How to build a fake decentralized cross-chain protocol
Written by: Kang Shuiyue, Founder of Fox Tech and Way Network, Chairman of Danyang Investment
Adam Back (Bitcoin core development team leader, BlockStream CEO) has a saying that impressed me deeply, "Great design looks very simple, but the process of designing it is actually extremely complicated." However, not all product designs that look simple can be called great, such as LayerZero.
Before the cross-chain protocol has an accident, everyone feels that it is very safe and there is no problem, but once an accident occurs, it is a horror event. From the perspective of the amount of losses caused by security incidents that occurred on each chain in the past two years, the losses caused by security incidents on cross-chain protocols topped the list. The importance and urgency of solving cross-chain protocol security issues even exceeds the Ethereum expansion plan. Interoperability between cross-chain protocols is an inherent requirement for Web3 to form a network. Such agreements often raise a huge amount of money, and the TVL and number of transactions are also growing driven by rigid demand. However, due to the low degree of public recognition, it is impossible to recognize the security level of these cross-chain protocols.
image description
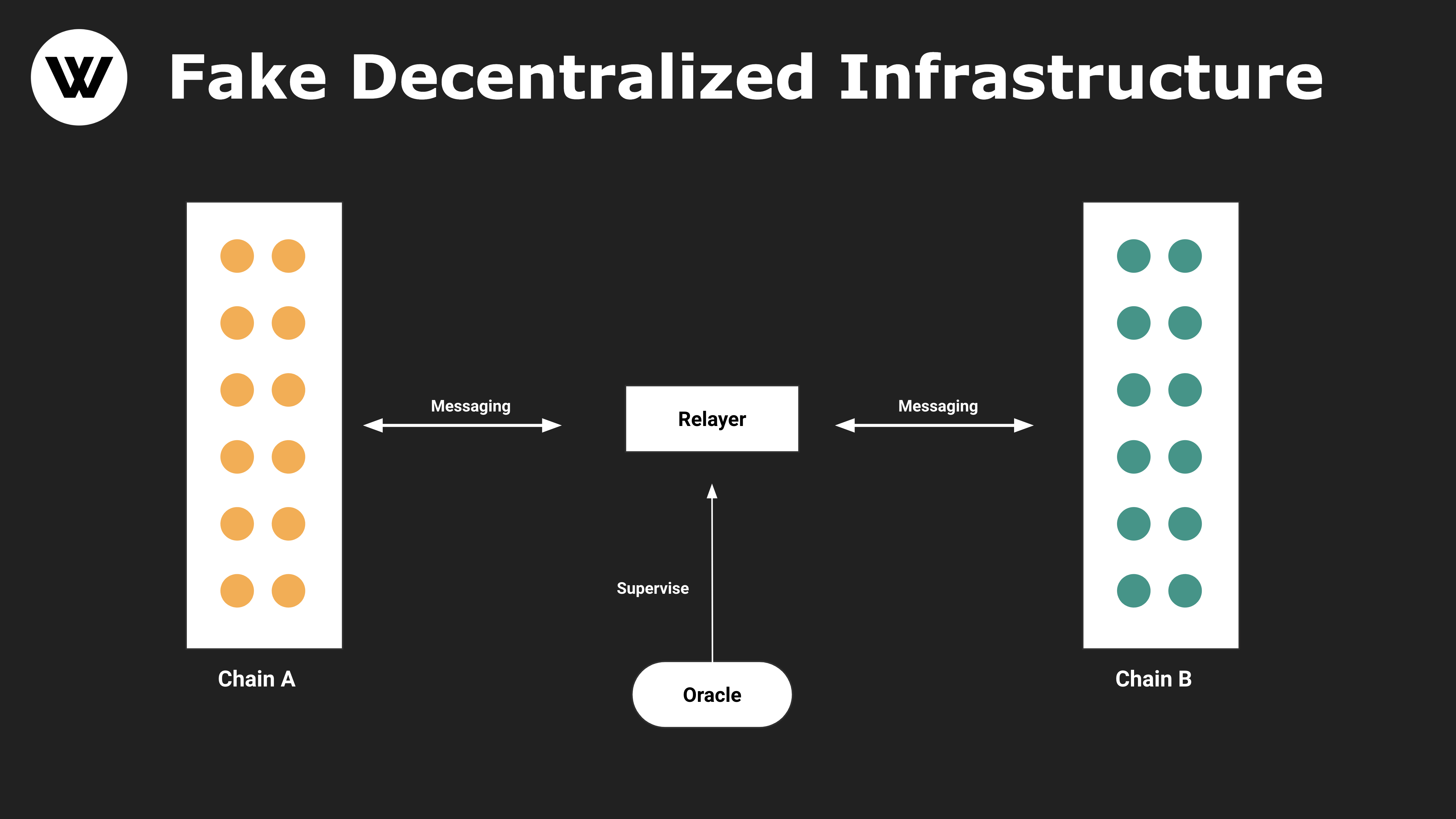
Figure 1: The basic version of the pseudo-decentralized cross-chain protocol
There are at least 2 problems with the above architecture:
1. LayerZero reduces dozens of node verifications to a single Oracle verification, and the safety factor is naturally greatly reduced.
2. After simplifying to a single verification, it must be assumed that the Relayer and Oracle are independent, and this trust assumption cannot be established forever, which is not enough for Crypto Native, and cannot fundamentally guarantee that the two cannot conspire to do evil.
