A look at 35 modular protocols worth noting
Original author: THOR
Original translation: Vernacular Blockchain
What exactly does modular currency mean? Why are there hundreds of new “modular” protocols on the market now?
Modularity has been a hot topic this year, and the launch of Celestia and TIAToken last year kicked off the trend. It’s more than just a buzzword, however, as modular infrastructure components can solve blockchain’s scaling bottlenecks by moving certain components into specialized infrastructure.
It’s important to stress that modularity is not a short-term narrative that peters out as we move further into a bull market. Rather, it is a core design principle of blockchain that is likely to play an increasingly important role in the future of cryptocurrencies. In this case, it is important to understand what modularity means and which protocols you should focus on.
1. What is modularity?
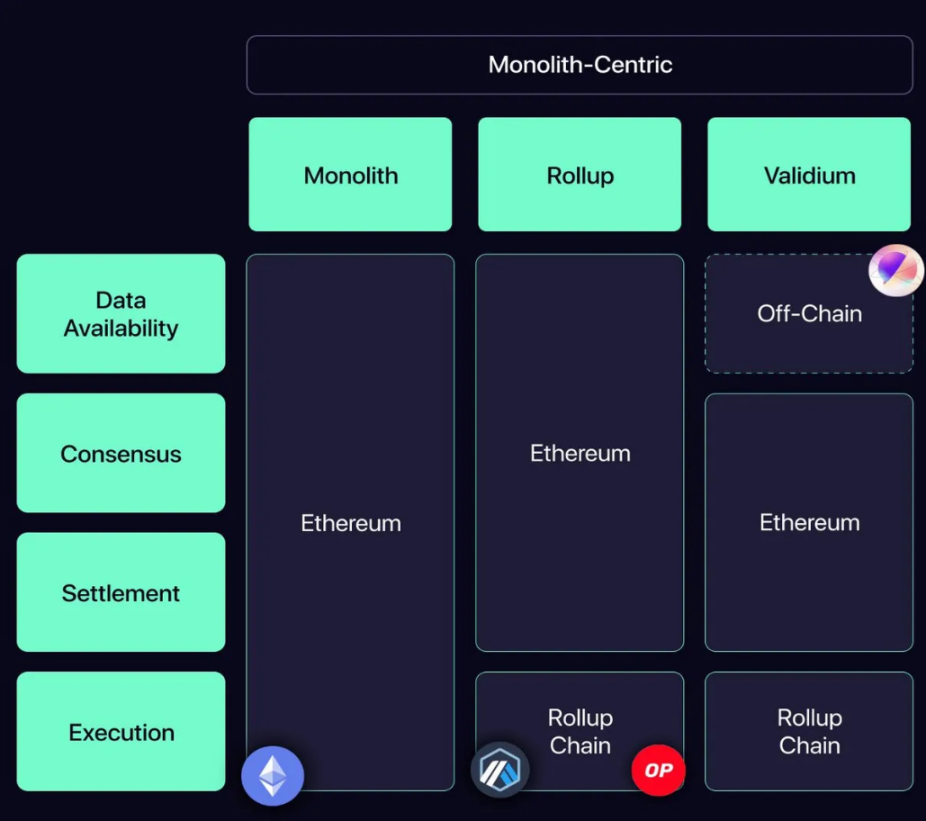
What does modularity mean in blockchain architecture? Youve probably heard of this concept, but as a quick refresher, the image below illustrates it nicely:
Comparison of monolithic and modular blockchain architectures
At its core, blockchain has four roles, or layers:
Execution layer - processes transactions for dapps on the chain and executes smart contracts. This is where calculations take place and account balances are updated.
Settlement layer - determines the overall state of the blockchain. The status of the completed on-chain transaction is determined.
Consensus layer - orders transactions by ensuring that nodes agree on the state of the chain.
Data Availability Layer - Ensures that data (transactions, blocks, etc.) are publicly available to all network participants, i.e. accessible to everyone.
Monolithic chains like Ethereum mainnet, Solana, Avalanche, Sui, Sei, etc. are all monolithic chains that handle all these components. Optimistic rollups like Arbitrum and Optimism are part of the modular stack because they serve as execution environments that move data availability, settlement, and consensus to the Ethereum mainnet.
