Understand the "mixed liquidity" exchange "IDEX" in one article
「x * y = k」。
In a sense, this may be the most important mathematical model in the cryptocurrency market in the past year or two - the decentralized automated market-making (AMM) model developed based on this formula and its variants. Exchanges (DEX) have played a vital role in this DeFi wave.
Since the rise of the concept of cryptocurrency, "trading" has always been the most daily form of activity for users, but in this industry advocating "decentralization", centralized exchanges (CEX) have long dominated the transactions in the cryptocurrency world aisle. Before the AMM concept was implemented, there were early projects such as Counterparty and Airswap that tried to challenge the centralized giants, but they gradually faded away.
The reason is that the core concept of early DEX at the beginning of development is still to reproduce the highly mature CEX model, such as order book + matching in the market-making mechanism. However, affected by factors such as block generation time, block generation sequence, and gas fees, the on-chain is more complicated and less flexible than the off-chain (centralized server), so the actual transactions and operations of these "CEX replica DEX" The city experience is often far from the real CEX. Simply put, these early bird DEXs failed to find a trading model that can adapt to the on-chain environment.
And AMM is exactly the "transaction model that can adapt to the environment on the chain" that the industry has been waiting for. AMM started from a paper "Improving front running resistance of x*y =k market makers" by V God, and it was developed in Uniswap, the current leader of DeFi. Based on the classic mathematical model of "x * y = k", AMM broke the inherent thinking limitation of the previous order book + matching DEX, and successfully liberated DEX from the model copy and quotation dependence on CEX.
Today, the top ten spot DEXs with the highest trading volume all adopt AMM and its variant models. The daily trading volume of top projects such as Uniswap, Sushiswap, and Curve has reached hundreds of millions or even more than one billion US dollars, which is no less than that of CEX Let more. It is no exaggeration to say that it was the emergence of AMM that helped DEX break CEX's monopoly on the cryptocurrency trading market, and made permissionless, open, free, simple and efficient on-chain transactions a reality.
AMMs are not perfect
Although AMM has emerged, there are gains and losses in everything, and AMM is not perfect. In detail, the main "defects" of AMM can be summarized into the following four points:
The first is the limitation at the functional level. The quotation and transaction of AMM DEX must be completed according to the real-time status and changes of the exchange pool. Therefore, without adding auxiliary services, most DEXs can only support flash exchange transactions. It is the traditional order book + the market price in the matching exchange to directly take the order, and it is impossible to place the order at the ideal price position. For users, there will be a certain lack of operational flexibility.
Secondly, the liquidity of AMM DEX depends entirely on the target exchange pool. When the size of a single transaction is too large compared to the exchange pool, a large slippage loss will often occur. One way to solve this problem is to split a single trade into multiple trades and wait for arbitrage bots to fix prices across multiple exchanges, but doing so obviously adds additional operational costs.
Then, as the trading mechanism most suitable for the environment on the chain, the full set of procedures from market making to trading of AMM DEX is completed on the chain, so all transactions need to wait for the packaging on the chain. During periods of network congestion, it may take a considerable wait In addition, on-chain transactions also mean a lot of gas costs. For small transactions, in many cases, the transaction profit cannot even cover the transaction fee. Although with the collective explosion of the new generation of public chains and Layer 2, the current network performance in multiple new ecosystems has been greatly improved, and the gas cost has also dropped to a fairly low level, but given that most of the transaction activities still occur in Ethereum, so this problem still exists.
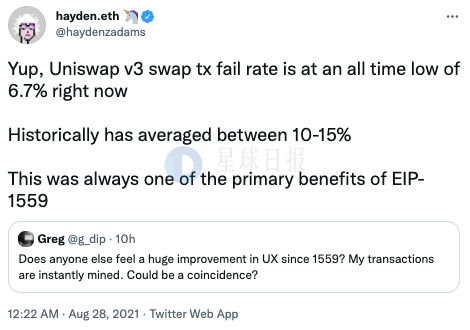
Finally, because the transactions on the chain will be sorted when they are packaged and confirmed, they will often face a certain risk of being snatched away during actual operations (especially large-value transactions), and certain benefits will be taken away by miners. In addition, many users who have used AMM DEX may have encountered transaction failures. At the end of August, Uniswap founder Hayden Adams tweeted that Uniswap’s historical transaction failure rate is about 10% - 15%.
