From the perspective of blockchain universe value capture, analyze why blockchain needs Web3.0
This article is reproduced from Web3 Explorer, reproduced with authorization,
Original Title "Why Blockchain Needs Web3.0"
foreword
foreword
In the previous article "Why Web3.0 Needs Blockchain", we discussed why Web3.0 applications/platforms need to build and drive blockchains as underlying components. In this article, we will analyze that the blockchain is different from the blockchain, and it is impossible for one chain to solve all problems. The blockchain in the Web3.0 platform should specifically refer to the application-oriented blockchain—it is very different from a public chain like Ethereum.
first level title
world computer
world computer
Around 2017, Ethereum was conceived as a "world computer"—a machine that never goes down and that everyone in the world can write code to run on.
As far as these two points are concerned, Ethereum has indeed achieved it (never down, everyone runs). But the "computer" generally understood by the public is a tool that can do general calculations. However, the calculation cost of Ethereum is very high, and it cannot be used for general-purpose calculations, let alone big data calculations. From this definition, Ethereum is not a general-purpose computer, it can only be regarded as a special-purpose calculator at best. Calculating without considering cost is playing hooliganism. At present in 2021, no one has mentioned the concept of "world computer". Ethereum has already changed its own positioning, and its ideal as a "world computer" has failed. See: "Why I Stop Explaining Ethereum as a 'World Computer'".
Regarding the world computer, we have a good analogy - the current hot post-cloud native serverless technology stack. Serverless also has the characteristics of a "world computer": it only cares about the realization of business functions, does not care about system resource allocation and operation and maintenance, does not care about expansion issues, and everyone in the world can write code to run on it, etc. Because of this analogy, we can use some problems in the development process of the serverless field to illustrate the problems that the blockchain will have if it is used as a world computer:
Cost issue: Serverless has an advantage in short-term, flat and fast services in dedicated fields. It is used for long-term services and general-purpose computing, but the cost exceeds traditional container computing. See: "Serverless is more expensive than you'd expect
》,《Serverless vs Docker Containers— what to choose in 2020? (updated)》
Expansion problem: One of the basic requirements of the world computer is: automatic expansion. For customers, the computing power and storage capacity of the world computer should have no upper limit (although there is a limit for each calculation, it should be able to accommodate almost unlimited function instance services horizontally, and there will be no gap between different parallel functions. obvious competition for resources). The expansion problem is the most difficult problem in the blockchain field, none of them (see: "Blockchain Scalability Overview [2020]"). From this point of view, the blockchain is more pessimistic in this direction.
Platform binding problem: At present, Serverless still has an extremely serious problem: platform binding. The serverless program you develop is strongly bound to a certain cloud platform (Amazon Lambda, Microsoft Azure, etc.). If you want to switch platforms, you have to rewrite the code for the new platform and undergo verification again, which is too expensive. This is also one of the most important issues for many customers, especially enterprise customers. Even if the world computer is realized based on the blockchain, this problem is a problem that must be faced.
Finally, let's ask a question from a soul: Is the world computer another form of centralization?
secondary title
DeFi Explosion
The world computer can't do it, where is the way out for Ethereum?
As early as 2018, the article "Ethereum's story ending is not "world computer", but "open finance"" believed that Ethereum is most suitable for DeFi, that is, open finance. Because there are gradually rich financial protocols established on Ethereum, the article classifies these financial applications and sees the possibility of DeFi challenging the traditional financial system.
In 2020, due to the maturity of objective conditions and the triggering of some accidental factors (such as liquidity mining), Ethereum ushered in a DeFi explosion, and DeFi officially became the killer application on Ethereum. Top applications such as Compound, Maker, Aave, Synthetix, and Curve Finance ushered in a large number of user growth. See: "DeFi explosion pushes Ethereum price to 2020 high". Everyone is cheering, Ethereum has finally found its core value.
However, the explosion of DeFi has also caused some serious problems on the Ethereum platform: network congestion and high handling fees have limited the expansion of mortgage scale and user scale. This is classic negative network effect.
secondary title
value overflow
Because Ethereum is so congested at this stage, and Eth 2.0 is nowhere in sight, the community has conducted a lot of discussions and innovations on the issue of capacity expansion, and now basically reached a consensus to build a second-tier network first—expansion through the second-tier network. At present, there are multiple directions of the two-layer network being explored at the same time, such as Optimism Rollup, ZK Rollup, Arbitrum, Polygon, etc. The competition in different directions is very fierce.
