecosystem, users also need to buy SPL assets through FTX first, and then recharge to the Solana chain.
In addition to Wormhole, there are more and more cross-chain bridges focusing on non-EVM public chains such as Solana, such as Allbridge.
Rainbow Bridge
text
Official website: https://ethereum.bridgetonear.org/
Rainbow Bridge has optimized the account system. Usually, when the user's assets cross-chain, the wallet needs to be switched to the target network first, and it is generally only supported to connect to the same wallet address. But in Rainbow Bridge, users only need to log in with the Near account, and then they can fill in the address and amount of the on-chain wallet that they want to transfer in or out, and Rainbow Bridge will automatically perform this operation.
Multichain
text
Official website: https://multichain.xyz/
multichain.xyz is mainly aimed at the cross-chain between platforms that support the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM). It is a cross-multi-chain platform jointly developed by the Anyswap team and Andre Cronje, the founder of yearn.finance (YFI).
text
Polygon Bridge
text
Official website: https://wallet.polygon.technology/bridge
Currently Polygon Bridge supports both PoS Bridge and Plasma Bridge. PoS Bridge is the officially recommended bridge, it has a faster withdrawal time (about 30 minutes), supports more Ethereum asset standards, and Plasma Bridge needs to wait for a 7-day challenge period when withdrawing funds, but it is safe The level will be higher.
Arbitrum Bridge
text
Official website: https://bridge.arbitrum.io/
Arbitrum Bridge is a cross-chain bridge officially launched by Arbitrum, the Ethereum Layer 2 expansion protocol, which is mainly used to solve the transfer of assets between Ethereum Layer and Arbitrum.
It should be noted that when withdrawing deposited assets from the Arbitrum network to Layer 1 through Arbitrum Bridges, there is a withdrawal period of at least 7 days after the withdrawal application. In other words, the user needs to wait at least 7 days until the Layer 1 main network receives the withdrawal to prove that your withdrawal is successful.
Optimism Gateway
text
Official website: https://gateway.optimism.io/
Also note that there is also a 7-day withdrawal period for withdrawing deposited assets from Optimism.
secondary title
asset class bridgeProfessional, asset-based bridges, in the early days and even now,
Most of it is focused on getting Bitcoin across to other networks.
On the one hand, due to the explosion of the application side (DeFi), cross-chain assets debuted ahead of schedule, without even relying on the main cross-chain platforms Polkadot and Cosmos, but first in the mode of wrapping tokens (Wrapped Token) and operating in the mode of smart contracts stand up.
In the face of such a large-scale market, there are already many projects dedicated to crossing Bitcoin to other networks, and have achieved good growth in the past DeFi Summer. The model of Wrapped Token also makes capital efficiency relatively low.
WBTC
Official website:https://wbtc.network/
Official website:
The Bitcoin funds of wBTC are stored in the cold wallet of the custodian agency BitGo. Founded in 2013, BitGo specializes in providing custody services for digital assets to institutional clients. Organizations like BitGo are themselves registered companies governed by local laws, and most have certain insurance plans. Therefore, law and insurance are the two layers of protection for centralized custody services.
For wBTC, this organization includes many famous projects of DeFi and wallets. As merchants, they will also hold a large amount of wBTC in their hands. The so-called "too big to fail", once there is a problem with financial security, all members of the organization will suffer losses. Therefore, as an ordinary user, it is not so much the trust in the custodian BitGo, but the trust in the entire project organization. I believe that members of each organization will supervise each other in the face of systemic risks.
In addition, wBTC also uses Chainlink's savings proof mechanism to make up for the centralization problem. The specific process is that the DApp on Ethereum can be connected to the proof of savings contract. The oracle network supported by Chainlink checks the balance of BitGo's wBTC managed wallet every 10 minutes. When the deviation exceeds the defined threshold, Chainlink will use New balance and data push on the chain. This approach allows all users to view the pledge status on wBTC in real time, further ensuring asset security.First-class warehouse view:Overall, WBTC has established a huge advantage over other competing products, and has become the default BTC anchor currency on Ethereum.
Keep Network
Official website:https://keep.network/
Official website:
Keep Network's main focus is on cross-chain BTC assets. tBTC is a cross-chain project of the decentralized relay solution. In terms of security, tBTC has three guarantees:
1) Encryption with threshold ECDSA signature; 2) Random beacon; 3) Signers need to over-mortgage ETH, increasing the economic cost of doing evil.
