[Virtual Machine Column] Understand the application of Rust smart contracts in three minutes
【Guide】
In previous issues of "The Past and Present of Smart Contract Execution Engines" and "A Familiar New Friend - On-Chain JVM", we introduced the origin of smart contracts and the self-developed execution engine HVM that can execute Java smart contracts. Although the performance of HVM has been greatly improved compared with EVM, due to the large number of bytecodes, the execution performance in the interpretation execution scenario is very limited. On the other hand, security problems caused by contract loopholes (regardless of business logic loopholes) occur every year, causing serious economic losses. Is there a solution that allows users to put aside personal factors and write as much as possible Safe contract?
In order to solve these two urgent problems, we introduced the wasm virtual machine FVM and the Rust contract writing framework. The following article will introduce the application of these two parts in the field of smart contracts in detail.
【safety】
people"people", often brings the color of quantum science, it is better to have another set of mechanisms to ensure the correctness of the contract.
Rust as an efficient and reliable general-purpose language is without a doubt the best solution available.
The reliability of the Rust language relies on a rich type system and ownership model, as well as a powerful compiler that can catch classic errors at compile time. This forces developers to think about the accuracy of each line of code they write in the process of writing the contract, and confirm it through the compiler to ensure that the contract code checked by the compiler must be safe, which greatly improves the security of the contract and reliability.
In addition, our self-developed contract framework provides a runtime testing framework, allowing developers to simulate contract operation and find problems in the contract off-chain without deployment. This undoubtedly adds a layer of insurance to the contract on the chain.
In addition, our contract framework uses rust's macro expansion technology to place operations in macro annotations. This allows developers to pay more attention to the business logic of their own contracts during use, which ensures the security of the contract logic to a certain extent. After all, only one part needs to be focused on without interference from other factors, allowing developers to devote themselves more To polish the details of the logic.
【effectiveness】
EVM is essentially a script program and a stack-based virtual machine, which needs to be translated into instructions by a compiler and then executed, that is, interpreted and executed, which leads to very low execution efficiency of EVM. In contrast, wasm uses the method of compilation and execution, adopts virtual machine/bytecode technology, and defines a compact binary format, which has higher and faster execution speed of smart contracts. Therefore, we introduced wasm to greatly improve the operating efficiency of the entire contract.
WASM (WebAssembly) literally means web assembly, an assembly language customized for web browsers. Although it is said to be customized here, with the development of spirituality, it is not only applicable to the web, and its "core specification" has nothing to do with the platform. Since it is called assembly, it obviously has the characteristics of assembly language:
1) Low level, close to machine language, improving operating efficiency;
2) Suitable as object code, generated by other high-level language (C/C++/Rust/Go, etc.) compilers to expand applicability;
 In addition, the module is the unit of wasm program compilation, transmission and loading. wasm defines two module formats:
In addition, the module is the unit of wasm program compilation, transmission and loading. wasm defines two module formats:
Binary format: It is the main encoding format of the wasm module, and the file is suffixed with .wasm. Due to its very compact format design, the binary size can be reduced, and it has faster transmission and execution efficiency.
Text format: the file is suffixed with .wat, and will not be expanded in detail here.
The division of modules makes the organizational structure of wasm clearer, the analysis is more convenient, and the efficiency of analysis is greatly improved.
[FVM detailed explanation]
So in addition to using Rust to write the contract and compile the contract into wasm bytecode, to actually run the contract, it is still necessary to provide an operating environment for wasm, which is what FVM does.
Semantically speaking, a wasm module can be divided into three stages from binary format to final execution: decoding, verification, and execution. The decoding phase decodes the binary module into memory format; the verification phase statically analyzes the module to ensure that the structure of the module meets the specification requirements, and the bytecode of the function has no bad behavior; the execution phase can be divided into two parts: instantiation and function calling .
