Only technology and time can change.
Authorized translation: Carrie | Chain Hill Capital
Authorized translation: Carrie | Chain Hill Capital
Original link:
Original link:https://medium.com/
Chain Hill Capital (Qianfeng Capital) is authorized by the original author to translate and reprint. The following is the translation:
This is the second article in this series of articles. There are five articles in this series.
The first article in this series covered monetary economics and the stages of currency evolution. It also explains why the value of money is derived from the willingness to hold cash. However, this is not meant to be against the use of Bitcoin for commerce, nor is it an argument for its mere use as a store of value and not for exchange.
secondary title
Availability of Bitcoin as a Medium of Exchange
First, let's look at availability with a focus on capacity.
Bitcoin's base layer protocol cannot scale exponentially. Linear and incremental scaling is possible, and it will be continuously upgraded to accommodate more throughput and other optimizations. However, if Bitcoin wants to host billions of users, it must scale exponentially, and the blockchain is not suitable for this demand. Any cryptocurrency that claims to be able to do so sacrifices some of the key properties of the blockchain to do so, often without its creators disclosing or even realizing it. On-chain exponential scalability with maximum security and decentralization is not feasible, there are bound to be engineering compromises.
Similar to the Internet protocol stack, many blockchain projects strive to avoid protocol layered development at all costs. While this article is not a technical discussion of scalability, it cannot be avoided because the concept is so closely tied to the debate between stores of value and mediums of exchange.
A reasonable solution to the problem of technical limitations on the Bitcoin chain is to build protocols based on Bitcoin. The Lightning Network is by far the most promising second-layer solution to increase transaction throughput and reduce confirmation times. It is not the only or the last decentralized and trust-minimized layered solution for scaling problems. What most people fail to understand is that the Lightning Network is not a currency network, so the Lightning Network protocol does not create new currencies. It is just a payment network, no currency is issued on it, and no currency is transferred through it. The Lightning Network enables payment routing by transferring ownership of on-chain balances that are cryptographically linked to specific "unspent transaction outputs" (UTXOs) on the Bitcoin network.
The Lightning Network builds on pioneering ideas like eCash, which allows private, untraceable payments through its system's native currency (dubbed "CyberBucks") or national fiat currencies. In this way, the payment network can provide greater capacity and better privacy.
Layered development will make Bitcoin similar to the current financial system, but this similarity is only from a functional point of view. In terms of security, there is a big difference between the two, as there will be fewer (if any) trusted third parties that are inevitable in Bitcoin's monetary order.
The fiat currency of each country is not scalable by design. Including gold itself does not scale. Banks are essentially payment networks built on fiat currencies, which enable exponentially expanded usage of fiat currencies. PayPal is another payment network that makes fiat currencies more widely available in the digital world.
image description

Bank deposits are promises that can be exchanged back to fiat currency (the base currency) at any time
On the other hand, assets held by banks. These assets have varying degrees of liquidity, maturity and default risk. Banks must use market-acceptable instruments such as cash, securities, and loans to manage their liquidity in order to adequately and prudently meet their debt service obligations. Thus, although individuals use demand deposits to transact in the economy, demand deposits themselves are not money. Bank deposits may serve as money, but it is essentially a promise to pay, so granting this privilege (legal tender status) to commercial bank debt (demand deposits) is ludicrous.
As a result, our current financial system features a variety of payment networks (layered, parallel, subordinate, and, often, overlapping) filled with (for better or worse) trusted relationships. This "need for trust" is what makes the Lightning Network different, as its payment channel is not a payment promise, but a bilateral contract, driven and secured by clever cryptography, linked to specific UTXOs on the Bitcoin chain. bound.
When envisioning the development of the Bitcoin Stack protocol, its functional parallels to the current financial system include:
1) Base layer protocols (or strong money, base money, and foreign money): gold, fiat paper money, and bitcoin.
2) Secondary and outer layer protocols (or payment networks): banks, financial institutions, PayPal, ApplePay, WeChat Pay, and Lightning Network.
The difference between a fiat currency (or gold) based financial system and a Bitcoin based financial system is the security model, i.e., a trusted interconnected party security model vs. a trust-minimized network security model, or, centralized Trusted security model vs. distributed trustless security model. This distinction holds true for both base-layer protocols (fiat currencies vs. Bitcoin) and outer-layer protocols (banks vs. Lightning Network). However, gold's "basic agreement" is more similar to bitcoin in that it is no one's debt.
Therefore, the argument that the Lightning Network is a copy of the traditional banking system using encryption technology ignores the most significant difference between the two. The former is an open network of bilateral contracts with a minimum degree of trust, and there is no unilateral custody of the underlying assets by either party. The latter is a closed and trusted network where centralized institutions and customers contractually agree on the transfer of ownership, control over the underlying asset, and the promise of immediate payment (in short, the relationship between the bank and the depositor). Therefore, the Lightning Network payment channel is a contract between two parties with equal rights, while the nature of the contract between the bank and the depositor is the relationship between the debtor and the creditor.
