LD Capital: Looking back at the decentralized storage track that was left out by the market from EthStorage
Original author: Alfred, LD Capital

One of the most popular tracks this year should be the L2 track that enhances the scalability of blockchain. After its successful implementation, faster speeds and lower costs will lead to the gradual prosperity of Web3 applications. The generation of large amounts of data in the future will Storage presents an explosion of demand. This article will focus on EthStorage, which ranked first in this year’s EDCON Spuer Demo, and review the decentralized storage track that has been relatively low in recent market popularity but has great potential.
1. Development process of network storage
Consensus, computing and storage are collectively known as the three pillars and underlying infrastructure of web3. When data and information are generated, storage is required. Since the birth of computers, storage technology has been developing through exploration and breakthroughs. This article divides it into four stages. .
1. Centralized storage: centralized storage + centralized management
Computers first began to use paper tape to record data. Later, IBM produced the first hard disk as a storage medium in 1956 and entered the computer storage method we are familiar with today.
Centralized storage devices have been iterating, such as hard disks, tapes, memory cards, SSDs, etc., but the storage architecture is fixed. Terminal devices can access and request data from storage resources through the network, but all data storage resources are concentrated in one Central location or server, unified control and management.
2. Cloud storage: distributed storage + centralized management
In 2006, Amazon AWS went online and launched EC 2 and S 3 cloud storage services. Storage has entered a new era. Microsoft, Google, Alibaba, etc. have also followed suit, becoming the most widely used storage method today.
Cloud storage applies a distributed storage architecture, uses multiple servers to store data in a decentralized manner, splits data into multiple servers for backup, reduces single points of failure, and has the characteristics of reduced data redundancy and elastic expansion. However, the cloud storage servers are centrally managed by the cloud service provider, and the actual control of the data does not belong to the user.
3. Traditional blockchain storage: distributed, full-node storage + decentralized management
Since the birth of Bitcoin, blockchain network storage has become a solution that is opposite to centralized storage and management. Blockchain ensures data security and non-tampering through distributed storage, consensus mechanism and transaction verification mechanism, while meeting the requirements of It has the characteristics of decentralized storage and decentralized management.
However, blockchain networks such as Bitcoin and Ethereum have high storage costs and low efficiency. The main reason is that the network architecture of these blockchains is not designed from the perspective of storage. Each node must store a copy of data, and Block space is limited. Taking the Boring Ape NFT as an example, storing one on the Bitcoin or Ethereum network requires at least several hundred dollars or more.
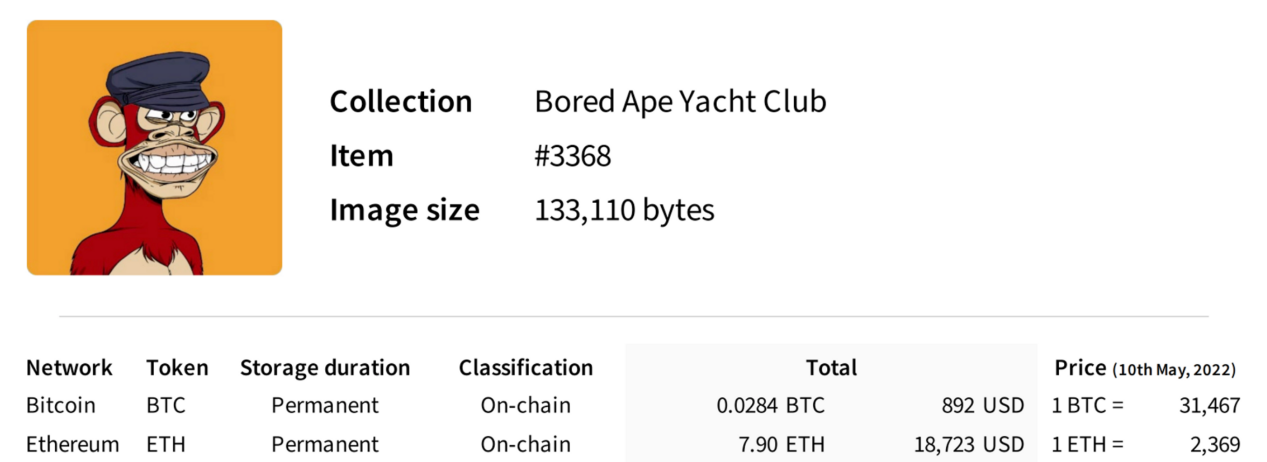
Source: Fundamental Labs
4. Web3 decentralized storage: distributed, multi-node storage + decentralized management
Because it is very expensive to store data directly on the blockchain, many web3 decentralized storage solutions and projects have emerged, such as IFPS, Filecoin, Storj, Arweave, Swarm, EthStorage, etc. The goal of these projects is to maintain decentralization On the basis of centralized storage and management, increasing storage space and reducing costs are achieved through a combination of technologies such as data segmentation, multi-node storage, and on-chain certification.