For trading users, such detailed "defects" obviously have a negative impact on the experience of AMM DEX; for professional market makers, AMM's automatic market-making is essentially an inert market-making mechanism, so it is also It is not conducive to these professional teams to give full play to their own technical advantages and amplify profits through flexible operations.
So, is there any way to improve this? For a long time, players in the DEX track have been exploring solutions to the above problems at various levels, such as implementing the pending order function by integrating auxiliary services such as Gelato, expanding to new ecology to solve the gas cost problem, and improving the AMM mathematical model ( Such as DODO's PMM) to improve liquidity utilization efficiency, but in IDEX's view, there may be a more direct solution.
IDEX's solution: order book + AMM
In order to solve the above problems, IDEX turned its attention to the highly mature order book and transaction matching system in the CEX field, and proposed the concept of "Hybrid Liquidity" for the first time in the industry. In IDEX's view, the order book + matching model, as the most classic and mature exchange operation model, obviously has its reasons for success, and its advantages may just make up for the disadvantages of AMM.
Specifically, IDEX will not only build an AMM-type exchange pool on the chain, but also build an order book system based on off-chain matching. Afterwards, IDEX will quantify the price curve in the AMM exchange pool into orders at different price levels through its unique mapping system, and place them on the order book at the same time as the off-chain matching orders. The transaction engine will automatically match the most The best price combination to find the most cost-effective transaction path for users.
In this way, IDEX will be able to take advantage of the openness, freedom, and ease of use of AMM, as well as the richness of operations and performance advantages of order book + matching.
For ordinary users, trading operations based on IDEX can freely place orders at the ideal price position, and the flexibility of operation will be greatly improved; at the same time, there is no need to pay too much cost and time cost for a single transaction, and the trading engine of IDEX will quickly By processing all matched orders, the risk of transaction failure or front-running will be completely resolved; in addition, thanks to the dual order types, the slippage of users when trading on IDEX will be greatly reduced, and the overall quotation feedback will be more reasonable.
For market makers, the changes brought about by this innovation of IDEX are even more obvious. Ordinary liquidity providers (LPs) who are accustomed to AMM DEX can continue to form LP mining in IDEX's AMM exchange pool, while more professional market-making teams can use the API tools provided by IDEX on its order book system Execute more flexible and high-frequency market making. Compared with the active market-making method based on the lazy system such as Uniswap v3, IDEX's more active market-making mechanism at the bottom has higher capital utilization efficiency, which can help professional teams amplify their market-making benefits.
The above solutions will be officially launched in the latest v3 version of IDEX. Currently, this version of the sandbox environment has been deployed to Polygon's test network, which means that API users and programmatic trading users (market makers, algorithmic traders, etc.) can now test the mixed liquidity function of IDEX v3.