Its security technology is currently at the forefront of the entire BTC asset cross-chain, but it requires a 450% over-collateralization, which is poor in terms of capital efficiency. However, the team has included this as an improvement point in the subsequent tBTC v2 version.
The recent work of Keep Network mainly revolves around the merger with NuCypher. At that time, the protocol functions and communities of the two projects will be merged into the Threshold Network, not the merger of the company, and a new token "T" Token will be issued. According to the team, the merger is in its final stages and will go live soon. In the near future, Threshold Network will increase the adoption rate of tBTC and possibly introduce other cross-chain assets.First-class warehouse view:
At present, tBTC only accounts for 0.26% of the BTC anchor currency market share (a total of 793 tBTC), and the TVL is 285 million US dollars. If the v2 version can attract enough LPs, and coupled with the current popularity of the cross-chain bridge sector, there may be certain opportunities in the future.
Ren Protocol
Official website:https://renproject.io/
Official website:
Ren is a cross-chain project using a decentralized witness solution. Its main product is RenVM. Currently, RenVM's cross-chain supports ETH, BSC, Solana, Avalanche, Fantom, Polygon, and Arbitrum. In addition, support for Terra will be added in the future , among which renBTC occupies the third position in the entire BTC anchor currency market, accounting for 5.38% of the market.
RenVM is used to encrypt locked assets. It uses the Hyperdrive consensus algorithm to run blocks, and uses SSS to encrypt private keys, making the network safe when less than 1/3 of the nodes do evil. It uses sharding to randomly shuffle all dark nodes to reduce the possibility of collusion. Finally, it adopts the scheme of mortgaging REN to increase the economic cost of doing evil.Currently, the Ren team is actively cooperating with DeFi projects and adding cross-chain support to continuously expand ecological use cases. Recently, the mining revenue on public chains such as Fantom, Polygon, Solana, and Avalanche has surged, and the TVL growth rate has been obvious. The cross-chain support newly added by RenVM has achieved good results for the ecology. From the end of September to the present (11 2) TVL has increased by about 2 times, and has increased by about 3 times compared with the end of August. Currently, RenVM's TVL has reached 1.75 billion US dollars. The business situation continues to grow and deserves attention.
pNetwork
Official website:https://p.network/
Official website:
pNetwork is an asset issuance platform that utilizes TEE and MPC to support cross-chain functions, allowing trusted execution environments (TEEs) and MPC-supported networks to issue cross-chain composable or pToken assets to protect underlying assets.
Among them, pBTC is a BTC-anchored token issued by pTokens, which is based on various decentralized witness cross-chain solutions. pBTC uses trusted computing for security, BTC addresses are managed by a set of validators running a Trusted Execution Environment (TEE, a type of hardware), and are also coordinated using a threshold signature scheme. It currently supports use on Ethereum, BSC, Polygon, xDAI, Arbitrum, Telos, and EOS chains, and the current TVL is $227 million.
In addition, according to the pNetwork team, pNetwork will release version v2, pNetwork v2 is a cross-chain routing protocol, which enables users and smart contracts on any blockchain platform to send and receive asset and data information across chains, improving and expanding the applicability of the previous version. pNetwork v2 will introduce Postman, a general-purpose messaging system for transferring data across chains, and the pTokens bridge will also be upgraded to support direct transfers from one blockchain to another (for example, pBTC on Ethereum can be transferred directly to Arbitrum or Polygon without going back to the Bitcoin network).text
summary:
summary:
Of course, there are many other solutions. There is still a lot of room for innovation in BTC anchor assets that do not require trust. At present, the centralized method is the best, but in the future, as the industry continues to improve, it may gradually move towards decentralization. The way of evolution. For the best practice, it needs to be further explored.
third party bridge
text
Official website:
AnySwap
Official website:https://anyswap.exchange/
IntroductionIntroduction: AnySwap is a public blockchain based on FusionDecentralized cross-chain exchange
, the exchange part adopts the same technology as Uniswap, with automatic pricing function and liquidity system. The difference is that the exchange pairs provided by Uniswap are limited to Ethereum and ERC20 tokens, while AnySwap realizes cross-chain token exchange through Fusion's DCRM technology.