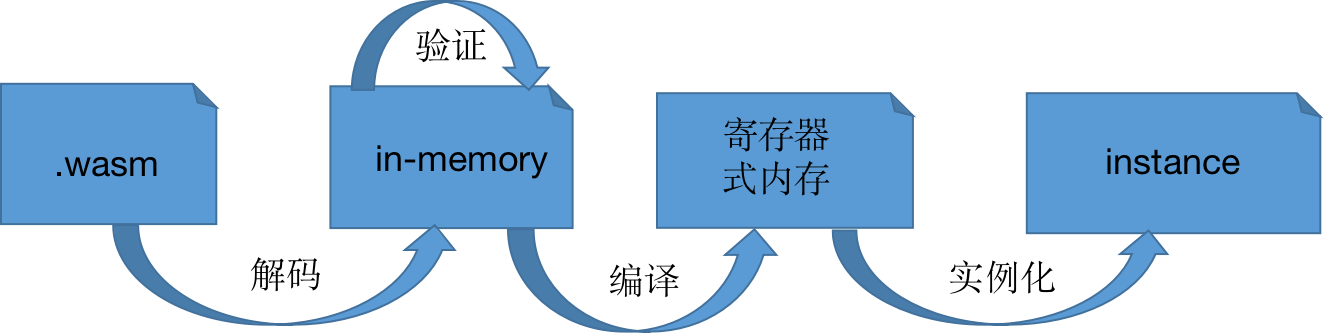 (1) Composition of FVM
(1) Composition of FVM
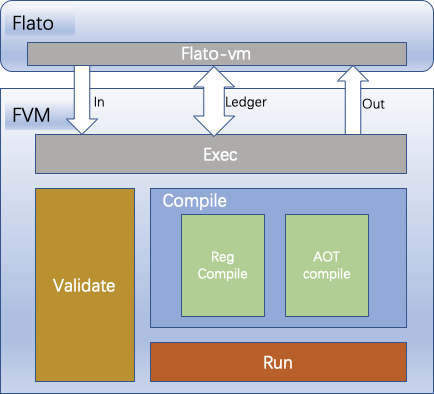
Obviously, the complete function of FVM should include the decoding, verification, instantiation and function calls mentioned above. We implemented FVM according to the entire process, but in actual operation, we found that the execution process consumes a lot of performance in memory reading, writing and allocation. In order to further improve the execution performance of FVM, we have added a layer of compilation module, which converts wasm stack memory into register-based memory, marks and reuses the memory, avoids frequent allocation of memory, and greatly improves the overall execution efficiency.
 text
text
text
(3) Overall process
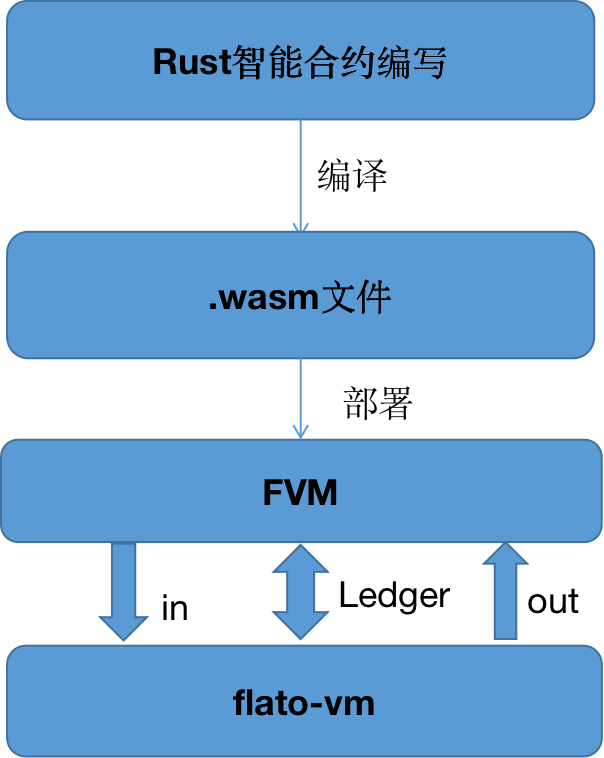
After the whole introduction, I believe everyone has a general impression of the use of Rust smart contracts. Here is a summary of the whole process:
step1: The user writes the smart contract through the Rust contract framework (must be tested)
step2: Compile the contract into a wasm file
step3: Deploy the wasm contract file to FVM
After completing the above steps, you have successfully run a contract❤.
text
The current contracts are only for relatively simple businesses. In our plan, FVM can be applied not only to existing contract scenarios, but also to scenarios with complex business and high requirements for contract execution speed. At the same time, non-blockchain industry technicians are given a "zero learning cost" method of going to the chain - using their familiar programming language to write contracts. The application scenarios and scope of influence of blockchain technology have been expanded in order to explore more blockchain technology landing solutions.
At present, the performance of FVM has well met expectations, but we will not be satisfied with the current status quo and stagnation. In the follow-up planning, we will continue to explore some optimization solutions, such as:
1) Optimization of virtual machine cache;
2) Introduce AOT (Ahead-of-Time), that is, the way of pre-compilation, replace the existing bytecode interpretation and execution, directly compile the wasm module into go code, use the plug-in mechanism of go to directly load and run, and get the ultimate performance experience.
Technology is constantly introducing new ones, and the optimization work will continue. "Keep advanced" is our goal.
【summary】
About the Author
About the Author
Li Kai
references
references
[1] rust programming language
[2] "WebAssembly principle and core technology"