Among them, Polygon is currently the most popular (see: "DappRadar Second Quarter Report: DeFi lockups are still concentrated in Ethereum, and the Polygon ecosystem is growing rapidly"). Strictly speaking, the current implementation of Polygon cannot be considered a Layer 2 network, it is actually a side chain. The side chain itself is just a concept, not a specific expansion technology. A sidechain is a mutual relationship, that is, two chains connected by a bridge that are sidechains to each other. It’s just that Eth is basically the only one at present, almost all valuable assets are on Eth, and Eth’s own performance is weak, so it makes people feel that all chains that “build a bridge to Eth” can be regarded as Eth’s side chains (see : "Blockchain Expansion History: State Channels, DPoS, Large Blocks, and Sidechains"). From this point of view, Polygon's solution can actually be classified into the same category as NEAR, BSC and other public chains that expand the capacity of Ethereum.
For example, Ethereum is like a cistern. Although it is trying its best to dig it wide and deep, it still can’t keep up with the inflow of water (value), so it gradually cannot accommodate so much value, so it will ( value) overflows. This is the value spillover effect of Ethereum.
Not only the second-tier network, but also various public chains (which can be classified as side chain networks) want to seize the opportunity to compete for this spillover effect. Such as: BSC, Solana, NEAR, Polkadot, etc. See: "Analysis of Layer 1 Competitive Landscape: Where Are the Opportunities for New Public Chains?" ".
first level title
Layered Structure of Blockchain
As mentioned before, we firmly believe that the future is a multi-chain world. So, is there a chaotic and chaotic form of existence between these chains?
To study the structure of a system, a fundamental quantity should be found. Starting from different basic quantities, the system can be divided into different structures. Here, we continue to use the basic quantity mentioned in the previous section: value capture.
image description
Blockchain Universe Hierarchical Structure Diagram
This hierarchical structure diagram is explained as follows:
We start from the innermost circle layer Circle0 or C0. In the innermost circle are Bitcoin and Ethereum, whose combined value accounts for the majority of the current blockchain market (about 64% as of this writing). Bitcoin enters the DeFi space by encapsulating staking on Ethereum. Ethereum is the core of the value of the entire blockchain universe and the source of value output.
The second circle layer, Circle1 or C1, includes the various second-layer networks of Ethereum, various side chains, and other so-called layer1 public chains. They capture the value overflowing from Ethereum and jointly participate in the formation of the DeFi ecosystem.It is worth noting that all contract-based Dapp applications belong to this layer。
The third circle, Circle2 or C2, is a variety of application-specific blockchains, Application-specific Blockchain, or Appchain for short. These Appchains are used to carry various landing applications that are in line with the real world, that is, Web3.0 App. The author tends to distinguish these applications from applications related to financial (DeFi) or asset (such as NFT) attributes. Web3.0 App corresponds more to applications in the traditional Web2.0 world, or applications in some new scenarios. Appchain is the core component of these Web3.0 Apps (see "Why Web3.0 Needs Blockchain").The blockchain in Web3.0 refers to Appchain。
There are three circles C0, C1, and C2, of which C0, C1 are mainly used for assets and DeFi-related applications, and C2 is mainly for specific landing applications, namely Web3.0 applications.
So why can't C2 be used as DeFi? In fact, it is not ruled out. But generally speaking, C0 and C1 have been able to solve the DeFi problem, and there is no need for C2 to participate. The C2 layer should focus on Web3.0 issues.
Here, the layered theory we put forward has several meanings:
The first meaning is the layering of value capture: one chain cannot hold all the value, so it must be distributed to multiple chains.
The second meaning is the layering of security: not all chains require the same security level, some pursue higher security, some pursue higher performance, and some pursue higher scalability. From the inside to the outside of the three circles, it can be considered that the security requirements are gradually weakened, and the performance requirements are gradually increased.
The third meaning is the layering of business focus: DeFi and Web3.0 businesses are separated from each other, each focusing on different concerns and solving their own problems. At the same time, it is also necessary to study an appropriate mechanism so that the two parts can interact and cooperate.
Simply put, it isfirst level title。
DeFi and Web3.0
Looking back at the development of blockchain, we will find that it was originally a series of innovations around financial issues. It is also under the accumulation of these massive innovations that DeFi exploded. As mentioned earlier, we separate DeFi from Web3.0. DeFi is the abbreviation of Decentralized Finance, which refers to those financial applications built on the blockchain network, andWe define Web3.0 specifically to refer to all non-financial applications built on open protocols. There is a clear boundary between the two.