This is the basic pattern employed by LayerZero. As an "ultra-light" cross-chain solution of an independent security type, it is only responsible for forwarding messages, and is not responsible for the security of applications, nor is it capable of being responsible.
image description
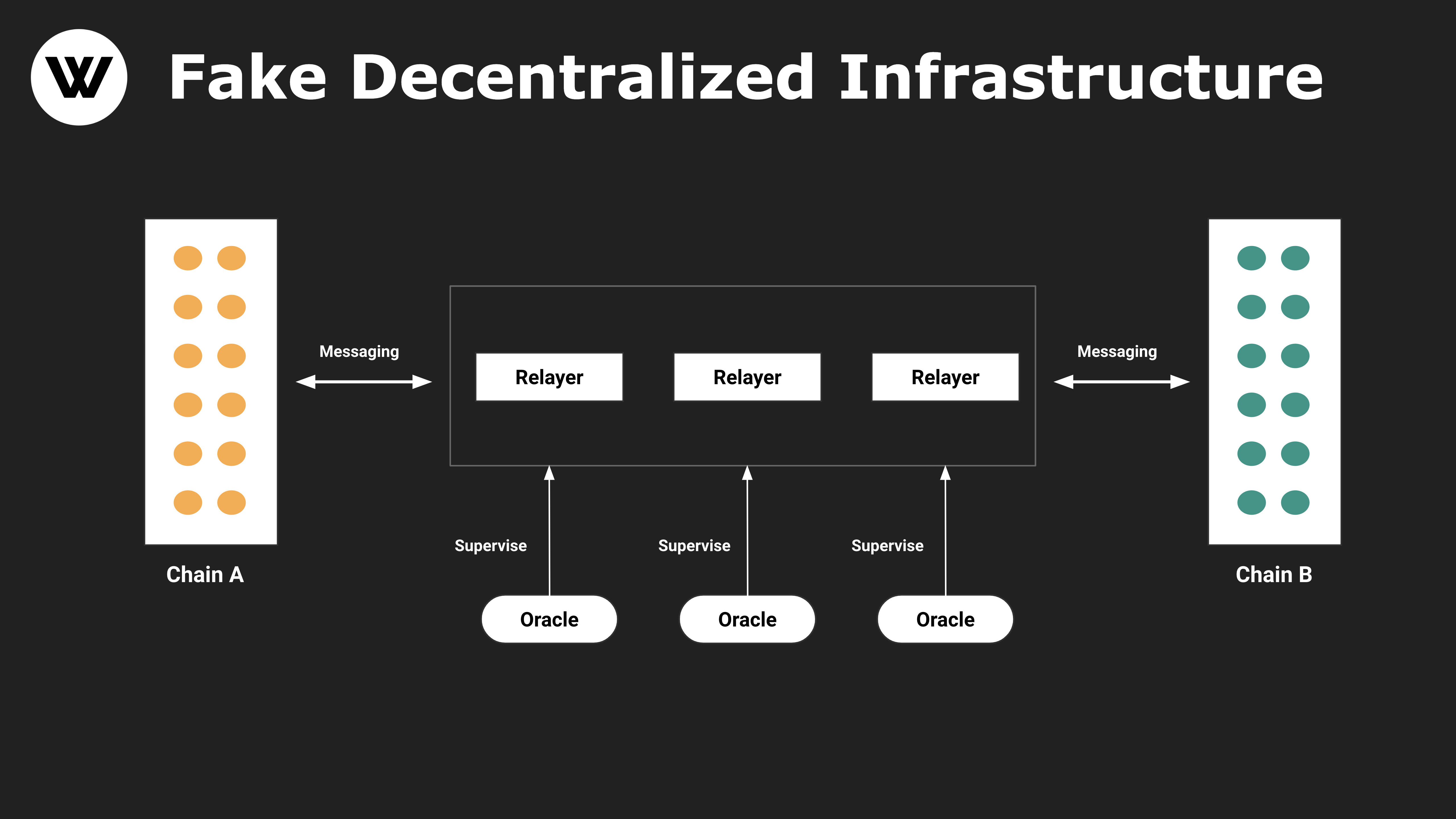
Figure 2: Advanced version of fake decentralized cross-chain protocol
If a cross-chain token project allows modifying the configured LayerZero node, it is possible for an attacker to replace it with its own "LayerZero" node and forge arbitrary messages. As a result, there are still huge security problems in projects using Layerzero, and this problem will be more serious in more complex scenarios. As long as one link in the huge system is replaced, it may cause a chain reaction. LayerZero itself does not have the possibility to solve this problem. If there is a security incident, LayerZero will naturally shift the responsibility to external applications. Because end users need to carefully judge the security of each project that uses LayerZero, those "user-oriented" projects will carefully access LayerZero to avoid being polluted by malicious applications that belong to this ecology, so the difficulty of ecological construction is not small .
If Layer 0 cannot share security like Layer 1 and Layer 2, then this Layer 0 cannot be called Infrastructure, because the reason why the infrastructure is "basic" is that it can share security. If a project party claims to be Infrastructure, it should provide consistent security for all its ecological projects like other infrastructure, that is, all ecological projects share the security of the infrastructure. So, to be precise, LayerZero is not infrastructure, but middleware. Application developers accessing this Middleware SDK/API are indeed free to define their security policies. The L 2B EAT team published Circumventing Layer Zero: Why Isolated Security is No Security on January 5, 2023, pointing out that their assumption that the application owner (or the person with the private key) will not do evil is incorrect . The bad guy Bob gained access to the LayerZero configuration. The bad guy Bob can change the oracle and repeater from the default components to components controlled by him, and persuade the smart contract using the LayerZero mechanism on Ethereum to let him withdraw all the tokens of the good guy Alice on Ethereum. Original link:https://medium.com/l 2b eat/circumventing-layer-zero-5 e 9 f 652 a 5 d 3 eOriginal link:
Original link:https://prestwich.substack.com/p/zero-validation
When you are confused by fancy appearance, try to go back to the source. On October 31, 2008, the Bitcoin white paper came out. On January 3, 2009, the BTC genesis block was born.A summary of the white paper "Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Currency System" is as follows:
Abstract. A purely peer-to-peer version of electronic cash would allow online payments to be sent directly from one party to another without going through a financial institution. Digital signatures provide part of the solution, but the main benefits are lost if a trusted third party is still required to prevent double-spending. We propose a solution to the double-spending problem using a peer-to-peer network. The network timestamps transactions by hashing them into an ongoing chain of hash-based proof-of-work, forming a record that cannot be changed without redoing the proof-of-work. The longest chain not only serves as proof of the sequence of events witnessed, but proof that it came from the largest pool of CPU power. As long as a majority of CPU power is controlled by nodes that are not cooperating to attack the network, they'll generate the longest chain and outpace attackers. The network itself requires minimal structure. Messages are broadcast on a best effort basis, and nodes can leave and rejoin the network at will, accepting the longest proof-of-work chain as proof of what happened while they were gone.
