Quick look at the hot racetrack DePIN: development potential, challenges, and key players
Hot spots in the field of Web 3 are constantly rotating, including DeFi summer, NFT craze, the first year of Layer 2... Concept first seems to have become one of the typical paradigms for the development of the encryption field. With diverse narratives that are highly creative and imaginative, the industry has experienced wave after wave of development boom.And when the heat dissipates, it can’t help but lead to reflection, what benefits can the new use cases of Web 3 bring to the real world? Do we really need encrypted networks?
Discover the real-world value of encrypted networks, in late 2022, Messari, a well-known encryption research organization, released a survey soliciting an official title for Web 3 physical infrastructure. Physical Proof of Work (PoPw), Token Incentivized Physical Network (TIPIN), EdgeFi or Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Network (DePIN), etc. are all among the options. In the end, DePIN (Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Networks) stood out and became the common name of this potential track of Web 3.
What is DePIN? In summary, it is a network that connects digital space and physical space in a decentralized manner based on encryption technology. According to researcher Messari, The adoption of DePIN will go beyond the early financial transaction use cases in the encryption field and has the potential to further promote the encryption industrys position in the Internet and ultimately promote the development of the Web 3 value network. In order to further understand the DePIN track situation, this article will analyze the following three aspects:
What is DePIN? How does it work?
Opportunities and challenges facing the development of DePIN track
Development status of DePIN project
DePIN practice, encryption technology empowers real-life use cases
DePIN is built on the basic concept of the Internet of Things (IoT). So before introducing how DePIN works, let us first understand the Internet of Things (IoT). The Internet of Things refers to the process of connecting daily physical objects to the Internet. Its concept can be traced back to 1980. The worlds first Coke vending machine with the concept of the Internet of Things was born. It is connected to the Internet and can check inventory and inventory on the Internet. Confirm the number of drinks available. With the rapid development of the Internet and related technologies, there are more and more application scenarios for the Internet of Things, including connected vehicles, home automation, connected wearable devices, connected health monitoring devices, and remote monitoring devices.
DePIN concept interpretation
Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Network (DePIN) is the name of a blockchain network that uses crypto assets to incentivize the community to build physical infrastructure networks. There are two points worthy of attention here. One is that the DePIN network relies on decentralized networks and communities rather than centralized companies for transactions and business logic. Second, unlike most Web 3 products, virtual assets on this network can be used to purchase tangible assets in the real world, such as electricity, telecommunications services, network access, etc. All in all, DePIN was created to provide real value.
Based on the differences in hardware and resources, goods and services provided by the network, the DePIN project is divided into the following two categories:
Physical Resource Network (PRN): PRN encourages participants to use location-based hardware to provide unique goods and services in the real world, such as wireless networks, energy networks, and sensor networks.
Digital Resource Network (DRN): DRN encourages participants to use hardware to provide interchangeable digital resources, such as cloud storage networks, bandwidth, or network computing.
Note: There is currently no consensus on the distinction between the above concepts. If you want to know whether the project is DePIN and whether it belongs to the PRN or DRN category, you can go to the link below to test it.
🔗https://2hd1brbnhvd.typeform.com/to/YzJbOSYh
DePIN Hardware Network and Economic Operations
Unlike traditional centralized companies that invest a lot of time and money in building and maintaining infrastructure, DePIN attempts to outsource this construction and maintenance process to a community inspired by crypto assets. DePIN networks usually include the following key components:
Crypto-assets and community members: Crypto-assets (such as Tokens) for specific projects that pay hardware operators for services. Each crypto-asset has different economic characteristics according to the rules set by the project. Under this incentive, community members maintain and build infrastructure.
Hardware devices: The physical components that help connect a network to the physical world. For example, hotspots can be used for wireless networking, and extra space on the hard drive can be used for storage networks.
Hardware Operators: Users who purchase or loan hardware and connect it to their respective networks.
End user: A user of the infrastructure supported by network hardware. For example, end users may prefer to rely on the DePIN project rather than a company to obtain a WiFi signal and pay to receive services provided by the network.
It can be seen that the DePIN network first incentivizes participants in the decentralized community to become the supply side through encrypted assets. As the supply side grows, capital drives the value of crypto assets, allowing the supply side to provide competitively priced services. On the basis of creating an attractive ecosystem, it will attract more developers, builders and end users.