So, what is the relationship between DeFi and Web3.0? This is a subject worthy of in-depth exploration.
Let's start with finance. What is finance? Professor Liu Qiao once concluded in "How to Reshape China's Finance in Our Era": Under the modern economic system, finance is a system formed by the interaction of modules such as the real economy, the financial system, government macro policies, international capital flows, and asset pricing. complex ecosystem. At the same time, he believes that good finance must be finance that minimizes intermediary costs.
In the Web2.0 Internet era, Professor Xie Ping and Dr. Zou Chuanwei proposed the concept of Internet finance. In the article "Basic Theory of Internet Finance", they believe that the Internet can reduce transaction costs and information asymmetry, improve risk pricing and risk management efficiency, expand the boundaries of transaction possibilities, and enable direct transactions between the supply and demand sides of funds, thereby changing financial transactions and organizational form.
Ideally, in the Internet age, capital should flow seamlessly like information, and transaction costs should be minimal. However, Professor Liu Qiao believes that the average cost of financial assets has basically remained unchanged in the past 130 years. He called this phenomenon the "mystery of financial development", that is, the continuous evolution of finance has not brought about a decline in the cost of financial intermediaries.
How to reduce the cost of financial intermediaries? This is the exploration and experiment that engineers and entrepreneurs who build the encrypted world of DeFi are doing.
DeFi hopes to use blockchain technology to create a more open and transparent financial service system, whose salient features are permissionless openness and transparency of transaction data. At the same time, its settlement is instant, and its financial services are available 7*24 hours a day, while our current global financial system only operates during nine-to-five hours (not weekends and holidays).
image description
Image source: "Encrypted assets are not scourges, understand the basic characteristics and potential for change of DeFi infrastructure"
By simply comparing the architecture diagrams of the two, DeFi applications are trying to rebuild financial services from the basic layer, and their operating costs will be several orders of magnitude lower than traditional finance.
The current DeFi mainly focuses on financial payment and settlement, financial intermediation and other functions. It is far from the development of financial technology in terms of financial risk assessment, social resource allocation, especially financial compliance and supervision. Let's compare it with the example of traditional lending. Enterprises borrow money to do business, generate value income to repay the loan, and banks charge interest. However, most of DeFi is only transferred between protocols, and the funds have not entered the social field, and have not formed an effective closed loop, and have not exerted the function of finance in the allocation of social resources.
Therefore, DeFi is just a step ahead in financial services, and representative projects such as MakerDAO, Compound, Uniswap, Synthetix and so on have triggered a wave of DeFi. However, after nearly a year of explosive development, the development status of DeFi is very "involved", and various tracks (different blockchain infrastructures such as Ethereum, Polkadot, etc.) are crowded with homogeneous projects . DeFi urgently needs to break through outwards, find new market space, and find a real value closed loop that can be combined with the real industry.
image description
Traditional Finance and the Internet
Traditional finance provides financial support (in the form of angels, seeds, loans, etc.) to Internet start-ups, while Internet companies return part of the profits generated by them to financial institutions as principal and interest, realizing a closed loop between finance and the real industry.
image description
Decentralized Finance and Web3.0
In the above picture, DeFi finances Web3.0 application projects (Apps). Web3.0 application projects generate lasting profits (similar to the lasting profits of Web2.0 Internet applications), and generate (return, distribute) interest income to investors. Thus realizing real value input to DeFi.
The blockchain has developed to the DeFi stage. If the value of the blockchain technology is to be realized for a long time, it needs to rely on the value input of Web3.0. Web3.0 is the interface between DeFi and the real world.
image description
Web3.0 Times
first level title
Contract and Appchain
There is a difference between the blockchain in the DeFi infrastructure layer and the blockchain in Web3.0 applications.
Looking back at the development history of the blockchain, the Bitcoin project that gave birth to the blockchain concept opened the door to challenge the central bank’s monopoly on the currency and financial system. From this perspective, Bitcoin is the original form of DeFi. Subsequently, Bitshares (Chinese name BitShares BTS) created by Daniel Larimer (BM) can be regarded as the first project to try DeFi. But the ideal is plump and the reality is skinny, BTS's exploration eventually aborted. Later, Vitalik Buterin proposed Ethereum, which established a programmable, Turing-complete smart contract blockchain, and expected to become a decentralized application development platform. So far, based on smart contract technology, global encryption developers have carried out various active explorations and developed various types of decentralized projects (finance, games, social media, etc.). According to the current market value classification data of Coingecko, we will find that the top three in market value are stable coins, trading, and DeFi, which are all financial asset trading applications. From this perspective, smart contracts are not suitable for developing DApps in all fields, but are more suitable for DeFi applications in the financial field.