Rollups like Manta are even more modular as it is an execution environment that uses Celestia for cheap data availability and the Ethereum mainnet for consensus and settlement.
There are many examples and many different combinations of modular infrastructure. By understanding the following, youll be on the right track on your modular journey.
2. Modular Ecosystem (in alphabetical order)
1)Aethos
Decentralized strategy engine for smart contracts. Allows embedding requirements in smart contracts, such as completing game milestones to obtain game items, prohibiting exploiters from using smart contracts, integrating identities on Rollup, embedding token policies, etc. Aethos is an AVS that utilizes EigenLayer.
2)AltLayer
Offers Rollup as a Service and Rollup Remortgage. Re-staking Rollup leverages Eigenlayer’s re-staking functionality and further provides decentralized ordering. AltLayer is working with Arbitrum to make it easy to create Arbitrum Orbit L3 chains, with the option of further using EigenDA or Celestia for data availability. AltLayer completed a $14.4 million round led by Polychain and leveraged EigenLayers AVS.
3)Astria
Shared sequencer network for Rollup. With Astria, Rollup can leverage a unified decentralized network of orderers for fast, censorship-resistant, and permissionless block confirmations. Astria appears to be working closely with the Celestia team.
4)Avail
The base layer of the blockchain - Avail recently announced the Aval Trinity: 1. Data availability, 2. Consensus, 3. A shared security layer suitable for various rollups (zk, optimistic, sovereign and application specific). Avail also closed $27 million in funding, led by Dragonfly and Founders Fund.
5)Babylon
Providing native, permissionless staking on Bitcoin, earn money by securing Rollups. Babylon is working with AltLayer to build a “decentralized verification layer for Bitcoin-secured Rollup.”
6)Blockless
Modular infrastructure for launching network neutral applications (nnApps). With Blockless, applications can be powered by the use of community devices linked to computing tasks. Blockless is an AVS that utilizes EigenLayer.
7)Caldera
Rollup as a service. Rollup can be easily deployed with just a few clicks on Arbitrum, Optimism or Polygon, and choose between numerous data availability providers. See the video below.
8)Cartesi
Specific application protocols built using Cartesi virtual machines, which include the Linux operating system. The power of Linux is enabling Web3 developers to access decades of existing code bases, programming languages, and open source tools. $CTSI, this native governance token has been around since 2020.
9)Celestia
As a data availability provider built on the Cosmos chain. Celestia has provided support for Aevo, Lyra, Manta, Dymension, Arbitrum Orbit chain, AltLayer, Berachain, Eclipse and many other projects. Celestia ushered in the modular era, with $TIA valued at more than $15 billion.
10)Conduit
Rollup is available as a service on Arbitrum and Optimism and offers a variety of data availability solutions. Some Rollups that have been built using Conduit include Zora, Aevo, Lyra, Mode, Parallel, etc.
11)Drosera
Decentralized Automatic Responder Collective (DARC). Drosera provides a permissionless security marketplace for mitigating and containing attacks. Drosera has raised $1.5 million in funding from Arrington Capital, Comfy capital and others, and is AVS powered by EigenLayer.
12)Dymension
The protocol that drives Rollapps, a standardized template for modular Rollups built on the Dymension central hub and powered by the Cosmos IBC bridge. RollApps is like an ERC-20 Token on the chain. The Dymension central hub handles settlement and consensus for Rollapps while offloading data availability to Celestia.
13)Eclipse
An upcoming Rollup on Ethereum. Solana virtual machine is used for execution, Ethereum is used for settlement, Celestia provides data availability, and Risc 0 is used for proof. Aims to bring Solana’s dapp to Ethereum.
14)EigenLayer
A permissionless Ethereum re-hypothecation market. Ethereum validators can deposit ETH and choose to “re-stake” to power rollups, bridges, oracles or other services (AVS) that wish to inherit the native security of Ethereum. These AVS will pay re-hypothecaters. EigenLayer recently announced a $100 million Series B investment led by a16z.
15)EigenDA
The first EigenLayer AVS. EigenDA is an Ethereum-native data availability layer. Once online, EigenDA will provide support for Mantle, Celo, Caldera, certain Arbitrum Orbit chains, and several other projects.