2. ETH Modularity and World Computer
1. ETH modularization
Since ETH planned a Rollup-centered roadmap in 2021, the modularity of Ethereum has begun to be established, splitting each layer of a single omnipotent chain (*monolithic blockchain), and the functions of different layers can be managed by different Module or chain undertakes to expand capacity, this direction is also called by Vitalik Endgame-Endgame.
The blockchain represented by Ethereum splits the chain into four key levels:
(1) Execution Layer (*Execution Layer): transaction processing, smart contract execution and calculation, etc.
(2) Settlement Layer (*Settlement Layer): Verify execution results, resolve disputes and promise settlement status.
(3) Consensus Layer (*Consensus Layer): determines the order, validity and consistency of transactions between nodes
(4) Data Availability Layer (*Data Availability Layer): Ensure that data can be used, stored and verifiable
In the monolithic blockchain chain, the blockchain is a chain that handles all four functions, and will face the trilemma of the blockchain. Blockchain modularity allows for the splitting of the four functions into multiple specialized layers, each addressing a different problem.
After ETH was modularized, the ETH main chain became L1, on which many L2s were born, mainly serving as the execution layer of ETH. For example, the L2 technology of OP Stack has also developed a modular architecture to enhance future reliability. scalability. Through the direction of modularization + Rollup, ETH will mainly maintain the data availability layer (*DA) and consensus layer in the future, becoming the mainstream and most secure basic layer. The functions of other layers will be upgraded through other chains and solutions to carry out the entire ETH Ecological expansion and improved scalability.
2. World Computer
The goal of Ethereum is to build a world supercomputer. Currently, Ethereum is doing very well in terms of security, but it is still making breakthroughs in scalability. Rollup is an important direction to solve the problem of scalability. The modular approach can solve this problem to a certain extent. The trilemma of the blockchain, but to become a supercomputer, it also needs to face three difficulties, namely consensus, calculation and storage. These three problems also restrict each other.
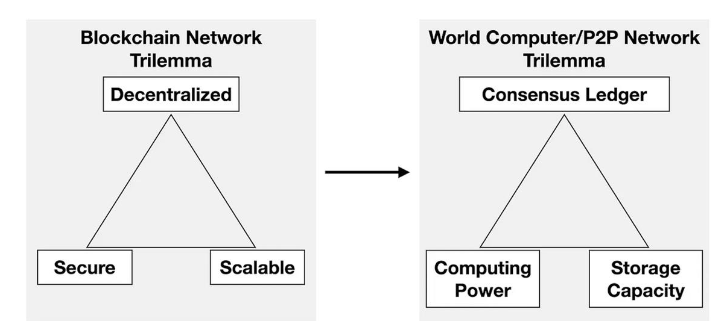
Source: Towards World Supercomputer
Different priorities for this trilemma will result in different trade-offs:
Strong consensus ledger: essentially requires repeated storage and calculation, so it is not suitable for expanding storage and calculation.
Strong computing power: Consensus needs to be reused when performing a large number of calculations and proof tasks, so it is not suitable for large-scale storage.
Strong storage capacity: Need to reuse consensus when performing frequent random sampling space proofs, so it is not suitable for computing.
Currently, traditional L2 solutions still face the problem of balancing centralized sorters and computing efficiency, and are unable to provide strong storage capabilities. The authors of the article Towards World Supercomputer proposed a way to solve the three dilemmas of becoming a world computer by dividing the world computer by function as the underlying architecture and expanding them separately.
That is, the final world supercomputer will be composed of three topologically heterogeneous P2P networks. Similar to building a physical computer, the consensus ledger, computing network and storage network will be connected through trustless buses (*connectors) such as zero-knowledge proof technology, and assembled into a world supercomputer. Other components can be added based on the needs of specific applications. Appropriate selection and connection of each component will achieve the balance of the trilemma of consensus ledger, computing power and storage capacity, ultimately ensuring the decentralization, high performance and security of the worlds supercomputers. Among them, EthStorage serves as a solution for the storage block in supercomputers in the architecture.