With the development of blockchain technology, blockchain development frameworks such as Cosmos SDK, Substrate, and Muta have emerged, which provide developers with a completely different way from smart contracts to create decentralized applications. The contract is developed for a general-purpose virtual machine, which is limited by the underlying virtual machine, and the customizability is weak; while using the blockchain development framework, developers can choose various available modules in the framework (such as consensus, governance, etc.) and other components) or build custom modules to quickly customize and launch a blockchain, which greatly improves flexibility. For example: since security tokens require more functions in the infrastructure layer to ensure regulatory compliance and enhance institutional confidence, Polymath has specially built a blockchain Polymesh to better implement security tokens. Creation, issuance and management of certificates. Compound specially built the Gateway blockchain to realize the cross-chain interest rate market. Due to some limitations of the smart contract platform, these teams chose to build the application chain, which to a certain extent shows that the application chain is more suitable for developing Web3.0 App.
first level title
Smart Contract vs. Appchain
Smart Contract Appchain
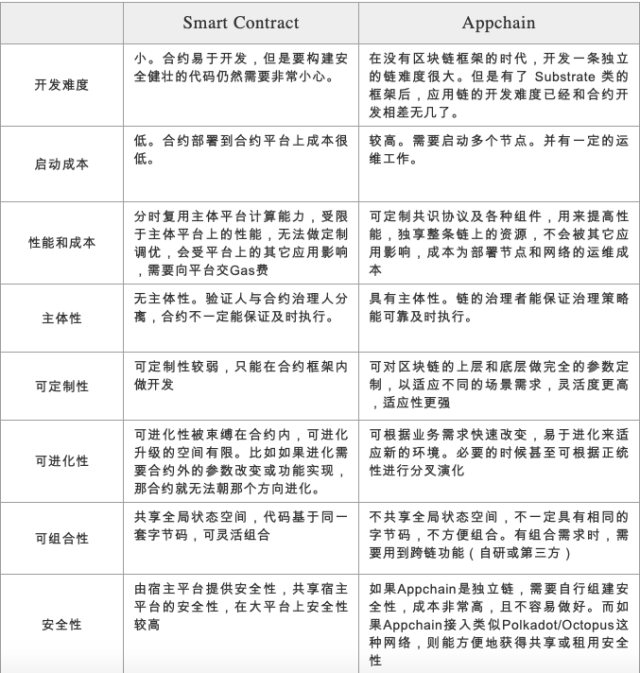
Appchain related research
secondary title
Tokens in Appchain
As we analyzed in the previous article "Why Web3.0 Needs Blockchain", Token is an essential part of blockchain.
But there is a serious misunderstanding: all Tokens are cryptocurrencies. In fact, not all Tokens issued on the blockchain are currencies (digital currencies). Tokens can be broadly divided into the following three categories:
1. Currency Token: Currency Token
2. Utility Token: Functional Token
3. Security Token: Securities (options, stocks, etc.) type Token
image description
"Five Dimensions of Token Classification"
This article is not going to describe the classification theory of Token. Readers can refer to the reference materials at the end of the article for further understanding.
In June 2017, the SEC (US Securities Regulatory Commission) announced that DAO Token is a security (see "SEC Issues Investigative Report Concluding DAO Tokens, a Digital Asset, Were Securities"), which is regulated in accordance with securities-related laws. This is a major characterization of blockchain Token.
The article "Regulatory Paradigm Change of Security Token Issuance" also believes that Token issued by STO (Security Token Offering) should be included in the regulatory framework in the form of securities. Under the premise of effectively guaranteeing national financial stability and maintaining market order, sufficient innovation space should be reserved for financial innovation models, and system changes should be accepted conditionally.Among them, the method of obtaining profits has become a key factor in determining whether a security is constituted.
And Appchain or Web3.0 App, as a landing application that enters people's daily life, naturally should actively embrace supervision.
Based on the above background information, back to the Appchain, in the Web3.0 App, we should issue security tokens and functional tokens instead of Currency Tokens in the Appchain. In fact, in the entire blockchain universe, there are very few Tokens that can be classified as cryptocurrencies. Currencies, as general equivalents, are the medium of value exchange. Only extremely limited Tokens (such as Bitcoin) have the potential to take on this role. In addition, if the application-level tokens are not classified as security tokens or functional tokens, they will encounter serious obstacles at the regulatory level.