16)Espresso
Provides Espresso Sequencer for Rollup. Espresso recently announced the launch of Based Espresso, a shared sequencing market where different types of Rollups can sell block space to block proposers. Espresso raised $32 million in 2022 from Electric Capital, Sequoia, and others, and is backed by EigenLayer for alignment with Ethereum and strong economic security.
17)Ethos
Bringing Ethereum security to the Cosmos ecosystem through integration with EigenLayer and restaking. EigenLayer restakers can choose to provide security for Ethos, an AVS used to support the Ethos L1 chain. Re-stakeholders can take advantage of this security and earn additional benefits through the Cosmos chain.
18)Fluentxyz
Fluent zkWasm L2 is built on Ethereum, providing a Fluent virtual machine (VM) and a modular framework for creating Wasm execution environments. Wasm stands for WebAssembly and is a platform-independent and efficient binary instruction format for stack-based virtual machines. The Fluent execution environment has multiple data availability layers as the protocol is integrating EigenDA, Celestia, and others.
19)Fuel
Ethereums Rollup Operating System. Taking a UTXO approach, Fuel is a design framework and SDK for parallel transactions and high-throughput execution environments/rollups on Ethereum. Fuel created its own programming language called Sway, inspired by Rust and other languages. Fuel raised $80 million in 2022, led by Blockchain Capital.
20)Hyperlane
An interoperability layer designed to connect blockchains. Hyperlane enables modular rollups to integrate Hyperlane interoperability with just a few clicks to avoid liquidity fragmentation. Hyperlane raised $18.5 million in 2022, led by Variant.
21)Hyperspace AI
A peer-to-peer artificial intelligence network. Hyperspace AI is a large-scale LLM network project designed to be used by anyone in a permissionless manner. The network runs on community infrastructure with a low barrier to entry (smartphones, browsers, etc. can run nodes).
22)Initia
Intertwined Rollup Network. Initia makes it possible to build and scale interconnected blockchains with different modular components. The first Rollup launched on Initia is Blackwing, a modular Rollup for margin trading. Initia raised $7.5 million in funding led by HackVC and Delphi Ventures.
23)Karak
A second layer of blockchain for risk management, powering re-hypothecation, artificial intelligence and next-generation security applications. Karak provides support for “rollaps” through its modular security, highly customizable and built-in machine learning tools. Karak recently announced $48 million in Series A funding from Lightspeed, Pantera and others.
24)LaGrange
Construct a state committee for optimistic rollup to generate zero-knowledge proofs. These can be embedded into bridges and other cross-chain messaging protocols, improving security by orders of magnitude. LaGrange operates as EigenLayer AVS, the power of remortgage drives the LaGrange zk light client. LaGrange raised $4 million from 1kx, Maven 11, Lattice Fund and others.
25)Lava Network
A modular data layer for chain and rollup use. Lava is essentially the rpc and indexing layer of the chain. In many cases, data access is decentralized, so by using the Lava network, the chain ensures that users and developers can access data easily and quickly. Lava raised $15 million from Hashkey, Jump, Tribe Capital and others.
26)MegaETH
Building an EVM-compatible second layer with ultra-high throughput and low latency. MegaETH focuses on improving the Ethereum execution client and extending L2 Rollup through parallel execution and other methods. The vision is to provide MegaRollups capable of handling 100,000 to 200,000 transactions per second, including zk and optimistic rollups. MegaETH will use EigenDA for data availability.
27)Mitosis
Modular Liquidity Protocol. Mitosis aims to unify the increasingly fragmented DeFi liquidity landscape by building cross-chain protocols for facilitating the transfer of assets and messages between blockchains. Mitosis enables efficient use of capital by making bridging assets liquid. Mitosis has partnered with Hyperlane to make it easier to deploy Mitosis smart contracts and connect modular chains.
28)Movement labs
Create a modular blockchain network built with the Move programming language. Movement ran a builder program to attract developers and created M2: a MoveEVM zk second layer with parallel execution and shared ordering on Ethereum. Movement raises $3.4 million in seed funding to drive adoption of Move.
29)Neutron
A Cosmos application chain for building integrated applications, providing a framework for building DeFi applications on Neutron L1, inheriting the characteristics of application chains and smart contracts. Integrated applications can access features such as mempools, block automation, custom block spaces, and more. Neutron raised US$10 million in 2023, led by BN labs.