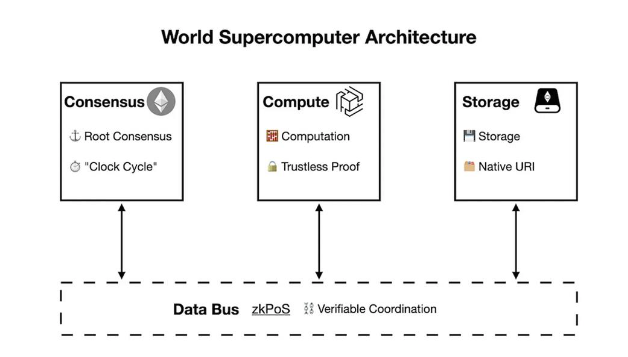
Source: Towards World Supercomputer
If based on this framework, the transaction process of Ethereums world supercomputer will be divided into the following steps:
(1) Consensus: Use Ethereum to process and reach transaction consensus.
(2) Calculation: The zkOracle network performs relevant off-chain calculations by quickly verifying the proof and consensus data delivered by zkPoS as a bus.
(3) Consensus: In some cases, such as automation and machine learning, the computing network will pass data and transactions back to Ethereum or EthStorage through proofs.
(4) Storage: For storing large amounts of data from Ethereum (*such as NFT metadata), zkPoS acts as a messenger between Ethereum smart contracts and EthStorage.
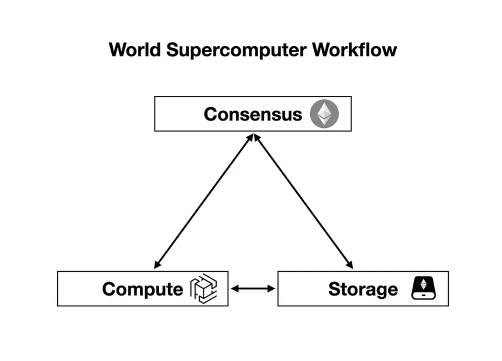
Source: Towards World Supercomputer
3. ETH Storage
1 Introduction
EthStorage is the first layer-2 solution that provides programmable dynamic storage based on Ethereum data availability (*Data Availability), which can expand programmable storage at a cost of 1/100 to 1/1000 to hundreds of terabytes or even petabytes.
The team has twice won funding (*Grant) support from the Ethereum Foundation to help Ethereum conduct research on data availability (*Data Availability) and L2 dynamic data set storage proof using Ethereum L1 contracts. And won the first place in the 2023 EDCON Spuer Demo.
2. Technical features
(1) Highly integrated ETH
The client of EthStorage is a superset of the Ethereum client Geth, which means that when running an EthStorage node, it can still participate in any process of Ethereum normally. A node can be an Ethereum validator node and also be the data of EthStorage. node. The Data Provider module of each EthStorage Node will initiate a connection request with the Data Provider of other EthStorage Node. When they are connected to each other, they actually form a decentralized storage network.
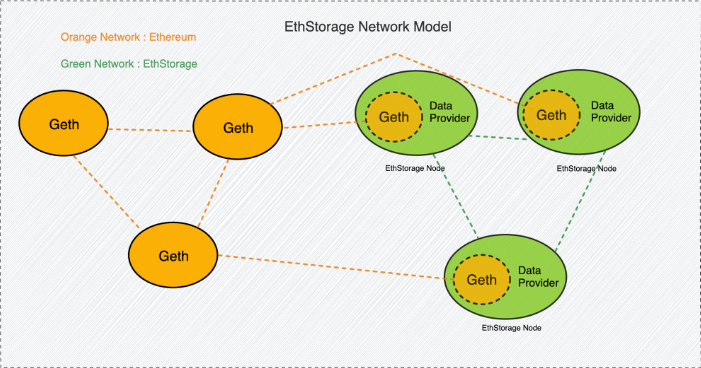
Source: EthStorage — The First Ethereum Storage L2
Users using EthStorage can directly use existing wallets to interact with all applications built on storage, whether it is NFT, decentralized social networks or decentralized games, which can minimize the users time to enter EthStorage. threshold. At the same time, EVM-compatible EthStorage can bring excellent interoperability to smart contracts. For example, if user A wants to set a picture for his mint NFT, he only needs to execute an Ethereum transaction through Ethstorage. When using Arweave, A One Arweave transaction and two Ethereum transactions need to be submitted, and there is no way to execute them synchronously like EthStorage.