On the other hand, securities/functional tokens also need to enter the market circulation. Once asset circulation is involved, we should strip the relevant business logic to the DeFi layer for execution. At the Appchain layer, try to only deal with specific application business-related transactions.
By the way, the Chinese translation of Token is more accurate than "token". It is recommended not to mistranslate Token as "token" in the future.
Consensus in Appchain
Generally speaking, the most suitable consensus for Appchain is PoS type consensus.
First, we exclude PoW consensus in Appchain for the following reasons:
1. PoW consumes a lot of energy, and the PoW chains that can be accommodated in the world are limited, and there may be only a few
2. The cold start of the PoW chain is very difficult. When the total computing power of the platform does not reach a critical value, the security of the PoW chain is very fragile
In contrast, the PoS chain has the following basic characteristics:
1. The energy consumption is very small (compared to PoW), and the evaluation of Ethereum is less than 1% of the energy consumption of PoW
2. When the PoS chain starts, it needs to use other assets as collateral. Its security has been guaranteed from the very beginning, and as the value of the application chain increases, its mortgage for security will also increase accordingly, that is, security is also a positively related growth curve
Of course, PoS also has its own problems. Countless smart brains all over the world are trying various innovations to solve these problems, and have proposed various improved PoS protocols, such as DPoS, NPoS, LPoS, etc. The comparison of the advantages and disadvantages of PoS and PoW is not the focus of this article. You can refer to relevant information for in-depth research.
On the other hand, PoS-type protocols are more like traditional joint-stock companies, but now they have become community-based companies (see: "Companies of the Future: Blockchain Technology + Token Economy"). The Appchain or Web3.0 App entrepreneurial team based on the PoS protocol still needs to rely on the team's own characteristics and efforts to make innovations, push them to the market, solve specific problems, generate value feedback, and develop It grows big and eventually develops into a platform-level project owned by the community.
As far as the classic PoS is concerned, it is not suitable for small teams to use directly. It is a bit like a wild horse, which is difficult to control. A start-up team can easily be led into a pit by PoS. Because it is not only a technical issue, but also a sociological issue. And once there is a problem with governance, there is often no turning back.
Generally speaking, Appchain will not have too many nodes. There may be only a few at the beginning, and there may be only a few dozen in the mature stage. Too many nodes will affect the operating efficiency of the business system. Appchain attaches great importance to user experience, and the project needs to strike a balance between security, operating efficiency, and user experience.
Considering that Web3.0 App is a product that truly affects people's lives, it will definitely embrace regulation in the future. In the case of regulatory participation, it is more appropriate for Appchain to choose PoS. Because in theory, the supervisor can directly join the network as a node to conduct first-hand data supervision and analysis.
Appchain Independent Chain Problems
Although Appchain has many advantages, its disadvantages are also obvious. This section analyzes in detail the shortcomings of Appchain as an independent chain.
Development difficulty. In the past, it was very difficult to develop an independent blockchain from the bottom layer. Many blockchain projects are to clone a copy of the source code of Bitcoin or Ethereum, modify the parameters and modules, and it is a new blockchain project. Even so, the development difficulty is still high. It is more difficult to operate, maintain and launch an independent chain. But later, after the Cosmos-sdk, Substrate, Muta and other frameworks came out, it became a very easy thing to start a new chain. These development frameworks greatly reduced the development cost of the blockchain.
Launch Difficulty and Security. Startup difficulty refers to the difficulty of successfully starting a chain, which is closely related to security. For the PoS chain, its initial pledge amount, the number of verifier nodes, the rationality of STO distribution, and the Token issuance mechanism all directly affect the security of the chain. It is not easy for an entrepreneurial team to consider everything carefully. The startup of the independent chain also requires each validator to start its own node, which has certain requirements on the technical and operation and maintenance capabilities of the validator. There are some auxiliary services such as third-party hosting node operation, which can reduce such requirements to a certain extent.
Difficulty in operation and maintenance. The validator node needs to operate and maintain its own independent server. Operation and maintenance is reflected in several aspects:
●Stable operation of the server. Monitor its CPU load, memory load, network load, storage space, etc., and increase configuration in time to prevent node failure due to hardware reasons
● Anti-attack. Do a good job of node protection to prevent external hackers or unknown sources from attacking, which will have an impact on the security of the chain
●Timely upgrade and follow-up of the code version on the chain. Some versions can be automatically upgraded through technologies such as wasm, while some versions need to upgrade the entire node content, which needs to be followed up manually or automatically by DevOps
In contrast, contract developers on the contract platform do not need to care about such detailed operation and maintenance content.