Take the process of recharging BTC to complete asset mapping as an example. The user deposits assets into the Anyswap custody account, and the smart contract constructed by Anyswap through the cross-chain bridge realizes the generation of mapped assets on the chain according to the state changes of the custody account, and distributes them to the user's account on the chain, thereby completing the cross-chain mapping of assets .
It should be noted that Anyswap's multi-chain router v3 version was hacked before, and the cross-chain fund pool lost about 8 million US dollars. The main reason is that hackers discovered Anyswap's code loopholes, obtained the public-private key pair, and stole assets.
user experience:user experience:
The advantage is that the withdrawal period does not need to be 7 days, which is usually enough for ordinary users, but it is not very friendly for large accounts.
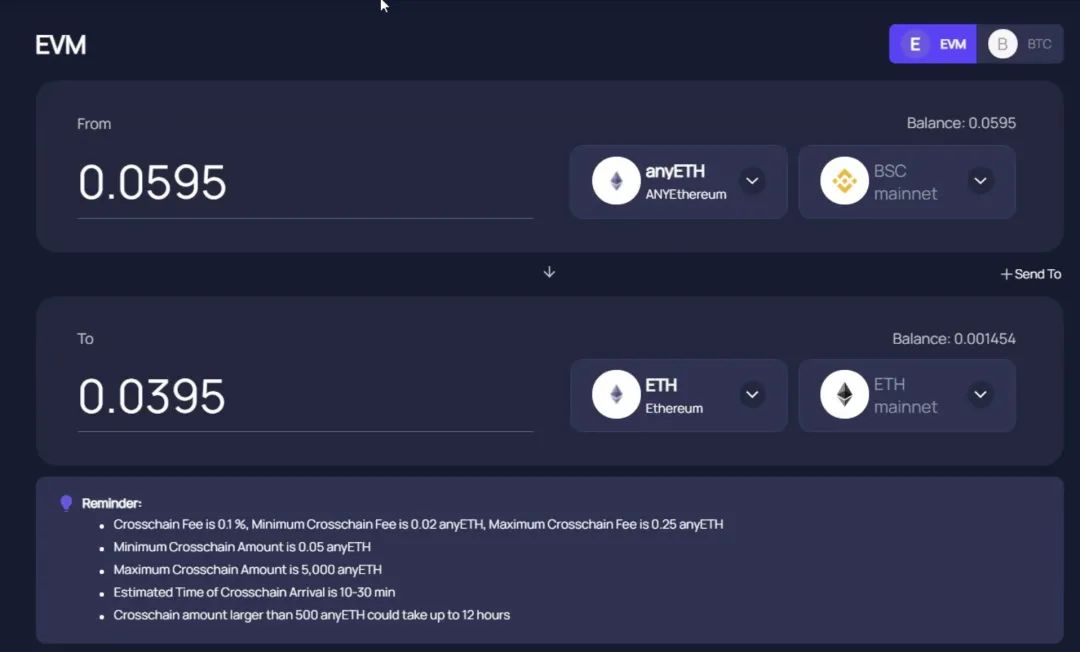
image description
Figure 2-1 An example of the Swap method being limited by the size of the fund pool (data as of November 12, 2021)As of November 10, 2021, AnySwap currently supports 901 token exchanges including 23 chains including Ethereum, Fusion, BSC, Fantom, Polygon, and Arbitrum, with 35 nodes and cross-chain locked assets reaching 4.96 billion US dollars , is currently the project with the highest TVL on the cross-chain bridge track.
Economic Model:Economic Model:
The token of Anyswap is ANY token, with a total of 100 million tokens, currently 17.25% in circulation.
Official website:
cBridge
Official website:https://cbridge.celer.network/#/transfer
Introduction:Introduction:
cBridge is a cross-chain bridge tool developed by the Celer team, based on atomic swap technology.
The current focus of Celer Network is cBridge (cross-chain asset transfer). Version 1.0 will be launched at the end of July 2021, and the 2.0 testnet will be launched in October.