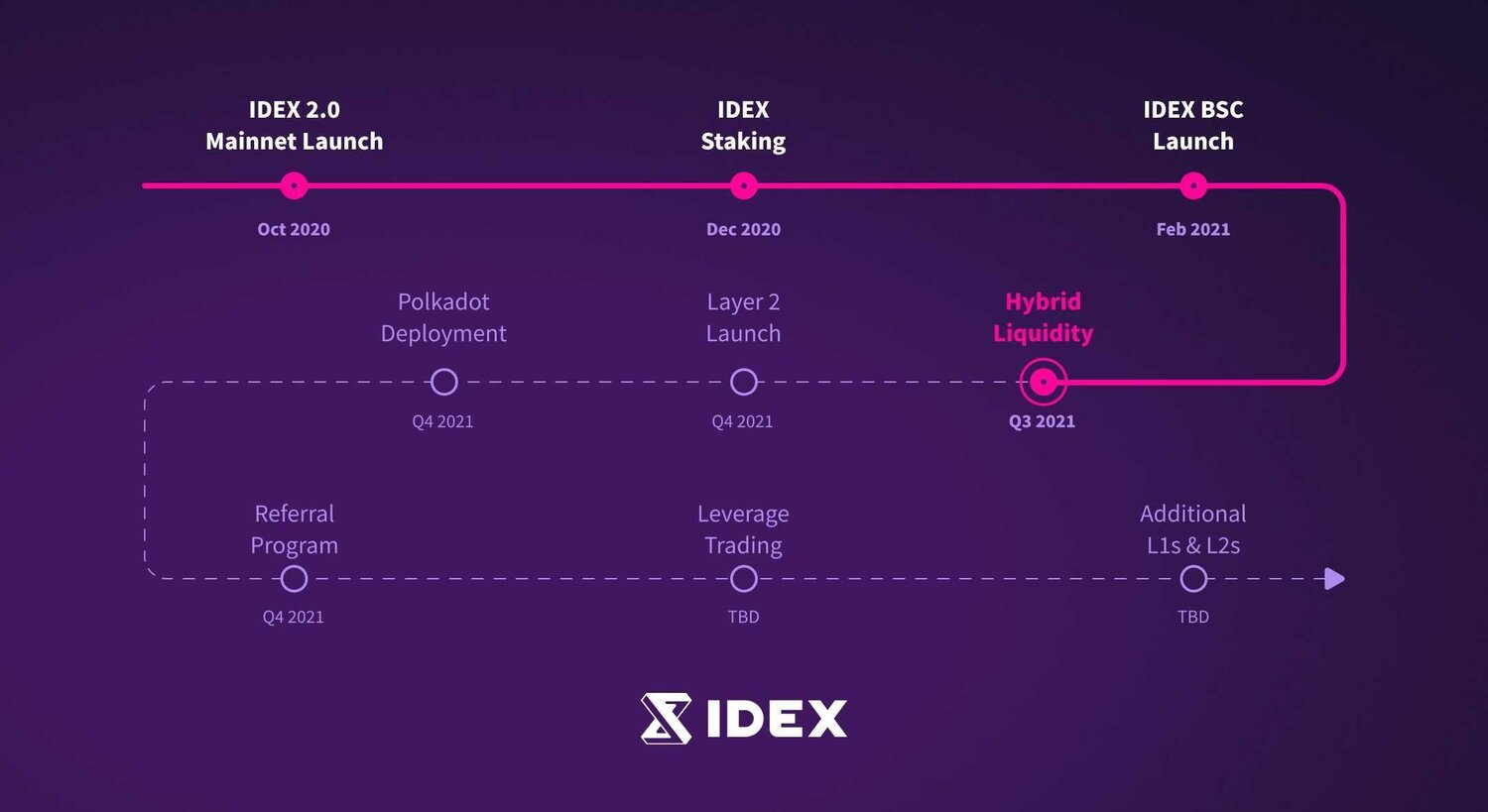
According to the roadmap plan released in May, IDEX plans to officially launch hybrid liquidity in the third quarter of this year. Judging from the current actual progress, it has been slightly delayed. However, since the test product has been released, it must be a short time before the official launch of the mainnet. Not far away.
AMMs and order books are not necessarily "one or the other"
After an in-depth understanding of IDEX's product design, we found that IDEX did not solidify its own thinking and fell into the choice of the two major market-making mechanisms of AMM and order book, but proceeded from the demand and rationally analyzed the respective differences Strengths and weaknesses, and uses a clever way to integrate the two mechanisms.
After the explosion of DeFi, many people in the industry believe that AMM is an upgrade compared to the order book, but this statement may not be accurate. Although AMM has promoted the successful rise of DEX, as a market-tested Market mechanism, order book obviously has its own advantages. AMM cannot be higher than the order book, but it is more suitable for market development needs in a specific environment.
After all, AMM and order books have never been in an "either-or" relationship. As long as they are properly designed, they can also "complement each other".