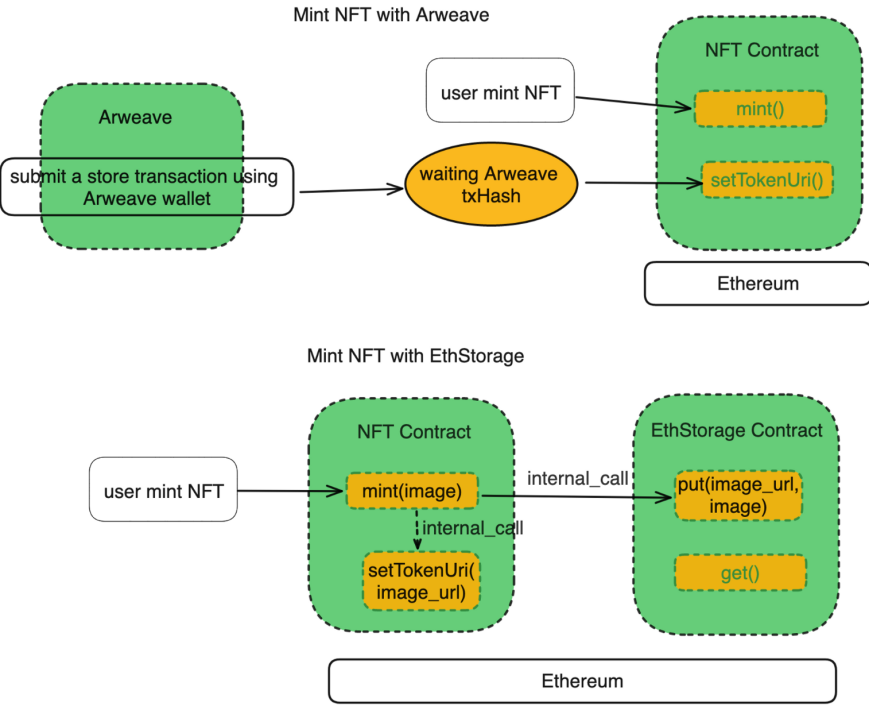
Source: EthStorage — The First Ethereum Storage L2
(2) L2 decentralized solution based on DA layer
EthStorage actually uses an L2-like architecture. A storage contract will be deployed on Ethereum as the entrance to EthStorages data operations. At the same time, the proof of data node off-chain storage data (*off chain storage data) also needs to be verified through this contract. .
Comparison with current L2:
Rollup (L2) stores a state tree off-chain, and the commitment (*commitment) on the chain is the state tree root. At the same time, after receiving new data, Rollup still needs to execute transactions off-chain to complete the state transformation process and establish a new state. state tree;
EthStorage stores data off-chain, and the commitment (*commitment) on the chain is the proof of data storage. At the same time, after EthStorage receives a request to update the stored data, it will regenerate a new storage proof for the data.
As can be seen from the above, the expansion direction of the current Optimism Rollup or ZK-Rollup is to expand the computing power of Ethereum, while the expansion direction of EthStorage Rollup is to expand the data storage capacity of Ethereum.
At the same time, EthStorage is a modular storage layer. As long as there is EVM and DA to reduce storage costs, it can run on any blockchain (*but many Layer 1s currently do not have a DA layer), even on Layer 2 Thats ok too. For example, EthStorage is currently considering how to use its technology to implement fraud proofs on Optimism. The corresponding DA layer is also enabled on Optimism.
(3) Dynamic storage can be achieved
From the perspective of system design architecture, Filecoin and Arweave are more used for static purposes. Large amounts of data can be uploaded to decentralized storage, but they cannot be modified or deleted, and new data can only be re-uploaded. Thanks to the key-value storage paradigm, EthStorage can support CRUD, that is, creating new storage data, updating storage data, reading storage data, and deleting storage data. This is easy to achieve in the field of centralized storage, but currently only EthStorage can do it in the field of decentralized storage.