As end users continue to adopt, the structural demand for the network increases, driving supply-side revenue to increase. Additionally, this crypto network economic model will align crypto asset prices with increases in network utilization. As the adoption rate of the network increases and the value of the network continues to be captured, the price of crypto assets will rise accordingly, and more participants and speculative capital will enter, forming a positive feedback loop that attracts more builders and users to continue to join.
DePIN development, potential and challenges coexist
While DePIN provides a paradigm for combining cryptography with real-world use cases, why do we need to change the status quo and leverage DePIN to decentralize physical infrastructure networks? In fact, technological innovation needs to be based on clear market needs and business advantages to achieve long-term development. The development potential and challenges of DePIN will be introduced below.
DePIN’s development potential
On the one hand, DePIN aims to create a fairer and more efficient process for bootstrapping infrastructure networks compared to traditional top-down, capital-intensive approaches to IoT. It has the following advantages:
Safe and efficient. Leveraging blockchain technology, DePIN offers secure peer-to-peer payments to its network participants without relying on payment processing intermediaries for fees. Through distributed physical infrastructure and community participants, DePIN will achieve ultra-large scale expansion faster than traditional projects, and DePINs operating capital and operating costs are only a fraction of traditional companies. Telecommunications companies must invest billions in infrastructure and real estate to host it and retain large numbers of employees to support it, whereas DePIN hosts it while incentivizing network membership to make everyone profit.
High adoption rate. The ability of the community to own the hardware that makes up the network, as well as the hardware or services they need to use, i.e. they are both providers and users of services, will facilitate adoption of the network. Therefore, users trust in the network service comes from the alignment of interests, rather than relying on a centralized company that provides quarterly reports.
Openness. Traditional infrastructure projects often end up with a centralized entity dictating the terms and conditions you can enforce and use, in which users rarely have a say. But DePIN is open, democratic and accessible.
Censorship resistance. In addition to being permissionless and open, DePIN is censorship-resistant and no one can deny you access for any reason.
On the other hand, the use of blockchain technology in DePIN, in addition to the Internet of Things, will also promote the innovative development of Web 2 and Web 3 in multiple fields:
As a Web 3 native network, DePIN also allows network participants to directly access various Web 3 tools and DeFi services, such as financing new hardware, which can provide more potential users for the Web 3 multi-track.
By significantly reducing upfront capital requirements and lowering barriers to entry, DePIN empowers traditional industries in real life and brings new competitiveness to traditional telecommunications, energy and other industries, thereby stimulating comprehensive innovation.
DePIN development challenges
Incentive Burden: The DePIN project uses cryptocurrency to incentivize and reward those who use and or maintain the hardware that powers the network. Under a highly diluted incentive model, on the one hand, it can continue to motivate and attract community builders, but on the other hand, an overly diluted incentive model will cause the interests of the original holders to shrink and cause problems in the economic structure of the entire project.
Development Cost: Compared to purely consumer-oriented Web 3 applications such as games, DePIN takes much longer to build applications and requirements, and developers face more development challenges.
Competition is fierce: choose to replace an existing service or create a new one? Although the market is currently large, it is still a very big challenge to compete with Web 2 giants such as Amazon, Microsoft and Google.
In short, subverting traditional industries requires more efforts and professional technical support, and DePIN has a long way to go.
DePIN project, development status review
DePIN uses blockchain and cryptoassets to create and incentivize the deployment and usage of real-life physical infrastructure. Although the DePIN ecosystem is still being explored, existing projects have made significant progress. Messari Research Institute has summarized the current overview of the DePIN project for everyone. See the figure below for details.