The main problems of cBridge 1.0 include: 1) Centralization, user requests and allocations are centrally allocated through the gateway; 2) Service nodes may go offline before completing the service, resulting in user funds being stuck. In addition, in version 1.0, only nodes can provide liquidity, so there will be insufficient liquidity, and it will not be possible to provide cross-chain services for large amounts of funds.
cBridge 2.0 is a brand new asset and information cross-chain solution (the focus of development in the short term is still on asset cross-chain), based on DPoS. In addition, 2.0 has designed a set of incentive mechanisms to allow users and LPs to balance liquidity, similar to Curve's AMM mechanism, which promotes the balance of liquidity in different chains.
user experience:user experience:
cBridge currently supports relatively few types of tokens for transfer, but it feels good to use. The cross-chain fee is divided into two parts: the transaction fee of the network itself + the operating fee paid to the relay node (priced by the node itself). At present, the transfer between different chains only requires a transaction fee of about 0.5 knives, while the Ethereum main network involves The transaction fee for asset transfer is still relatively expensive. Compared with the transfer through the native cross-chain bridge, the transaction fee is lower. In addition, the exit period does not need 7 days. The disadvantage is that the liquidity of assets in the agreement will limit the scale of cross-chain assets.scale:
In addition, according to the Celer block browser [28], as of November 10, 2021, the total number of unique addresses that have interacted with the cBridge cross-chain bridge reached 34,091, and the total historical cross-chain transactions reached 879 million US dollars.
Economic Model:Economic Model:
Celer Network token symbol: CELR, the total number of tokens is 10 billion, and 56.45% of them are currently in circulation.
The economic model in the cBridge 1.0 version can be said to perform poorly. The main reason is that if users want to do LP in the original version, they must operate and maintain a node independently, and the threshold is relatively high. In the atomic swap mode, the liquidity may not be so high, because it is a way to split liquidity, but it will perform better in terms of security.
However, the team also made some trade-offs in the 2.0 version, and launched the DPoS model, users can directly choose to trust the relay nodes on the chain, instead of running a separate node.First-class warehouse view:
After the SGN of cBridge 2.0 is used as a public liquidity pool, users who do not want to operate nodes can also provide liquidity for cBridge, which makes it easier for Layer 2 or other Layer 1 project parties to provide liquidity on celer, which is conducive to increasing the liquidity of cBridge depth. As a node gateway and arbitrator, SGN is also beneficial for Bridge to provide better services.
On the other hand, although cBridge adopts a bonding curve algorithm similar to Curve, when a large amount of funds enters and exits, there may still be a relatively large slippage, so the applicability of large amounts of funds across chains still needs to be observed. In addition, when there is a liquidity overflow event like Arbitrum, nodes can ensure liquidity balance through denial of service, and it is still doubtful that SGN, as a public pool, can maintain liquidity balance among multiple chains in such events.
NXTP(Connext)
official:https://connext.network/
Introduction:Introduction:
The full name of NXTP: Noncustodial Xchain Transfer Protocol (Noncustodial Xchain Transfer Protocol), released by the Connext team, this protocol uses an atomic transaction mechanism similar to hash time locks, but does not rely on hash preimages, but is based on smart contracts. The trigger condition of one transaction is directly set to provide the signature of another transaction.
NXTP's cross-chain transactions are mainly completed through 3 steps:1) Selection and auction of transaction routing (Route selection)
, the user selects a specific chain and asset, and then submits the transfer information to start the auction (Router). After the routing node obtains this information, it needs to submit a private bid information, which must include the time and price range for completing the transfer.From this point of view, the Router in NXTP and the relay node in cBridge take on the same role, the difference is that the former isCustomize the price of its services and bid on users
, while the price of the latter service is uniformly regulated by the agreement and adjusted through governance.2) Prepare to trade (Prepare)
, after the user submits a bid information containing the signature of the routing node to the Nxtp contract, the transaction will lock the user's assets in the chain. When the routing node detects a transaction event in the contract, it can lock the asset liquidity of this chain on the target chain. The amount of funds locked by the routing node = sending amount - auction fee, so the routing node can earn part of the income from this transaction.3) Execute the transaction (Fulfill)
, the user provides a transaction signature to unlock the assets on the target chain, and the routing node can use the user's public signature information to obtain assets from the original chain.
At any point in the process, the deal could be canceled, the team said. Once the transaction times out, the transaction can be canceled by either party.
In addition, NXTP's liquidity provides a virtual AMM (Virtual AMM) mechanism, which means that the user pays 1 USDC on the source ledger, and may not get (1 - r) USDC on the target ledger (set the handling fee as r ), and may be (0.99-r) or (1.02-r), the specific value depends on the total liquidity ratio of the source book and the target book (the more unbalanced the pool ratio, the larger the price difference will be, but The opposite also creates more arbitrage opportunities). The purpose of this design is to add a negative feedback mechanism to promote the Router to balance the liquidity on different books according to demand.