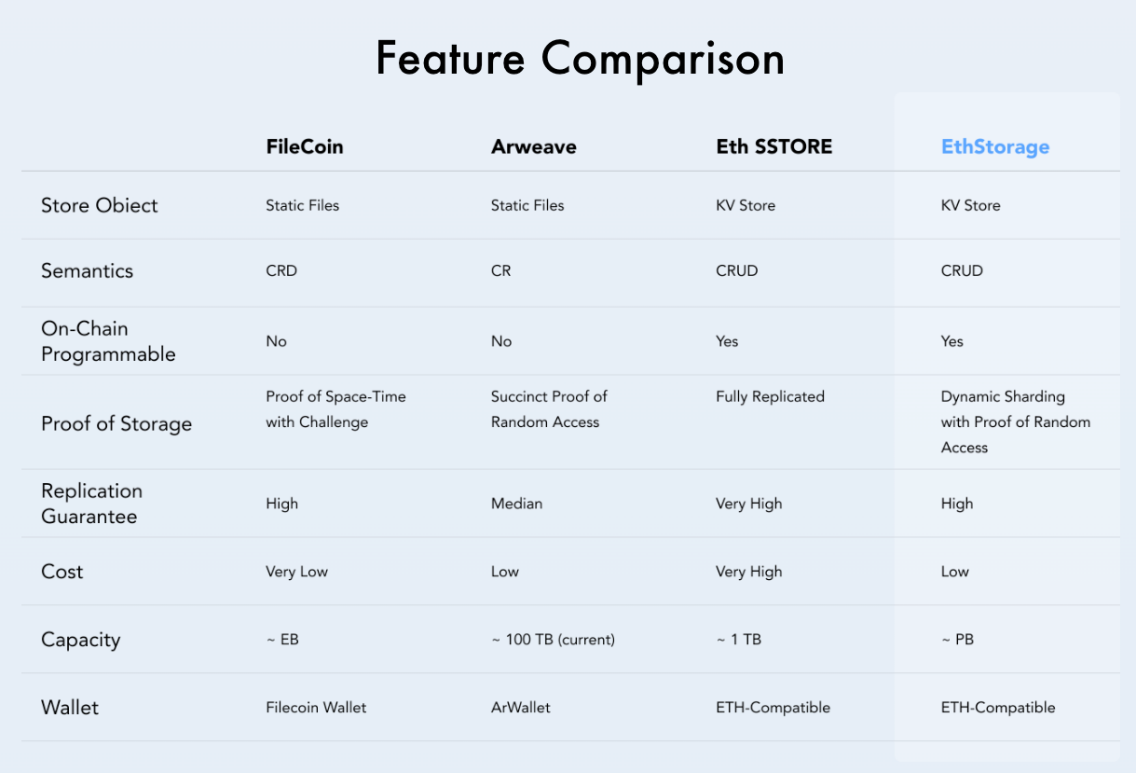
Source: EthStorage official
(4) Create Ethereum network access protocol
A series of behaviors such as browsing web pages, sending emails, and downloading files on the Web2 Internet are inseparable from the HTTP protocol, which is one of the most common protocols on the Internet. The HTTP protocol defines how to transmit and exchange resources between clients and servers, and URLs are identifiers that specify the locations of these resources on the Internet. When a web address is entered into a web browser or a link is clicked, an HTTP request is triggered which uses the URL to identify the resource to be requested. A web browser parses the URL, then communicates with the server using the HTTP protocol, requests a specific resource, and displays the resource to the user after the server responds. The HTTP protocol and URLs work closely together to form the basis for browsing, interacting with, and transferring resources on the Web. However, the data of Web2 web pages or Internet services is hosted in a centralized server. When the renewal of the server is stopped, the cloud service used by the application will stop, and the application data will be deleted by the centralized service provider.
The founder of EthStorage proposed a Web3-based network access protocol — ERC-4804, which passed the final review of EIP and was approved. ERC-4804, the full name is Web3 URL interpreted by EVM call information, it is an HTTP-style Web3 URL (*web3://) to EVM information call, and it is the first network access protocol on Ethereum. Different from the way web2 accesses server resources, the web3:// Access protocol directly renders resources hosted on Ethereum smart contracts through Web3 URLs, including files such as HTML, CSS, and PDF.
In simple terms, web3:// (*http://web3 url.io) is a decentralized http://. It adds a decentralized presentation layer to Ethereum, allowing users to directly browse web content on EVM, such as web pages, pictures, songs, etc., while EVM serves as a decentralized backend.