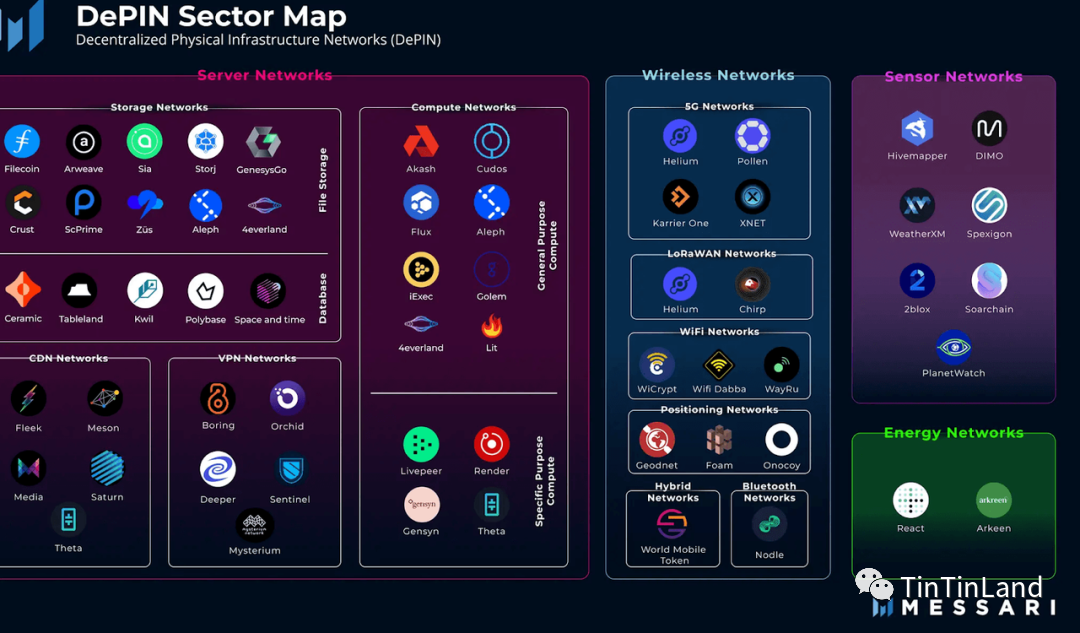
Among them, the top 10 companies in DePIN are server network Filecoin, Arweave, Sia and Storj in the digital resource network (DRN) category, wireless network Helium and Pollen Mobile in the physical resource network (PRN) category, and sensor network Network Hivemapper and DIMO, Energy Network React Protocol and Arkreen. The following will introduce the development status of specific projects. Interested parties can go to the corresponding project official website to view the details of project development.
Helium
Helium is one of DePINs pioneer projects. In July 2019, Helium led the DeWi movement with its LoRaWAN network designed to power the Internet of Things (IoT). Its initial goal is to create a low-power wide area network (LoRaWAN) for IoT devices to connect to each other. A unique service at the time, it enjoyed first-mover advantage in the field and had partnerships with projects aimed at tracking weather, monitoring air quality and integrating GPS.
In 2022, the project adjusted its development goals and committed to becoming a network of networks to help support other DePIN projects, such as building decentralized solutions for Wi-Fi, 5G, VPN, etc. To date, nearly 1 million hotspots have been connected to the Helium network. But Web 3 critic Liron Shapira believes that Heliums use case is overstated, with most of its revenue coming from selling hardware to new network providers and that supply is increasing, but the actual demand for Heliums products is negligible.
Filecoin
Launched in 2020, Filecoin offers cloud storage services similar to Web 2 giants Google Cloud and Amazon Web Services. However, Filecoin is not controlled by a centralized provider, but instead offers a distributed storage solution secured by cryptoeconomic incentives. Filecoin connects users who need space to store data with users who have free space on their hard drives. Users who provide storage space will pay through FIL.
Currently, Filecoins monthly revenue has dropped significantly during the bear market. Researcher Domica believes that after the expansion and development in the summer of 2021, Filecoins scale and utility have been exaggerated. The project is solving this problem by launching Filecoin Plus, a new product that provides free storage space to verified users, and a large number of users have already switched to Filecoin Plus.
Conclusion
As a Web 3 network that powers the Internet of Things economy, is the centralized physical infrastructure network DePIN a new concept and hype, or a new flywheel that drives development? As far as the current development of the leading project on the track is concerned, barriers still exist between the huge market and DePIN services, and how to make encryption technology and incentive models truly applicable to real-life use cases has become a key issue that needs to be solved urgently. But from another perspective, compared to mature projects such as DeFi and NFT, DePIN is in a blue ocean market that needs to be explored. It is expected that more developers will use technological innovation to promote the development of the DePIN track and promote the realization of the Web 3 value network in the future.
References:
https://www.bitstamp.net/learn/web3/what-are-decentralized-physical-infrastructure-networks-depin/
https://messari.io/report/the-telecom-cowboys-of-the-decentralized-wireless-movement?utm_medium=organic_social&utm_source=twitter_messaricrypto&utm_campaign=dewi_movement
https://coinmarketcap.com/alexandria/article/a-deep-dive-into-depin-decentralized-physical-infrastructure