Now that we have seen the similarities and differences between the two financial systems,Next we will answer the question of how to use Bitcoin as a medium of exchange.
Consider the following: Today, when you pay through your bank or PayPal, is it correct to say that you are using U.S. dollars? Are U.S. dollars in wire transfers used as a medium of exchange? The notes are not actually handed over to the other party, are they? We can conclude that USD is not the medium of exchange in this transaction. This transaction is a transfer of title to the Immediate Payment Note Promise.
The above discussion is technically correct, but it has little practical significance. However, Bitcoin Cash proponents use this line of reasoning, namely, that Bitcoin is transacted off-chain meaning it is not used as a medium of exchange.
The fact that money is a medium of exchange, and the dollar is a medium of exchange, does not mean that every transaction in an economy should be made directly with paper money (or gold, or bitcoin on-chain). This doesn't scale, so we need to use payment networks, and those payment networks have to be pegged to (or backed by) fiat currencies. That is, it doesn't matter whether we pay with physical currency or a payment network.
If the medium of exchange function of money can only be realized when two parties actually transfer paper money (or gold), then we can argue that money is rarely used as a medium of exchange, especially in advanced economies where cash payments are increasingly rare. At present, the base currency is so separated from daily economic life that it is meaningless to discuss whether the function of the medium of exchange exists from the perspective of the base currency. Most payments are not made in currency, but are denominated in currency, and payment commitments are settled in currency.
Paper money forms the basis of our current financial system (i.e. the monetary standard), upon which the payment network (i.e. off-chain) runs and payments are settled (i.e. on-chain). In this system, the dollar is the store of value (albeit volatile in the long run), medium of exchange and measure of value.
The same model applies to a bitcoinized financial system. Bitcoin can be used as a store of value, a medium of exchange, and a measure of value (at least in theory). However, that doesn't mean every transaction has to happen on-chain. Bitcoin can (and will) be used as a medium of exchange. But in the long run, a large number of transactions are likely to occur on the payment network, and these transactions transfer the ownership of the balance on the chain. These titles may or may not be payment commitments (i.e. there could be both Lightning Network and traditional banks - like current centralized exchanges), and these titles are then settled on the Bitcoin chain via UTXO transfers.
At present, Bitcoin is already a very safe and smooth means of global transactions. For medium-to-large transactions, bitcoin is an excellent "wealth transfer medium," to borrow Szabo's term.
But frequent and small payments could end up being mostly made through payment networks. They don’t need to be done with actual bitcoins, but are denominated in bitcoins and use bitcoins as the settlement asset for bilateral contracts (such as the Lightning Network or other trust-minimized third parties) or payment promises (trusted third parties).
In this sense, the base protocol can be seen as the final settlement layer, on which only large transactions tend to take place, while the second layer caters for recurring payments and smaller payments.
secondary title
Liquidity, Store of Value, and Transaction Costs
Now let's discuss another fundamental question,volatility.
From 2012 to 2015, the number of merchants accepting Bitcoin as a payment method continued to grow. Bitpay and Coinbase started out as intermediaries or payment gateways, allowing customers to pay with bitcoin, with merchants having the option to receive local fiat currency or bitcoin. Of course, most merchants prefer to use local currency.
image description
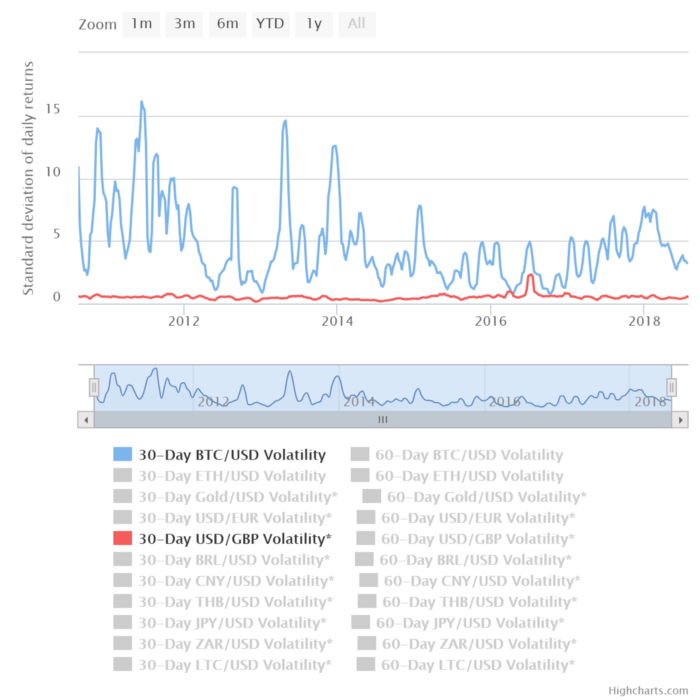
Bitcoin Volatility Has Declined, But Still Pretty Significantly Relative to Fiat
If merchants are not holding Bitcoin due to lack of trust in Bitcoin and unwillingness to tolerate its unpredictable short-term price fluctuations, then they will not have demand for Bitcoin and will not be able to promote its price stability. Instead, they quickly put bitcoins back on the market as soon as they receive them, effectively meaning less demand for them.