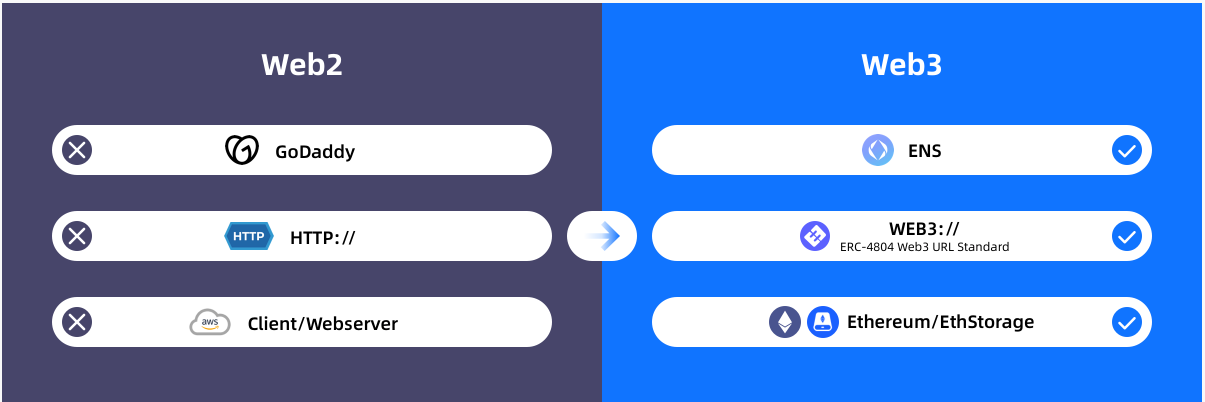
Source: EthStorage official
3. Current situation and plan
(1) Product application
Through EthStorage, it will be possible to re-enable Internet applications with decentralized storage as the bottom layer (*currently many Dapps still use a centralized way to store data), such as dynamic NFT, music NFT on the chain, personal website, hostless wallet, Dapp, Deweb et al.

Source: EthStorage official
Take DeWeb as an example:
We know that Ethereum is a decentralized network. Many decentralized dapps have been born on Ethereum, but these dapps are not completely decentralized. The front-ends of many applications are still hosted by centralized cloud services. For example, Uniswap’s front-end webpage was down, trading pairs were deleted, and Tornado.Cash’s front-end services were suspended because it was regulated for money laundering, all because its front-end is hosted on a centralized server and cannot effectively resist censorship. However, using the EthStorage solution, webpage files and data are hosted in smart contracts, which are jointly operated and maintained by a decentralized network, which greatly improves the resistance to censorship. Realizing DeWeb through the programmability of smart contracts can realize many interesting applications, such as De-github, De-blog, and the front end of various dapps.
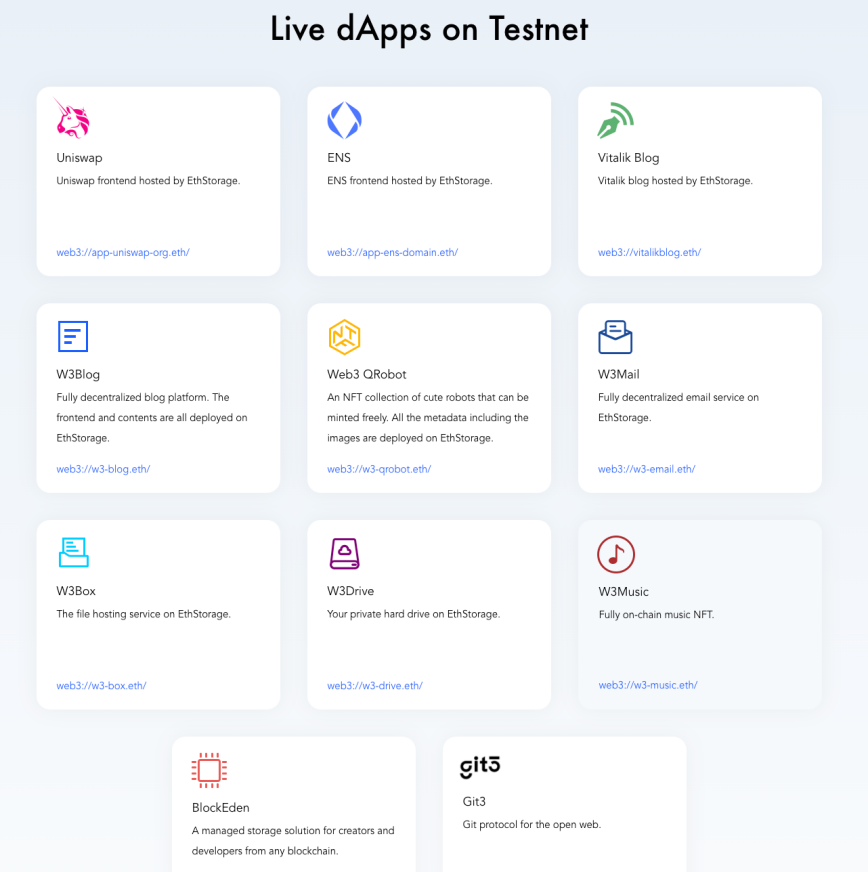
Source: EthStorage official
At present, EthStorage has not announced the token plan, but the testnet can be used and interacted with the testnet through the test token W 3 Q .