Official website:
- Hop Protocol
Official website:https://hop.exchange/
Introduction:Introduction:
Hop Protocol is a cross-chain bridge developed by the former smart contract wallet development team Authereum. In their plan, a Rollup-to-Rollup universal asset bridge is designed to realize asset transfer between Layer 2 networks and the Ethereum mainnet.
Hop Protocol has two core components: Automated Market Maker (AMM) component and Connector (Bonder).
When using Hop, assets need to be transferred to the Layer 2 network through Hop. For example, ETH entering the second layer through Hop's asset bridge is called Hop ETH (or hETH). hETH and ETH are theoretically completely equivalent, but due to liquidity reasons, there may be some price differences.
So Hop Protocol introduces AMM components and connectors. AMM is designed to solve the short-term price difference between ETH and hETH, and the role of the connector (Bonder) is to provide liquidity for users who need to release liquidity in advance. Provide liquidity to help users convert hETH into ETH, and at the same time obtain some benefits (because it saves users a 7-day withdrawal cycle).
The simple understanding is that the user converts Token into hToken in Hop Protocol, and then uses Hop Bridge to send hToken from Rollup 1 to Rollup 2. At this time, since the connector (Bonder) has provided early liquidity for hToken in Rollup 2, Therefore, Hop's AMM can automatically help users convert hToken to the original Token, thus eliminating the 7-day withdrawal cycle in Rollup.
user experience:user experience:
The exit period on Hop does not need 7 days, and the transaction fee may be higher than other networks, because the cross-chain cost includes: the transaction fee of the network itself + the protocol transaction fee (0.04%), and there is also transaction slippage . In addition, the overall user experience is relatively smooth.First-class warehouse view:
Official website:
- O3 Swap
Official website:https://o3swap.com/
Introduction:Introduction:
O3 Swap is a cross-chain aggregation transaction protocol incubated by the O3 Labs team. It currently supports cross-chain interaction with a total of 6 chains including Ethereum, BSC, Polygon, Arbitrum, Heco, and Neo. By deploying the "aggregator + asset cross-chain pool" model on different public chains and Layer2 networks, the free exchange of mainstream assets on different chains is realized.
The main functional module of O3 Swap consists of two parts: O3 Aggregator (transaction aggregator) and O3 Hub (cross-chain transaction pool). O3 Aggregators are aggregators deployed in various mainstream networks to help users find the best price and the most effective transaction path; O3 Hub is the hub of cross-chain transactions, connecting various public chains and Layer 2 networks through the cross-chain protocol Poly Network The mainstream assets on the platform are aggregated in the Cross-chain Pool to create a cross-chain asset transaction pool, thereby helping users realize cross-chain transactions of assets on different chains. In addition, users can add liquidity to O3 Hub to obtain cross-chain transaction fee rewards and O3 rewards.At present, the liquidity scale on O3 is 199 million US dollars. After the previous hacking incident, it has dropped from the peak value of 783 million US dollars to a large extent.
Economic Model:Economic Model:
The token symbol of O3 Swap: O3, the total number of tokens is 100 million, and 27.67% of them are currently in circulation.
There are three main uses of O3 tokens: 1) Participate in staking to obtain income distribution in the O3swap treasury; 2) Provide LPs to unlock frozen O3 or conduct new mining; 3) Participate in the governance of the DAO organization of O3 Swap .First-class warehouse view:
After the incident with the hacker attack, although the hacker returned all the assets in the end, it still had a considerable negative impact on O3.
Official website:
- StarkEx Bridge
Official website:https://starkware.co/
Introduction:Introduction:
StarkWare is a zero-knowledge proof research and development organization and the developer of the ZK Rollup layer-2 network StarkNet. StarkEx is an extensible toolset developed by StarkWare for StarkNet, including StarkEx Bridge.
StarkEx’s current service model is L2 as a Service, which supports other projects to use StarkNet technology to build their own independent L2 network. At present, StarkEx’s customers include Immutable X, dYdX, DeversiFi, and Sorare, all of which have built their own networks with the support of StarkNet. L2 network. Therefore, StarkEx Bridge first needs to solve the cross-layer transaction problem of the L2 network within the StarkEx ecosystem, and then gradually expands to adapt to all L2 solutions.