Difficulty of cross-chain interaction. If all the chains are independent and do not interact with each other, then only islands of value will be formed in the end. Only by connecting chains and increasing the liquidity of value can more value be created. Therefore, cross-chain interaction is an issue that Appchain must consider from the very beginning. For Ethereum, the above contract does not need to consider this issue: internally, Ethereum assets share the same state space, and different contract assets can be combined and interacted with each other. Externally, as long as Ethereum and other chains are cross-chain bridges, these bridges can be used to transfer assets conveniently. But Appchain has to face this problem by itself, either by implementing cross-chain bridges with other chains, or using cross-chain communication interfaces like Cosmos IBC, or joining Appchain network clusters like Polkadot and Octopus.
Among them, it is basically not feasible to realize the cross-chain bridge with other chains by yourself, because under the multi-chain architecture, there are so many cross-chain bridges, and it is not worth the loss to realize them one by one.
In addition to the above four difficulties, there are other difficulties such as governance: Appchain implements on-chain governance through the PoS mechanism, and contracts implement on-chain governance through DAO facilities, which are quite difficult. How to use PoS itself well is a non-technical problem, which is quite difficult. Token Economics Design Difficulty: In terms of Token economics design, Appchain can do more things and is more flexible, but the implementation is also more complicated, which is more difficult than the contract (or this is the objective complexity).
Combining the above factors, we can conclude that the small founding team is basically unable to afford the development and operation of the Appchain independent chain.
Appchain independent chain cluster
In order to solve the above problems of Appchain independent chains, some teams have proposed solutions. These programs have their own characteristics, and the focus of solving the problem is also different.
Cosmos
Cosmos is committed to solving the problem of cross-chain interaction between different blockchains, with the goal of building an internet of blockchains.
First of all, Cosmos-sdk is used to quickly develop and start a chain, which solves the problem of difficult development.
Then, it designed the IBC protocol, which is a general solution. Between chains that implement the IBC protocol, messages can be exchanged across chains without barriers. Using the independent chain developed by Cosmos-sdk can easily integrate the implementation of the IBC protocol. In this way, the chains developed based on Cosmos-sdk can communicate without barriers.
However, the Cosmos Appchain still has not solved the security startup problem at the initial stage of the chain, and left the security startup problem to Appchain itself to solve.
Polkadot
Polkadot aims to be a perfect blockchain expansion solution.
Polkadot's Substrate is a rapid development framework for blockchain, which is very good. For details, please refer to the author's "Why Compound Gateway uses Substrate for the development of independent chains".
Polkadot shares security, and its pledge security is very high, which is at the same level as the contract platform.
Polkadot also supports cross-chain messages between parallel chains, allowing seamless asset circulation between parallel chains.
The above three points have solved the three biggest problems described above, and it seems that Polkadot's solution is perfect.
But it also created new problems. The security level of the Polkadot relay chain is very high, and the security mechanism is very complicated, which leads to a very high cost of bidding and pledge for parachain slots, which in turn brings about a very high annual rent for its parachain, which affects the design and economics of the parachain Token. Distribution brings a lot of pressure. From this point of view, it is not friendly to the development of parachains. Due to this feature, Polkadot has gradually changed from an Appchain-oriented relay network to a platform-oriented platform (Platform of platform), which is what Gavin calls layer0. Each slot of Polkadot is actually connected to a homogeneous shard. And each shard is a platform. 100 slots equals 100 shards. Therefore, Polkadot can connect 100 platforms, which is a network of 100 shards. The development model of applications in the Polkadot network has returned to the model of contract development and deployment on a certain parachain. From this model, it is the same as Ethereum 2.0.
Octopus
The goal of Octopus is to provide a complete base protocol for Appchain.
The design of Octopus: choose a contract chain platform as the main chain, instead of running its own main chain or relay chain, all Appchains directly interact with the main chain. The advantage of this is that it reduces the cost of independent operation and maintenance of a relay chain, thereby reducing the access cost of Appchain (the operating cost of a relay chain like Polkadot will be passed on to the access cost of Appchain). Let the startup cost of the Appchain track be lower and the survival rate higher.