The Chinese translation of the abstract is as follows:
A fully peer-to-peer electronic currency should allow online payments to be sent directly from one party to another without going through a financial institution. Digital signatures provide a partial solution, but if a trusted third party is still required to prevent double spending, the main benefits of electronic money are lost. We propose a solution to the double spending problem using a peer-to-peer network. The network timestamps transactions by "hashing" (verb) them into a continuously growing chain of hash-based proof-of-work, forming a record that cannot be changed unless the proof-of-work is redone. The longest chain is not only evidence of the sequence of events that was witnessed, but proof that it was itself produced by the largest pool of CPU power. As long as a majority of CPU power is controlled by nodes that do not intend to jointly attack the network, those nodes will generate the longest chain and outpace attackers. The network itself requires only a minimal architecture. Information will be broadcast on a best-effort basis, and nodes can leave and rejoin the network at any time, simply by accepting the longest proof-of-work chain as proof of what happened while they were gone.
From this paper, which is of great importance to future generations, people extracted the widely recognized "Satoshi Nakamoto Consensus", especially from this abstract. Its core feature is to prevent the appearance of a Trusted Third Party and realize trustless Decentralized Decentralized. The "center" here is A Trusted Third Party. The cross-chain communication protocol is essentially the same as Bitcoin. It is a Peer to Peer system. One party sends directly from Chain A to the other party in Chain B without going through any trusted party. The "Satoshi Nakamoto Consensus" with Decentralized and Trustless features has become the common goal pursued by all subsequent infrastructure developers. It can be said that a cross-chain protocol that does not meet the "Satoshi Nakamoto Consensus" is a fake decentralized cross-chain protocol, and high-level words such as Decentralized and Trustless cannot be used to describe its product characteristics. And LayerZero introduced itself as Omnichain communication, interoperability, decentralized infrastructure. LayerZero is an omnichain interoperability protocol designed for lightweight message passing across chains. LayerZero provides authentic and guaranteed message delivery with configurable trust lack.
In fact, LayerZero not only requires that the two roles of Relayer and Oracle will not conspire to do evil, but also requires users to trust the developers who use LayerZero to build applications as a trusted third party, and the trusted subjects participating in the "multi-signature" are all Pre-arranged privileged role; at the same time, it did not generate any fraud proofs or validity proofs during the entire cross-chain process, let alone put these proofs on the chain and perform on-chain verification. Therefore, LayerZero does not satisfy the "Satoshi Nakamoto Consensus" at all, and it is not Decentralized and Trustless at all.
After the L2B EAT team and the Nomad team published well-meaning articles from the perspective of problem finders, LayerZero responded with "deny" and "deny". There were many electronic currencies before Bitcoin, but they all failed. Because none of them can achieve the goal of decentralization, anti-attack and inherent value, and the same is true for cross-chain protocols. The probability is that it will end due to insufficient resilience against attacks. A friend whose position should be highly consistent with LayerZero once asked me a question: "If LayerZero wants to use zero-knowledge proof to upgrade their cross-chain protocol like Way Network, will it be difficult and will there be any obstacles? "It's an interesting question, and the point is that they don't think they have a problem.
As for how to build a truly decentralized cross-chain protocol, you can refer to my previous article "Why use zero-knowledge proofs to develop cross-chain protocols?" "