(2) Roadmap
According to the roadmap announced by EDCON, in 2023, EthStorage will be mainly in the testnet stage, and will adapt to the Ethereum Cancun upgrade for development and testing. The mainnet may be launched in 2024, and Danksharding, CL+EL client and Web3 browser access will be fully integrated.

Source: EthStorage official
4. Quick overview of other storage projects
(1) Filecoin: Filecoin is a decentralized storage network with an incentive system built on top of IPFS. IPFS uses Distributed Hash Table (*DHT), which is a protocol for storing, addressing and transmitting data (*analogous to http protocol). Filecoin acts as the incentive layer of IPFS and also acts as an open storage market. Filecoin uses a contract-based model to ensure data persistence combined with zero-knowledge proofs, especially space-time proofs and replication proofs. On March 14 this year, Filecoin announced the official launch of a virtual machine (*FVM) to support smart contracts and user programmability.
The characteristics of Filecoin are: it has a separate chain and incentive system; it has large space for static storage and low cost; it supports FVM virtual machine after upgrading.
(2) Arweave: Arweave adopts a “pay once, store forever” model, where the one-time payment covers the cost of permanently storing data, and there are no additional charges to retrieve the data. Arweave uses a concise proof of random access to create a native data structure of *Blockweave, that is, each block is linked to the previous block and a historical Recall Block. For nodes, the prerequisite for casting a new block is to synchronize a Recall-Block and the latest generated block data.
The characteristics of Arweave are: a separate chain and incentive system; on-chain storage and permanent storage; weak interoperability with other chains.
(3) BNB Greenfield: Greenfield focuses on promoting decentralized data management and access, aiming to simplify data storage and management and link data ownership with the DeFi environment of the BNB Smart Chain (*BSC). The complete BNB Greenfield system can interoperate with the mature BSC public chain and BN community users. When users want to create and use data on Greenfield, they can interact with BNB Greenfield core through BNB Greenfield dApps (*decentralized applications) infrastructure to interact.
The characteristics of BNB Greenfield are: the last puzzle of Binances Trinity ecological network, strong operability within the ecology, and BNB can be used in various chains; it adopts the structural concept of Amazon S3 storage bucket; off-chain storage, on-chain verification.
V. Summary
Storage is one of the three pillars of the Web3 network. Decentralized storage can only be implemented to truly realize data rights verification and a sovereign network. Otherwise, it is of little significance to develop a blockchain network at the expense of centralized efficiency. This track belongs to the underlying foundation, has potential and is of great significance.
Currently, compared to other tracks, decentralized storage is less popular in the market. This is mainly due to the fact that it has not yet reached the development stage and lacks demand. When the development of L2 makes the application of Dapp cheap and fast, the accumulation of large amounts of data and value demands will push the market heat to the decentralized storage track.
As an emerging project, EthStorage has a good ecological foundation in Ethereum and has strong interoperability. It can be combined with other L1 and L2 with DA layer to provide new development directions and solutions. Nowadays, each decentralized storage project also has its main focus and continues to develop. We look forward to the era when the market gears will shift to the storage track.
References
1. EthStorage official
2、《Towards World Supercomputer》,Xiaohang Yu, Kartin, msfew — Hyper Oracle, Qi Zhou — ETHStorage
3. EthStorage — The First Ethereum Storage L2, 0x hhh, 0x Cryptolee
4、《Decentralized Storage:A Pillar of Web3》,Fundamental Labs
5. Modular Blockchain: An Engineering Solution for Ethereum to Become a World Computer, IOBC Capital
6. EthStorage: Expanding the storage performance of the Ethereum ecosystem, Mint Ventures