This is why forcing merchants to adopt Bitcoin at this stage is futile and should not be a priority for the Bitcoin community. Committing now to promoting the use of Bitcoin in transactions is putting the cart before the horse. First, we need to establish Bitcoin as a good store of value. Then, medium-of-exchange adoption quickly and naturally follows. So instead of simply having merchants allow customers to pay in bitcoin, we have to have them expect customers to pay in bitcoin and want to hold bitcoin as a cash reserve.
So, how should we get rid of the circular trap where merchants do not hold Bitcoin due to volatility, and the lack of stable demand will cause Bitcoin volatility? The answer is through education and understanding, solid protocol development, and most importantly, time. Below, we discuss this.
All other things being equal, people always prefer the more versatile (liquid) medium of exchange. Only if Bitcoin significantly reduces transaction costs, or if merchants understand the potential of the technology and want to hold Bitcoin for future value addition, will they be willing to accept Bitcoin instead of USD (or local fiat currency) .
Borrowing from Peter Šurda's analysis, three factors influence the choice of medium of exchange: liquidity, store of value, and transaction costs in the narrow sense. But broadly speaking, all three factors can be considered transaction costs.
First of all, let’s understand transaction costs in a narrow sense, which include handling fees, storage and transportation costs, verification costs, resistance to censorship, counterparty risk, and compliance costs. Currently, Bitcoin has significantly improved in many respects compared to existing base currencies, which reduces transaction costs in a narrow sense for its users. This is especially evident in cross-border payments, where Bitcoin is a far superior medium of exchange than paper money or gold. In cross-border payments, banknotes or gold use the payment network (off-chain), while Bitcoin uses the base currency (on-chain) for cross-border transactions.
But in many everyday payment scenarios, whether using the base currency (on-chain) or through the payment network (off-chain), Bitcoin has no comparative advantage. Because in the vast majority of jurisdictions, domestic transactions are frictionless and nearly instant, via cash, the banking system or other methods such as credit and debit cards or mobile payments.
As cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology bring more competition to the financial world, it is only a matter of time before the existing financial infrastructure improves substantially. Although, the possible improved transaction cost reduction is still not as good as that of Bitcoin, but should be enough to reduce the gap.
However, in other areas, Bitcoin is likely to continue to maintain its dominance. No other financial system is as open and inclusive as anyone with access to the network can initiate transactions in seconds and is censorship resistant, which is true for both the base currency and the payment network (e.g., on-chain and off-chain) established.
In only a narrow sense, reducing transaction costs can itself influence currency choice. However, in the midst of stiff competition, its effect is limited and short-lived. Although bitcoin has lower transaction costs in the narrow sense than paper money or gold as the base currency, when overall (broad sense) transaction costs are taken into account, the digital currency has little appeal in day-to-day transactions.
let's go back toLiquidity and Volatility. The price of Bitcoin remains volatile and unpredictable, which has greatly hindered it from becoming widely accepted as an everyday medium of exchange and held by businesses and individuals. Currently, only those who expect bitcoin to hold or appreciate in value over the long term accept bitcoin for payment and hold it as cash reserves. These people do it because of its attractive store-of-value properties, not because it's a highly liquid commodity. Bitcoin is currently accepted and held not because it is a more "universal medium of exchange" but because it holds value better and becomes a more general medium of exchange in the future. Therefore, for the present stage,Store of value is more important than liquidity.
As Bitcoin's value proposition gains traction, demand for it as a cash reserve grows, and more people observe and imitate these behaviors, Bitcoin will become more liquid and less volatile . The network effect will create a positive feedback loop, and the increased liquidity of Bitcoin will further promote price stability, reduce overall transaction costs, and make it increasingly used as a medium of exchange.
About Chain Hill Capital
About Chain Hill Capital
Supported by a professional team with multicultural backgrounds, members of the core departments - Investment Research Department, Trading Department, and Risk Control Department are all from well-known universities and institutions at home and abroad. They have a solid financial background, excellent investment research capabilities, and a keen sense of the market Sensitive ability, highly awe of the market and risks. The Investment Research Department combines rigorous basic research with mathematical and statistical models to obtain investment strategies such as "Pure Alpha" and "Smart Beta", and will soon export institutional-level research reports and project due diligence reports.
Supported by a professional team with multicultural backgrounds, members of the core departments - Investment Research Department, Trading Department, and Risk Control Department are all from well-known universities and institutions at home and abroad. They have a solid financial background, excellent investment research capabilities, and a keen sense of the market Sensitive ability, highly awe of the market and risks. The Investment Research Department combines rigorous basic research with mathematical and statistical models to obtain investment strategies such as "Pure Alpha" and "Smart Beta", and will soon export institutional-level research reports and project due diligence reports.