On the other hand, due to the DeFi characteristics of the main chain (contract chain), Octopus has actually created a two-sided market: one side is the DeFi investor side, and the other side is the Appchain entrepreneurial team side. The employer voluntarily stakes the Appchain (similar to the traditional Angel, but more decentralized), and becomes the Validator of this Appchain. When the amount of staking exceeds a threshold, Appchain enters the startup pipeline. At the same time, Octopus also provides a complete set of cloud platform automation tools, so that employers who lack sufficient operation and maintenance knowledge can also be validators. Since Octopus strongly binds the Staking role to the Validator role, the security problem of the Appchain is solved in the process of starting the mortgage. That is to say, the security of Appchain is a by-product of Stakeholder and Staking amount. It’s just that the value of this security is low at the beginning, and with the development of Appchain, this value will gradually increase. So this kind of security is called leased security (lease security). This design is also more in line with the valuation growth curve of traditional Internet entrepreneurial teams.
The problem with Octopus is that since its main chain is an existing contract chain, its flexibility and customizability will be somewhat restricted, and it is not as flexible and controllable as a fully autonomous relay chain. The protocol design of Octopus conforms to the basic rules of capital and finance, but it remains to be seen how well it will work in practice.
In this section, we analyze several typical Appchain cluster solutions on the market. It can be seen that the problem is indeed very complicated, and it is not so easy to get a perfect solution. There are infinite possibilities for innovation, and the core lies in the art of compromise. In the future, it is not ruled out that there will be better designs that can better (compromise) solve those problems of Appchain.
Introduction to Appchain Development Framework
Almost every blockchain has its own SDK, but not all SDKs are designed for Appchain development. Here we mainly introduce several development frameworks for developing Appchain.
Cosmos-sdk
https://tendermint.com/sdk/
"Cosmos SDK Developer Documentation" describes Cosmos-sdk as follows:
Cosmos-sdk is an open source framework for building multi-asset public blockchains based on PoS consensus algorithms like Cosmos Hub, and permissioned chains based on Proof of Authority consensus algorithms. Blockchains built using the Cosmos SDK are often referred to as application-specific blockchains.
The goal of the Cosmos SDK is to allow developers to quickly build a customizable blockchain that can natively interoperate with other blockchains. In their vision, this SDK is like a web application framework, allowing developers to quickly build secure blockchain applications based on the Tendermint algorithm. Blockchains developed by the Cosmos SDK are built from modular modules, most of which are open source and available to any developer. Anyone can create new modules for the Cosmos SDK and integrate already built ones, as easily as importing them into your blockchain application. Another point is that the Cosmos SDK is a capability-based system, which allows developers to better consider the security of interactions between modules.
Substrate
https://substrate.dev
In the process of developing Polkadot, Paritytech disassembled all the functions of the blockchain into abstract designs, implemented them into an open source, general-purpose blockchain framework, and used this framework as a tool to build Polkadot products. This framework is Substrate.
Substrate is a general-purpose blockchain development framework developed in the Rust language. Its design elements, such as cryptographic algorithms, storage structure MPT tree, account system, etc., are mostly borrowed from the most successful Ethereum infrastructure in history (this is understandable, Paritytech was originally started as an Ethereum client, Gavin Wood is also one of the co-founders of Ethereum). For a framework to be universal, it needs to be highly abstract. However, the cost of high abstraction often appears to be complex in structure and not easy to use. So Substrate also provides a lot of DSL (domain-specific language), which is convenient for novices to learn and use. To briefly summarize, Substrate has the following characteristics:
1. For general purpose. Its design is oriented to the general field, rather than an SDK specially developed for a certain chain. Each team can use Substrate to develop a completely independent chain that does not depend on any existing network (for example, the blockchain developed using Substrate can be completely independent of Polkadot, which is also one of Paritytech's design goals)
2. Comprehensive functions. It can cover almost all scenarios of the blockchain, and can be said to be the most comprehensive blockchain framework currently on the market
3. Runtime code is compiled into wasm for execution. Wasm is the mainstream choice of VM bytecode in the blockchain industry today
4. Super customizable. Substrate itself is a bunch of scattered components, which can be freely replaced and combined under a set of specification constraints
As one of the strongest blockchain development frameworks so far, Substrate has been welcomed by more and more innovative teams.