30)Omni
By re-mortgaging the security of ETH, Ethereum Rollup is securely connected through a low-latency interoperable network. Omni L1 (communication layer) is secured by re-staking ETH and has received a commitment of $600 million in re-staking ETH from EtherFi. Omni has also partnered with Mantle, Injective, and several others, and has raised $18 million from Pantera, Two Sigma, Coinbase, and others.
31)Plume
The Plume network is a modular second layer designed for RWA (Real World Asset) applications. This means it focuses on compliance (with built-in KYC and AML capabilities), easy onboarding for users, instant settlement, and more. Plume L2 integrates with Celestia, Hyperlane, EigenLayer, Omni, and more. learn more.
32)Risc Zero
ZK-proof that can be integrated with modular infrastructure components. Bonsai smart contract SDK, Risc Zero zkVM and Risc Zero proof system are provided. For example, the SVM L2 (Eclipse) described above uses Risc Zero for zero-knowledge proofs. Other protocols built with Risc Zero include Altlayer, Citrea, Drosera, Layer N, Optimism, Avail, and more. Risc Zero raised US$40 million in 2023, led by Blockchain Capital.
33)Ritual
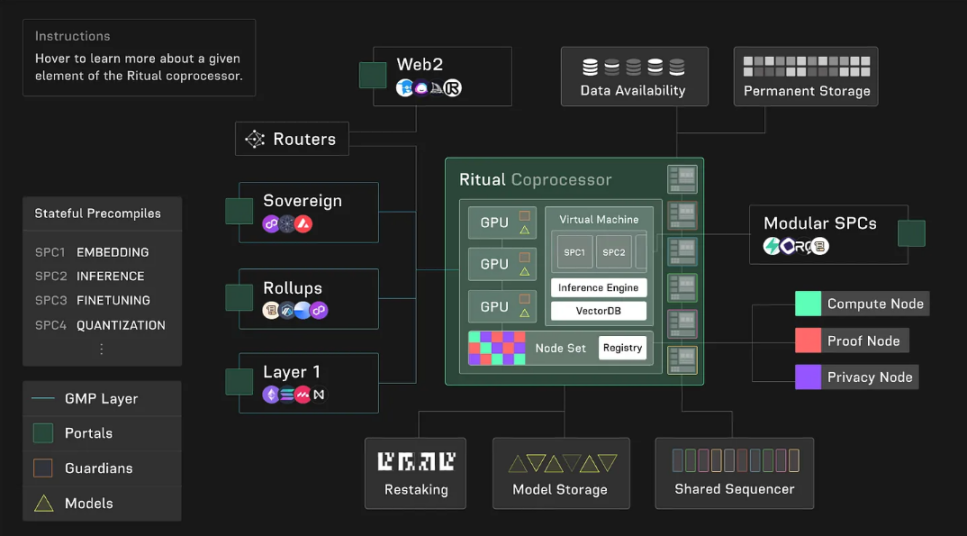
A community-owned artificial intelligence network. Ritual provides an AI co-processor for blockchain, making it easy to integrate AI models into crypto applications. Ritual Superchain is a set of modular execution layers surrounding different AI models. To launch the ecosystem, Ritual will use EigenLayer to provide security. Ritual raised $25 million in Series A funding led by Archetype.
34)Ternoa
A cross-layer, multi-chain technology stack designed to maximize developer accessibility. Ternoa provides a privacy-focused file system and a layer-1 blockchain, among other features. The chain has been operational since 2022 and has more than 50 dapps built on it. Ternoa’s native governance token ($CAPS) has been trading since 2021.
35)Taiko
Build the Ethereum equivalent (type 1) zkEVM. Taiko also designed a competitive rollup-based architecture with a competition-based order and dispute mechanism. Competition-based ordering is a decentralized and permissionless way of ordering L2 transactions. The Taiko technology stack is unique in that it is equivalent to Ethereum while being highly scalable. Taiko has raised $22 million in funding led by Sequoia China and Generative Ventures.
3. Summary
Note that these are just some of the protocols in a rapidly expanding ecosystem. In addition, more familiar names such as Ethereum, Arbitrum, Optimism, zkSync, Polygon, Near, etc. are also building their own modular stacks, including L3 and DA layers.