Muta
https://docs.muta.dev
Muta is a blockchain Appchain development framework developed by the Nervos team. Its documentation describes it like this:
Muta is a multi-faceted, high-performance blockchain development framework that makes building blockchains easy and flexible. Blockchain developers can use Muta to quickly build their own blockchains, focusing on business functionality, thereby eliminating the huge amount of work to build the underlying network and consensus mechanism from scratch.
The basic core components provided by Muta are:
●A newly designed consensus algorithm - Overlord, with high throughput and low latency
●Fast and stable storage
●Modular p2p network
●High performance memory pool
The parts that Muta provides for customization are:
By developing services—including governance mechanisms, business logic, and even virtual machines connected to the blockchain—developers can easily customize the functionality of the chain.
In Muta, services are an abstraction layer used to extend the Muta framework. Each service is a relatively independent unit and maintains its own storage and operation interface. These services together form the state machine part of the chain, and after connecting with the underlying components of the blockchain, it becomes a unique blockchain that belongs to you.
Summarize
Summarize
This article proposes a C0, C1, C2 layered theory for the current blockchain universe from the perspective of value capture. And theoretically analyzed the difference and connection between DeFi and Web3.0, and demonstrated why the blockchain (DeFi part) needs Web3.0. Then, the advantages and disadvantages of Smart Contract and Appchain are compared in detail. Finally, a comprehensive research has been done on the main block chain used to carry Web3.0 App - the application chain, which has laid a theoretical foundation for the future practical innovation based on the application chain.
From ideal to reality, Web3.0 requires countless teams to fully practice in various fields. Summarize experience in practice, revise theory, and explore new programming paradigms, product paradigms, and governance paradigms. In the struggle of the market, obtain first-hand feedback from users, improve product form, upgrade user experience, and finally step on a broad road.
refer to
refer to
"Why Web3.0 Needs Blockchain"
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/h76lTnFWlvpXs72aBVs3FA
"Why I No Longer Explain Ethereum as a World Computer" https://ethfans.org/toya/articles/why-i-no-longer-explain-ethereum-as-a-world-computer
Serverless is more expensive than you'd expect
https://dev.to/colinchartier/serverless-is-more-expensive-than-you-d-expect-30o1
Serverless vs Docker Containers— what to choose in 2020? (updated)
https://medium.com/techmagic/serverless-vs-docker-what-to-choose-in-2019-80cb80f4b680
[Translation] Blockchain Scalability Overview [2020] - Zhihu (zhihu.com)
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/111750788
"The ending of Ethereum's story is not "world computer", but "open finance""https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/8WvURohy1WD4tbf0nfbdrw
DeFi explosion pushes Ethereum price to 2020 high
https://dappradar.com/blog/defi-explosion-pushes-ethereum-to-all-time-high-price
"DappRadar's second quarter report: DeFi lockups are still concentrated in Ethereum, and the Polygon ecosystem is growing rapidly"
https://www.chainnews.com/articles/805269754120.htm
"Blockchain Expansion History: State Channels, DPoS, Large Blocks and Sidechains"
https://www.chainnews.com/articles/692744578850.htm
"Analysis of Layer 1 Competitive Landscape: Where Are the Opportunities for New Public Chains?" "
https://www.chainnews.com/articles/281730625621.htm
DeFi in Ethereum 2.0: Cities, Suburbs, and Rural Areas
https://ethfans.org/posts/defi-in-eth2-cities-suburbs-farms
"How to Reshape Chinese Finance in Our Era"
http://finance.sina.com.cn/zl/china/2020-08-19/zl-iivhuipn9458143.shtml
"Basic Theory of Internet Finance"
http://www.jryj.org.cn/CN/abstract/abstract373.shtml
"Crypto-assets are not scourges, understand the basic characteristics and transformative potential of DeFi infrastructure"
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/Zm-RCSJWRzFfGur4XQ4pqw
"Five Dimensions of Token Classification"
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/9IW1yGB2hM8PtDnm6gmrFg
SEC Issues Investigative Report Concluding DAO Tokens, a Digital Asset, Were Securities
https://www.sec.gov/news/press-release/2017-131
"Regulatory Paradigm Change of Security Token Issuance"
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/oLOwrgUmB-ynvOGv0zT_iA
"Future Company: Blockchain Technology + Token Economy"
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/JWoVlcdmMYmiZfwvOCJc8w
"Why Compound Gateway uses Substrate for independent chain development"
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/DmkAX1TcfDCeWBJudqZFxg
"Cosmos SDK Developer Documentation"
https://github.com/cosmos/cosmos-sdk/blob/master/docs/intro/overview.md



